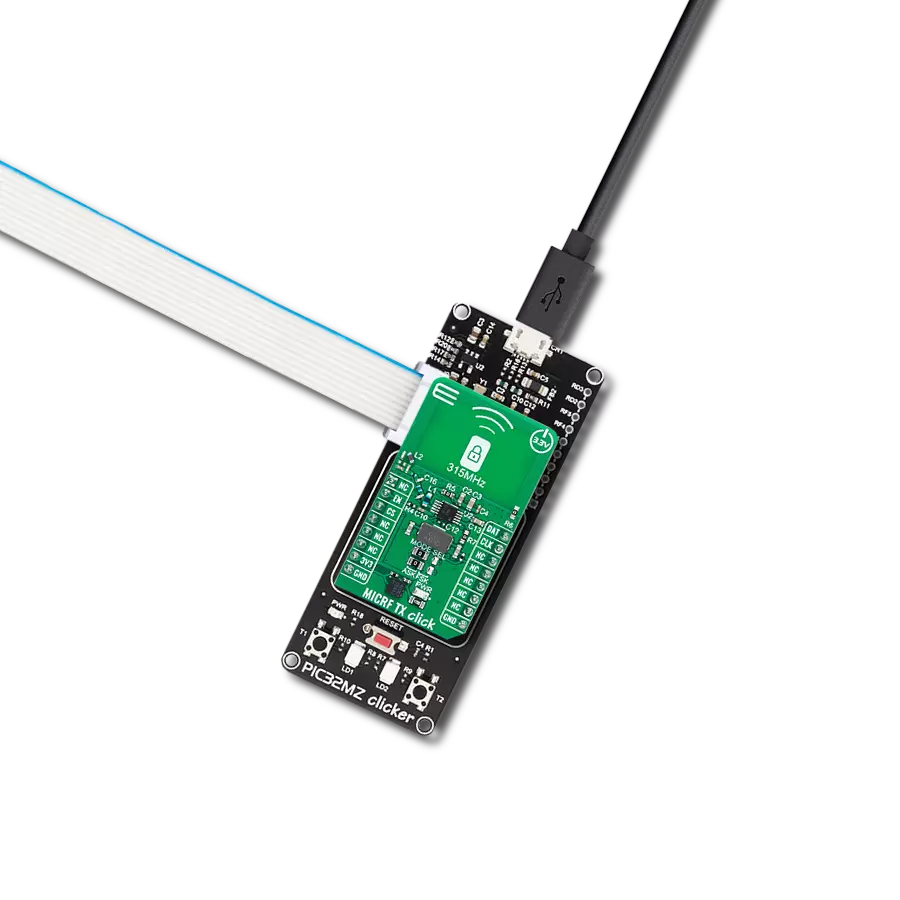
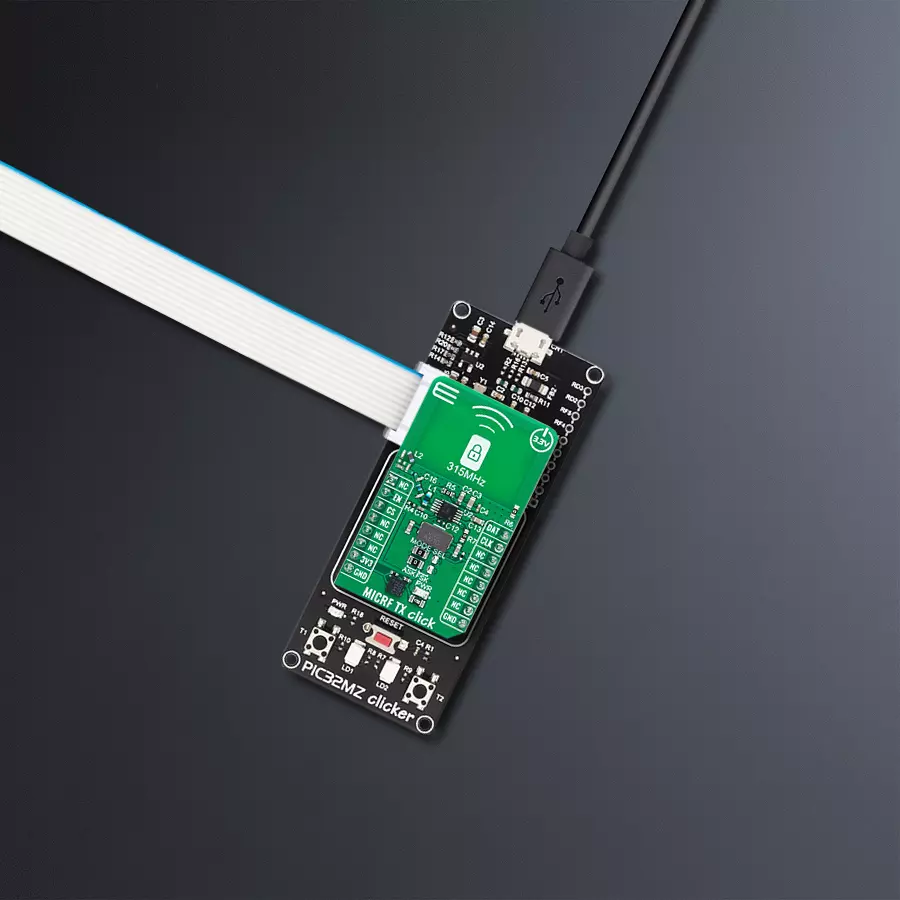
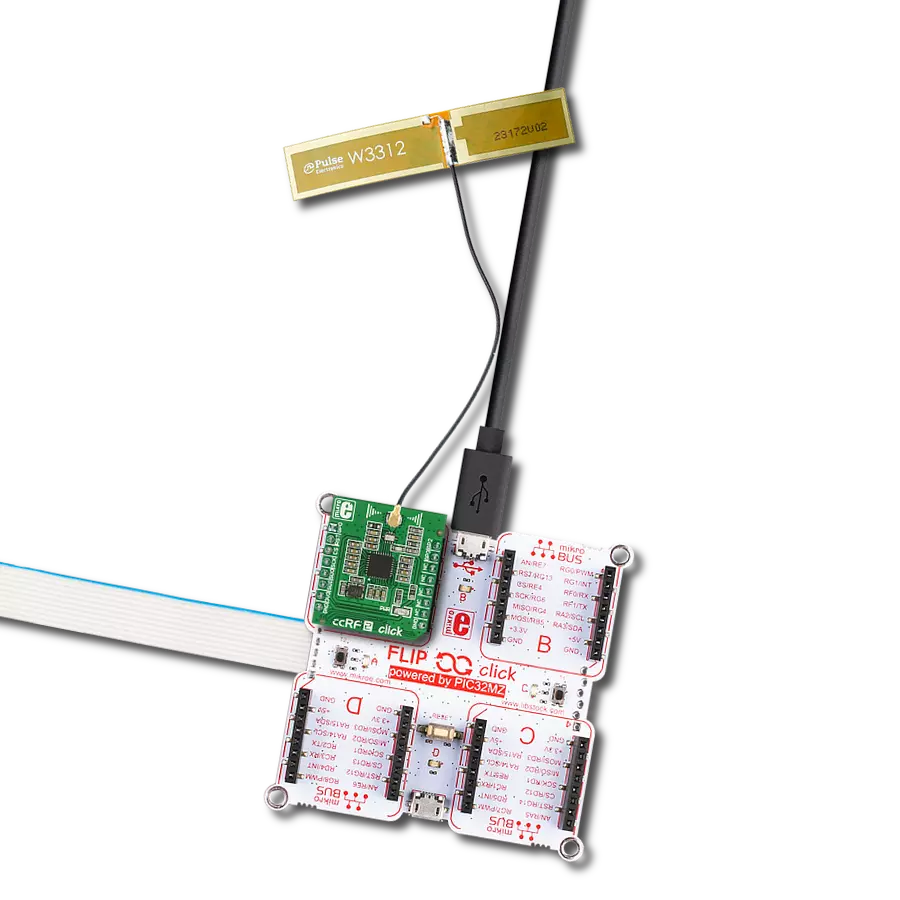
非常适用于需要可靠和灵敏信号接收的汽车和楼宇门禁控制系统。
A
A
硬件概览
它是如何工作的?
MICRF TX Click 基于来自Microchip的RF发射器IC MICRF112。这款高性能IC设计简单,基于“数据输入,射频输出”的原理运行。它支持幅度键控调制(ASK)和频率键控调制(FSK)两种调制类型,并集成了相位锁定环(PLL)以实现可靠的频率稳定。专门为315MHz频段设计的MICRF112只需要一个基本的晶体振荡器 - 例如板载的9.84375MHz晶体 - 来准确建立其工作频率,并且只需要最少的外部元件来匹配功率放大器的输出与天线。它在各种应用中都能发挥作用,如远程无钥匙进入(RKE)系统、各种遥控器(用于机顶盒、暖通空调系统和家电)、车库
门开启器(GDO)、轮胎压力监测系统(TPMS)、户外气象站以及用于安全、警报、照明和风扇控制、门铃、灌溉等系统。关于板与MCU的连接,此板使用mikroBUS™插槽上的几个引脚。EN引脚用作切换设备开启或关闭状态的芯片使能功能。DAT引脚直接接受调制数据输入(ASK或FSK,由MODE SEL跳线的设置确定)。在FSK调制的情况下,MICRF112的XTLOUT和XTAL_MOD引脚之间需要额外的电容器,如C12(默认情况下C12未焊接)。如果用户希望使用不同于板载振荡器的频率,则应将板上的R7电阻退焊,从而断开板载振荡器。然后,
应将1nF电容器焊接在C13电容器的位置,并将CLK引脚用作参考振荡器输入。使用来自mikroBUS™电源供应的3.3V输入,MICRF112可以产生+10dBm的连续波(CW)输出功率到50Ω天线负载。它还拥有一种高效节能的关机模式,仅消耗50nA,非常适合于依赖电池的设备。此Click板只能使用3.3V逻辑电压级别。在使用具有不同逻辑电平的MCU之前,板必须执行适当的逻辑电压级别转换。此外,它配备了一个包含函数和示例代码的库,可用作进一步开发的参考。
功能概述
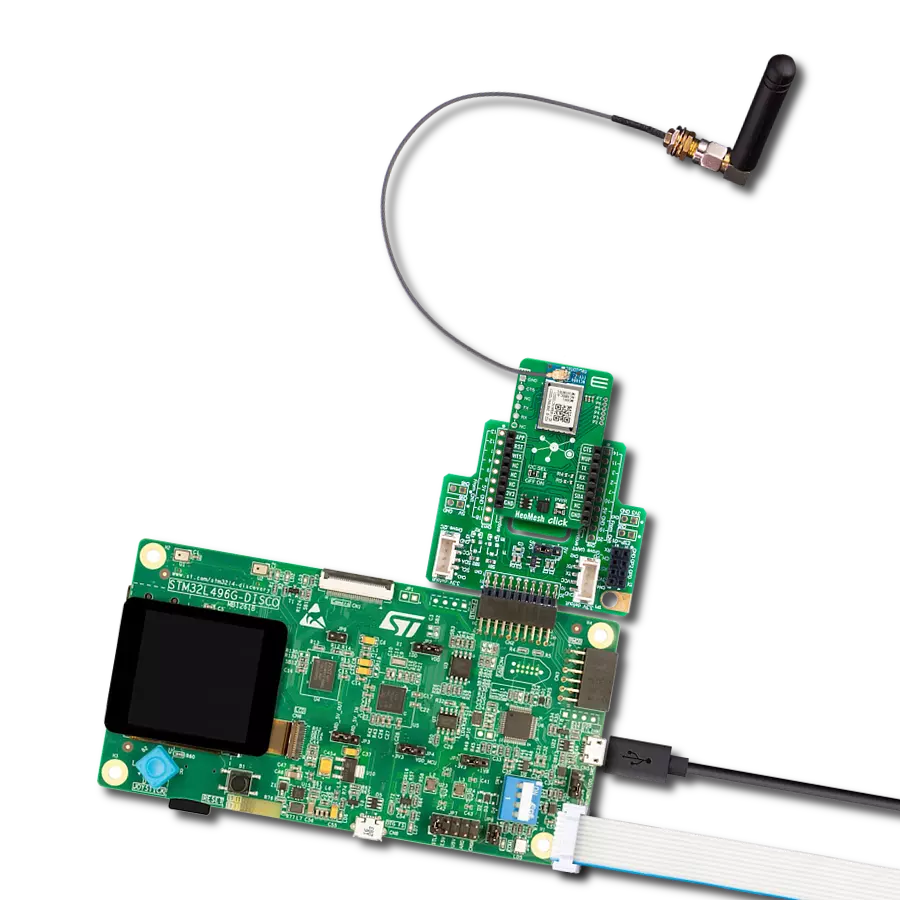
开发板
PIC32MZ Clicker 是一款紧凑型入门开发板,它将 Click 板™的灵活性带给您喜爱的微控制器,使其成为实现您想法的完美入门套件。它配备了一款板载 32 位带有浮点单元的 Microchip PIC32MZ 微控制器,一个 USB 连接器,LED 指示灯,按钮,一个 mikroProg 连接器,以及一个用于与外部电子设备接口的头部。得益于其紧凑的设计和清晰易识别的丝网标记,它提供了流畅且沉浸式的工作体验,允许在任
何情况下、任何地方都能访问。PIC32MZ Clicker 开 发套件的每个部分都包含了使同一板块运行最高效的必要组件。除了可以选择 PIC32MZ Clicker 的编程方式,使用 USB HID mikroBootloader 或通过外部 mikroProg 连接器为 PIC,dsPIC 或 PIC32 编程外,Clicker 板还包括一个干净且调节过的开发套件电源供应模块。USB Micro-B 连接可以提供多达 500mA 的电流,这足以操作所有板载和附加模块。所有
mikroBUS™ 本身支持的通信方法都在这块板上,包 括已经建立良好的 mikroBUS™ 插槽、重置按钮以及若干按钮和 LED 指示灯。PIC32MZ Clicker 是 Mikroe 生态系统的一个组成部分,允许您在几分钟内创建新的应用程序。它由 Mikroe 软件工具原生支持,得益于大量不同的 Click 板™(超过一千块板),其数量每天都在增长,它涵盖了原型制作的许多方面。
微控制器概述
MCU卡片 / MCU

建筑
PIC32
MCU 内存 (KB)
1024
硅供应商
Microchip
引脚数
64
RAM (字节)
524288
使用的MCU引脚
mikroBUS™映射器
“仔细看看!”
Click board™ 原理图

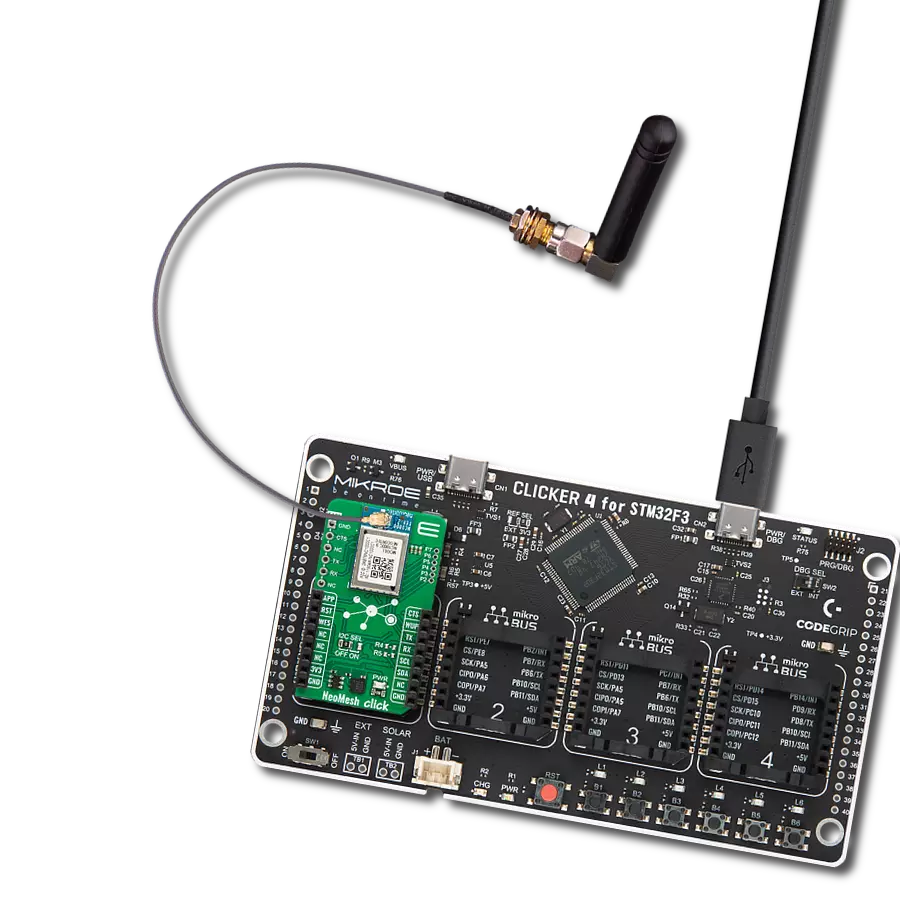
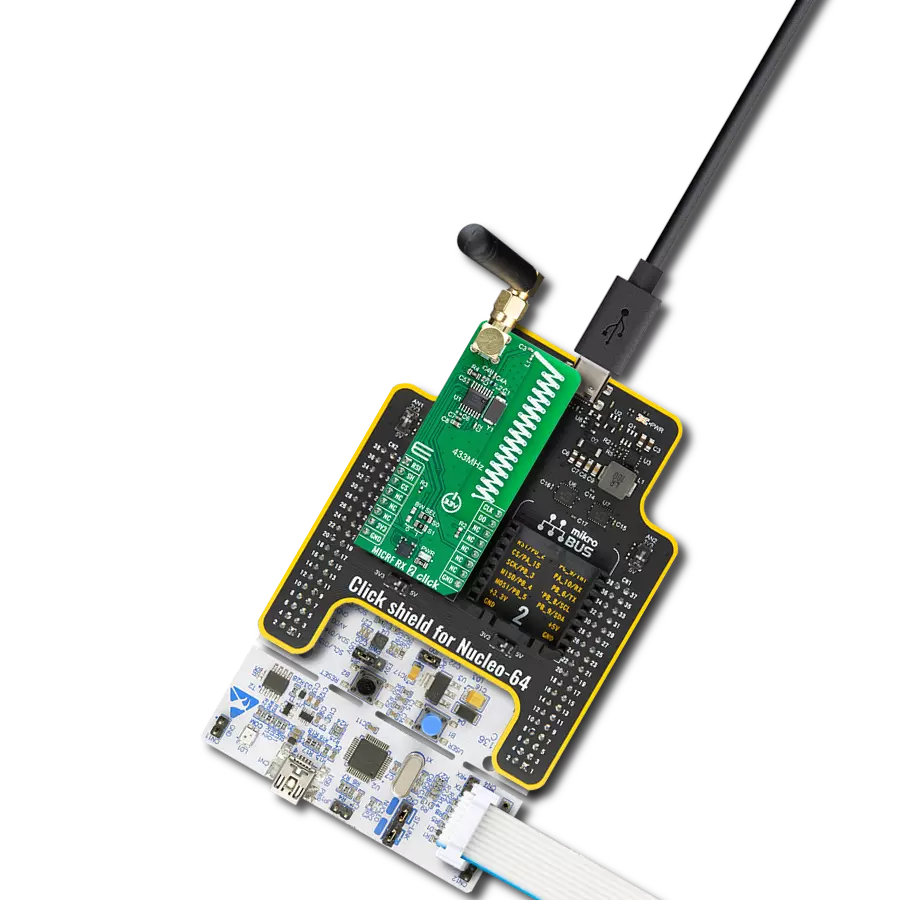
一步一步来
项目组装
实时跟踪您的结果
应用程序输出
1. 应用程序输出 - 在调试模式下,“应用程序输出”窗口支持实时数据监控,直接提供执行结果的可视化。请按照提供的教程正确配置环境,以确保数据正确显示。

2. UART 终端 - 使用UART Terminal通过USB to UART converter监视数据传输,实现Click board™与开发系统之间的直接通信。请根据项目需求配置波特率和其他串行设置,以确保正常运行。有关分步设置说明,请参考提供的教程。

3. Plot 输出 - Plot功能提供了一种强大的方式来可视化实时传感器数据,使趋势分析、调试和多个数据点的对比变得更加直观。要正确设置,请按照提供的教程,其中包含使用Plot功能显示Click board™读数的分步示例。在代码中使用Plot功能时,请使用以下函数:plot(insert_graph_name, variable_name);。这是一个通用格式,用户需要将“insert_graph_name”替换为实际图表名称,并将“variable_name”替换为要显示的参数。

软件支持
库描述
该库包含 MICRF TX Click 驱动程序的 API。
关键功能:
micrftx_send_data- 此函数构建并发送数据包。数据包格式如下(先最高位,曼彻斯特 IEEE 802.3):MICRFTX_TRAINING_BYTES、前导码、长度、DATA_IN、CRC16(从整个数据包除去训练字节计算)。
开源
代码示例
完整的应用程序代码和一个现成的项目可以通过NECTO Studio包管理器直接安装到NECTO Studio。 应用程序代码也可以在MIKROE的GitHub账户中找到。
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief MICRF TX Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of MICRF TX Click board by sending
* a predefined message to the receiver.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger.
*
* ## Application Task
* Sends a predefined message every 3 seconds and displays it on the USB UART.
*
* @note
* The MICRF RX Click board is a compatible receiver for the MICRF TX Click.
* Here are a few steps for troubleshooting if you are experiencing issues running
* this example:
* - Make sure the MICRF TX Click is set to ASK mode with on-board jumpers.
* - Check the MCU clock configuration, use an external oscillator instead of the MCU's
* internal one for better accuracy on manchester data rate delay.
* - Measure the actual data rate on the data line and adjust the MICRFTX_MAN_BIT_LEN_US
* value accordingly.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "micrftx.h"
#define MICRFTX_PREAMBLE 0x5AA5 /**< Packet preamble word. */
#define MICRFTX_MESSAGE "MIKROE" /**< Text message to send. */
static micrftx_t micrftx; /**< MICRF TX Click driver object. */
static log_t logger; /**< Logger object. */
/**
* @brief MICRF TX send data function.
* @details This function builds and sends a packet of data.
* The packet format is as follows (MSB first, manchester IEEE 802.3):
* MICRFTX_TRAINING_BYTES, PREABMLE, LEN, DATA_IN, CRC16 (calculated from whole packet excluding training bytes).
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #micrftx_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @param[in] preamble : Preamble word.
* @param[in] data_in : Data buffer.
* @param[in] len : Number of bytes in data buffer.
* @return None.
* @note Default manchester bit length is set to 2000us.
*/
static void micrftx_send_data ( micrftx_t *ctx, uint16_t preamble, uint8_t *data_in, uint8_t len );
/**
* @brief Manchester encode bits.
* @details This function encodes a data byte to manchester word (IEEE 802.3).
* @return Manchester word.
* @note None.
*/
static uint16_t micrftx_man_encode ( uint8_t data_in );
/**
* @brief Reflect bits.
* @details This function reflects a desired number of bits in data.
* @return Reflected data.
* @note None.
*/
static uint16_t micrftx_reflect_bits( uint16_t data_in, uint8_t len );
/**
* @brief CRC-16/MAXIM calculation for CRC16 function.
* @details This function calculates CRC16 with parameteres:
* @li @c Width 16 bit
* @li @c Polynomial 0x8005 ( x16 + x15 + x2 + x0 )
* @li @c Initialization 0x0000
* @li @c Reflect input True
* @li @c Reflect output True
* @li @c Final Xor 0xFFFF
* @li @c Example { 69, 00 } - 0xAFD1
* @param[in] data_buf : Array of bytes to calculate crc from.
* @param[in] len : Number of bytes to calculate crc from.
* @return Calculated CRC.
* @note None.
*/
static uint16_t micrftx_calculate_crc16 ( uint8_t *data_buf, uint16_t len );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
micrftx_cfg_t micrftx_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
micrftx_cfg_setup( &micrftx_cfg );
MICRFTX_MAP_MIKROBUS( micrftx_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( DIGITAL_OUT_UNSUPPORTED_PIN == micrftx_init( &micrftx, &micrftx_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " Sending data: %s\r\n\n", ( char * ) MICRFTX_MESSAGE );
micrftx_send_data ( &micrftx, MICRFTX_PREAMBLE, MICRFTX_MESSAGE, strlen ( MICRFTX_MESSAGE ) );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void micrftx_send_data ( micrftx_t *ctx, uint16_t preamble, uint8_t *data_in, uint8_t len )
{
uint8_t training[ ] = MICRFTX_TRAINING_BYTES;
uint8_t packet_buf[ MICRFTX_MAX_DATA_LEN + 5 ] = { 0 };
uint16_t crc = 0;
uint16_t man_data = 0;
uint8_t byte_cnt = 0;
uint8_t bit_cnt = 0;
packet_buf[ 0 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( preamble >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
packet_buf[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( preamble & 0xFF );
packet_buf[ 2 ] = len;
memcpy ( &packet_buf[ 3 ], data_in, len );
crc = micrftx_calculate_crc16 ( packet_buf, len + 3 );
packet_buf[ len + 3 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( crc >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
packet_buf[ len + 4 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( crc & 0xFF );
micrftx_enable_device ( ctx );
Delay_10ms( );
// Send training bytes first
for ( byte_cnt = 0; byte_cnt < sizeof ( training ); byte_cnt++ )
{
man_data = micrftx_man_encode ( training[ byte_cnt ] );
for ( bit_cnt = 0; bit_cnt < 16; bit_cnt++ )
{
if ( man_data & MICRFTX_MAN_MSB )
{
micrftx_set_data_pin ( ctx );
}
else
{
micrftx_clear_data_pin ( ctx );
}
man_data <<= 1;
Delay_us ( MICRFTX_MAN_BIT_LEN_US / 2 );
}
}
// Send the packet bytes
for ( byte_cnt = 0; byte_cnt < ( len + 5 ); byte_cnt++ )
{
man_data = micrftx_man_encode ( packet_buf[ byte_cnt ] );
for ( bit_cnt = 0; bit_cnt < 16; bit_cnt++ )
{
if ( man_data & MICRFTX_MAN_MSB )
{
micrftx_set_data_pin ( ctx );
}
else
{
micrftx_clear_data_pin ( ctx );
}
man_data <<= 1;
Delay_us ( MICRFTX_MAN_BIT_LEN_US / 2 );
}
}
Delay_10ms( );
micrftx_disable_device ( ctx );
}
static uint16_t micrftx_man_encode ( uint8_t data_in )
{
uint16_t man_data = 0;
for ( uint8_t bit_cnt = 0; bit_cnt < 8; bit_cnt++ )
{
man_data <<= 2;
if ( data_in & ( 0x80 >> bit_cnt ) )
{
man_data |= 1; // 1: low going to a high
}
else
{
man_data |= 2; // 0: high going to a low
}
}
return man_data;
}
static uint16_t micrftx_reflect_bits( uint16_t data_in, uint8_t len )
{
uint16_t data_out = 0;
for ( uint16_t cnt = 0; cnt < len; cnt++ )
{
data_out |= ( ( data_in >> cnt ) & 1 ) << ( len - cnt - 1 );
}
return data_out;
}
static uint16_t micrftx_calculate_crc16( uint8_t *data_buf, uint16_t len )
{
uint16_t crc16 = 0x0000;
for ( uint16_t cnt = 0; cnt < len; cnt++ )
{
crc16 ^= ( micrftx_reflect_bits( data_buf[ cnt ], 8 ) << 8 );
for ( uint8_t bit_cnt = 0; bit_cnt < 8; bit_cnt++ )
{
if ( crc16 & 0x8000 )
{
crc16 = ( crc16 << 1 ) ^ 0x8005;
}
else
{
crc16 <<= 1;
}
}
}
return micrftx_reflect_bits( crc16, 16 ) ^ 0xFFFF;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
额外支持
资源
类别:1GHz以下收发器