Electrically erasable programmable memory (EEPROM) with enhanced hardware write protection that stores important data securely, like settings or information, even when the power is turned off
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
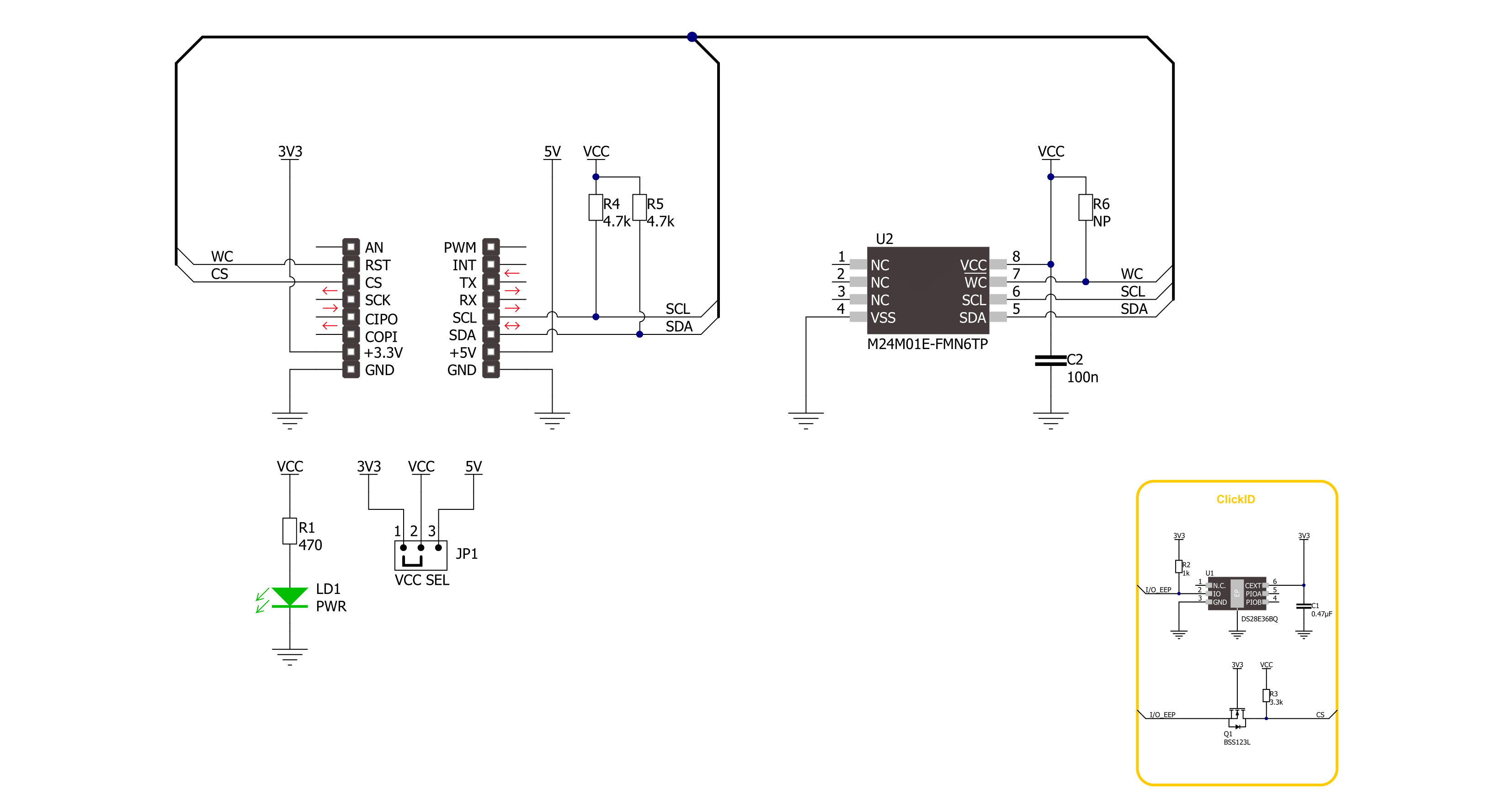
EEPROM 13 Click is based on the M24M01E, an electrically erasable programmable memory with enhanced hardware write protection for entire memory from STMicroelectronics. The M24M01E has software and hardware write protection features and random and sequential read modes. If the address area is write-protected, the write instruction is not executed. During the internal write cycle, the serial data is turned off internally, and the
device does not respond to any requests. The performance features cover enhanced ESD/latch-up protection, more than 4 million write cycles, more than 200 years of data retention, and a very fast wake-up time (less than 5μs). EEPROM 13 Click uses a standard 2-wire I2C interface to communicate with the host MCU, supporting standard, fast, and fast mode plus with up to 1MHz of frequency clock. The write control WC pin serves
as a write protect option and is active with a High logic state. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
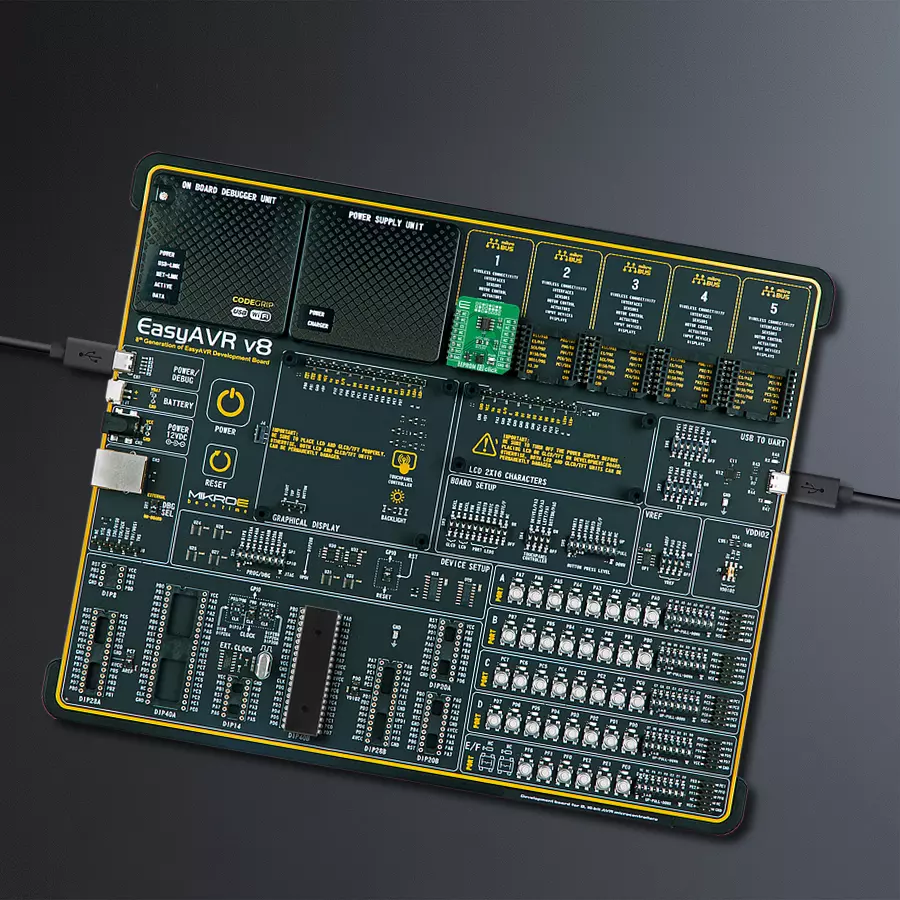
EasyAVR v8 is a development board designed to rapidly develop embedded applications based on 8-bit AVR microcontrollers (MCUs). Redesigned from the ground up, EasyAVR v8 offers a familiar set of standard features, as well as some new and unique features standard for the 8th generation of development boards: programming and debugging over the WiFi network, connectivity provided by USB-C connectors, support for a wide range of different MCUs, and more. The development board is designed so that the developer has everything that might be needed for the application development, following the Swiss Army knife concept: a highly advanced programmer/debugger module, a reliable power supply module, and a USB-UART connectivity option. EasyAVR v8 board offers several different DIP sockets, covering a wide range of 8-bit AVR MCUs, from the smallest
AVR MCU devices with only eight pins, all the way up to 40-pin "giants". The development board supports the well-established mikroBUS™ connectivity standard, offering five mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing access to a huge base of Click boards™. EasyAVR v8 offers two display options, allowing even the basic 8-bit AVR MCU devices to utilize them and display graphical or textual content. One of them is the 1x20 graphical display connector, compatible with the familiar Graphical Liquid Crystal Display (GLCD) based on the KS108 (or compatible) display driver, and EasyTFT board that contains TFT Color Display MI0283QT-9A, which is driven by ILI9341 display controller, capable of showing advanced graphical content. The other option is the 2x16 character LCD module, a four-bit display module with an embedded character-based display controller. It
requires minimal processing power from the host MCU for its operation. There is a wide range of useful interactive options at the disposal: high-quality buttons with selectable press levels, LEDs, pull-up/pulldown DIP switches, and more. All these features are packed on a single development board, which uses innovative manufacturing technologies, delivering a fluid and immersive working experience. The EasyAVR v8 development board is also integral to the MIKROE rapid development ecosystem. Natively supported by the MIKROE Software toolchain, backed up by hundreds of different Click board™ designs with their number growing daily, it covers many different prototyping and development aspects, thus saving precious development time.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
40
RAM (Bytes)
16384
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for EEPROM 13 Click driver.
Key functions:
eeprom13_memory_write- This function writes a desired number of data bytes starting from the selected memory addresseeprom13_memory_read- This function reads a desired number of data bytes starting from the selected memory addresseeprom13_hw_write_enable- This function disabled hardware write protection of the entire memory
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief EEPROM 13 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of EEPROM 13 Click board.
* The demo app writes specified data to the memory and reads it back.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* The initialization of I2C module, log UART, and additional pins.
*
* ## Application Task
* The demo application writes a desired number of bytes to the memory
* and then verifies if it is written correctly
* by reading from the same memory location and displaying the memory content.
* Results are being sent to the UART Terminal, where you can track their changes.
*
* @author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "eeprom13.h"
#define STARTING_ADDRESS 0x12345
#define DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_1 "MikroE"
#define DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_2 "EEPROM 13 Click"
static eeprom13_t eeprom13;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
eeprom13_cfg_t eeprom13_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
eeprom13_cfg_setup( &eeprom13_cfg );
EEPROM13_MAP_MIKROBUS( eeprom13_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == eeprom13_init( &eeprom13, &eeprom13_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
uint8_t data_buf[ 128 ] = { 0 };
memcpy( data_buf, DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_1, strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_1 ) );
if ( EEPROM13_OK == eeprom13_memory_write( &eeprom13, STARTING_ADDRESS,
data_buf,
strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_1 ) ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Write data: %s\r\n", data_buf );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
memset( data_buf, 0, sizeof( data_buf ) );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
if ( EEPROM13_OK == eeprom13_memory_read( &eeprom13, STARTING_ADDRESS,
data_buf,
strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_1 ) ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " Read data: %s\r\n\n", data_buf );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
memcpy( data_buf, DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_2, strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_2 ) );
if ( EEPROM13_OK == eeprom13_memory_write( &eeprom13, STARTING_ADDRESS,
data_buf,
strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_2 ) ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Write data: %s\r\n", data_buf );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
memset( data_buf, 0, sizeof( data_buf ) );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
if ( EEPROM13_OK == eeprom13_memory_read( &eeprom13, STARTING_ADDRESS,
data_buf,
strlen( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE_2 ) ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " Read data: %s\r\n\n", data_buf );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END