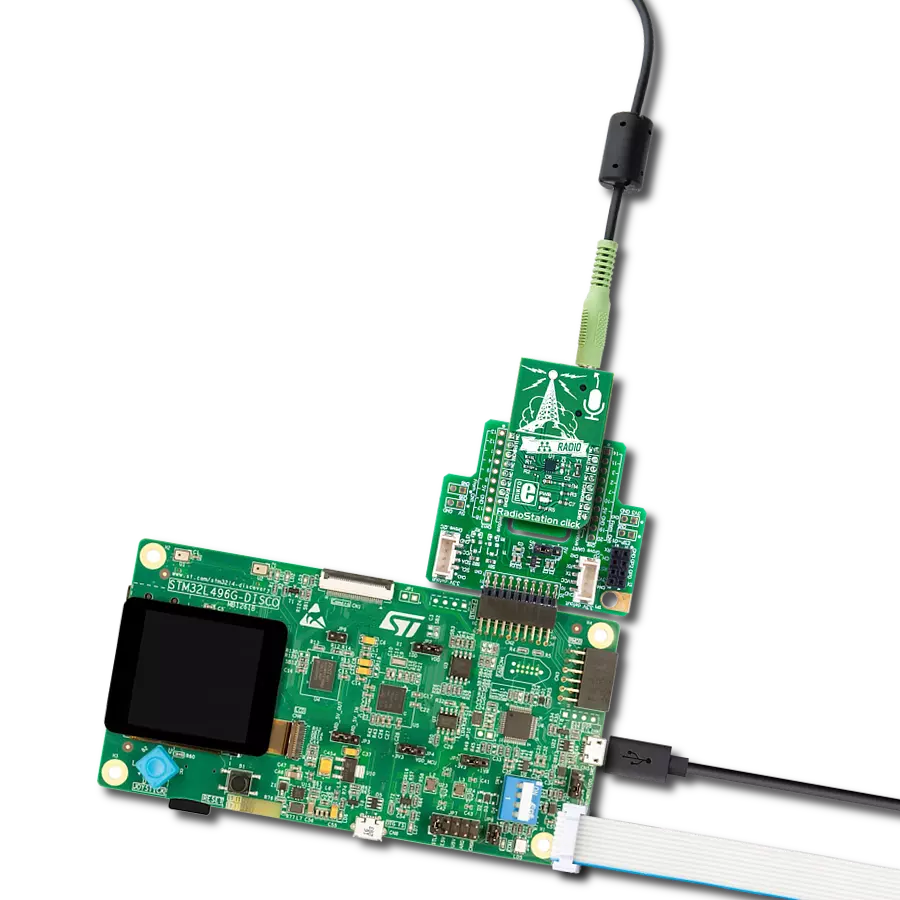
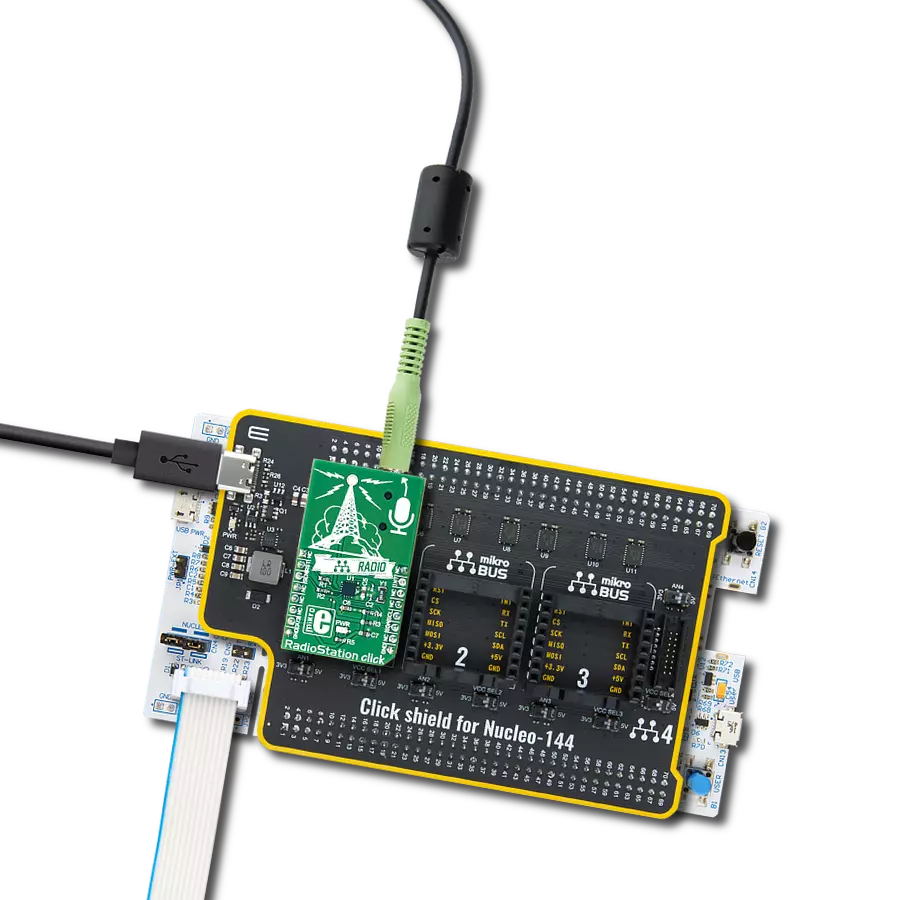
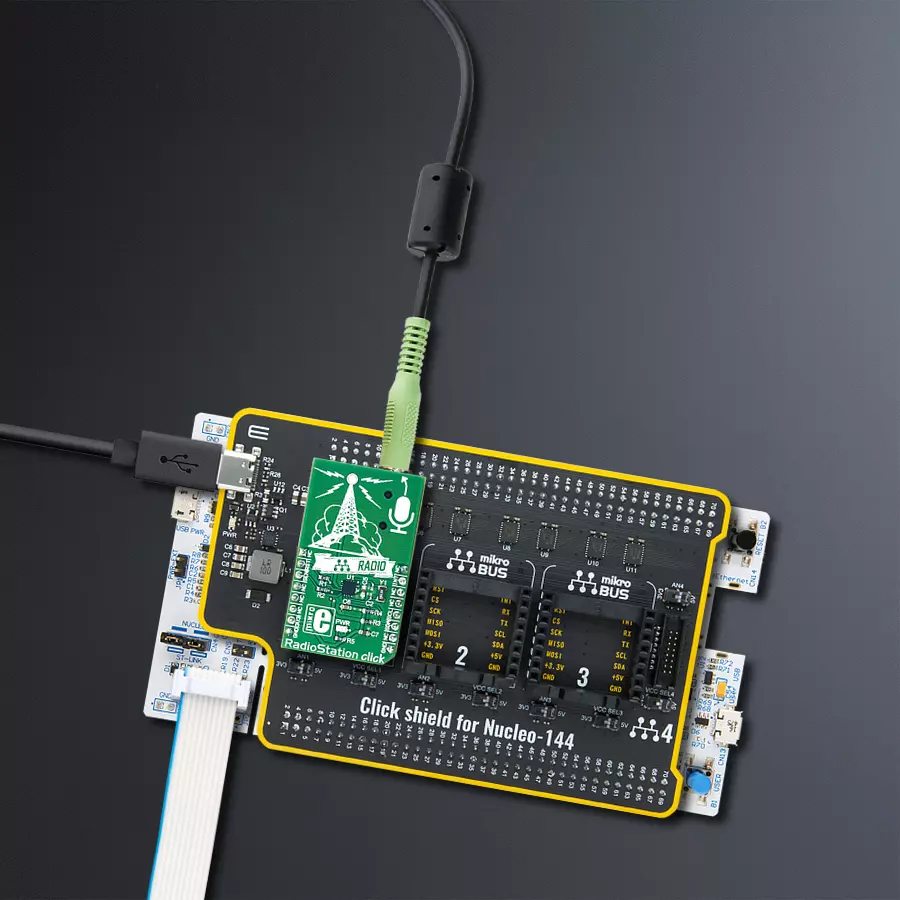
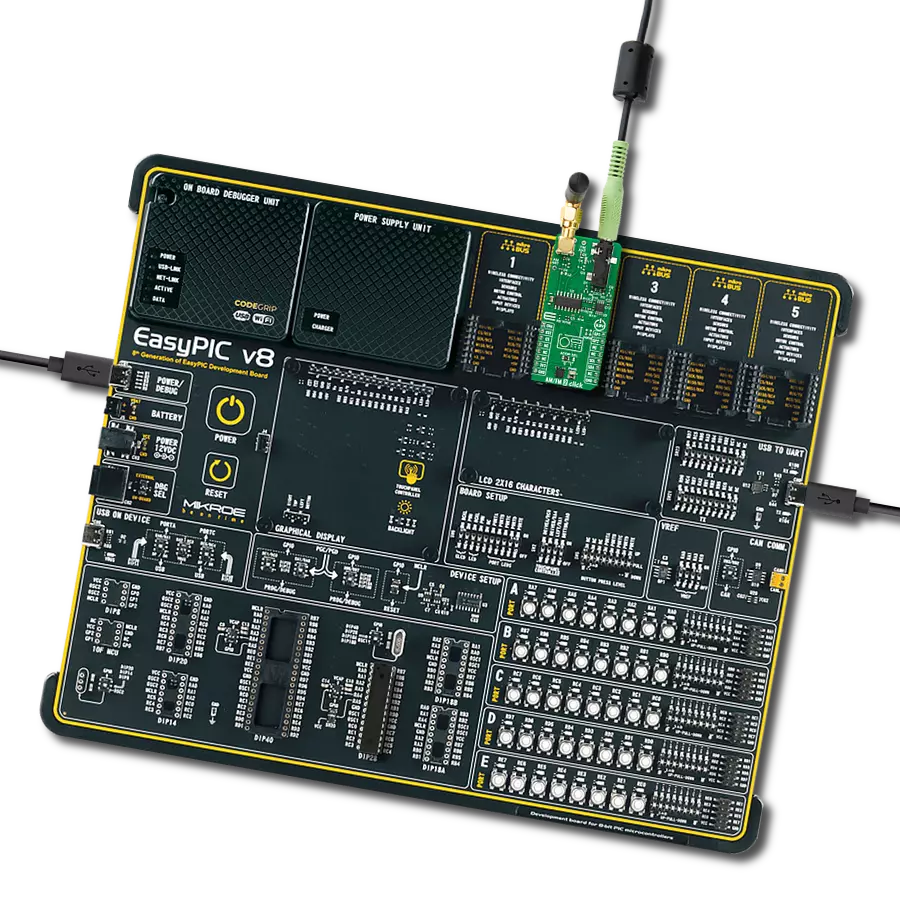
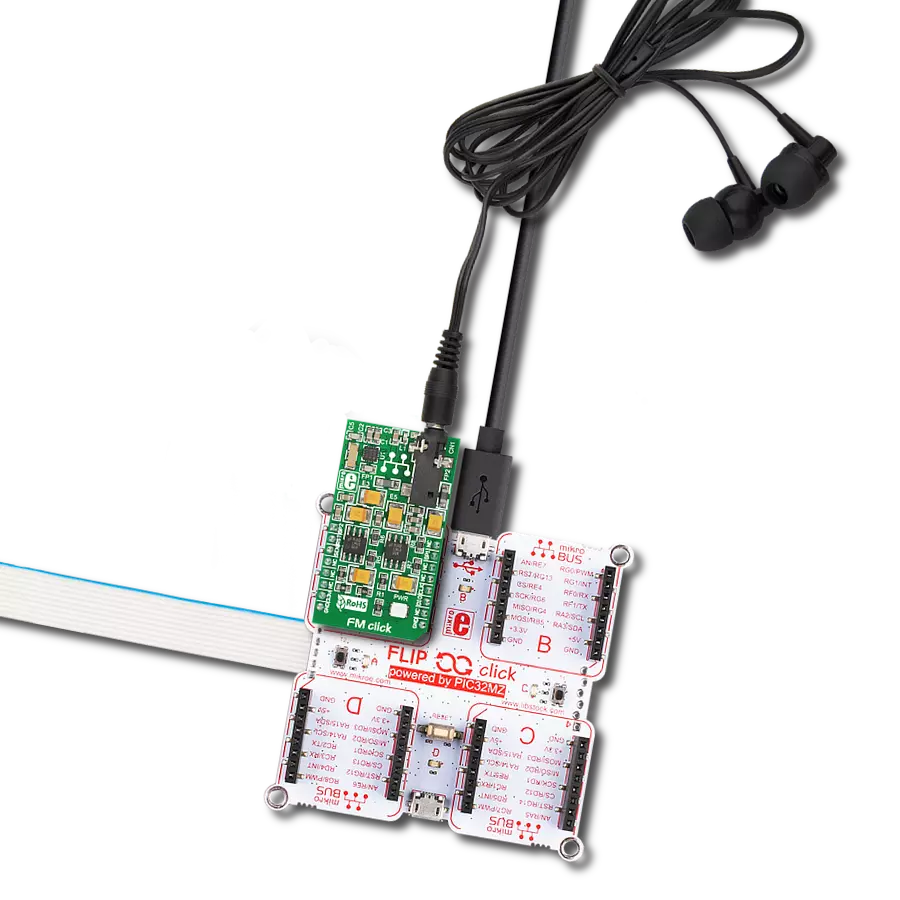
Combined with the capability to broadcast both music and informational data, this project is a match for anyone looking to explore the world of FM broadcasting or to develop applications requiring FM signal transmission
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
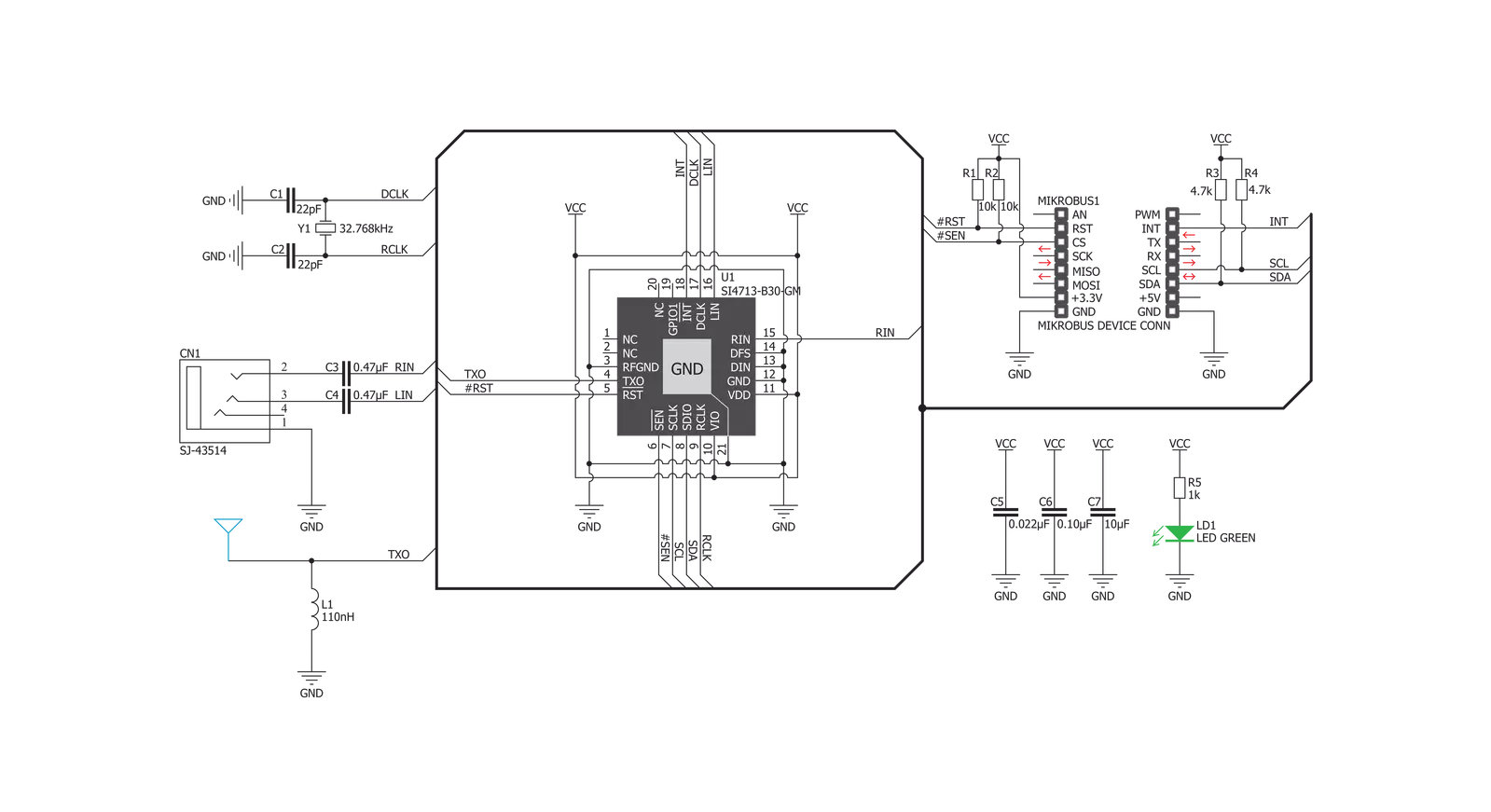
RadioStation Click is based on the Si4713-B30, an FM radio transmitter with receive power scan from Silicon Labs. The RadioStation Click broadcasts the audio signal by utilizing the principles of FM radio broadcasting. The audio signal, brought to the low noise analog input terminals of the Si4713-B30 routed to a mini 3.5 female jack on board, is attenuated and converted into an alias-free, digital format. The digitalized audio is then sent to the digital signal processor (DSP) section of the Si4713-B30 IC, which provides modulation adjustment and audio dynamic range control of the signal for the best listening experience. The audio signal is processed to have the optimal dynamic qualities. Also, Si4713 has programmable low audio and high audio-level indicators that enable and
disable the carrier signal based on the presence of audio content. The Si4713-B30 IC can be used to measure the received signal. The antenna which is used to broadcast the signal can also be used to accept the incoming signal sent by the receiving device. Although it can be used both to receive and transmit signals, the antenna can't operate in both modes simultaneously. This feature can be useful when calibrating the transmission power of the Click board™. The Si4713-B30 integrates the complete transmit functions for standards-compliant unlicensed FM broadcast stereo transmission. The user application must comply with the local radio frequency (RF) transmission regulations. RadioStation Click uses a standard 2-Wire I2C interface to communicate with the host
MCU, supporting clock frequency of up to 400KHz. The I2C address can be selected over the SEN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, depending on the logic state. The radio transmitter can be reset over the RST pin, which will, among others, disable analog and digital circuitry. The device will interrupt the host MCU over the INT pin if a condition occurs, such as the frequency exceeding the deviation level. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Nucleo-144 with STM32H743ZI MCU board offers an accessible and adaptable avenue for users to explore new ideas and construct prototypes. It allows users to tailor their experience by selecting from a range of performance and power consumption features offered by the STM32 microcontroller. With compatible boards, the
internal or external SMPS dramatically decreases power usage in Run mode. Including the ST Zio connector, expanding ARDUINO Uno V3 connectivity, and ST morpho headers facilitate easy expansion of the Nucleo open development platform. The integrated ST-LINK debugger/programmer enhances convenience by
eliminating the need for a separate probe. Moreover, the board is accompanied by comprehensive free software libraries and examples within the STM32Cube MCU Package, further enhancing its utility and value.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M7
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
144
RAM (Bytes)
1048576
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-144 comes equipped with four mikroBUS™ sockets, with one in the form of a Shuttle connector, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the STM32 Nucleo-144 board with no effort. This way, MIKROE allows its users to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™, such as WiFi, GSM, GPS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, environmental sensors, LEDs, speech recognition, motor control, movement sensors, and many more. Featuring an ARM Cortex-M microcontroller, 144 pins, and Arduino™ compatibility, the STM32 Nucleo-144 board offers limitless possibilities for prototyping and creating diverse applications. These boards are controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and efficiently debug the Nucleo-144 board out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB mini port on the board. Simplify your project development with the integrated ST-Link debugger and unleash creativity using the extensive I/O options and expansion capabilities. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the STM32 Nucleo-144 board with our Click Shield for Nucleo-144, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for RadioStation Click driver.
Key functions:
radiostation_get_asq_status- This function returns status information about the audio signal quality and current FM transmit frequencyradiostation_power_up- This function powers up the chip with default settingsradiostation_get_tune_status- This function returns status information which is set by radiostation_get_tune_measure, radiostation_set_tune_frequency or radiostation_set_tune_power
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief RadioStation Click example
*
* # Description
* RadioStation Click can be used to broadcast the music via the FM radio band
* ( which operates in the frequency range of 76MHz to 108MHz ).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver enable's - I2C and sets transmit_frequency.
*
* ## Application Task
* In this example Radio Station Click is receiving signal from audio connector and broadcasting
* it on 100.00 MHz frequency.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "radiostation.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static radiostation_t radiostation;
static radiostation_cmd_t radiostation_cmd;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t buff[ 16 ];
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
radiostation_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
radiostation_cfg_setup( &cfg, true );
RADIOSTATION_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
radiostation_init( &radiostation, &cfg );
radiostation.transmit_frequency = 10000;
radiostation.status = 0xFF;
radiostation_default_cfg( &radiostation, &radiostation_cmd );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
radiostation_get_asq_status( &radiostation, &radiostation_cmd, &buff[ 0 ] );
Delay_ms ( 50 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END