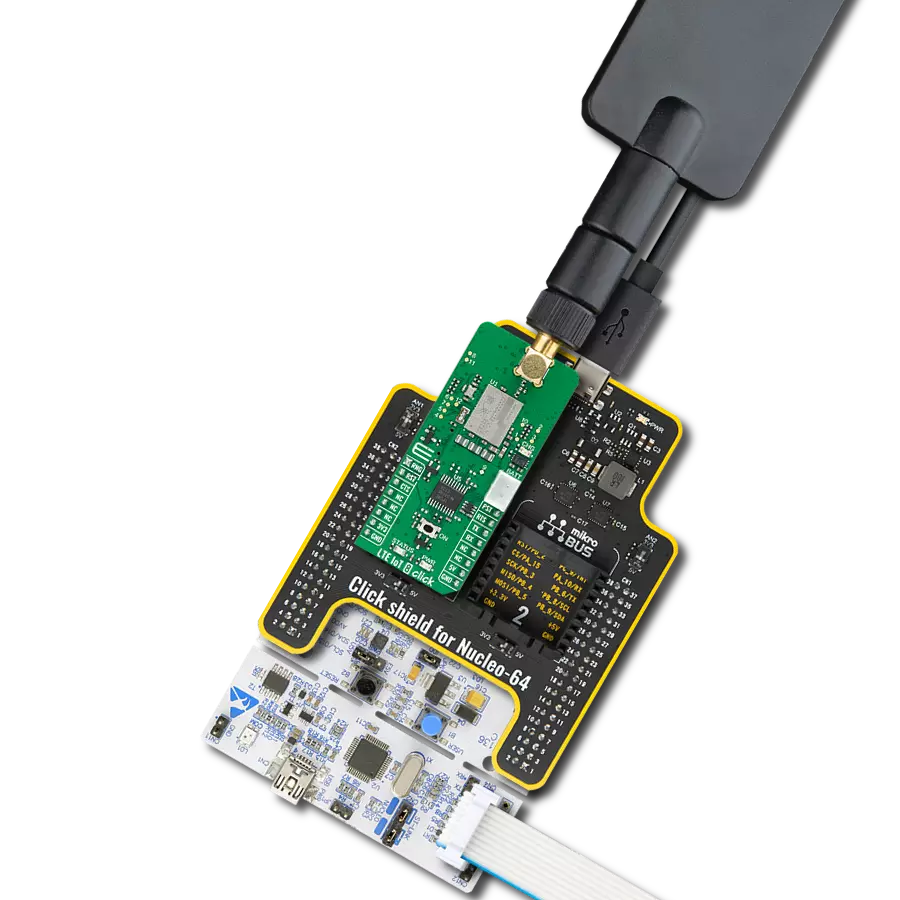
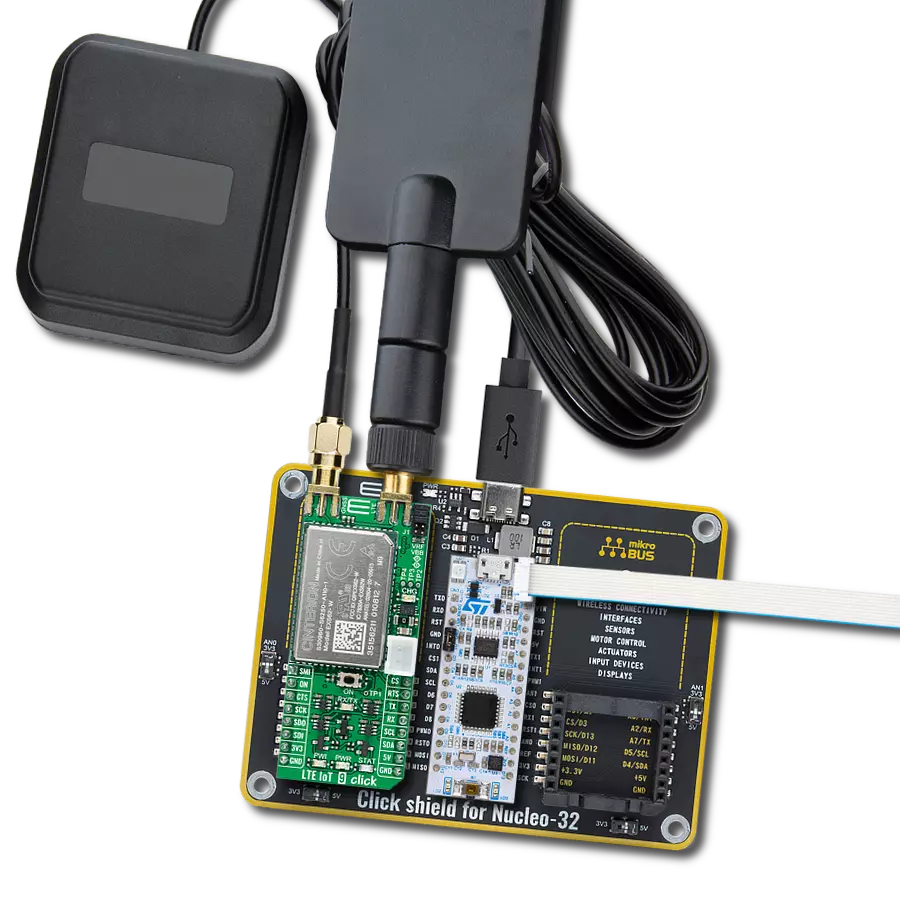
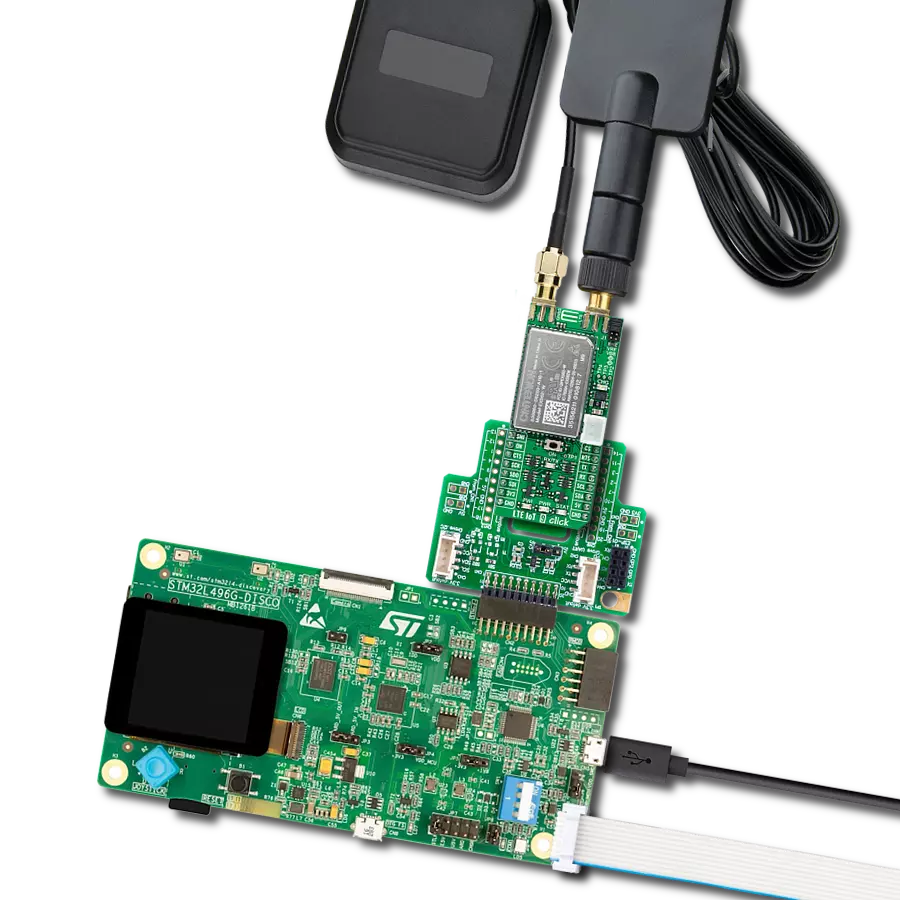
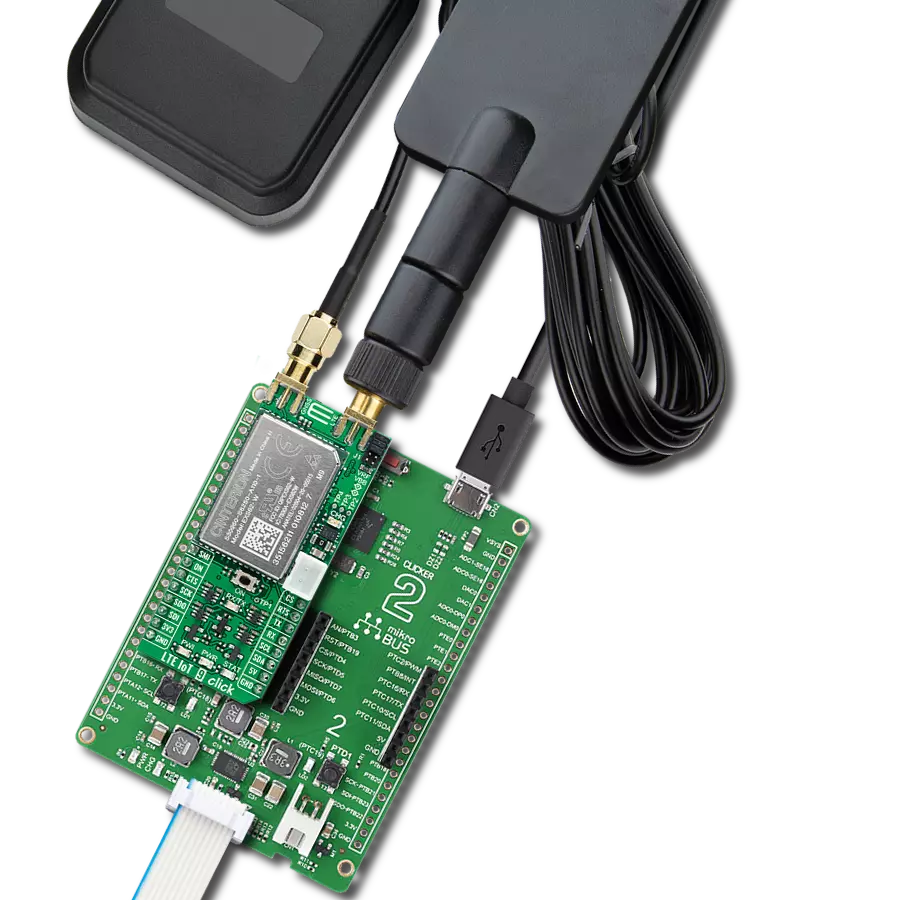
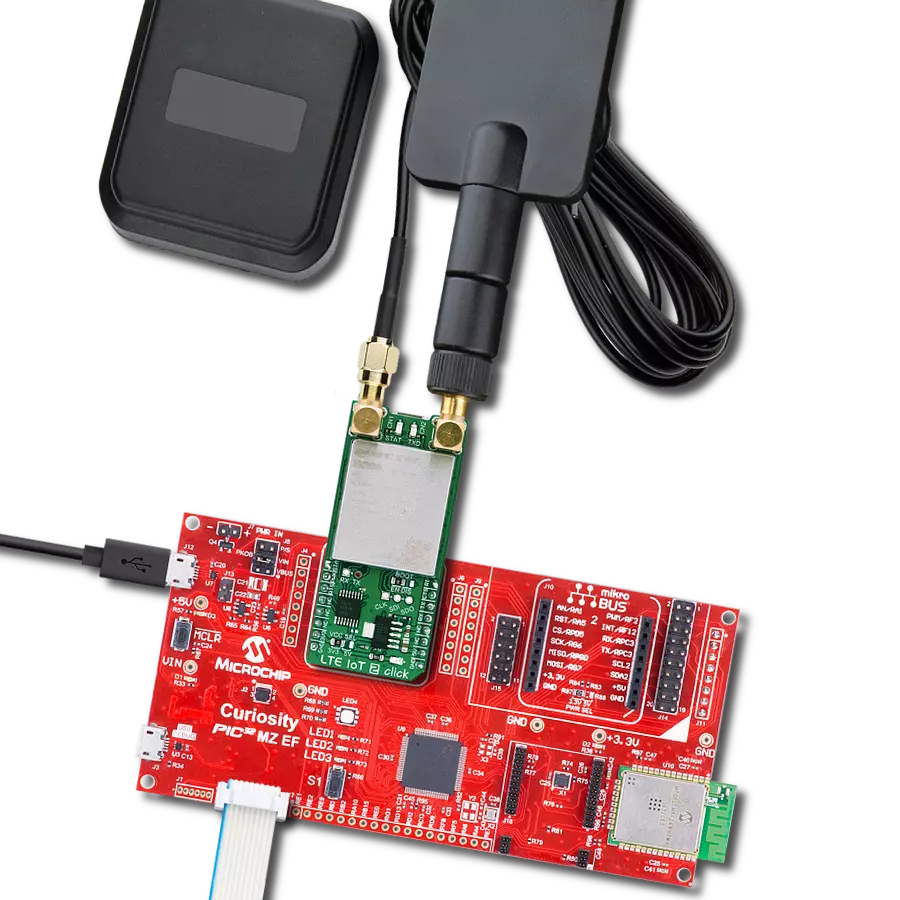
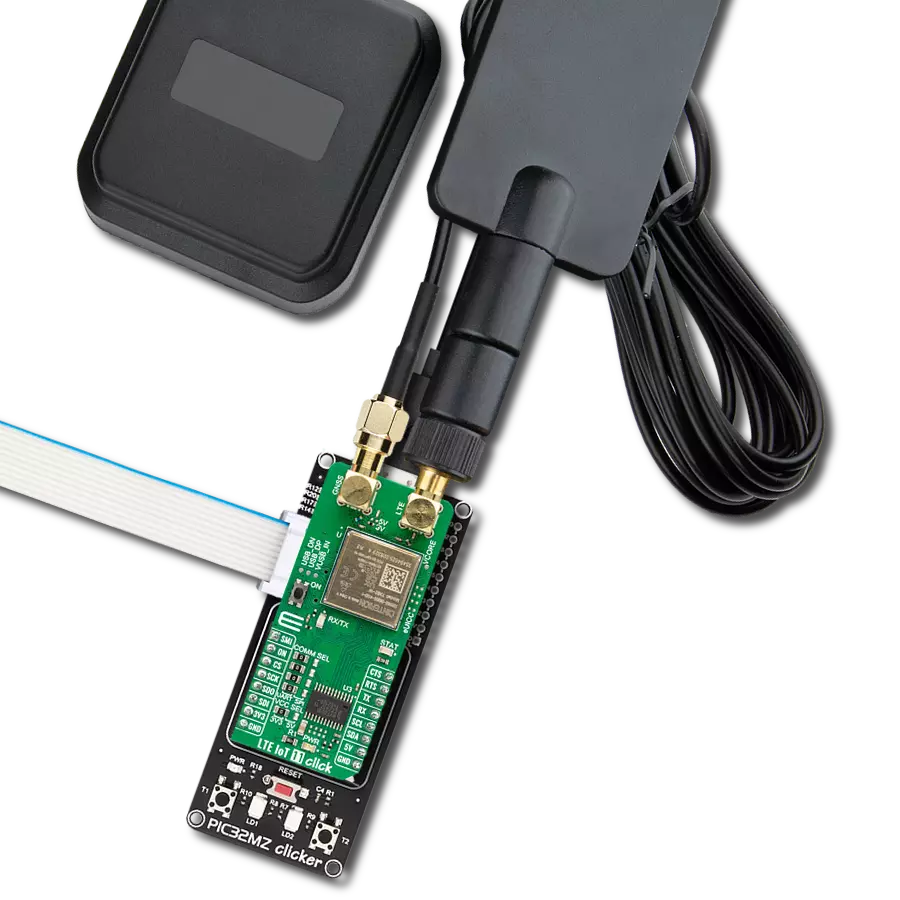
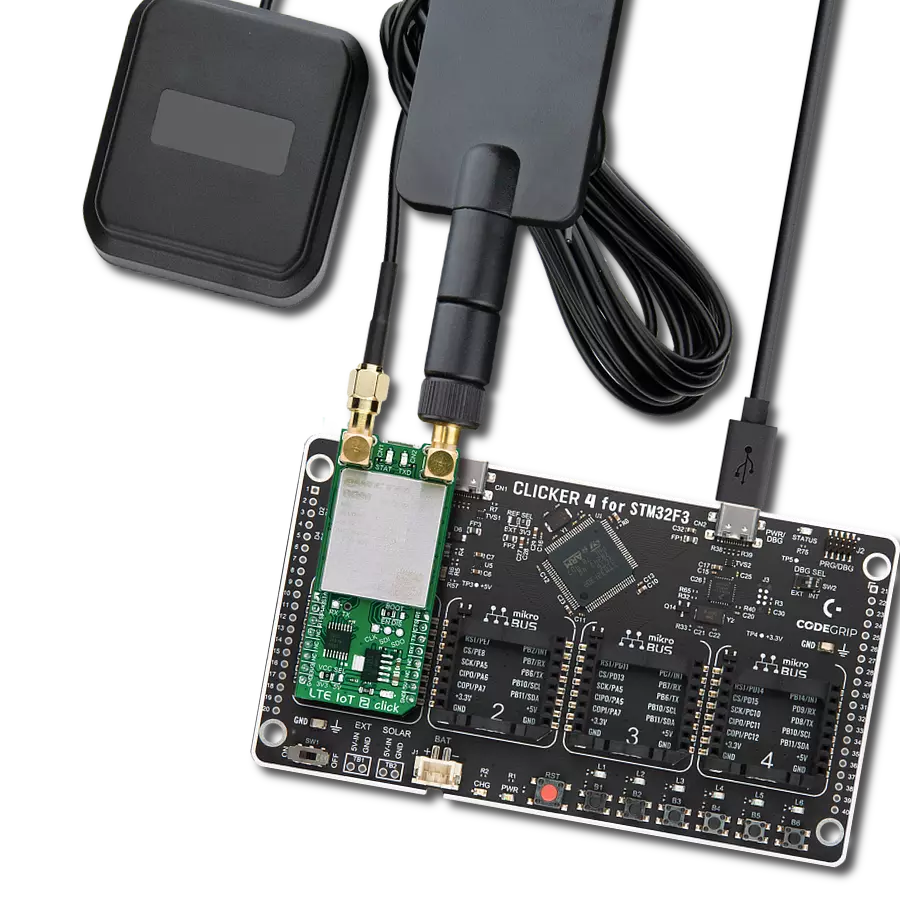
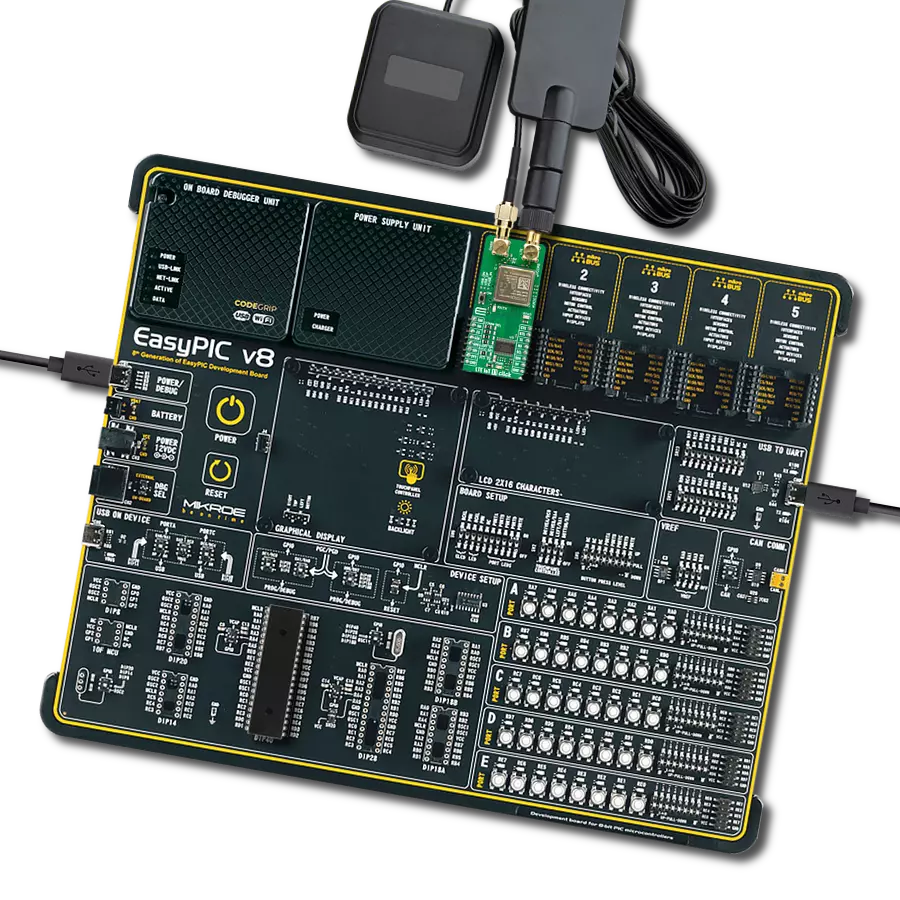
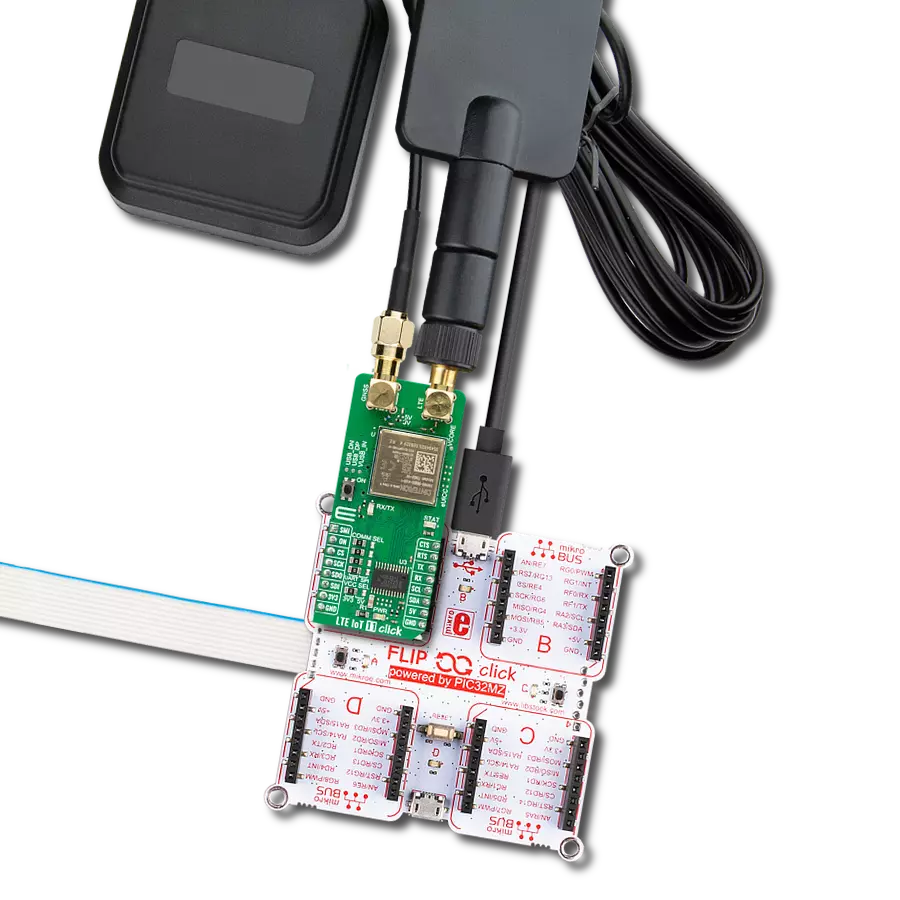
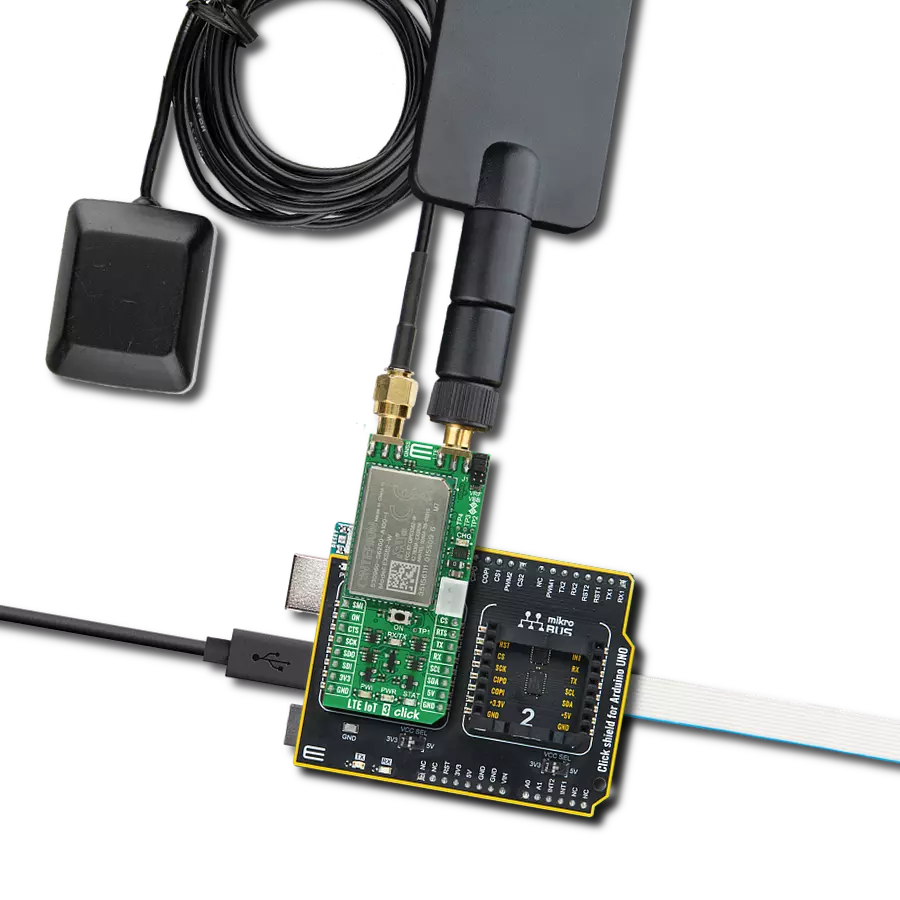
Join the seamless IoT revolution by adopting NB-IoT, and witness how it transforms the IoT landscape into a smarter, more efficient world
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
NB IoT 4 Click is based on the C1-RM, the LTE CAT NB-IoT intelligent cellular module with a 2G fall-back option based on 3GPP Release 13 with an integrated eSIM feature for global data connectivity from Cavli Wireless. It supports a broad range of frequency bands such as NB-IoT: B3/B5/B8/B20/B28 and GPRS: GSM850/EGSM900/DCS1800/PCS1900 with automatic search of frequency bands and the band selection by AT command. It also provides several interfaces and protocol stacks such as UDP/TCP/CoAP/LWM2M and others, allowing data and SMS transmission using NB technology, making it the perfect choice for building various IoT solutions. This module is designed for countries with less than 100% NB-IoT coverage or upcoming NB-IoT network, where LPWAN deployments can happen in 2G and switch to NB-IoT when the network is ready. The integrated eSIM feature ensures that the module can be deployed globally. The C1-RM communicates with MCU using the UART interface with commonly used UART RX and
TX pins as its default communication protocol for exchanging AT commands operating at 115200 bps by default configuration to transmit and exchange data with the host MCU. It is also equipped with a USB type C connector, which allows the module to be powered and configured by a personal computer (PC) using FT230X, a compact USB to a serial UART interface bridge designed to operate efficiently with USB host controllers. With the help of FT230X, it is possible to access a debug serial port of C1-RM to upgrade firmware and check the log information. It also possesses the RX/TX blue LED indicator that indicates whether the bridge is in RX or TX mode. The users can also use other interfaces, such as SPI or I2C, to configure the module and write the library by themselves. The RI pin routed on the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ represents the external interrupt pin used for waking up the device from a power-saving mode, while the RST pin on the mikroBUS™ socket can perform Hardware Reset function by putting this pin in a logic low state. Next to these pins, this
Click board™ also provides a white LED indicator labeled as N/I to indicate the status of network communication in addition to an analog-to-digital conversion pin routed on the AN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, which can realize external temperature monitoring and can read voltage through AT command. NB IoT 4 Click has the SMA antenna connector with an impedance of 50Ω for connecting the appropriate antenna MIKROE offers. Besides the NB IoT SMA connector, this Click board™ has a Nano-SIM card slot that provides multiple connections and interface options. This Click board™ can operate with both 3.3V and 5V MCUs. Appropriate voltage level translator TXS0108E performs a proper logic voltage level conversion, while the on-board LDO, the TPS7A7002, ensures that the recommended voltage levels power module. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
EasyPIC v8 for PIC24/dsPIC33 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of 16-bit PIC24/dsPIC33 microcontrollers from Microchip and has a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, EasyPIC v8 for PIC24/dsPIC33 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere and under any circumstances. Each part of the EasyPIC
v8 for PIC24/dsPIC33 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module, which offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment, the board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. Communication options such as USB HOST/DEVICE, USB-UART, CAN, and LIN are also
included, including the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, two display options (graphical and character-based LCD), and several different DIP sockets. These sockets cover a wide range of 16-bit PIC24/dsPIC33 MCUs, from the smallest PIC24/dsPIC33 MCUs with only 14 up to 28 pins. EasyPIC v8 for PIC24/dsPIC33 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
Architecture
dsPIC
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
LTE Flat Rotation Antenna is a versatile choice for boosting the performance of 3G/4G LTE devices. With a wide frequency range of 700-2700MHz, it ensures optimal connectivity on major cellular bands worldwide. This flat antenna features an SMA male connector, making it easy to attach directly to your device or SMA module connector. One of its standout features is its adjustable angle, which can be set in 45⁰ increments (0⁰/45⁰/90⁰), allowing you to fine-tune the antenna's orientation for maximum signal reception. With an impedance of 50Ω and a VSW Ratio of <2.0:1, this antenna ensures a reliable and efficient connection. Its 5dB gain, vertical polarization, and omnidirectional radiation pattern enhance signal strength, making it suitable for various applications. Measuring 196mm in length and 38mm in width, this antenna offers a compact yet effective solution for improving your connectivity. With a maximum input power of 50W, it can handle the demands of various devices.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for NB IoT 4 Click driver.
Key functions:
nbiot4_set_sim_apn- This function sets APN for sim cardnbiot4_send_sms_text- This function sends text message to a phone numbernbiot4_send_sms_pdu- This function sends text message to a phone number in PDU mode
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief NB IoT 4 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* Application example shows device capability of connecting to the network and
* sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages using standard "AT" commands.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver, tests the communication by sending "AT" command, and after that restarts the device.
*
* ## Application Task
* Application task is split in few stages:
* - NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
* Sets configuration to device to be able to connect to the network.
*
* - NBIOT4_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
* Waits for the network registration indicated via CEREG URC event and then checks
* the connection status.
*
* - NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
* Sets the device configuration for sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages depending on the selected demo example.
*
* - NBIOT4_EXAMPLE:
* Depending on the selected demo example, it sends an SMS message (in PDU or TXT mode) or TCP/UDP message.
*
* By default, the TCP/UDP example is selected.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void nbiot4_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t nbiot4_process ( void )
* - static void nbiot4_error_check( err_t error_flag )
* - static void nbiot4_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t nbiot4_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
* - static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_connection( void )
* - static err_t nbiot4_check_connection( void )
* - static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_messages( void )
* - static err_t nbiot4_send_message( void )
*
* @note
* In order for the examples to work, user needs to set the APN and SMSC (SMS PDU mode only)
* of entered SIM card as well as the phone number (SMS mode only) to which he wants to send an SMS.
* Enter valid values for the following macros: SIM_APN, SIM_SMSC and PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE.
* Example:
SIM_APN "internet"
SIM_SMSC "+381610401"
PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "+381659999999"
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "nbiot4.h"
#include "conversions.h"
// Example selection macros
#define EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP 0 // Example of sending messages to a TCP/UDP echo server
#define EXAMPLE_SMS 1 // Example of sending SMS to a phone number
#define DEMO_EXAMPLE EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP // Example selection macro
// SIM APN config
#define SIM_APN "internet" // Set valid SIM APN
// SMS example parameters
#define SIM_SMSC "" // Set valid SMS Service Center Address - only in SMS PDU mode
#define PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "" // Set Phone number to message
#define SMS_MODE "1" // SMS mode: "0" - PDU, "1" - TXT
// TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
// Message content
#define MESSAGE_CONTENT "NB IoT 4 Click board - demo example."
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 256
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 256
/**
* @brief Example states.
* @details Predefined enum values for application example state.
*/
typedef enum
{
NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK = 1,
NBIOT4_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION,
NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE,
NBIOT4_EXAMPLE
} nbiot4_example_state_t;
static nbiot4_t nbiot4;
static log_t logger;
/**
* @brief Application example variables.
* @details Variables used in application example.
*/
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static err_t error_flag;
static nbiot4_example_state_t example_state;
/**
* @brief Clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application
* buffer and reset its length and counter.
*/
static void nbiot4_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and
* appends it to the application buffer.
* @return @li @c 0 - Some data is read.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_process ( void );
/**
* @brief Check for errors.
* @details This function checks for different types of
* errors and logs them on UART or logs the response if no errors occured.
* @param[in] error_flag Error flag to check.
*/
static void nbiot4_error_check ( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief Logs application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer.
*/
static void nbiot4_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Response check.
* @details This function checks for response and
* returns the status of response.
* @param[in] rsp Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp );
/**
* @brief Configure device for connection to the network.
* @details Sends commands to configure and enable
* connection to the specified network.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_network ( void );
/**
* @brief Wait for connection signal.
* @details Wait for connection signal from CREG URC.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_check_connection ( void );
/**
* @brief Configure device for example.
* @details Configure device for the specified example.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_example ( void );
/**
* @brief Execute example.
* @details This function executes SMS or TCP/UDP example depending on the DEMO_EXAMPLE macro.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t nbiot4_example ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
nbiot4_cfg_t nbiot4_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
nbiot4_cfg_setup( &nbiot4_cfg );
NBIOT4_MAP_MIKROBUS( nbiot4_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == nbiot4_init( &nbiot4, &nbiot4_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
nbiot4_process( );
nbiot4_clear_app_buf( );
// Check communication
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_AT );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable command echo
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_ATE1 );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Restart device
#define RESTART_DEVICE "1,1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CFUN, RESTART_DEVICE );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
example_state = NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK;
}
void application_task ( void )
{
switch ( example_state )
{
case NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
{
if ( NBIOT4_OK == nbiot4_configure_for_network( ) )
{
example_state = NBIOT4_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
}
break;
}
case NBIOT4_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
{
if ( NBIOT4_OK == nbiot4_check_connection( ) )
{
example_state = NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case NBIOT4_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
{
if ( NBIOT4_OK == nbiot4_configure_for_example( ) )
{
example_state = NBIOT4_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case NBIOT4_EXAMPLE:
{
nbiot4_example( );
break;
}
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Example state." );
break;
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void nbiot4_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static err_t nbiot4_process ( void )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t rx_size = 0;
rx_size = nbiot4_generic_read( &nbiot4, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
if ( ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) && ( app_buf_len > 0 ) )
{
buf_cnt = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE );
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE - buf_cnt ], buf_cnt );
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ buf_cnt++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
if ( app_buf_len < APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
app_buf_len++;
}
}
}
return NBIOT4_OK;
}
return NBIOT4_ERROR;
}
static err_t nbiot4_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 120000;
nbiot4_clear_app_buf( );
nbiot4_process( );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, rsp ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, NBIOT4_RSP_ERROR ) ) )
{
nbiot4_process( );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > timeout )
{
nbiot4_clear_app_buf( );
return NBIOT4_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
nbiot4_process( );
if ( strstr( app_buf, rsp ) )
{
return NBIOT4_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, NBIOT4_RSP_ERROR ) )
{
return NBIOT4_ERROR_CMD;
}
else
{
return NBIOT4_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
}
static void nbiot4_error_check ( err_t error_flag )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case NBIOT4_OK:
{
nbiot4_log_app_buf( );
break;
}
case NBIOT4_ERROR:
{
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
}
case NBIOT4_ERROR_TIMEOUT:
{
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
}
case NBIOT4_ERROR_CMD:
{
log_error( &logger, " CMD!" );
break;
}
case NBIOT4_ERROR_UNKNOWN:
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Unknown!" );
break;
}
}
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
static void nbiot4_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_network ( void )
{
err_t func_error = NBIOT4_OK;
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
// Enable extern SIM card channel
#define ENABLE_EXTERN_SIM "1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_SIMSWAP, ENABLE_EXTERN_SIM );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Restart the device in order for the change in SIM channel to take effect
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_TRB );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_REBOOTING );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
// Enable command echo
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_ATE1 );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Set SIM APN
nbiot4_set_sim_apn( &nbiot4, SIM_APN );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable full functionality
#define FULL_FUNCTIONALITY "1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CFUN, FULL_FUNCTIONALITY );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
#define ENABLE_EPS_REG "2"
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CEREG, ENABLE_EPS_REG );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t nbiot4_check_connection ( void )
{
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
#define CONNECTED "+CEREG: 2,1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_check ( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CEREG );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CONNECTED ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
// Check signal quality
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CSQ );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
#define NO_SIGNAL "99,99"
if ( !strstr( app_buf, NO_SIGNAL ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return error_flag;
}
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return NBIOT4_ERROR;
#endif
return NBIOT4_OK;
}
static err_t nbiot4_configure_for_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = NBIOT4_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
#define ENABLE_RESPONSE_HEADER "1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPHEAD, ENABLE_RESPONSE_HEADER );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CMGF, SMS_MODE );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t nbiot4_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = NBIOT4_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
uint8_t cmd_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
// Open TCP socket.
#define RESPONSE_CONNECT "CONNECT OK"
#define TCP_SERVICE_TYPE "\"TCP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, TCP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPSTART, cmd_buf );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Get message length
uint8_t message_len_buf[ 10 ] = { 0 };
uint16_t message_len = strlen( MESSAGE_CONTENT );
uint16_to_str( message_len, message_len_buf );
l_trim( message_len_buf );
r_trim( message_len_buf );
// Write message to TCP socket
uint8_t ctrl_z = 0x1A;
strcpy( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPSEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
nbiot4_generic_write ( &nbiot4, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
nbiot4_generic_write ( &nbiot4, &ctrl_z, 1 );
// Read response
#define RESPONSE_URC "+IPD"
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( RESPONSE_URC );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Close TCP socket
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPCLOSE );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Open UDP socket.
#define UDP_SERVICE_TYPE "\"UDP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, UDP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPSTART, cmd_buf );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
// Write message to UDP socket
strcpy( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
nbiot4_send_cmd_with_par( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPSEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
nbiot4_generic_write ( &nbiot4, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
nbiot4_generic_write ( &nbiot4, &ctrl_z, 1 );
// Read response
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( RESPONSE_URC );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Close UDP socket
nbiot4_send_cmd( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CIPCLOSE );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
// Check SMS mode
#define CMGF_PDU "+CMGF: 0"
#define CMGF_TXT "+CMGF: 1"
nbiot4_send_cmd_check( &nbiot4, NBIOT4_CMD_CMGF );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_PDU ) )
{
// Send SMS in PDU mode
nbiot4_send_sms_pdu( &nbiot4, SIM_SMSC, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_TXT ) )
{
// Send SMS in TXT mode
nbiot4_send_sms_text ( &nbiot4, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = nbiot4_rsp_check( NBIOT4_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
nbiot4_error_check( error_flag );
}
// 30 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:LTE IoT