Enhance your projects with accurate motion detection, capturing its speed and direction with precision
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
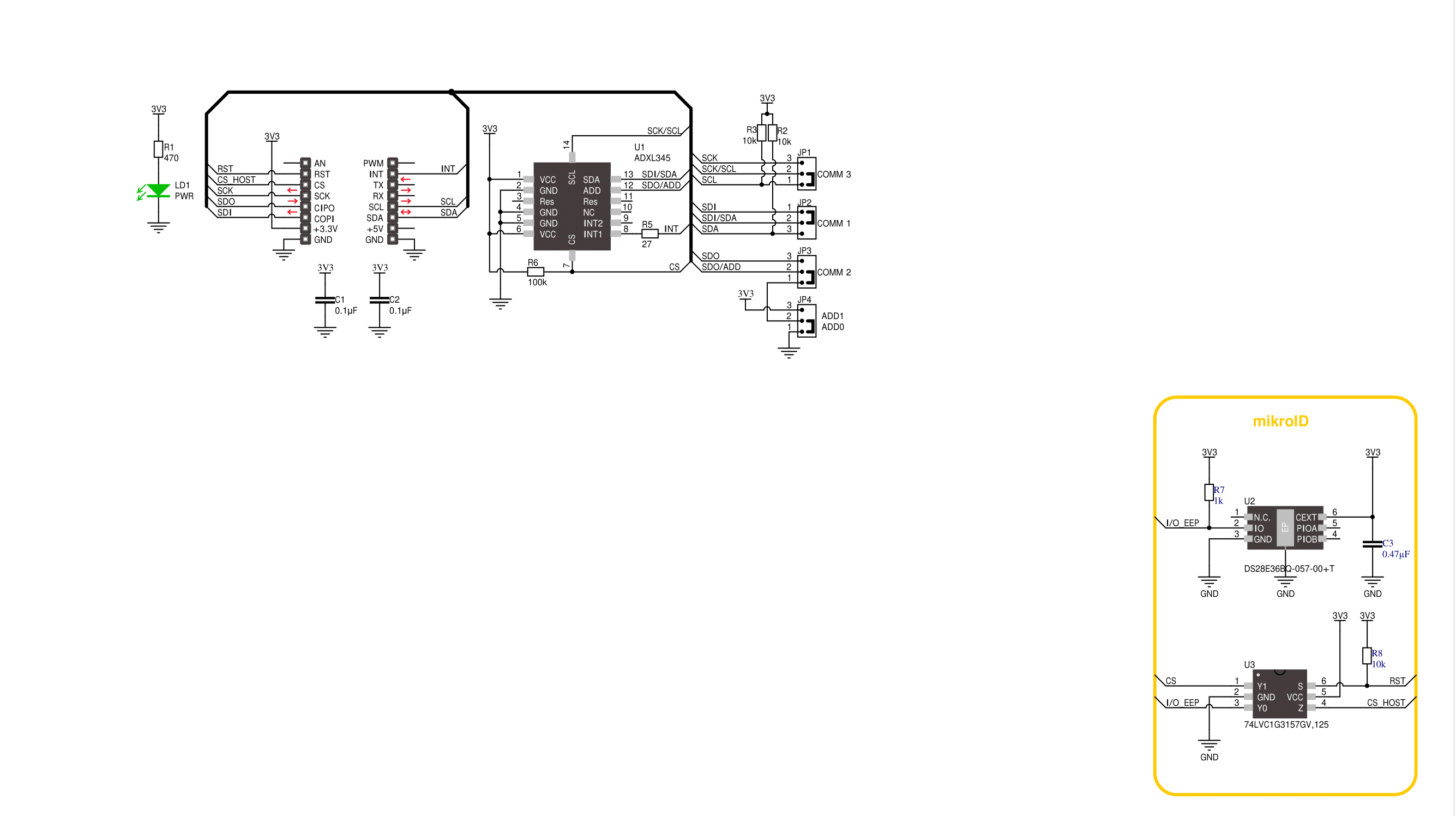
Accel Click is based on the ADXL345, a complete 3-axis acceleration measurement system that operates at low power consumption levels from Analog Devices. It measures both dynamic accelerations, resulting from motion or shock, and static acceleration, such as gravity, and allows selectable full-scale acceleration measurements in ranges of ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, or ±16g with a resolution of 4mg/LSB on the ±2g range. Acceleration is reported digitally, communicating via the SPI or the I2C protocol and providing 16-bit output resolution. Its high resolution also enables the measurement of inclination changes less than 1.0°. The ADXL345 supports several special sensing functions. Activity and inactivity sensing detect the presence or lack
of motion by comparing the acceleration on any axis with user-set thresholds, while tap sensing detects single and double taps in any direction. Besides, a free-fall sensing feature detects if the device is falling. All these functions can be mapped to the interrupt pin routed on the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. Accel Click allows the use of both I2C and SPI interfaces. The selection can be made by positioning SMD jumpers labeled as COMM SEL in an appropriate position. Note that all the jumpers' positions must be on the same side, or the Click board™ may become unresponsive. While the I2C interface is selected, the ADXL345 allows choosing the least significant bit (LSB) of its I2C slave address using the SMD jumper labeled ADDR
SEL. An integrated memory management system with a 32-level first in, first out (FIFO) buffer can store data to minimize host processor activity and lower overall system power consumption. Low power modes enable intelligent motion-based power management with threshold sensing and active acceleration measurement at low power dissipation. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Fusion for TIVA v8 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of microcontrollers, such as different 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M based MCUs from Texas Instruments, regardless of their number of pins, and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer over a WiFi network. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, Fusion for TIVA v8 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access
anywhere and under any circumstances at any time. Each part of the Fusion for TIVA v8 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module offers many valuable programming/debugging options, including support for JTAG, SWD, and SWO Trace (Single Wire Output)), and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides, it also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector.
Communication options such as USB-UART, USB HOST/DEVICE, CAN (on the MCU card, if supported), and Ethernet is also included. In addition, it also has the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and two display options for the TFT board line of products and character-based LCD. Fusion for TIVA v8 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
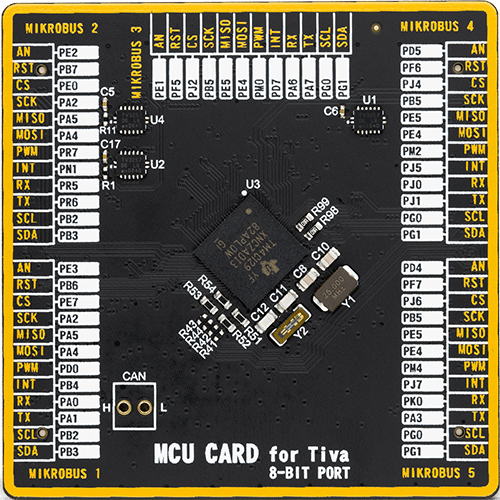
MCU Card / MCU
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
Texas Instruments
Pin count
212
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output via UART Mode
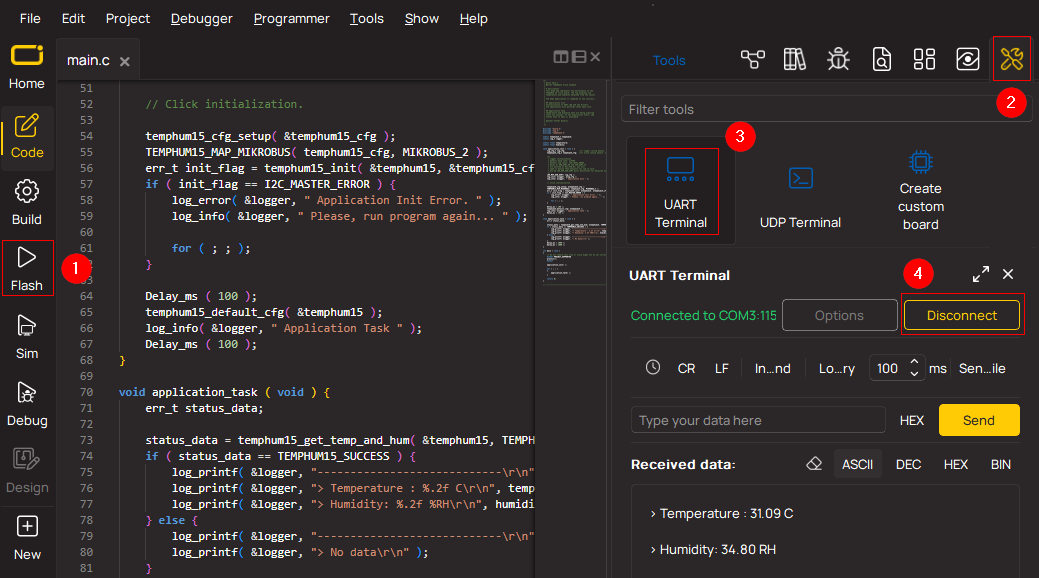
1. Once the code example is loaded, pressing the "FLASH" button initiates the build process, and programs it on the created setup.
2. After the programming is completed, click on the Tools icon in the upper-right panel, and select the UART Terminal.
3. After opening the UART Terminal tab, first check the baud rate setting in the Options menu (default is 115200). If this parameter is correct, activate the terminal by clicking the "CONNECT" button.
4. Now terminal status changes from Disconnected to Connected in green, and the data is displayed in the Received data field.
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Accel Click driver.
Key functions:
accel_read_x_axis- This function reads X axis value from Accelaccel_read_y_axis- This function reads Y axis value from Accelaccel_read_z_axis- This function reads Z axis value from Accel
Open Source
Code example
This example can be found in NECTO Studio. Feel free to download the code, or you can copy the code below.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Accel Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Accel click board by reading and
* displaying the accelerometer data (X, Y, and Z axis).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes SPI/I2C driver and settings data read format,
* power mode, FIFO control and baud rate ( 100Hz default ).
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads X, Y and Z axis and logs on usbuart every 100 ms.
*
* \author Jovan Stajkovic
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "accel.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static accel_t accel;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t tmp;
static int16_t val_x;
static int16_t val_y;
static int16_t val_z;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
accel_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
accel_cfg_setup( &cfg );
ACCEL_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
accel_init( &accel, &cfg );
accel_generic_read( &accel, ACCEL_REG_DEVID, &tmp, 1 );
if ( tmp == ACCEL_DEVID )
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Comunication OK!!! ----\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Comunication ERROR!!! ----\r\n" );
for ( ; ; );
}
accel_default_cfg ( &accel );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
val_x = accel_read_x_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis X : %.3f g\r\n", val_x / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
val_y = accel_read_y_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis Y : %.3f g\r\n", val_y / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
val_z = accel_read_z_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis Z : %.3f g\r\n", val_z / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms( 100 );
}
int main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END































