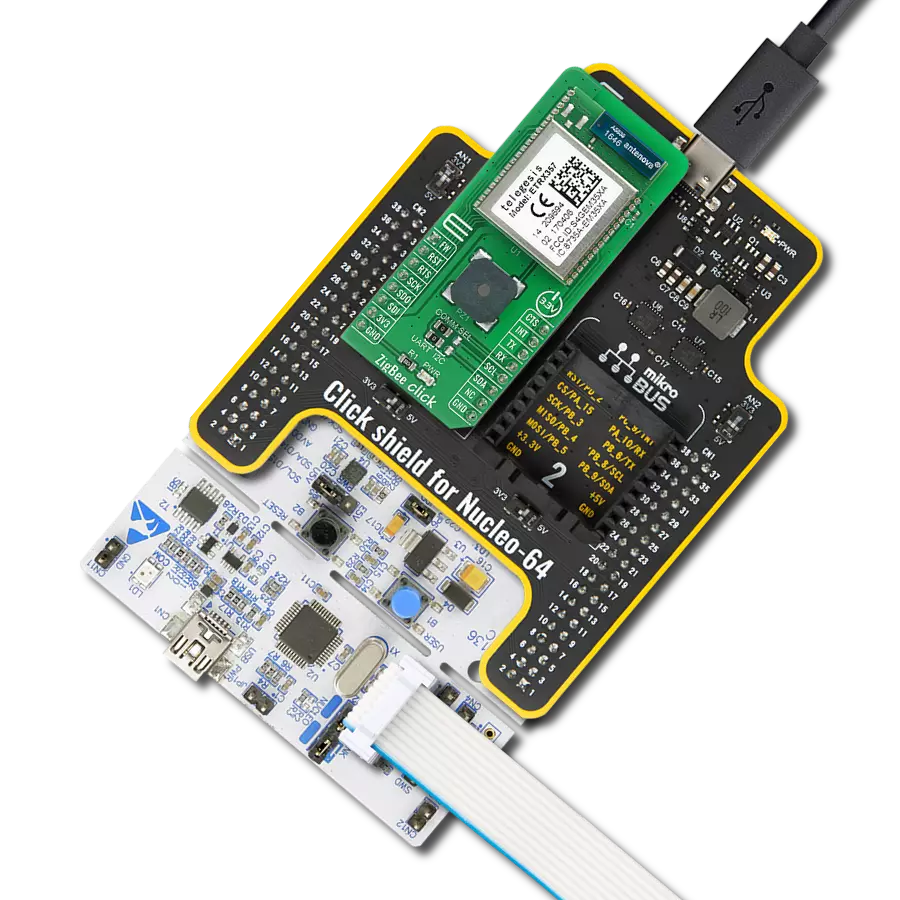
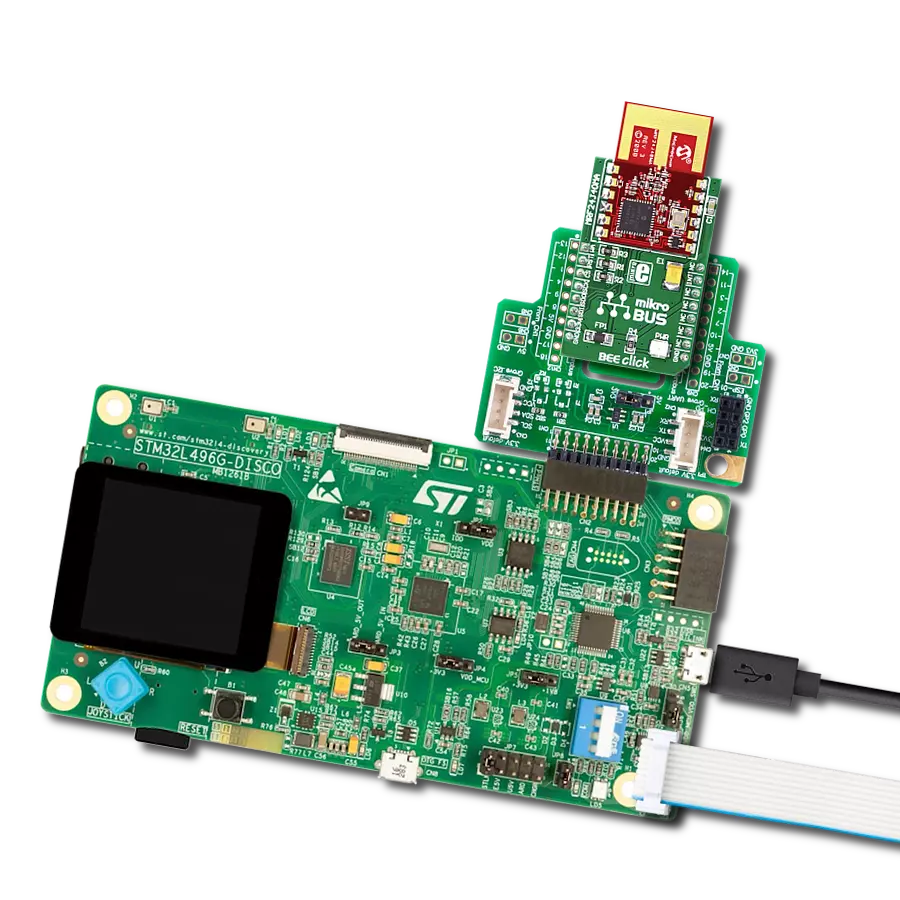
Discover the potential of our ZigBee Radio module, meticulously designed to conserve power while delivering robust wireless connectivity, ideal for IoT applications demanding efficiency and reliability.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
ZigBee Click is based on the ETRX357, a low power Zigbee Radio module integrating a 2.4 GHz compliant transceiver with many advanced peripherals from Silicon Labs. The ZigBee protocol is a set of standards for wireless connectivity for usage between any devices over short to medium distances. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 radio specification running on the 2.4GHz band, plus three additional layers for networking, security, and applications. What makes this module unique is its use of a mesh network architecture which, in bucket chain style, passes data from one node to the next until it lands at its destination. The ETRX357 module is pre-loaded with a standalone bootloader that supports over-the-air bootloading as well as serial bootloading of the new firmware, using the FW pin on the ZigBee Click. The module is controlled using the default firmware consisting of simple AT commands. Parameters that define the functionality of the module and also allow standalone functionality are saved in non-volatile memory organized in so-called S-Registers.
The commands and responses pass through the serial port of the ETRX357 as ASCII text, so a simple terminal application will usually suffice. The industry-standard serial wire, JTAG programming, and debugging interfaces together with the standard ARM system debug components help to streamline any custom software development. In addition to this, several MAC functions are also implemented in hardware to help to maintain the strict timing requirements imposed by the ZigBee and IEEE802.15.4 standards. The module is also able to act as a coordinator and Trust Centre through external host control. The AT-style command line supplies all the tools required to set up and manage a Zigbee network by allowing easy access to the low-level functionality of the stack. ZigBee Click communicates with MCU using the UART interface as its default communication protocol, but it is also left the option for the user to use other interfaces such as SPI and I2C if he wants to configure the module and write the library by himself. The selection
between UART and I2C can be done by positioning SMD jumpers labeled as COMM SEL to an appropriate position. Note that all the jumpers must be placed to the same side, or else the Click board™ may become unresponsive. Additional functionality such as reset and interrupt are provided and routed at RST and INT pins of the mikroBUSTM, as well as serial UART connections CTS and RTS, routed on the CS and PWM mikroBUSTM pins. To simplify deployment, the Click boardTM features the CMT-8540S-SMT magnetic buzzer controlled by the ZigBee module used for audible signalization and notification. You can create different sound patterns using the Sound library supported in our compilers. Signal frequency determines the sound pitch, and the duty cycle determines the amplitude (sound volume). This Click board™ is designed to be operated only with a 3.3V logic level. A proper logic voltage level conversion should be performed before the Click board™ is used with MCUs with different logic levels.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ZigBee Click driver.
Key functions:
zigbee_send_at- Function merges two string and sends it to device.zigbee_resp- Function checking driver buffer string.zigbee_set_pin_rst- Function setting RST pin status.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief ZigBee Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This is an example that demonstrates the use of the ZigBee Click board.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of driver, UART ISR and then configures device.
* Depending on previous selected device mode it creates new PAN network or joins to one.
*
* ## Application Task
* Host mode: Broadcasts message 'MikroE' every 3 seconds.
* User mode: Checks if something is received.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - void zigbee_clear_app_buf ( void ) - Clearing application buffer function.
* - void resp_wait ( zigbee_t *ctx ) - Function for waiting for complete response.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "zigbee.h"
static zigbee_t zigbee;
static log_t logger;
uint8_t dev_mode;
uint8_t app_mode;
static char app_buf[ ZIGBEE_DEV_BUFFER_MAX ] = { 0 };
char AT_BCAST_MSG[ 15 ] = ":00,MikroE";
char AT_HOST_CFG1[ 10 ] = "00=6314";
char AT_HOST_CFG2[ 20 ] = "0A=0914;password";
char AT_HOST_CFG3[ 50 ] = "09=5A6967426565416C6C69616E63653039;password";
/**
* @brief ZigBee clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset it's length and counter.
*/
void zigbee_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief ZigBee wait response.
* @details This function is used for waiting for complete response.
*/
void resp_wait ( zigbee_t *ctx );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
zigbee_cfg_t zigbee_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
app_mode = ZIGBEE_APP_INIT;
dev_mode = ZIGBEE_DEV_USER;
// Click initialization.
zigbee_cfg_setup( &zigbee_cfg );
ZIGBEE_MAP_MIKROBUS( zigbee_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == zigbee_init( &zigbee, &zigbee_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Restarting Device \r\n" );
zigbee_restart( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + DASSL \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_DASSL );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : ATZ \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_ATZ );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : ATI \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_ATI );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + N \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_N );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
if ( ZIGBEE_DEV_HOST == dev_mode )
{
// Setting the device into host mode and creating a network for other devices to connect.
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + HOST CFG 1 \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_at( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_ATS, &AT_HOST_CFG1[ 0 ] );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + HOST CFG 2 \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_at( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_ATS, &AT_HOST_CFG2[ 0 ] );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + HOST CFG 3 \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_at( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_ATS, &AT_HOST_CFG3[ 0 ] );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + EN \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_EN );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
}
else if ( ZIGBEE_DEV_USER == dev_mode )
{
// Setting the device into user mode and joining the existing network.
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + JN \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_JN );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
}
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + IDREQ \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_IDREQ );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Sending command : AT + N \r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_cmd( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_N );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
app_mode = ZIGBEE_APP_TASK;
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
if ( ZIGBEE_DEV_HOST == dev_mode )
{
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
zigbee_send_at( &zigbee, ZIGBEE_CMD_AT_BCAST, &AT_BCAST_MSG[ 0 ] );
resp_wait( &zigbee );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
else if ( ZIGBEE_DEV_USER == dev_mode )
{
resp_wait( &zigbee );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------------\r\n", app_buf );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
void zigbee_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, ZIGBEE_DEV_BUFFER_MAX );
}
void resp_wait ( zigbee_t *ctx )
{
uint8_t resp_flag;
for ( ; ; )
{
zigbee_generic_read( &zigbee, app_buf, ZIGBEE_DEV_BUFFER_MAX );
Delay_ms ( 50 );
resp_flag = zigbee_resp( ctx, app_buf );
if ( ( ZIGBEE_APP_TASK == app_mode ) && ( ZIGBEE_DEV_USER == dev_mode ) )
{
if ( ( ZIGBEE_OP_WAIT != resp_flag ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " %s ", app_buf );
zigbee_clear_app_buf( );
}
}
else
{
if ( ( ZIGBEE_OP_OK == resp_flag ) || ( ZIGBEE_OP_ERROR == resp_flag ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%s", app_buf );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
zigbee_clear_app_buf( );
break;
}
}
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:ZigBee