为您的物联网项目升级配备 IEEE802.15.4 兼容的 2.4GHz 射频收发器,支持 ZigBee、MiWi、MiWi P2P 和专有无线网络,提供无缝连接和无限创新的可能性。
A
A
硬件概览
它是如何工作的?
BEE Click 基于 Microchip 的 MRF24J40MA,这是一个 2.4GHz 射频收发器模块。它在 ISM 频段(从 2.405GHz 到 2.48GHz)上通过集成的 PCB 天线和匹配电路运行。您可以在频率范围内设置 16 个频道之一。该模块具有高达 36dB 的 TX 功率控制范围,能够实现高达 250Kbps 的数据传输速率。该模块集成了 PHY 和 MAC 功能,可以创建低成本、低功耗和低 数据速率的无线个人区域网络(WPAN)。为了减轻
主控 MCU 的负载,该模块具有自动数据包重传、自动应答、能量检测、CSMA-CA 算法、三种 CCA 模式、安全加密和解密等功能。为了与主控 MCU 通信,BEE Click 使用标准的 4 线 SPI 串行接口,并仅支持 SPI 模式 0,要求 SCK 在空闲状态下保持低电平。此外,BEE Click 还具有其他功能,例如 RST 引 脚用于以低电平有效的方式重置模块。WA 引脚是一个外部唤醒触发器,默认情况下被禁用,应在软件中
启用。这个引脚与睡眠模式相结合。此外,模块可以通过 INT 引脚传递八种中断事件之一。此 Click 板™ 只能在 3.3V 逻辑电压水平下操作。在使用具有不同逻辑水平的 MCU 之前,板必须执行适当的逻辑电压水平转换。此外,它配备了一个库,其中包含功能和示例代码,可以用作进一步开发的参考。
功能概述
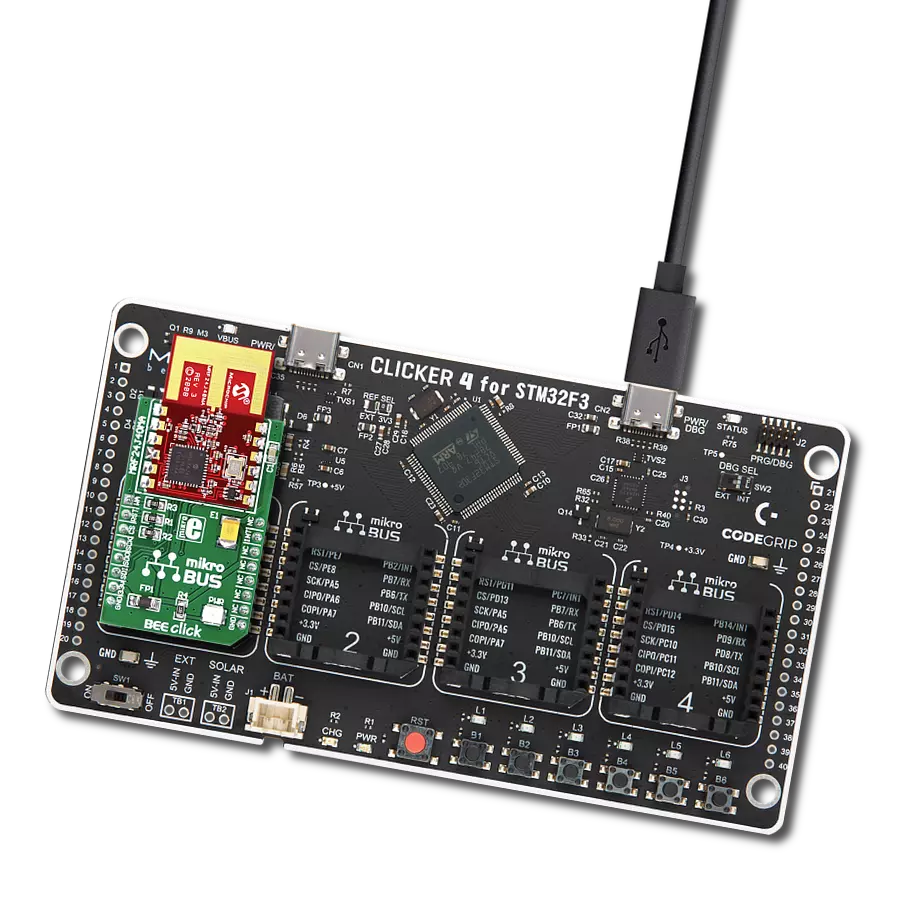
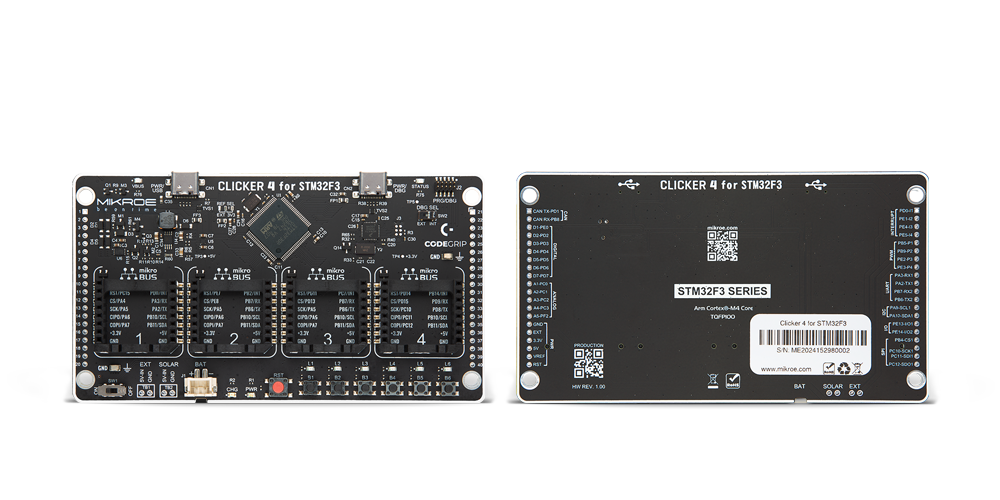
开发板
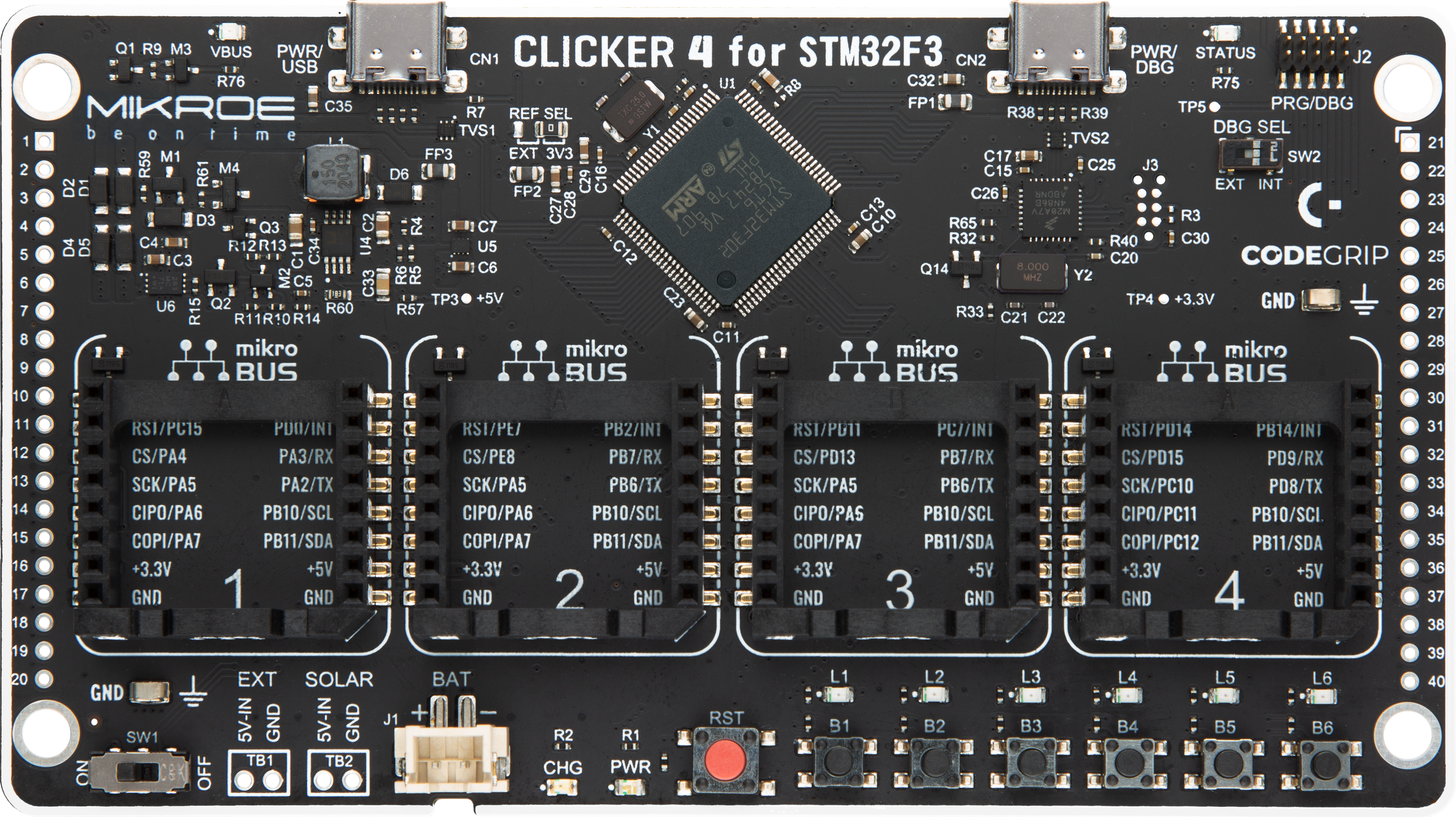
Clicker 4 for STM32F3 是一款紧凑型开发板,作为完整的解决方案而设计,可帮助用户快速构建具备独特功能的定制设备。该板搭载 STMicroelectronics 的 STM32F302VCT6 微控制器,配备四个 mikroBUS™ 插槽用于连接 Click boards™、完善的电源管理功能以及其他实用资源,是快速开发各类应用的理想平台。其核心 MCU STM32F302VCT6 基于高性能
Arm® Cortex®-M4 32 位处理器,运行频率高达 168MHz,处理能力强大,能够满足各种高复杂度任务的需求,使 Clicker 4 能灵活适应多种应用场景。除了两个 1x20 引脚排针外,板载最显著的连接特性是四个增强型 mikroBUS™ 插槽,支持接入数量庞大的 Click boards™ 生态系统,该生态每日持续扩展。Clicker 4 各功能区域标识清晰,界面直观简洁,极大
提升使用便捷性和开发效率。Clicker 4 的价值不仅在于加速原型开发与应用构建阶段,更在于其作为独立完整方案可直接集成至实际项目中,无需额外硬件修改。四角各设有直径 4.2mm(0.165")的安装孔,便于通过螺丝轻松固定。对于多数应用,只需配套一个外壳,即可将 Clicker 4 开发板转化为完整、实用且外观精美的定制系统。
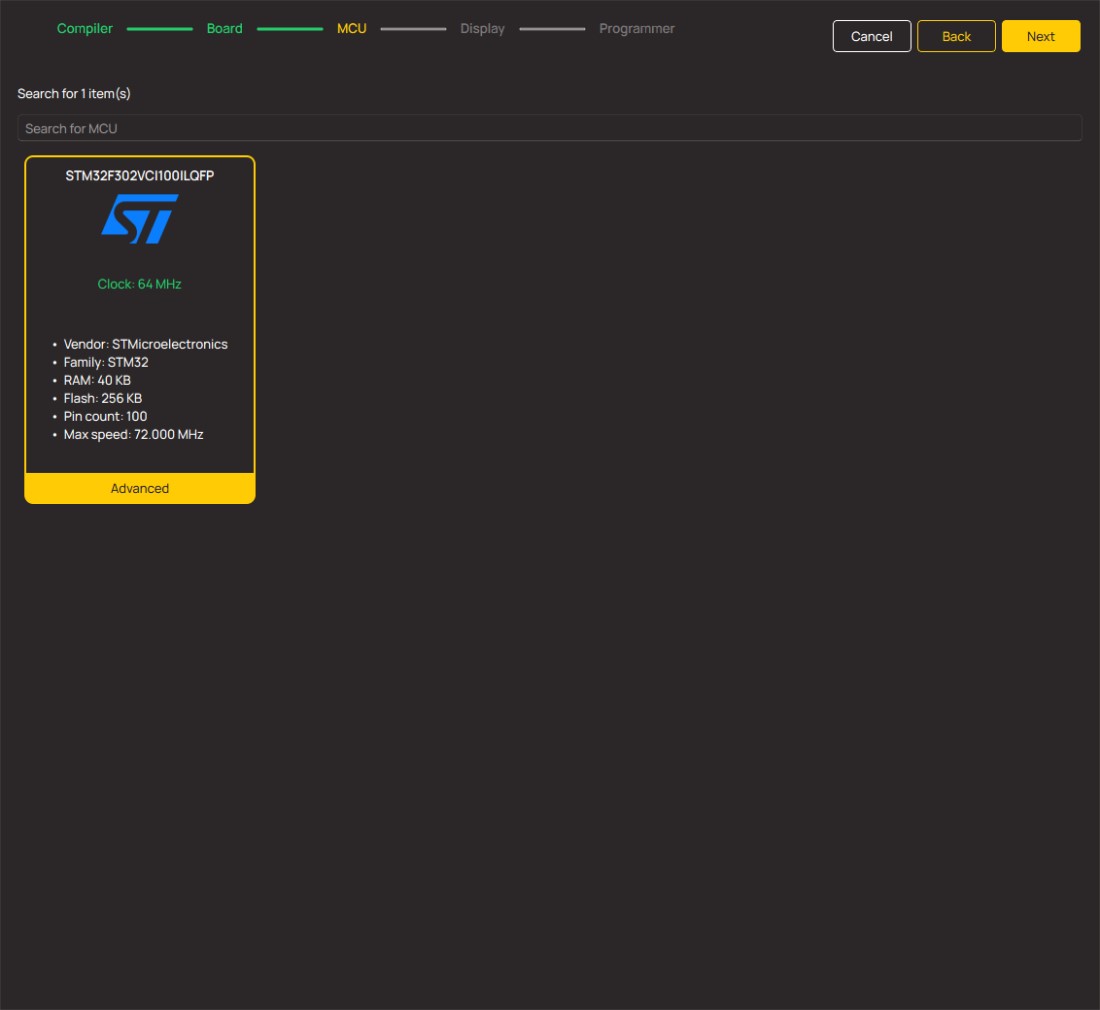
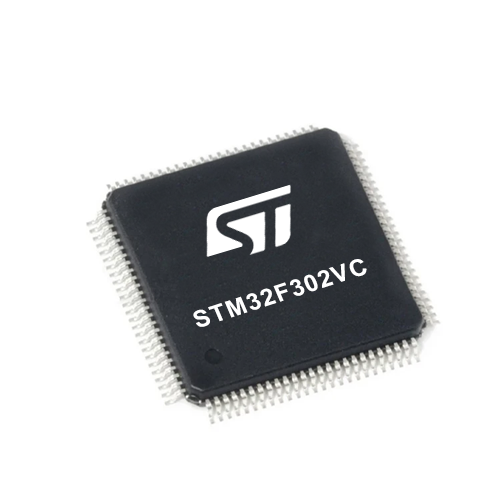
微控制器概述
MCU卡片 / MCU

建筑
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU 内存 (KB)
256
硅供应商
STMicroelectronics
引脚数
100
RAM (字节)
40960
使用的MCU引脚
mikroBUS™映射器
“仔细看看!”
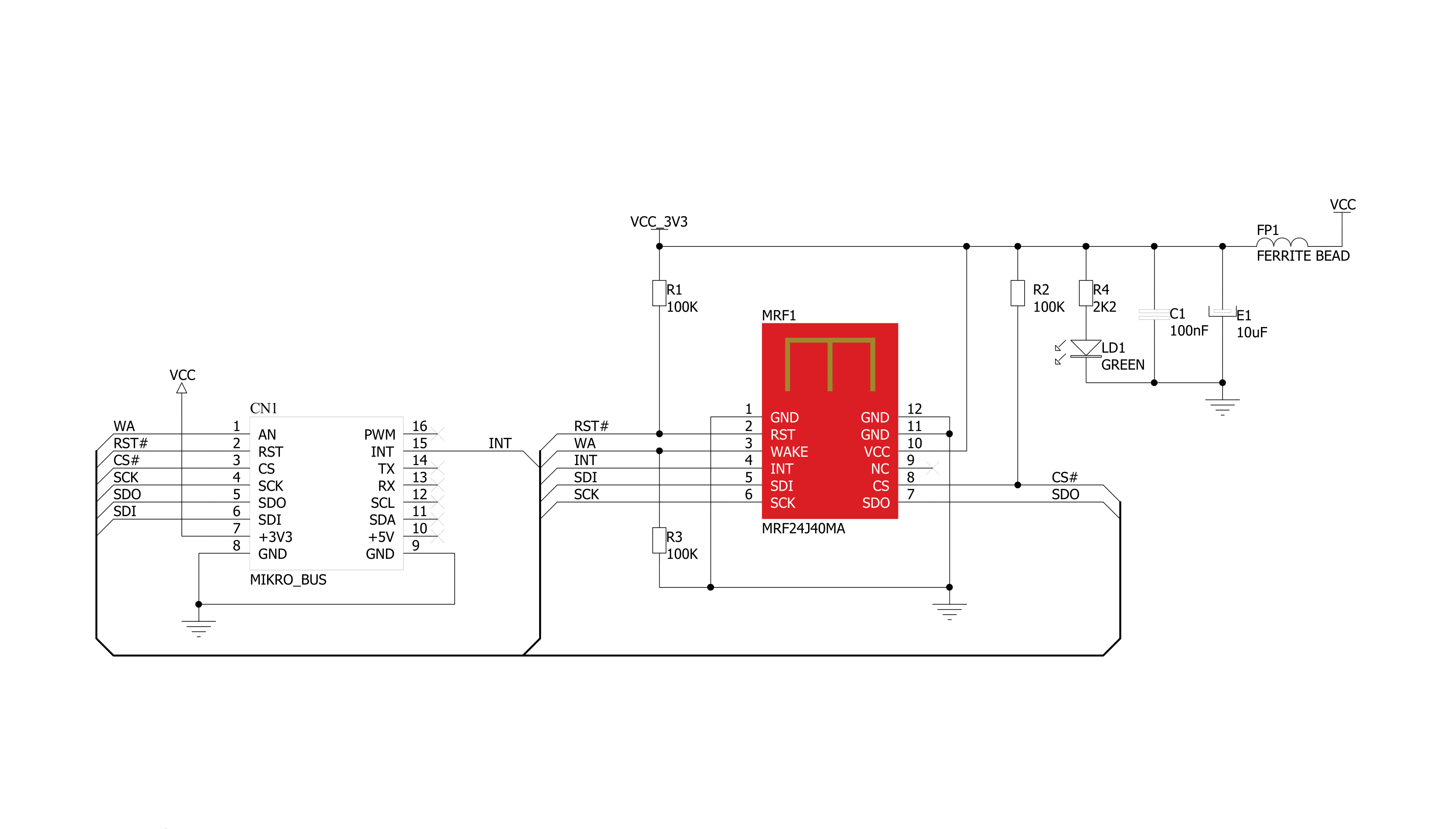
Click board™ 原理图
一步一步来
项目组装
实时跟踪您的结果
应用程序输出
1. 应用程序输出 - 在调试模式下,“应用程序输出”窗口支持实时数据监控,直接提供执行结果的可视化。请按照提供的教程正确配置环境,以确保数据正确显示。

2. UART 终端 - 使用UART Terminal通过USB to UART converter监视数据传输,实现Click board™与开发系统之间的直接通信。请根据项目需求配置波特率和其他串行设置,以确保正常运行。有关分步设置说明,请参考提供的教程。

3. Plot 输出 - Plot功能提供了一种强大的方式来可视化实时传感器数据,使趋势分析、调试和多个数据点的对比变得更加直观。要正确设置,请按照提供的教程,其中包含使用Plot功能显示Click board™读数的分步示例。在代码中使用Plot功能时,请使用以下函数:plot(insert_graph_name, variable_name);。这是一个通用格式,用户需要将“insert_graph_name”替换为实际图表名称,并将“variable_name”替换为要显示的参数。

软件支持
库描述
此库包含 BEE Click 驱动程序的 API。
关键功能:
bee_read_rx_fifo- 读取 RX FIFO 的功能bee_write_tx_normal_fifo- 写入 TX 普通 FIFO 的功能
开源
代码示例
完整的应用程序代码和一个现成的项目可以通过NECTO Studio包管理器直接安装到NECTO Studio。 应用程序代码也可以在MIKROE的GitHub账户中找到。
/*!
* \file
* \brief Bee Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of an BEE Click board by showing
* the communication between the two Click boards.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and configures the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Depending on the selected application mode, it reads all the received data or
* sends the desired message every 3 seconds.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "bee.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
// Comment out the line below in order to switch the application mode to receiver
#define DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
static bee_t bee;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t short_address1[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t short_address2[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t long_address1[ 8 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t long_address2[ 8 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t pan_id1[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t pan_id2[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t rx_data_fifo[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t rx_data_fifo_old[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t data_tx1[] = { 'M', 'i', 'k', 'r', 'o', 'E', 0 };
static uint8_t data_tx2[] = { 'B', 'E', 'E', ' ', ' ', ' ', 0 };
static uint8_t tx_data_fifo[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT + BEE_HEADER_LENGHT + 2 ] = { 0 };
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
bee_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
bee_cfg_setup( &cfg );
BEE_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
bee_init( &bee, &cfg );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 2; cnt++ )
{
short_address1[ cnt ] = 1;
short_address2[ cnt ] = 2;
pan_id1[ cnt ] = 3;
pan_id2[ cnt ] = 3;
}
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 8; cnt++ )
{
long_address1[ cnt ] = 1;
long_address2[ cnt ] = 2;
}
log_printf( &logger, " Reset and WakeUp \r\n" );
bee_hw_reset( &bee );
bee_soft_reset( &bee );
bee_rf_reset( &bee );
bee_enable_immediate_wake_up( &bee );
#ifdef DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
// Transmitter mode
log_printf( &logger, " Application Mode: Transmitter\r\n" );
tx_data_fifo[0] = BEE_HEADER_LENGHT;
tx_data_fifo[1] = BEE_HEADER_LENGHT + BEE_DATA_LENGHT;
tx_data_fifo[2] = 0x01; // control frame
tx_data_fifo[3] = 0x88;
tx_data_fifo[4] = 0x23; // sequence number
tx_data_fifo[5] = pan_id2[1]; // destinatoin pan
tx_data_fifo[6] = pan_id2[0];
tx_data_fifo[7] = short_address2[0]; // destination address
tx_data_fifo[8] = short_address2[1];
tx_data_fifo[9] = pan_id1[0]; // source pan
tx_data_fifo[10] = pan_id1[1];
tx_data_fifo[11] = short_address1[0]; // source address
tx_data_fifo[12] = short_address1[1];
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx1[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
log_printf( &logger, " Set address and PAN ID \r\n" );
bee_set_long_address( &bee, &long_address1 );
bee_set_short_address( &bee, &short_address1 );
bee_set_pan_id( &bee, &pan_id1 );
#else
log_printf( &logger, " Application Mode: Receiver\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Set address and PAN ID \r\n" );
bee_set_long_address( &bee, &long_address2 );
bee_set_short_address( &bee, &short_address2 );
bee_set_pan_id( &bee, &pan_id2 );
#endif
log_printf( &logger, " Init ZigBee module: \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set nonbeacon-enabled \r\n" );
bee_nonbeacon_init( &bee );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set as PAN coordinator\r\n" );
bee_nonbeacon_pan_coordinator_device( &bee );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set max TX power\r\n" );
bee_set_tx_power( &bee, 31 );
log_printf( &logger, " - All frames 3, data frame\r\n" );
bee_set_frame_format_filter( &bee, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set normal mode\r\n" );
bee_set_reception_mode( &bee, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Device Wake Up\r\n" );
bee_hw_wake_up( &bee );
bee_read_byte_short( &bee, BEE_INTSTAT ); // clears status register
Delay_1sec( );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
#ifdef DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
// Transmitter mode
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx1[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT);
bee_write_tx_normal_fifo( &bee, 0, &tx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " - Sent data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", data_tx1 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx2[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
bee_write_tx_normal_fifo( &bee, 0, &tx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " - Sent data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", data_tx2 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#else
// Receiver mode
bee_read_rx_fifo( &bee, &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
if ( memcmp( &rx_data_fifo_old[ 0 ], &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT ) )
{
memcpy( &rx_data_fifo_old [ 0 ], &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
log_printf( &logger, " - Received data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", rx_data_fifo );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
Delay_ms ( 500 );
#endif
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
额外支持
资源
类别:ZigBee