Effortlessly convert RS232 data into the SPI format with our user-friendly solution, streamlining the process of modernizing data communication
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
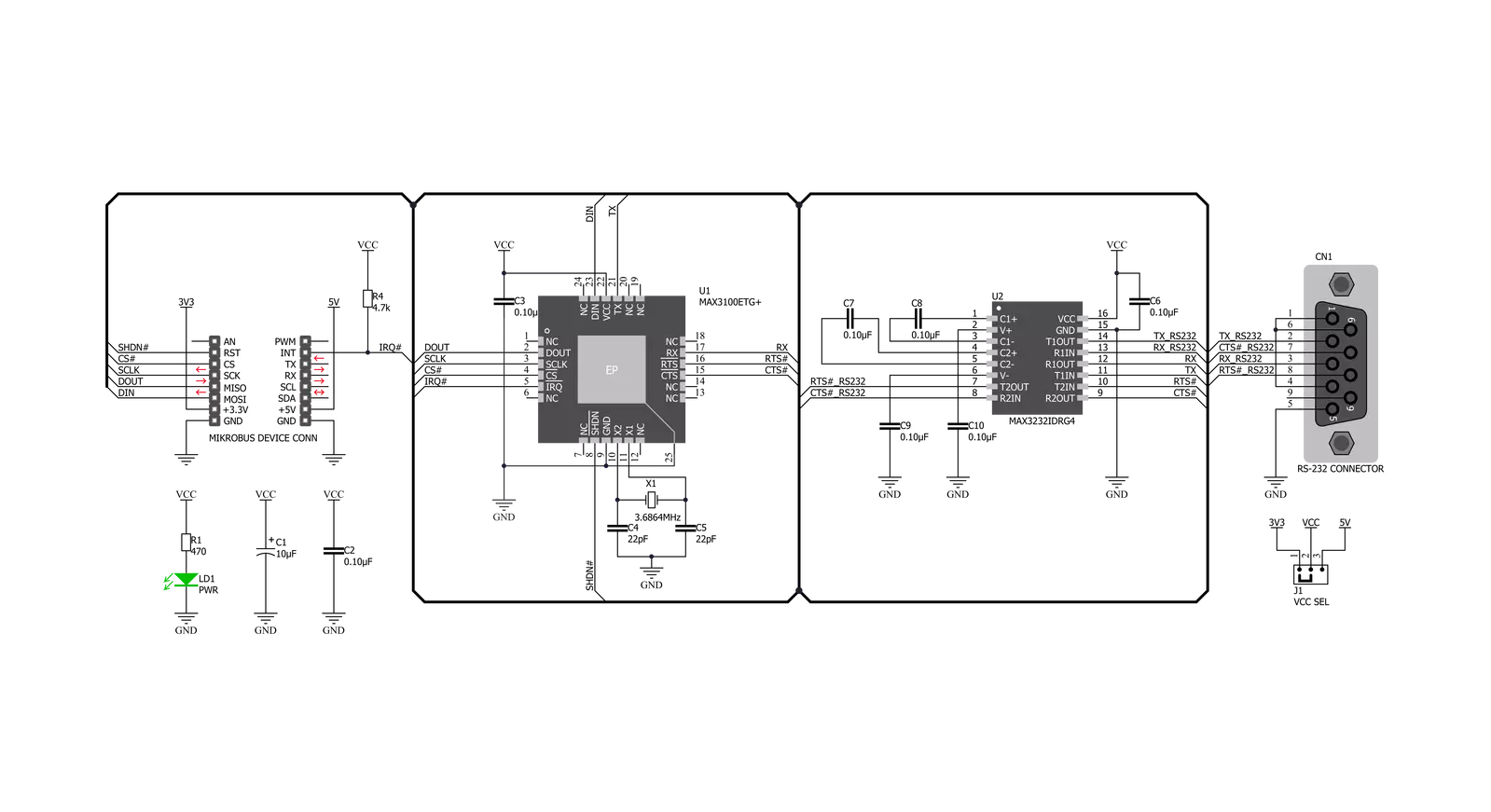
RS232 SPI Click is based on two ICs - MAX3100 and MAX3232. The MAX3100 serves as UART interface to the SPI/MICROWIRE compatible interface converter. In the same time, MAX3232 device enables RS232 SPI click to meet the requirements of TIA/EIA-232-F and also provides the electrical interface between an asynchronous communication controller and the serial-port connector. The charge pump and four small external capacitors allow operation from a single 3-V to 5.5-V supply. RS232 SPI click Uses an SPI™/MICROWIRE™ interface for communication with the host microcontroller (µC). Then, the MAX3100 is responsible for conversion from synchronous serial data from a microcontroller to asynchronous, serial-data communication port such as RS-232, RS-485, IrDA. In this case the
RS232 protocol is used. The MAX3100 includes a crystal oscillator and a baud rate generator with software-programmable divider ratios for all common baud rates from 300 baud to 230k baud. The transmitter section accepts SPI/MICROWIRE data, formats it, and transmits it in asynchronous serial format from the TX output. Data is loaded into the transmit buffer register from the SPI/MICROWIRE interface. The MAX3100 adds start and stop bits to the data and clocks the data out at the selected baud rate. A software- or hardware-invoked shutdown lowers quiescent current to 10µA, while allowing the MAX3100 to detect receiver activity. An 8-word-deep first-in/first-out (FIFO) buffer minimizes processor overhead. This device also includes a flexible interrupt with four maskable sources, including address recognition
on 9-bit networks. Two hardware-handshaking control lines are included (one input and one output). Because of the features contained in its modules, the RS232 SPI click can be used for handheld instruments, UART in SPI systems, small networks in HVAC or Building control, battery-powered systems, PDAs, notebooks and many more. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
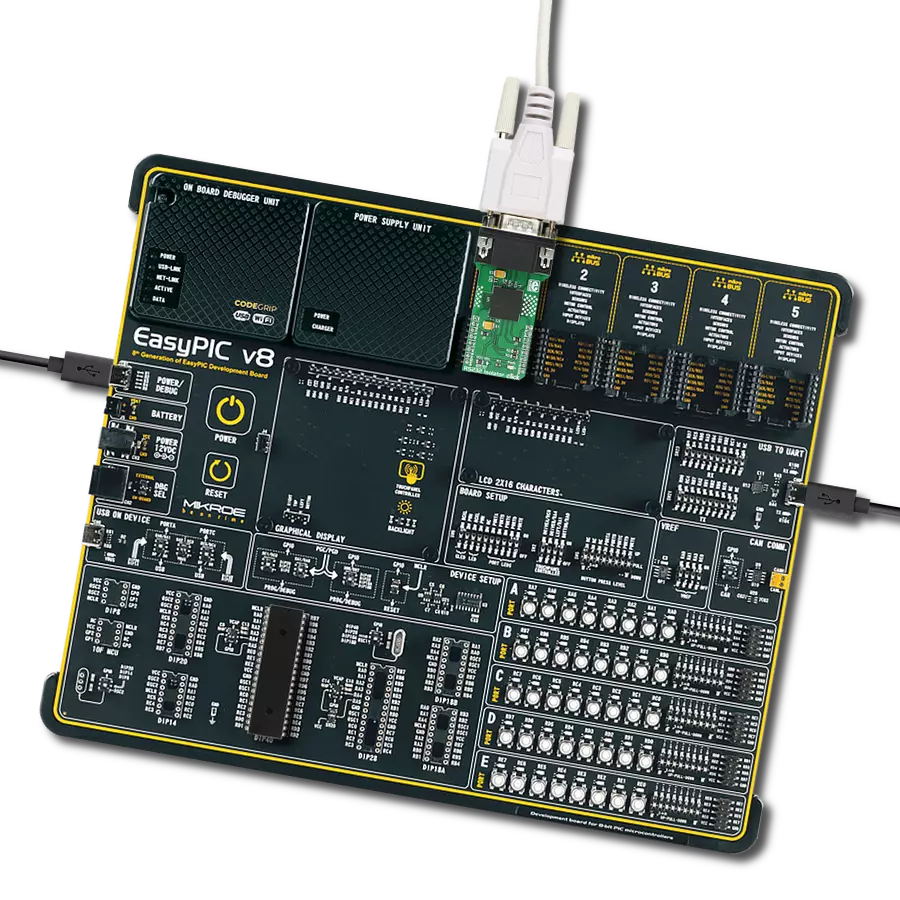
Development board
Explorer 16/32 development board is a flexible and convenient development, demonstration, and testing platform for 16-bit PIC24 MCUs, dsPIC® DSCs, and 32-bit PIC32 MCUs from Microchip Technology. It features all the necessary hardware to develop and debug a complete embedded application. The board accepts Processor Plug-In Modules (PIMs) designed for the Explorer 16 or Explorer 16/32 development board for easy device swapping. In addition to the hardware features provided by the board, hardware expansion is possible through the use of PICtail™ Plus
daughter cards and mikroBUS™ accessory boards. Coupled with the integrated PICkit™-On-Board (PKOB), MPLAB ICD In-Circuit Debugger real-time debug facilities enable faster evaluation and prototyping of applications. This development board supports all the Explorer PIMs. However, not all PIMs are supported by the PKOB. To check the list of supported and unsupported PIMs, refer to the PICkit™ On-Board 3 (PKOB3) Support List. For PIMs not on the PKOB3 support list, use the JP1 or J14 connectors to program the device with a newer generation programming tool. Explorer 16/32
development board offers only the main board, allowing customization of the other necessary components. Choose your PIM based on MCUs and DSCs under consideration from a wide range of Processor Plug-In Modules. This board is optimal for customers migrating from Classic Explorer 16 to the new Explorer 16/32 platform, while all the necessary additional components like Processor Plug-In Modules and PICtail™ Plus Daughter Boards are already available.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
512
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
32768
You complete me!
Accessories
DB9 Cable Female-to-Female (2m) cable is essential for establishing dependable serial data connections between devices. With its DB9 female connectors on both ends, this cable enables a seamless link between various equipment, such as computers, routers, switches, and other serial devices. Measuring 2 meters in length, it offers flexibility in arranging your setup without compromising data transmission quality. Crafted with precision, this cable ensures consistent and reliable data exchange, making it suitable for industrial applications, office environments, and home setups. Whether configuring networking equipment, accessing console ports, or utilizing serial peripherals, this cable's durable construction and robust connectors guarantee a stable connection. Simplify your data communication needs with the 2m DB9 female-to-female cable, an efficient solution designed to meet your serial connectivity requirements easily and efficiently.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for RS232 SPI Click driver.
Key functions:
rs232spi_reg_write- This function writes two bytes of data using the SPI serial interface.rs232spi_reg_read- This function reads two bytes of data using the SPI serial interface.rs232spi_digital_write_rst- This function writes the specified digital signal to the RST pin.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Rs232Spi Click example
*
* # Description
* This example showcases how to initialize and use the RS232 SPI Click. The Click has a uni-
* versal asynchronous transceiver which uses a SPI serial interface to communicate with the
* MCU. In order for this example to work, 2 Clicks are needed - a receiver and a transmitter.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* This function initializes and configures the logger and Click modules. Additional configura-
* ting is done in the default_cfg(...) function.
*
* ## Application Task
* This function receives and displays UART data in the "read mode" and sends the predefined
* message in the "write mode".
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "rs232spi.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static rs232spi_t rs232spi;
static log_t logger;
static const uint8_t message[ 9 ] = { 'M', 'i', 'k', 'r', 'o', 'E', 13, 10, 0 };
static const uint8_t RX_MODE = 1;
static const uint8_t TX_MODE = 0;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
rs232spi_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
rs232spi_cfg_setup( &cfg );
RS232SPI_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
rs232spi_init( &rs232spi, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
rs232spi_digital_write_rst( &rs232spi, 1 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
rs232spi_default_cfg( &rs232spi, 115200 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
rs232spi_flush( &rs232spi );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "App init done...\r\n" );
}
void application_task ( )
{
uint8_t mode = RX_MODE;
uint8_t cnt;
char txt;
if ( mode == RX_MODE )
{
if ( rs232spi_data_ready( &rs232spi ) != 0 )
{
txt = rs232spi_transfer( &rs232spi, RS232SPI_CMD_READ_DATA );
log_printf( &logger, "%c", txt );
}
}
else if ( mode == TX_MODE )
{
for ( cnt = 0; cnt < 9; cnt++ )
{
rs232spi_data_write( &rs232spi, message[ cnt ] );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END