提升您的温度测量能力,使用我们的解决方案,旨在适应您行业的独特需求。
A
A
硬件概览
它是如何工作的?
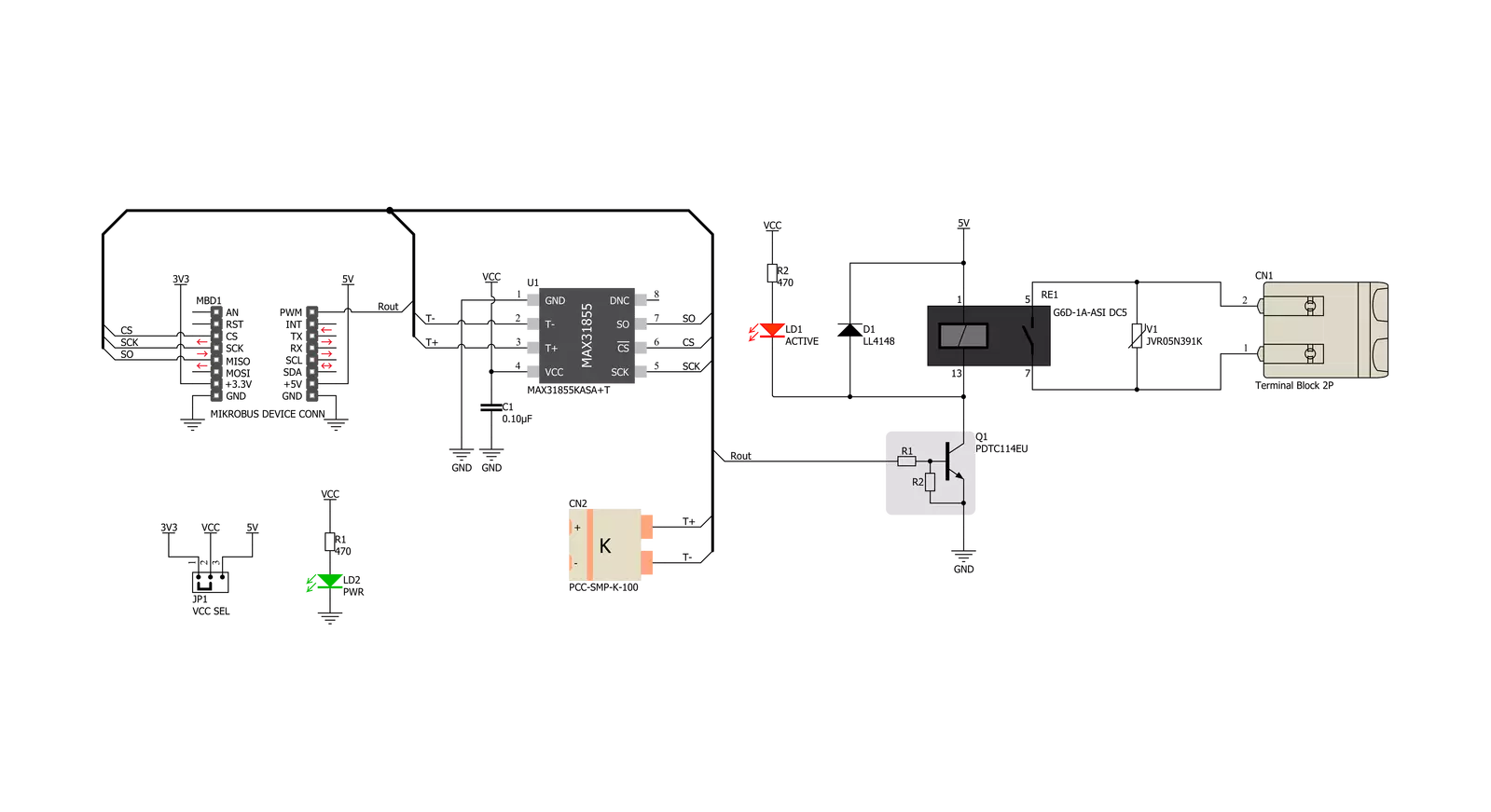
Thermostat 3 Click基于Analog Devices的MAX31855,这是一款带有内置14位模数转换器(ADC)的热电偶至数字转换器。该设备还包含冷结补偿传感和校正、数字控制器、SPI兼容接口和相关控制逻辑。Thermostat 3 Click设计用于与外部连接的K型热电偶传感器一起使用。与主机MCU的通信通过SPI接口完成,使用mikroBUS™的专用引脚。根据通过SPI接口获得的温度信息,主机MCU可以采取必要的措施:它可以打开或关闭继电器的触点。Click板™使用了来自Omron的G6D系列PCB电源继电器。这款高质量继电器在没有负载连接的情况下能够承受惊人的大量机械周期。然而,当其输出端连接有显著负载时,微电弧会导致触点随时间磨损。其最大负载电流为5A,能够承受高达70,000次循环。其触点由银合金制成,具有优异的最大100mΩ的导通电阻。继
电器由主机MCU激活。线圈激活电压为5V,线圈电流为40mA。MCU无法直接驱动线圈,因此需要添加一个NPN晶体管。其基极由主机MCU控制,允许线圈从5V mikroBUS™电源轨上吸收足够的电流。晶体管的基极连接到Click板™的CS引脚。晶体管内含两个偏置电阻,因此可以直接用于MCU引脚,无需外部偏置电阻。一个红色LED,标记为ACTIVE,用于指示晶体管处于打开状态,并且电流正在通过继电器线圈。当线圈(或任何其他电感器)的电流突然变化时,会产生反电动势,抵制电流的变化。这有时会导致控制电路损坏:在这种情况下,晶体管会变得反向极化。为防止这种情况发生,在线圈两端添加了一个续流二极管。在正常操作期间,这个二极管不导通任何电流。然而,当线圈关闭时,反向极化会导致电流通过这个二极管,以最小的电阻通
过。这样可以防止反向(续流)电压的积累,从而保护晶体管。输出端的触点可能连接到更高的电压,并且可能通过更大的电流。为了防止这种情况下的高压瞬变,续流二极管不是一个可行的选择。因此,Thermostat 3 Click使用了一个压敏电阻(VDR)。当电压超过其额定箝位电压时,这个元件会迅速降低其电阻。过高的电压瞬变会通过VDR,因为它会成为最小电阻的电流路径。在正常操作期间,当电压低于额定箝位电压时,VDR具有非常高的电阻,因此电流通过电气电路。Click板™的工作电压可以通过VCC SEL跳线选择。这个跳线允许从mikroBUS™选择3.3V或5V。选定的电压将应用于连接的MAX31855传感器的VCC引脚。
功能概述
开发板
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF 开发板是一个完全集成的 32 位开发平台,特点是高性能的 PIC32MZ EF 系列(PIC32MZ2048EFM),该系列具有 2MB Flash、512KB RAM、集成的浮点单元(FPU)、加密加速器和出色的连接选项。它包括一个集成的程序员和调试器,无需额外硬件。用户可以通过 MIKROE
mikroBUS™ Click™ 适配器板扩展功能,通过 Microchip PHY 女儿板添加以太网连接功能,使用 Microchip 扩展板添加 WiFi 连接能力,并通过 Microchip 音频女儿板添加音频输入和输出功能。这些板完全集成到 PIC32 强大的软件框架 MPLAB Harmony 中,该框架提供了一个灵活且模块化的接口
来应用开发、一套丰富的互操作软件堆栈(TCP-IP、USB)和易于使用的功能。Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF 开发板提供了扩展能力,使其成为连接性、物联网和通用应用中快速原型设计的绝佳选择。
微控制器概述
MCU卡片 / MCU

建筑
PIC32
MCU 内存 (KB)
2048
硅供应商
Microchip
引脚数
100
RAM (字节)
524288
你完善了我!
配件
使用的MCU引脚
mikroBUS™映射器
“仔细看看!”
Click board™ 原理图
一步一步来
项目组装
实时跟踪您的结果
应用程序输出
1. 应用程序输出 - 在调试模式下,“应用程序输出”窗口支持实时数据监控,直接提供执行结果的可视化。请按照提供的教程正确配置环境,以确保数据正确显示。

2. UART 终端 - 使用UART Terminal通过USB to UART converter监视数据传输,实现Click board™与开发系统之间的直接通信。请根据项目需求配置波特率和其他串行设置,以确保正常运行。有关分步设置说明,请参考提供的教程。

3. Plot 输出 - Plot功能提供了一种强大的方式来可视化实时传感器数据,使趋势分析、调试和多个数据点的对比变得更加直观。要正确设置,请按照提供的教程,其中包含使用Plot功能显示Click board™读数的分步示例。在代码中使用Plot功能时,请使用以下函数:plot(insert_graph_name, variable_name);。这是一个通用格式,用户需要将“insert_graph_name”替换为实际图表名称,并将“variable_name”替换为要显示的参数。

软件支持
库描述
此库包含Thermostat 3 Click驱动程序的API。
关键功能:
thermostat3_relay_control- 此功能使能继电器控制。thermostat3_get_fault_data- 此功能返回故障数据值。thermostat3_get_thermocouple_temperature- 此功能返回14位热电偶温度数据。
开源
代码示例
完整的应用程序代码和一个现成的项目可以通过NECTO Studio包管理器直接安装到NECTO Studio。 应用程序代码也可以在MIKROE的GitHub账户中找到。
/*!
* \file
* \brief Thermostat3 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application enables usage of the general puprose Thermostat click to be used with temperature sensors.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver init
*
* ## Application Task
* Waits for valid user input and executes functions based on set of valid commands
*
* *note:*
* - Additional Functions :
* -void _displayFault( uint8_t f_error ) - Display fault
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "thermostat3.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static thermostat3_t thermostat3;
static temp_vals_t temp_val;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------- ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS
static void display_fault ( uint8_t f_error )
{
switch ( f_error )
{
case 3:
{
log_printf( &logger, "# Active - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 2:
{
log_printf( &logger, "# SCV - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 1:
{
log_printf( &logger,"# SCG - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 0:
{
log_printf( &logger,"# OC - Fault flag " );
break;
}
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
thermostat3_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
// Click initialization.
thermostat3_cfg_setup( &cfg );
THERMOSTAT3_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
thermostat3_init( &thermostat3, &cfg );
// Power on delay
Delay_ms ( 200 );
log_printf( &logger, "---- Start Thermostat 3 ----\r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
// Task implementation.
float internal_temp;
float thermocouple_temp;
thermostat3_process( &thermostat3, &temp_val );
internal_temp = thermostat3_get_internal_temperature( &temp_val, THERMOSTAT3_TEMP_IN_CELSIUS );
log_printf( &logger, "# Internal Temperature: %.2f", internal_temp );
Delay_ms ( 200 );
thermocouple_temp = thermostat3_get_thermocouple_temperature( &temp_val, THERMOSTAT3_TEMP_IN_CELSIUS );
log_printf( &logger, "# Thermocouple Temperature: %.2f", thermocouple_temp );
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.relay_flag == 1)
{
thermostat3.relay_flag = 0;
thermostat3_relay_control( &thermostat3, THERMOSTAT3_RELAY_OFF );
log_printf( &logger, "# Relay OFF\r\n" );
}
else
{
thermostat3.relay_flag = 1;
thermostat3_relay_control( &thermostat3, THERMOSTAT3_RELAY_ON );
log_printf( &logger, "# Relay ON\r\n" );
}
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.fault_flag == 1 )
{
thermostat3.fault_flag = 0;
log_printf( &logger, "# Fault status -- OFF\r\n" );
}
else
{
thermostat3.fault_flag = 1;
log_printf( &logger, "# Fault status -- ON\r\n" );
}
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.fault_flag == 1 )
{
thermostat3.f_error++;
if( thermostat3.f_error > 3 )
{
thermostat3.f_error = 0;
}
display_fault( thermostat3.f_error );
thermostat3.fault_status = thermostat3_get_fault_data( &temp_val, 0x01 << thermostat3.f_error );
if ( thermostat3.fault_status == 1 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " -- ERROR\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " -- OK\r\n" );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
/*!
* \file
* \brief Thermostat3 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application enables usage of the general puprose Thermostat click to be used with temperature sensors.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver init
*
* ## Application Task
* Waits for valid user input and executes functions based on set of valid commands
*
* *note:*
* - Additional Functions :
* -void _displayFault( uint8_t f_error ) - Display fault
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "thermostat3.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static thermostat3_t thermostat3;
static temp_vals_t temp_val;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------- ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS
static void display_fault ( uint8_t f_error )
{
switch ( f_error )
{
case 3:
{
log_printf( &logger, "# Active - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 2:
{
log_printf( &logger, "# SCV - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 1:
{
log_printf( &logger,"# SCG - Fault flag " );
break;
}
case 0:
{
log_printf( &logger,"# OC - Fault flag " );
break;
}
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
thermostat3_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
// Click initialization.
thermostat3_cfg_setup( &cfg );
THERMOSTAT3_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
thermostat3_init( &thermostat3, &cfg );
// Power on delay
Delay_ms ( 200 );
log_printf( &logger, "---- Start Thermostat 3 ----\r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
// Task implementation.
float internal_temp;
float thermocouple_temp;
thermostat3_process( &thermostat3, &temp_val );
internal_temp = thermostat3_get_internal_temperature( &temp_val, THERMOSTAT3_TEMP_IN_CELSIUS );
log_printf( &logger, "# Internal Temperature: %.2f", internal_temp );
Delay_ms ( 200 );
thermocouple_temp = thermostat3_get_thermocouple_temperature( &temp_val, THERMOSTAT3_TEMP_IN_CELSIUS );
log_printf( &logger, "# Thermocouple Temperature: %.2f", thermocouple_temp );
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.relay_flag == 1)
{
thermostat3.relay_flag = 0;
thermostat3_relay_control( &thermostat3, THERMOSTAT3_RELAY_OFF );
log_printf( &logger, "# Relay OFF\r\n" );
}
else
{
thermostat3.relay_flag = 1;
thermostat3_relay_control( &thermostat3, THERMOSTAT3_RELAY_ON );
log_printf( &logger, "# Relay ON\r\n" );
}
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.fault_flag == 1 )
{
thermostat3.fault_flag = 0;
log_printf( &logger, "# Fault status -- OFF\r\n" );
}
else
{
thermostat3.fault_flag = 1;
log_printf( &logger, "# Fault status -- ON\r\n" );
}
Delay_ms ( 200 );
if( thermostat3.fault_flag == 1 )
{
thermostat3.f_error++;
if( thermostat3.f_error > 3 )
{
thermostat3.f_error = 0;
}
display_fault( thermostat3.f_error );
thermostat3.fault_status = thermostat3_get_fault_data( &temp_val, 0x01 << thermostat3.f_error );
if ( thermostat3.fault_status == 1 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " -- ERROR\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " -- OK\r\n" );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END

































