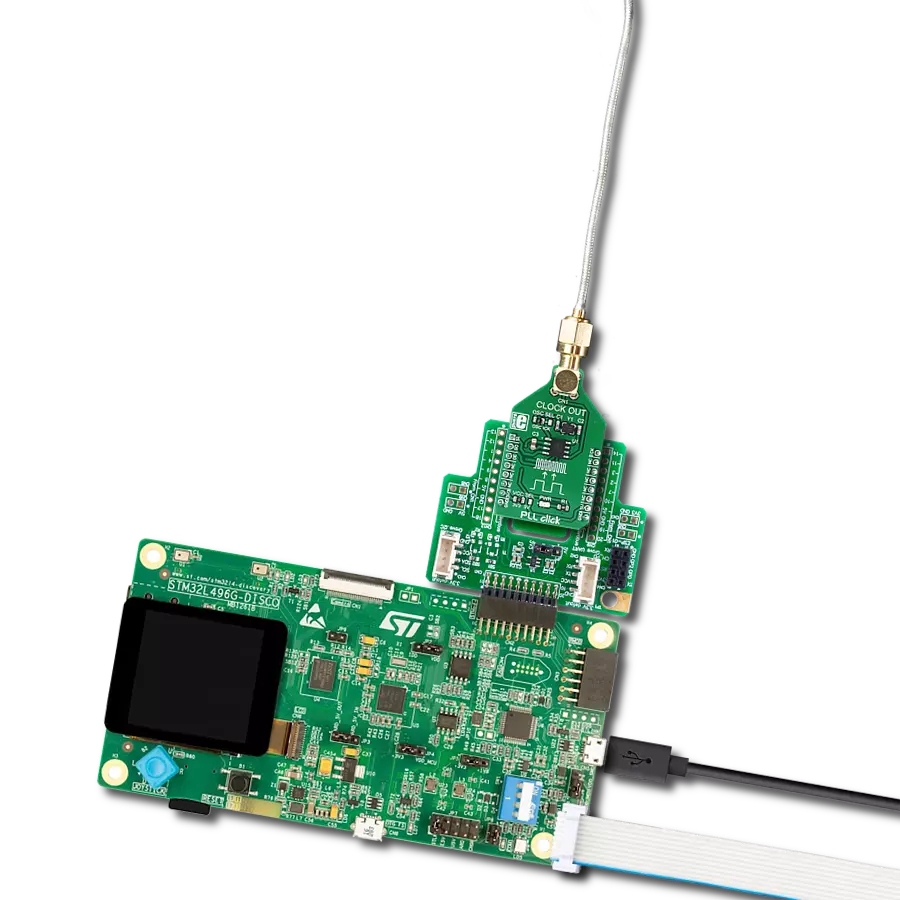
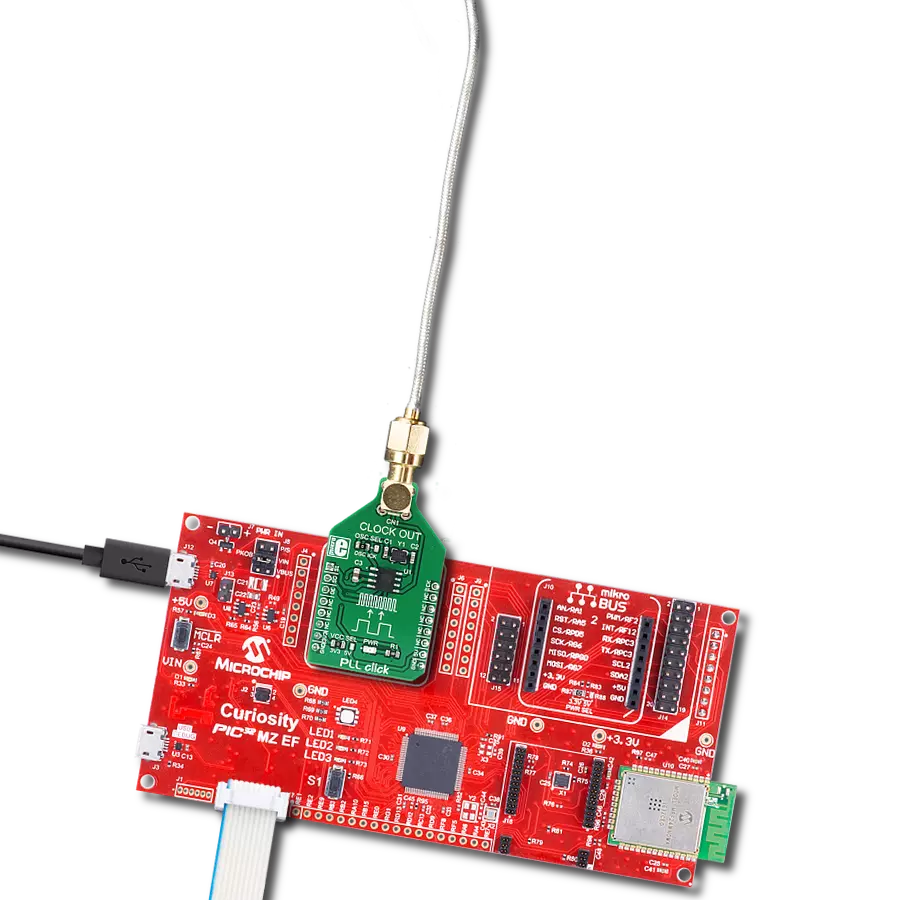
Generate highly stable and coherent high-frequency signals for applications requiring tight synchronization and minimal phase noise
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
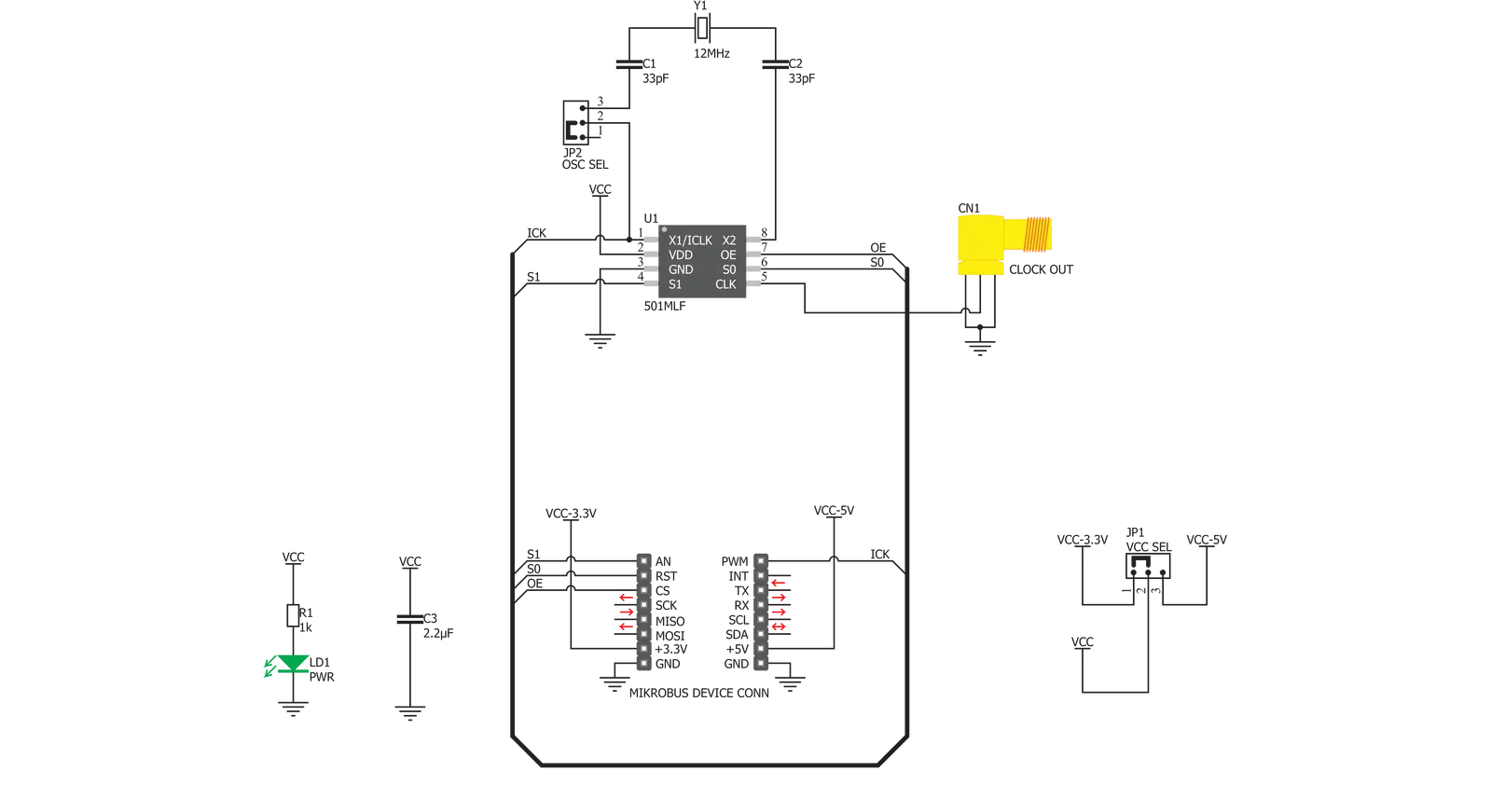
PLL Click is based on the ICS501, a LOCO™ PLL clock multiplier, from Integrated Device Technology. This IC uses the Phase-Locked Loop to provide a high-frequency clock output, deriving input from a much cheaper, standard fundamental frequency crystal oscillator. Besides the onboard crystal oscillator fixed at 12MHz, it is possible to select the signal from the mikroBUS™ PWM pin as the clock input source. To select the desired multiplication factor, the states of the two input pins, S0 and S1, are routed to the mikroBUS™ pins RST and AN, respectively. These pins can be set to a HIGH or LOW logic state or disconnected (by tri-stating the MCU pins). The combination of these pins states will set the PLL
Click to a specific multiplier. The Output Enable (OE) pin of the ICS501 is used to turn off the output clock by setting it to a LOW logic level. It will additionally set the clock output pin in high impedance (Hi-Z) mode, allowing complete disconnection and no influence on the rest of the circuit, which is useful for experimenting and prototyping purposes. This pin is internally pulled to a HIGH logic level. The OE pin is routed to the CS pin of the mikroBUS™. PLL Click is equipped with two onboard SMD jumpers. The SMD jumper labeled as the VCC SEL is used to select the operating voltage level, consequently limiting the amplitude of the clock output signal with respect to the selected voltage. The other SMD jumper
labeled as the OSC SEL chooses the clock input source between the onboard 12MHz crystal oscillator or the external clock signal. The output signal is routed through the onboard SMA connector, which provides a secure connection and good signal shielding. PLL Click has a library containing functions for all the MIKROE compilers (mikroBASIC, mikroPASCAL, and mikroC). Although relatively easy to control, the library offers comprehensive functions that make the code readable and easy to use. The included example application demonstrates the use of these functions, and it can be used as a reference for custom projects.
Features overview
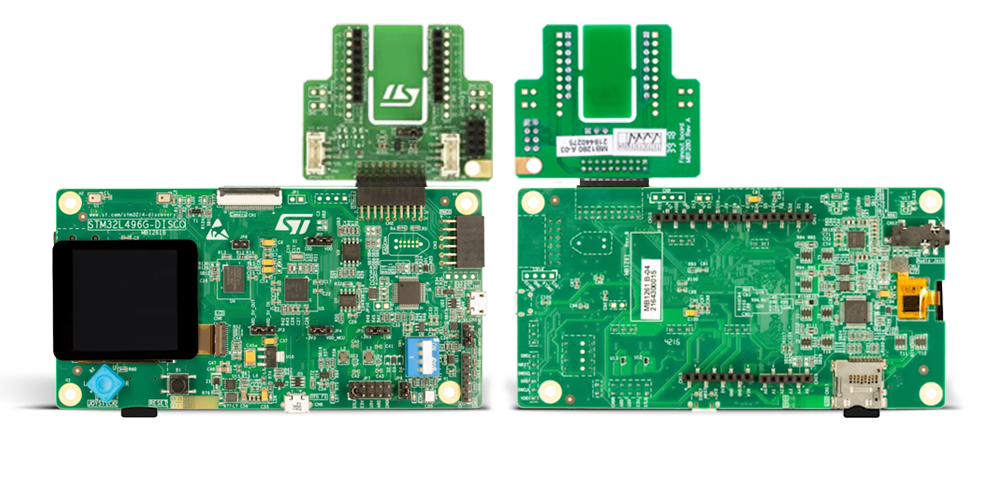
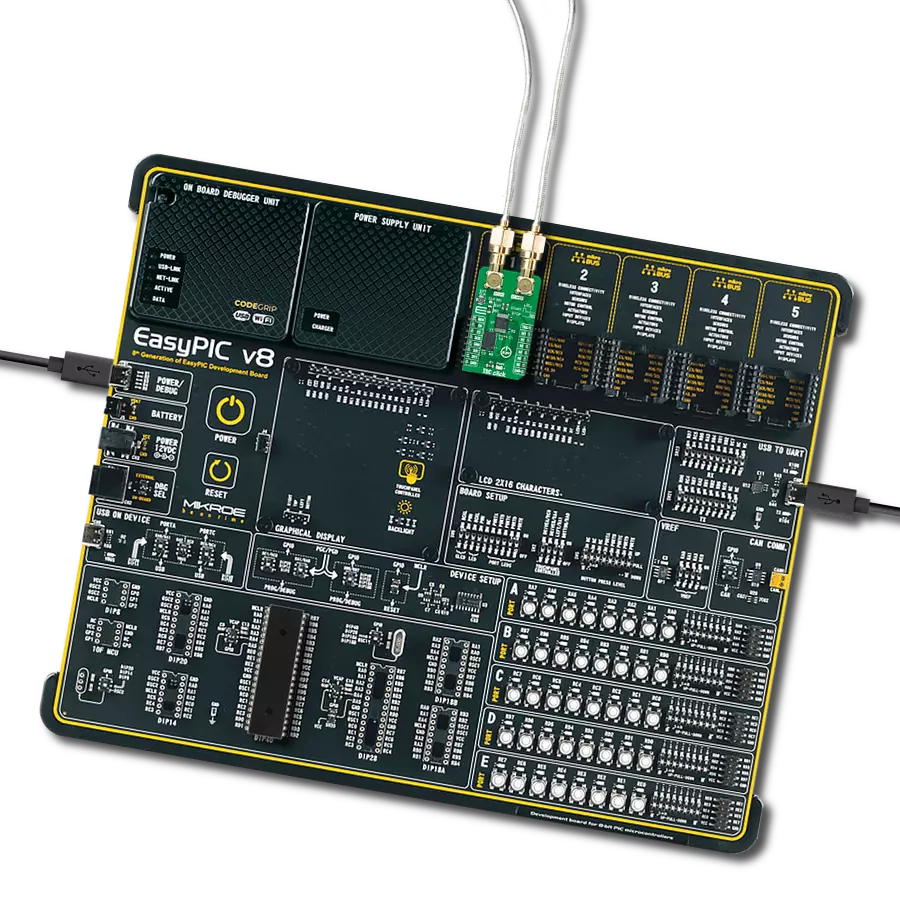
Development board
The 32L496GDISCOVERY Discovery kit serves as a comprehensive demonstration and development platform for the STM32L496AG microcontroller, featuring an Arm® Cortex®-M4 core. Designed for applications that demand a balance of high performance, advanced graphics, and ultra-low power consumption, this kit enables seamless prototyping for a wide range of embedded solutions. With its innovative energy-efficient
architecture, the STM32L496AG integrates extended RAM and the Chrom-ART Accelerator, enhancing graphics performance while maintaining low power consumption. This makes the kit particularly well-suited for applications involving audio processing, graphical user interfaces, and real-time data acquisition, where energy efficiency is a key requirement. For ease of development, the board includes an onboard ST-LINK/V2-1
debugger/programmer, providing a seamless out-of-the-box experience for loading, debugging, and testing applications without requiring additional hardware. The combination of low power features, enhanced memory capabilities, and built-in debugging tools makes the 32L496GDISCOVERY kit an ideal choice for prototyping advanced embedded systems with state-of-the-art energy efficiency.
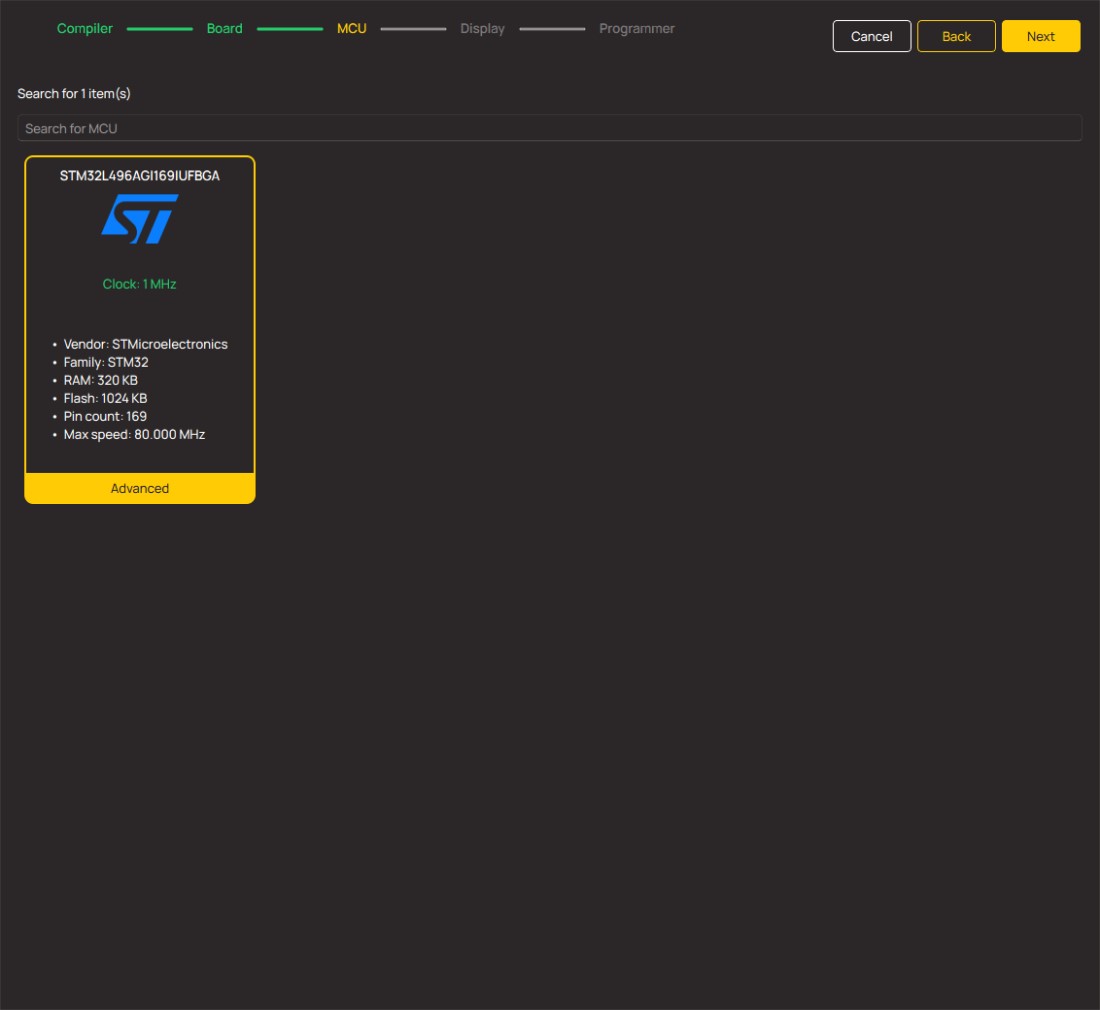
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
169
RAM (Bytes)
327680
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
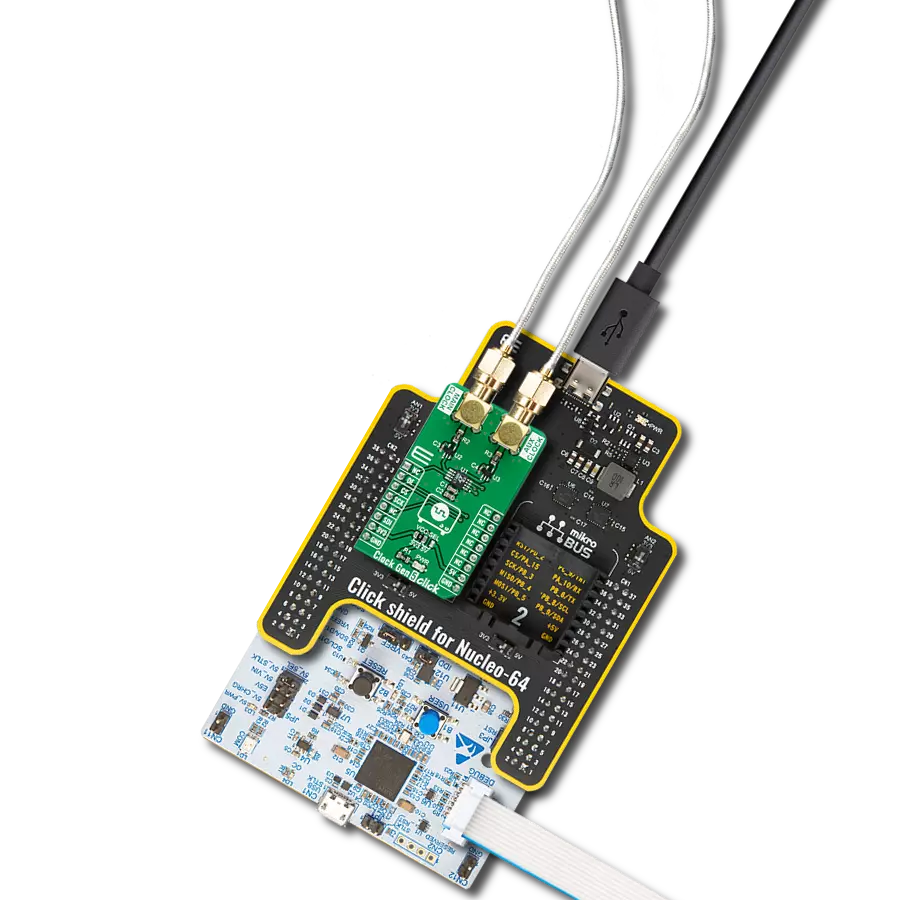
Step by step
Project assembly
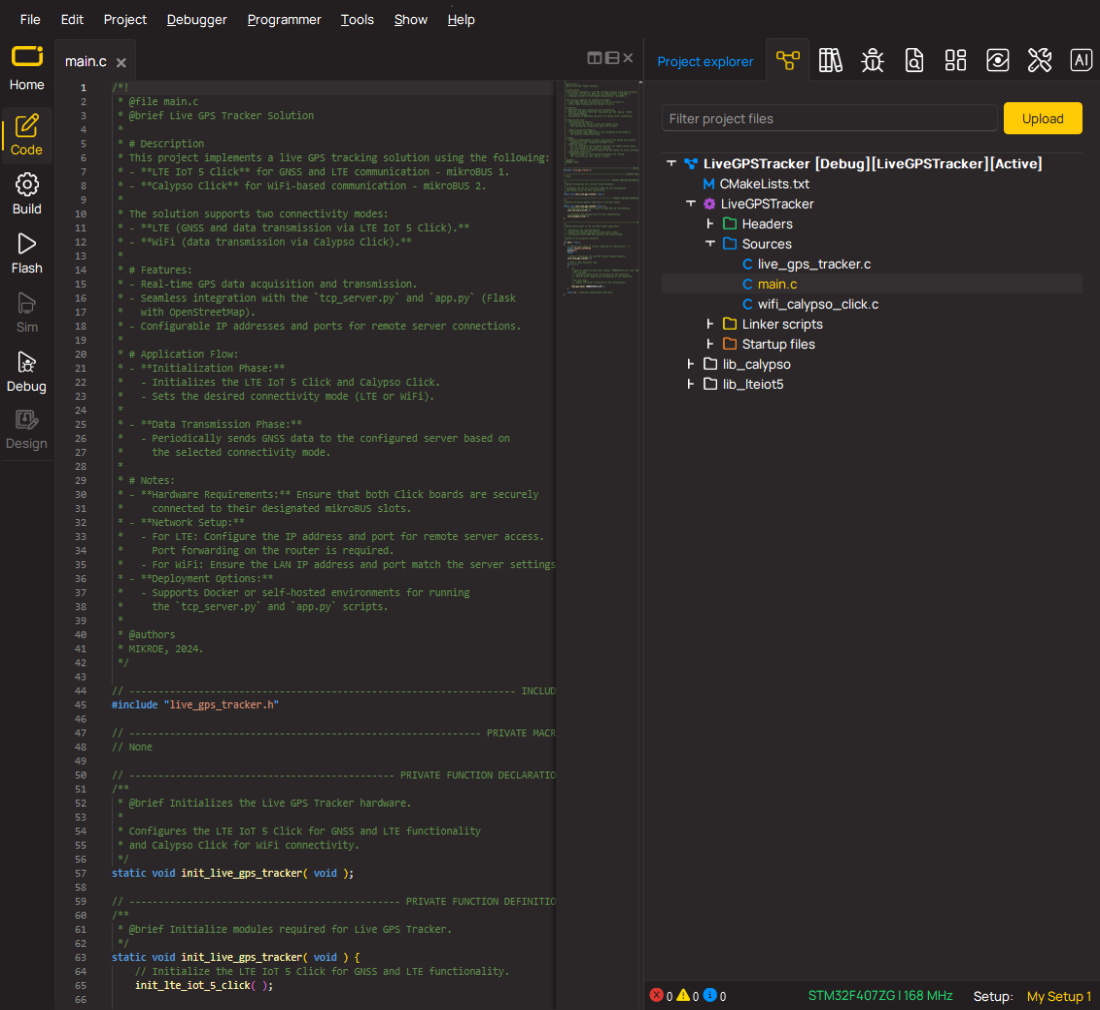
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for PLL Click driver.
Key functions:
pll_set_clock_output- This function settings clock outputpll_set_pll_4x- This function settings PLL x4pll_set_pll_6x- This function settings PLL x6
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief PLL Click example
*
* # Description
* This app sets PLL signals.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes device.
*
* ## Application Task
* Every 2 seconds, the PLL increases the input clock from min (x2) to max (x8) level.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "pll.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static pll_t pll;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
pll_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
pll_cfg_setup( &cfg );
PLL_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
pll_init( &pll, &cfg );
pll_set_clock_output( &pll, PLL_CLOCK_ENABLE );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x2\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_2x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x3\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_3x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x3.125\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_3_125x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x4\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_4x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x5\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_5x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x5.3125\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_5_3125x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x6\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_6x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x6.25\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_6_25x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " PLL level: x8\r\n\n" );
pll_set_pll_8x( &pll );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Clock generator