通过 GSM 网络进行通信,增强您的项目功能,实现远程监控、数据传输和各种应用的语音通话。
A
A
硬件概览
它是如何工作的?
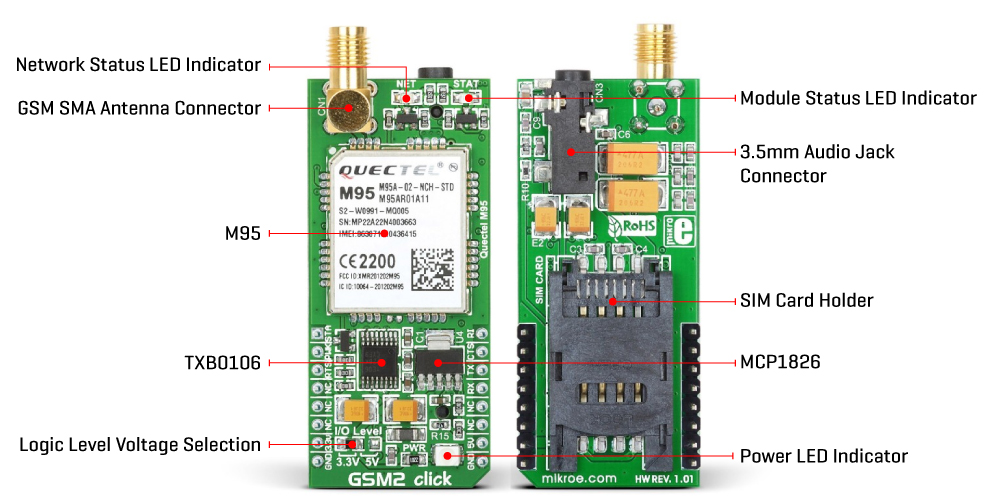
GSM 2 Click 基于 Quectel 的 M95 四频 GSM/GPRS 模块。该模块支持四频 GSM/GPRS,使其可以在全球范围内使用。它覆盖850/900 MHz 频率,最高可提供2W的传输功率,以及1800/1900 MHz频率,最高可提供1W的传输功率。M95模块还符合欧盟 eCall 指令。该模块是 Click board™ 的主要组成部分,包括几个内部模块或部分,如天线切换部分、RF收发器部分、内存、电源管理,以及最重要的 - 蜂窝基带处理 器。M95模块必须由干净且稳定的电源供电。模块正常工作所需的电压约为4V,通过 Microchip 的 MCP1826(一种1A低降压输出(LDO)调节器)从5V mikroBUS™轨道得到。虽然M95是一种低功耗设备,但一般来说,蜂窝网络模块因其高功耗而臭名昭
著,因此必须使用1A LDO。M95的数字部分内部由2.8V供电,因此必须调节连接主 MCU 和模块的通信总线线。M95从其内部LDO输出2.8V,为德州仪器的TXB0106(一种6位双向电平移位和电压转换器,具有自动方向感应)的一侧提供所需的参考电压。M95提供广泛的音频功能,包括半速率、全速率、增强全速率、自适应多速率语音编解码器、卓越的回声消除和降噪功能。耳机可以通过4极3.5毫米音频插孔连接。Click board™背面的Micro SIM卡插槽用于安装microSIM卡。未安装有效SIM卡则无法使用此设备, 因为需要连接到蜂窝网络。支持1.8V和3V的SIM卡类型。GSM 2 Click使用标准的2线UART接口与主MCU通信,使用常用的UART RX和TX引脚,并支持从
300bps到115200bps的数据速率,具有自动波特率检测功能。此外,还提供UART RTS和CTS硬件流控引脚。除了我们提供的库,您还可以使用AT命令。RI引脚用作振铃指示器。还有一个PWK引脚用于供电模块,以及一个STA引脚,用于指示设备状态。此状态也通过STA LED显示。另一个LED是NET LED,显示网络状态。此Click board™可以通过I/O Level跳线选择使用3.3V或5V逻辑电压级别,这样3.3V和5V能力的MCU都可以正确使用通信线。此外,这款Click board™配备了包含易于使用的功能和示例代码的库,可用作进一步开发的参考。
功能概述
开发板
EasyPIC v8 是一款专为快速开发嵌入式应用的需求而特别设计的开发板。它支持许多高引脚计数的8位PIC微控制器,来自Microchip,无论它们的引脚数量如何,并且具有一系列独特功能,例如首次集成的调试器/程序员。开发板布局合理,设计周到,使得最终用户可以在一个地方找到所有必要的元素,如开关、按钮、指示灯、连接器等。得益于创新的制造技术,EasyPIC v8 提供了流畅而沉浸式的工作体验,允许在任何情况下、任何地方、任何时候都能访问。
EasyPIC v8 开发板的每个部分都包含了使同一板块运行最高效的必要组件。除了先进的集成CODEGRIP程 序/调试模块,该模块提供许多有价值的编程/调试选项和与Mikroe软件环境的无缝集成外,该板还包括一个干净且调节过的开发板电源供应模块。它可以使用广泛的外部电源,包括电池、外部12V电源供应和通过USB Type-C(USB-C)连接器的电源。通信选项如USB-UART、USB DEVICE和CAN也包括在内,包括 广受好评的mikroBUS™标准、两种显示选项(图形和
基于字符的LCD)和几种不同的DIP插座。这些插座覆盖了从最小的只有八个至四十个引脚的8位PIC MCU的广泛范围。EasyPIC v8 是Mikroe快速开发生态系统的一个组成部分。它由Mikroe软件工具原生支持,得益于大量不同的Click板™(超过一千块板),其数量每天都在增长,它涵盖了原型制作和开发的许多方面。
微控制器概述
MCU卡片 / MCU

建筑
PIC
MCU 内存 (KB)
24
硅供应商
Microchip
引脚数
28
RAM (字节)
2048
你完善了我!
配件
橡胶天线 GSM/GPRS 直角型是我们丰富的 GSM Click boards™ 系列的完美配件。这款专业天线旨在通过令人印象深刻的功能优化您的无线连接。具有广泛的频率范围,覆盖 824-894/1710-1990MHz 或 890-960/1710-1890MHz,它可以处理各种频段,确保无缝且可靠的连接。该天线具有 50 欧姆的阻抗和 2dB 的增益,增强了信号接收和传输。其 70/180MHz 的带宽为多样化的应用提供了灵活性。垂直偏振进一步增强了其性能。该天线的最大输入功率容量为 50W,即使在苛刻条件下也能确保稳健的通信。天线长度为紧凑的 50mm,并配有 SMA 男性连接器,橡胶天线 GSM/GPRS 直角型是您无线通信需求的多功能紧凑解决方案。
使用的MCU引脚
mikroBUS™映射器
“仔细看看!”
Click board™ 原理图

一步一步来
项目组装
实时跟踪您的结果
应用程序输出
1. 应用程序输出 - 在调试模式下,“应用程序输出”窗口支持实时数据监控,直接提供执行结果的可视化。请按照提供的教程正确配置环境,以确保数据正确显示。

2. UART 终端 - 使用UART Terminal通过USB to UART converter监视数据传输,实现Click board™与开发系统之间的直接通信。请根据项目需求配置波特率和其他串行设置,以确保正常运行。有关分步设置说明,请参考提供的教程。

3. Plot 输出 - Plot功能提供了一种强大的方式来可视化实时传感器数据,使趋势分析、调试和多个数据点的对比变得更加直观。要正确设置,请按照提供的教程,其中包含使用Plot功能显示Click board™读数的分步示例。在代码中使用Plot功能时,请使用以下函数:plot(insert_graph_name, variable_name);。这是一个通用格式,用户需要将“insert_graph_name”替换为实际图表名称,并将“variable_name”替换为要显示的参数。

软件支持
库描述
此库包含 GSM2 Click 驱动程序的 API。
关键功能:
gsm2_set_sim_apn- 此功能用于为 SIM 卡设置 APN。gsm2_send_sms_text- 此功能用于向电话号码发送文本消息。gsm2_send_sms_pdu- 此功能用于以 PDU 模式向电话号码发送文本消息。
开源
代码示例
完整的应用程序代码和一个现成的项目可以通过NECTO Studio包管理器直接安装到NECTO Studio。 应用程序代码也可以在MIKROE的GitHub账户中找到。
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief GSM 2 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* Application example shows device capability of connecting to the network and
* sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages using standard "AT" commands.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver, tests the communication by sending "AT" command, and after that restarts the device.
*
* ## Application Task
* Application task is split in few stages:
* - GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
* Sets configuration to device to be able to connect to the network.
*
* - GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
* Waits for the network registration indicated via CREG URC event and then checks
* the connection status.
*
* - GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
* Sets the device configuration for sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages depending on the selected demo example.
*
* - GSM2_EXAMPLE:
* Depending on the selected demo example, it sends an SMS message (in PDU or TXT mode) or TCP/UDP message.
*
* By default, the TCP/UDP example is selected.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_process ( void )
* - static void gsm2_error_check( err_t error_flag )
* - static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
* - static err_t gsm2_configure_for_connection( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_check_connection( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_configure_for_messages( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_send_message( void )
*
* @note
* In order for the examples to work, user needs to set the APN and SMSC (SMS PDU mode only)
* of entered SIM card as well as the phone number (SMS mode only) to which he wants to send an SMS.
* Enter valid values for the following macros: SIM_APN, SIM_SMSC and PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE.
* Example:
SIM_APN "internet"
SIM_SMSC "+381610401"
PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "+381659999999"
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gsm2.h"
#include "conversions.h"
// Example selection macros
#define EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP 0 // Example of sending messages to a TCP/UDP echo server
#define EXAMPLE_SMS 1 // Example of sending SMS to a phone number
#define DEMO_EXAMPLE EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP // Example selection macro
// SIM APN config
#define SIM_APN "internet" // Set valid SIM APN
// SMS example parameters
#define SIM_SMSC "" // Set valid SMS Service Center Address - only in SMS PDU mode
#define PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "" // Set Phone number to message
#define SMS_MODE "1" // SMS mode: "0" - PDU, "1" - TXT
// TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
// Message content
#define MESSAGE_CONTENT "GSM 2 click board - demo example."
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 256
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 256
/**
* @brief Example states.
* @details Predefined enum values for application example state.
*/
typedef enum
{
GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK = 1,
GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION,
GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE,
GSM2_EXAMPLE
} gsm2_example_state_t;
static gsm2_t gsm2;
static log_t logger;
/**
* @brief Application example variables.
* @details Variables used in application example.
*/
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static err_t error_flag;
static gsm2_example_state_t example_state;
/**
* @brief Clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application
* buffer and reset its length and counter.
*/
static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and
* appends it to the application buffer.
* @return @li @c 0 - Some data is read.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_process ( void );
/**
* @brief Check for errors.
* @details This function checks for different types of
* errors and logs them on UART or logs the response if no errors occured.
* @param[in] error_flag Error flag to check.
*/
static void gsm2_error_check ( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief Logs application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer.
*/
static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Response check.
* @details This function checks for response and
* returns the status of response.
* @param[in] rsp Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp );
/**
* @brief Configure device for connection to the network.
* @details Sends commands to configure and enable
* connection to the specified network.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_network ( void );
/**
* @brief Wait for connection signal.
* @details Wait for connection signal from CREG URC.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_check_connection ( void );
/**
* @brief Configure device for example.
* @details Configure device for the specified example.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_example ( void );
/**
* @brief Execute example.
* @details This function executes SMS or TCP/UDP example depending on the DEMO_EXAMPLE macro.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_example ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
gsm2_cfg_t gsm2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
gsm2_cfg_setup( &gsm2_cfg );
GSM2_MAP_MIKROBUS( gsm2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == gsm2_init( &gsm2, &gsm2_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
gsm2_process( );
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
// Check communication
gsm2_send_cmd( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_AT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Restart device
#define RESTART_DEVICE "1,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CFUN, RESTART_DEVICE );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
example_state = GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK;
}
void application_task ( void )
{
switch ( example_state )
{
case GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_configure_for_network( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_check_connection( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_configure_for_example( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_EXAMPLE:
{
gsm2_example( );
break;
}
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Example state." );
break;
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static err_t gsm2_process ( void )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t rx_size = 0;
rx_size = gsm2_generic_read( &gsm2, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
if ( ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) && ( app_buf_len > 0 ) )
{
buf_cnt = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE );
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE - buf_cnt ], buf_cnt );
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ buf_cnt++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
if ( app_buf_len < APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
app_buf_len++;
}
}
}
return GSM2_OK;
}
return GSM2_ERROR;
}
static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 120000;
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
gsm2_process( );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, rsp ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, GSM2_RSP_ERROR ) ) )
{
gsm2_process( );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > timeout )
{
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
return GSM2_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms( 1 );
}
Delay_ms( 100 );
gsm2_process( );
if ( strstr( app_buf, rsp ) )
{
return GSM2_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, GSM2_RSP_ERROR ) )
{
return GSM2_ERROR_CMD;
}
else
{
return GSM2_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
}
static void gsm2_error_check ( err_t error_flag )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case GSM2_OK:
{
gsm2_log_app_buf( );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR:
{
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_TIMEOUT:
{
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_CMD:
{
log_error( &logger, " CMD!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_UNKNOWN:
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Unknown!" );
break;
}
}
Delay_ms( 500 );
}
static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_network ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
Delay_ms ( 5000 );
// Deregister from network
#define DEREGISTER_FROM_NETWORK "2"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_COPS, DEREGISTER_FROM_NETWORK );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Set SIM APN
gsm2_set_sim_apn( &gsm2, SIM_APN );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable full functionality
#define FULL_FUNCTIONALITY "1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CFUN, FULL_FUNCTIONALITY );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable network registartion
#define ENABLE_REG "2"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CREG, ENABLE_REG );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Automatic registration
#define AUTOMATIC_REGISTRATION "0"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_COPS, AUTOMATIC_REGISTRATION );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t gsm2_check_connection ( void )
{
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
#define CONNECTED "+CREG: 2,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_check ( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CREG );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CONNECTED ) )
{
Delay_ms( 100 );
// Check signal quality
gsm2_send_cmd( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CSQ );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#define NO_SIGNAL "99,99"
if ( !strstr( app_buf, NO_SIGNAL ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return error_flag;
}
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return GSM2_ERROR;
#endif
return GSM2_OK;
}
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
#define ACTIVATE_PDP_CONTEXT "1,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CGACT, ACTIVATE_PDP_CONTEXT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#define ENABLE_MULTI_SESSION "1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIMUX, ENABLE_MULTI_SESSION );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CMGF, SMS_MODE );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t gsm2_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
uint8_t cmd_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
uint8_t tcp_socket_num[ 2 ] = { '1', 0 };
uint8_t udp_socket_num[ 2 ] = { '2', 0 };
// Open TCP socket.
#define RESPONSE_CONNECT "CONNECT OK"
#define TCP_SERVICE_TYPE ",\"TCP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, TCP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIOPEN, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Open UDP socket.
#define UDP_SERVICE_TYPE ",\"UDP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, UDP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIOPEN, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Get message length
uint8_t message_len_buf[ 10 ] = { 0 };
uint16_t message_len = strlen( MESSAGE_CONTENT );
uint16_to_str( message_len, message_len_buf );
l_trim( message_len_buf );
r_trim( message_len_buf );
// Write message to TCP socket
uint8_t ctrl_z = 0x1A;
strcpy( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QISEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, &ctrl_z, 1 );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Read response
#define RESPONSE_URC "+RECEIVE: "
strcpy( cmd_buf, RESPONSE_URC );
strcat( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( cmd_buf );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Write message to UDP socket
strcpy( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QISEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, &ctrl_z, 1 );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Read response
strcpy( cmd_buf, RESPONSE_URC );
strcat( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( cmd_buf );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Close TCP socket
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QICLOSE, tcp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Close UDP socket
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QICLOSE, udp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
Delay_ms( 5000 );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
// Check SMS mode
#define CMGF_PDU "+CMGF: 0"
#define CMGF_TXT "+CMGF: 1"
gsm2_send_cmd_check( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CMGF );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_PDU ) )
{
// Send SMS in PDU mode
gsm2_send_sms_pdu( &gsm2, SIM_SMSC, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_TXT ) )
{
// Send SMS in TXT mode
gsm2_send_sms_text ( &gsm2, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
}
Delay_ms( 10000 );
Delay_ms( 10000 );
Delay_ms( 10000 );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END