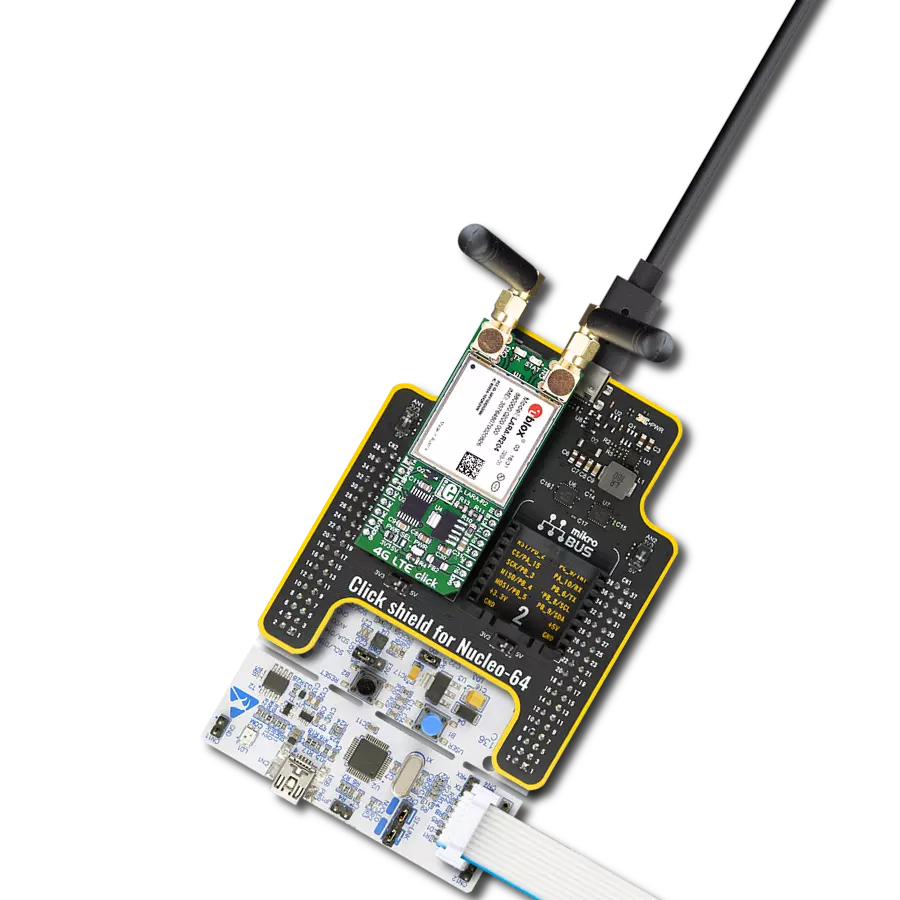
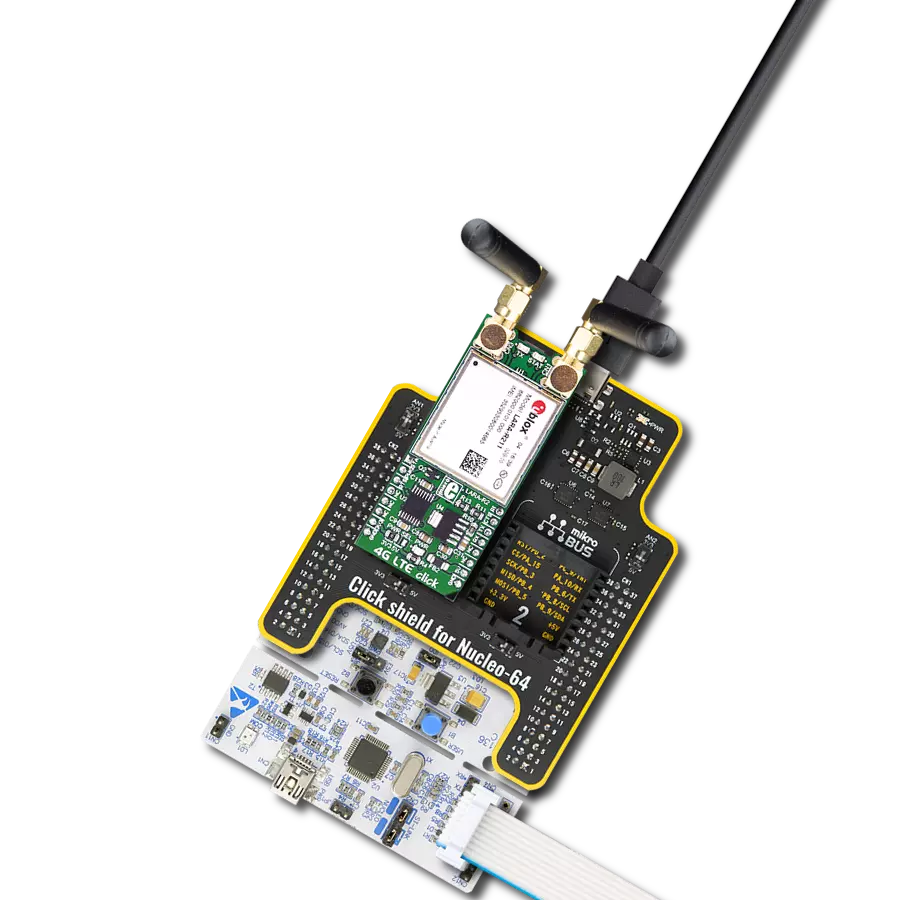
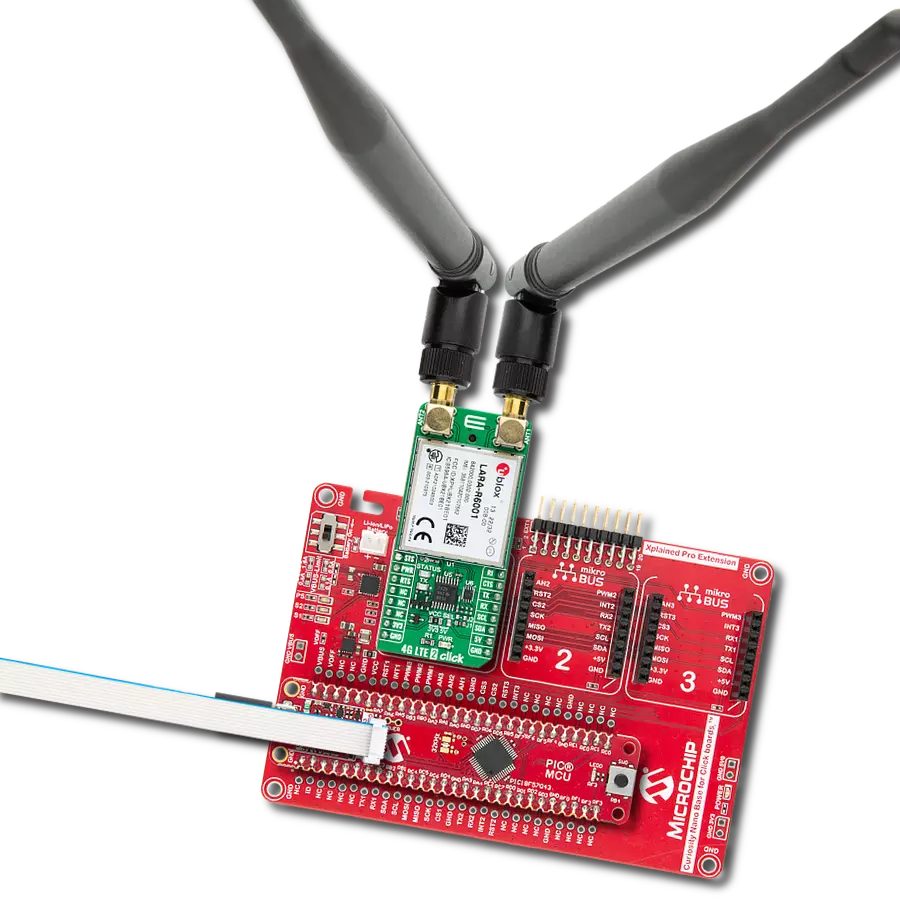
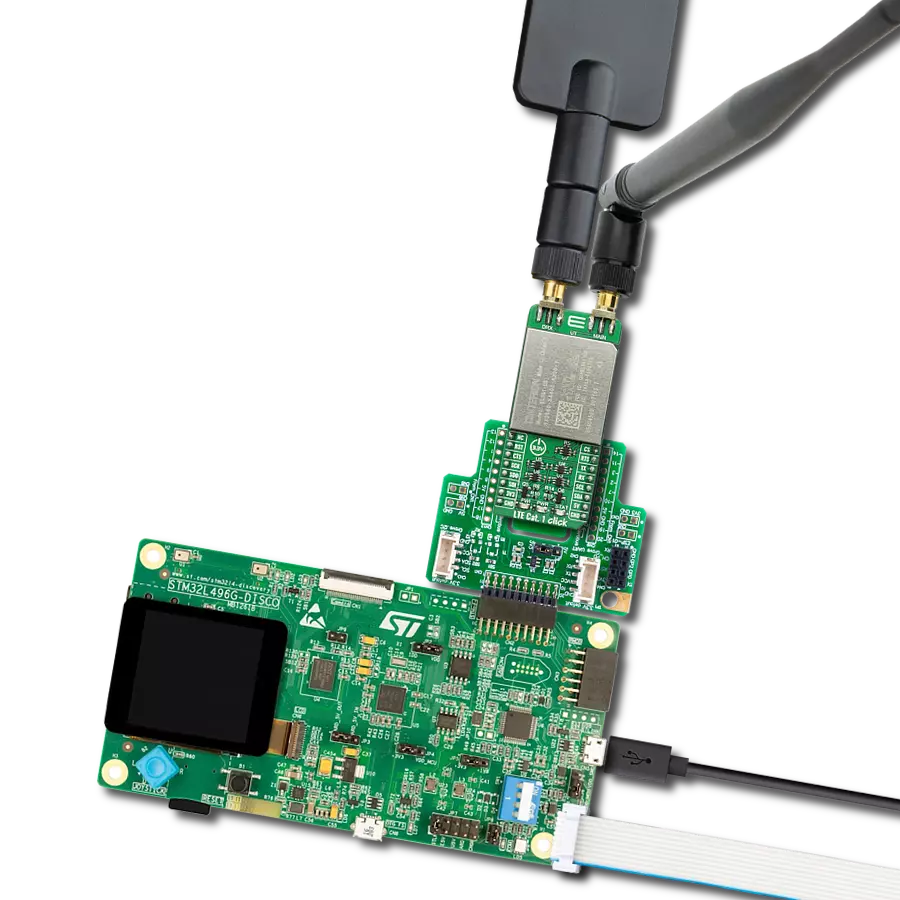
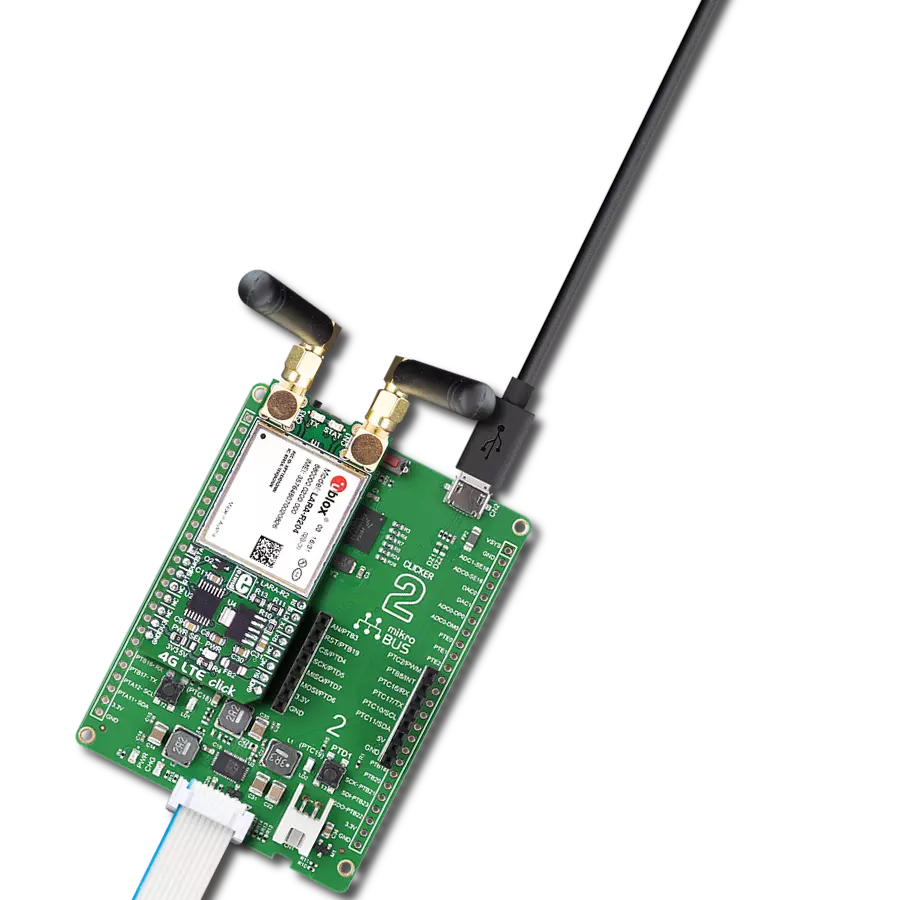
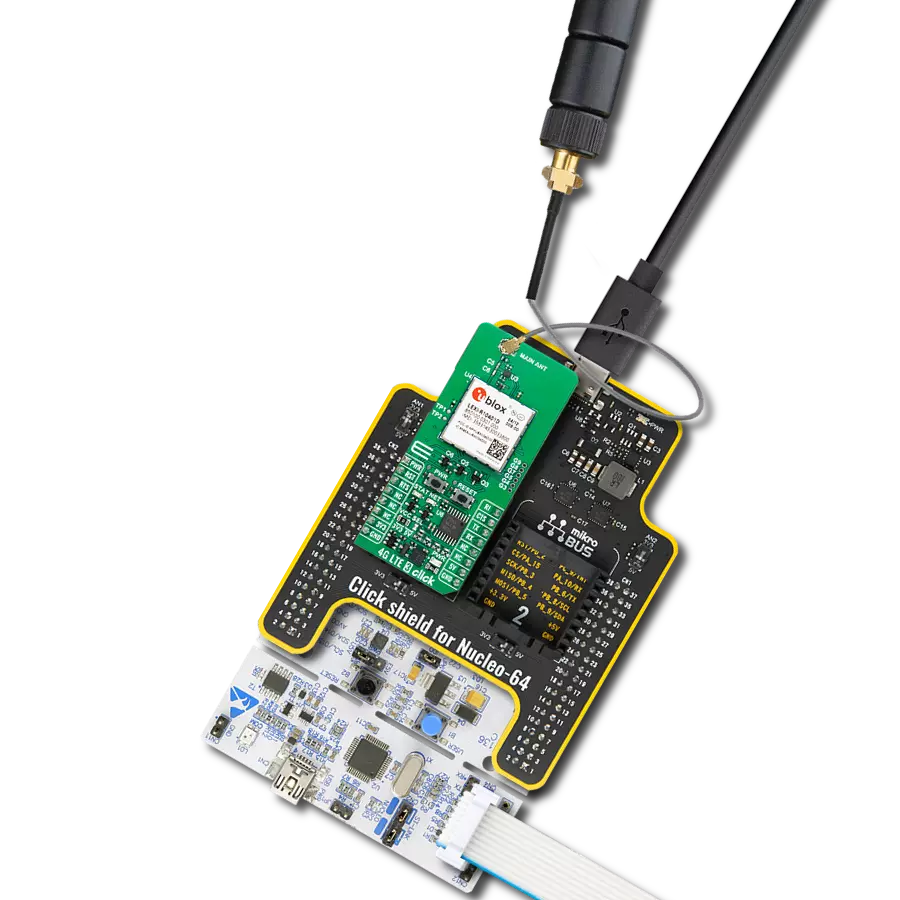
Enhance your project's capabilities with communication over GSM networks, enabling remote monitoring, data transmission, and voice calls for various applications
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
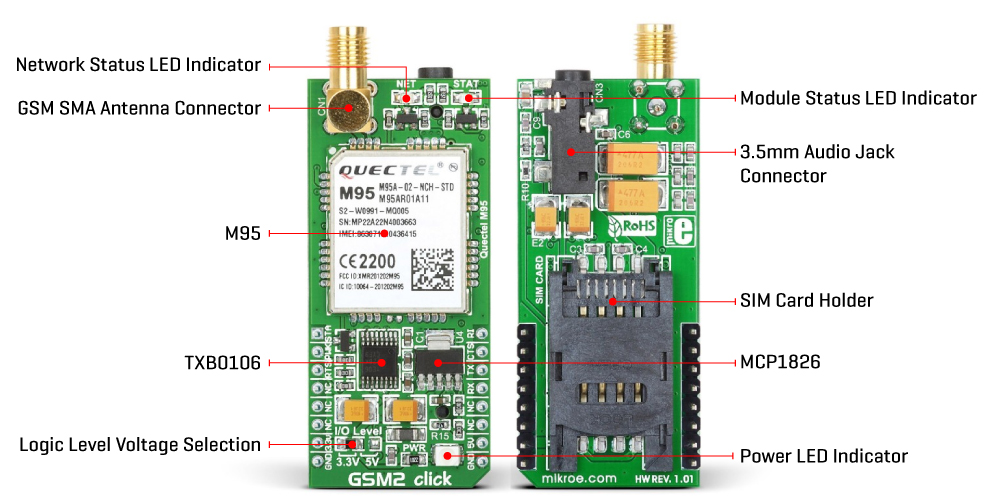
GSM 2 Click is based on the M95, a quad-band GSM/GPRS module from Quectel. The module supports quad-band GSM/GPRS, allowing it to be used worldwide. It covers frequencies of 850/900 MHz with up to 2W and frequencies of 1800/1900 MHz with up to 1W transmitting power. The M95 module is also compliant with the eCall EU Directive. The module is the Click board's main component, consisting of several internal blocks or sections, such as the antenna switching section, RF transceiver section, memory, power management, and most importantly - the cellular baseband processor. The M95 module has to be powered by a clean and stable power supply. The voltage needed for the module to work properly is about 4V, and it is derived from the 5V mikroBUS™ rail through the MCP1826, a 1A low drop output (LDO) regulator from Microchip. Although the M95 is a low-power device, the cellular network modules, in general, are notorious for their
high-power consumption, so the 1A LDO had to be used. Digital sections of the M95 are internally supplied by 2.8V, so it is necessary to condition the communication bus lines that connect the host MCU with the module. M95 outputs 2.8V output from its internal LDO, providing a needed reference voltage for one side of the TXB0106, a 6-bit bidirectional level shifting and voltage translator with automatic direction sensing from Texas Instruments. The M95 offers extensive audio features, including half rate, full rate, enhanced full rate, adaptive multi-rate voice codecs, superior echo cancellation, and noise reduction. The headset can be connected via the 4-pole 3.5mm audio jack. The Micro SIM card holder on the back of the Click board™ is used to install a microSIM card. This device cannot be used without a valid SIM card, which allows connection to the cellular network. Both 1.8V and 3V SIM card types are supported. GSM 2 Click uses a standard 2-wire
UART interface to communicate with the host MCU, with commonly used UART RX and TX pins, and supporting data rates from 300bps up to 115200bps with automatic baud rate detection. In addition, the UART RTS and CTS hardware flow control pins are also available. Besides the library we provide, you can also use the AT commands. The RI pin serves as a ringing indicator. There is also a PWK pin for powering the module and the STA pin, which indicates the device status. This status is also represented over the STA LED. The other LED is a NET LED, which indicates the network status. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the I/O Level jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
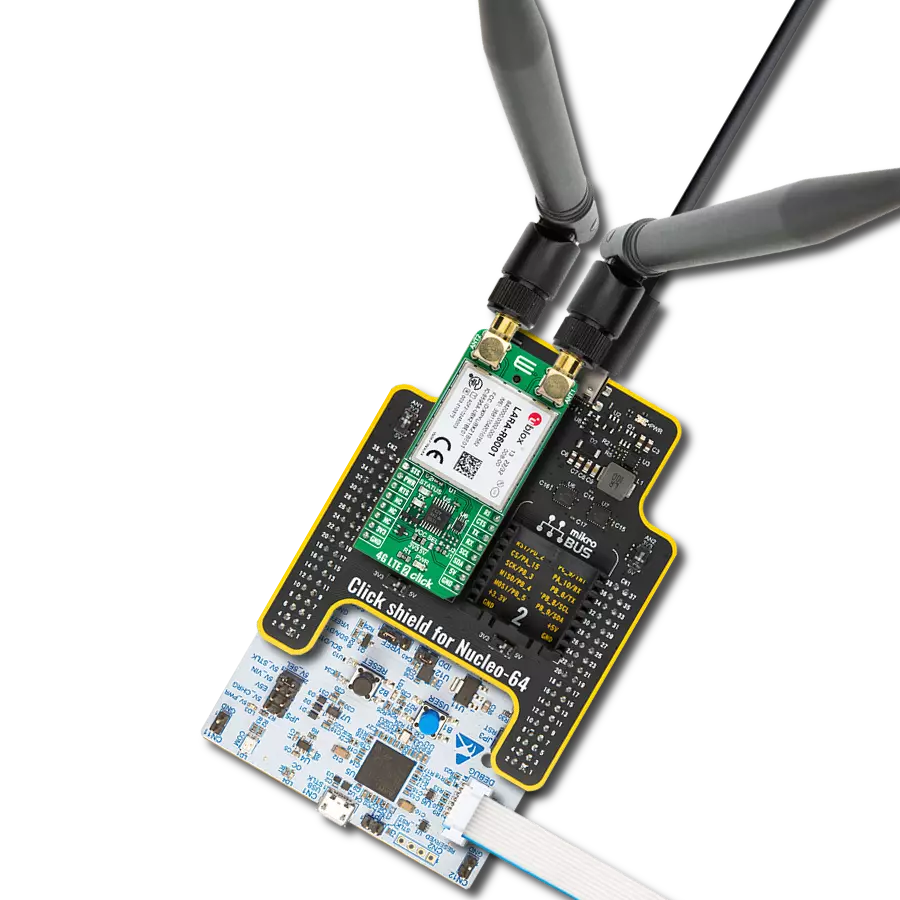
Development board
Nucleo-64 with STM32F410RB MCU offers a cost-effective and adaptable platform for developers to explore new ideas and prototype their designs. This board harnesses the versatility of the STM32 microcontroller, enabling users to select the optimal balance of performance and power consumption for their projects. It accommodates the STM32 microcontroller in the LQFP64 package and includes essential components such as a user LED, which doubles as an ARDUINO® signal, alongside user and reset push-buttons, and a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator for precise timing operations. Designed with expansion and flexibility in mind, the Nucleo-64 board features an ARDUINO® Uno V3 expansion connector and ST morpho extension pin
headers, granting complete access to the STM32's I/Os for comprehensive project integration. Power supply options are adaptable, supporting ST-LINK USB VBUS or external power sources, ensuring adaptability in various development environments. The board also has an on-board ST-LINK debugger/programmer with USB re-enumeration capability, simplifying the programming and debugging process. Moreover, the board is designed to simplify advanced development with its external SMPS for efficient Vcore logic supply, support for USB Device full speed or USB SNK/UFP full speed, and built-in cryptographic features, enhancing both the power efficiency and security of projects. Additional connectivity is
provided through dedicated connectors for external SMPS experimentation, a USB connector for the ST-LINK, and a MIPI® debug connector, expanding the possibilities for hardware interfacing and experimentation. Developers will find extensive support through comprehensive free software libraries and examples, courtesy of the STM32Cube MCU Package. This, combined with compatibility with a wide array of Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), including IAR Embedded Workbench®, MDK-ARM, and STM32CubeIDE, ensures a smooth and efficient development experience, allowing users to fully leverage the capabilities of the Nucleo-64 board in their projects.
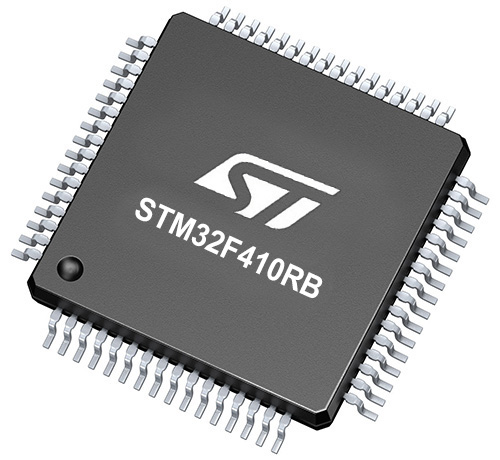
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
32768
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-64 comes equipped with two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with no effort. This way, Mikroe allows its users to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™, such as WiFi, GSM, GPS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, environmental sensors, LEDs, speech recognition, motor control, movement sensors, and many more. More than 1537 Click boards™, which can be stacked and integrated, are at your disposal. The STM32 Nucleo-64 boards are based on the microcontrollers in 64-pin packages, a 32-bit MCU with an ARM Cortex M4 processor operating at 84MHz, 512Kb Flash, and 96KB SRAM, divided into two regions where the top section represents the ST-Link/V2 debugger and programmer while the bottom section of the board is an actual development board. These boards are controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and efficiently debug the Nucleo-64 board out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB mini port on the board. Most of the STM32 microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with our Click Shield for Nucleo-64, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Rubber Antenna GSM/GPRS Right Angle is the perfect companion for all GSM Click boards™ in our extensive lineup. This specialized antenna is designed to optimize your wireless connectivity with impressive features. With a wide frequency range spanning 824-894/1710-1990MHz or 890-960/1710-1890MHz, it can handle various frequency bands, ensuring a seamless and reliable connection. The antenna boasts an impedance of 50 Ohms and a gain of 2dB, enhancing signal reception and transmission. Its 70/180MHz bandwidth provides flexibility for diverse applications. The vertical polarization further enhances its performance. With a maximum input power capacity of 50W, this antenna ensures robust communication even under demanding conditions. Measuring a compact 50mm in length and featuring an SMA male connector, the Rubber Antenna GSM/GPRS Right Angle is a versatile and compact solution for your wireless communication needs.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for GSM2 Click driver.
Key functions:
gsm2_set_sim_apn- This function sets APN for sim cardgsm2_send_sms_text- This function sends text message to a phone numbergsm2_send_sms_pdu- This function sends text message to a phone number in PDU mode.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief GSM 2 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* Application example shows device capability of connecting to the network and
* sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages using standard "AT" commands.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver, tests the communication by sending "AT" command, and after that restarts the device.
*
* ## Application Task
* Application task is split in few stages:
* - GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
* Sets configuration to device to be able to connect to the network.
*
* - GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
* Waits for the network registration indicated via CREG URC event and then checks
* the connection status.
*
* - GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
* Sets the device configuration for sending SMS or TCP/UDP messages depending on the selected demo example.
*
* - GSM2_EXAMPLE:
* Depending on the selected demo example, it sends an SMS message (in PDU or TXT mode) or TCP/UDP message.
*
* By default, the TCP/UDP example is selected.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_process ( void )
* - static void gsm2_error_check( err_t error_flag )
* - static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
* - static err_t gsm2_configure_for_connection( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_check_connection( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_configure_for_messages( void )
* - static err_t gsm2_send_message( void )
*
* @note
* In order for the examples to work, user needs to set the APN and SMSC (SMS PDU mode only)
* of entered SIM card as well as the phone number (SMS mode only) to which he wants to send an SMS.
* Enter valid values for the following macros: SIM_APN, SIM_SMSC and PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE.
* Example:
SIM_APN "internet"
SIM_SMSC "+381610401"
PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "+381659999999"
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gsm2.h"
#include "conversions.h"
// Example selection macros
#define EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP 0 // Example of sending messages to a TCP/UDP echo server
#define EXAMPLE_SMS 1 // Example of sending SMS to a phone number
#define DEMO_EXAMPLE EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP // Example selection macro
// SIM APN config
#define SIM_APN "internet" // Set valid SIM APN
// SMS example parameters
#define SIM_SMSC "" // Set valid SMS Service Center Address - only in SMS PDU mode
#define PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "" // Set Phone number to message
#define SMS_MODE "1" // SMS mode: "0" - PDU, "1" - TXT
// TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
// Message content
#define MESSAGE_CONTENT "GSM 2 Click board - demo example."
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 256
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 256
/**
* @brief Example states.
* @details Predefined enum values for application example state.
*/
typedef enum
{
GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK = 1,
GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION,
GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE,
GSM2_EXAMPLE
} gsm2_example_state_t;
static gsm2_t gsm2;
static log_t logger;
/**
* @brief Application example variables.
* @details Variables used in application example.
*/
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static err_t error_flag;
static gsm2_example_state_t example_state;
/**
* @brief Clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application
* buffer and reset its length and counter.
*/
static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and
* appends it to the application buffer.
* @return @li @c 0 - Some data is read.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_process ( void );
/**
* @brief Check for errors.
* @details This function checks for different types of
* errors and logs them on UART or logs the response if no errors occured.
* @param[in] error_flag Error flag to check.
*/
static void gsm2_error_check ( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief Logs application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer.
*/
static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief Response check.
* @details This function checks for response and
* returns the status of response.
* @param[in] rsp Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp );
/**
* @brief Configure device for connection to the network.
* @details Sends commands to configure and enable
* connection to the specified network.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_network ( void );
/**
* @brief Wait for connection signal.
* @details Wait for connection signal from CREG URC.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_check_connection ( void );
/**
* @brief Configure device for example.
* @details Configure device for the specified example.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_example ( void );
/**
* @brief Execute example.
* @details This function executes SMS or TCP/UDP example depending on the DEMO_EXAMPLE macro.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t gsm2_example ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
gsm2_cfg_t gsm2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
gsm2_cfg_setup( &gsm2_cfg );
GSM2_MAP_MIKROBUS( gsm2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == gsm2_init( &gsm2, &gsm2_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
gsm2_process( );
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
// Check communication
gsm2_send_cmd( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_AT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Restart device
#define RESTART_DEVICE "1,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CFUN, RESTART_DEVICE );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
example_state = GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK;
}
void application_task ( void )
{
switch ( example_state )
{
case GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_NETWORK:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_configure_for_network( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_check_connection( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_CONFIGURE_FOR_EXAMPLE:
{
if ( GSM2_OK == gsm2_configure_for_example( ) )
{
example_state = GSM2_EXAMPLE;
}
break;
}
case GSM2_EXAMPLE:
{
gsm2_example( );
break;
}
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Example state." );
break;
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void gsm2_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static err_t gsm2_process ( void )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t rx_size = 0;
rx_size = gsm2_generic_read( &gsm2, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
if ( ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) && ( app_buf_len > 0 ) )
{
buf_cnt = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE );
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE - buf_cnt ], buf_cnt );
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ buf_cnt++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
if ( app_buf_len < APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
app_buf_len++;
}
}
}
return GSM2_OK;
}
return GSM2_ERROR;
}
static err_t gsm2_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 120000;
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
gsm2_process( );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, rsp ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, GSM2_RSP_ERROR ) ) )
{
gsm2_process( );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > timeout )
{
gsm2_clear_app_buf( );
return GSM2_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
gsm2_process( );
if ( strstr( app_buf, rsp ) )
{
return GSM2_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, GSM2_RSP_ERROR ) )
{
return GSM2_ERROR_CMD;
}
else
{
return GSM2_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
}
static void gsm2_error_check ( err_t error_flag )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case GSM2_OK:
{
gsm2_log_app_buf( );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR:
{
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_TIMEOUT:
{
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_CMD:
{
log_error( &logger, " CMD!" );
break;
}
case GSM2_ERROR_UNKNOWN:
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Unknown!" );
break;
}
}
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
static void gsm2_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_network ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
// Deregister from network
#define DEREGISTER_FROM_NETWORK "2"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_COPS, DEREGISTER_FROM_NETWORK );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Set SIM APN
gsm2_set_sim_apn( &gsm2, SIM_APN );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable full functionality
#define FULL_FUNCTIONALITY "1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CFUN, FULL_FUNCTIONALITY );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Enable network registartion
#define ENABLE_REG "2"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CREG, ENABLE_REG );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Automatic registration
#define AUTOMATIC_REGISTRATION "0"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_COPS, AUTOMATIC_REGISTRATION );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t gsm2_check_connection ( void )
{
#if ( ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP ) || ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS ) )
#define CONNECTED "+CREG: 2,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_check ( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CREG );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CONNECTED ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
// Check signal quality
gsm2_send_cmd( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CSQ );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#define NO_SIGNAL "99,99"
if ( !strstr( app_buf, NO_SIGNAL ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return error_flag;
}
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
return GSM2_ERROR;
#endif
return GSM2_OK;
}
static err_t gsm2_configure_for_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
#define ACTIVATE_PDP_CONTEXT "1,1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CGACT, ACTIVATE_PDP_CONTEXT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#define ENABLE_MULTI_SESSION "1"
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIMUX, ENABLE_MULTI_SESSION );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CMGF, SMS_MODE );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
static err_t gsm2_example ( void )
{
err_t func_error = GSM2_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_TCP_UDP )
uint8_t cmd_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
uint8_t tcp_socket_num[ 2 ] = { '1', 0 };
uint8_t udp_socket_num[ 2 ] = { '2', 0 };
// Open TCP socket.
#define RESPONSE_CONNECT "CONNECT OK"
#define TCP_SERVICE_TYPE ",\"TCP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, TCP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIOPEN, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Open UDP socket.
#define UDP_SERVICE_TYPE ",\"UDP\","
strcpy( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, UDP_SERVICE_TYPE );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( cmd_buf, "\"" );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QIOPEN, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( RESPONSE_CONNECT );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Get message length
uint8_t message_len_buf[ 10 ] = { 0 };
uint16_t message_len = strlen( MESSAGE_CONTENT );
uint16_to_str( message_len, message_len_buf );
l_trim( message_len_buf );
r_trim( message_len_buf );
// Write message to TCP socket
uint8_t ctrl_z = 0x1A;
strcpy( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QISEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, &ctrl_z, 1 );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Read response
#define RESPONSE_URC "+RECEIVE: "
strcpy( cmd_buf, RESPONSE_URC );
strcat( cmd_buf, tcp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( cmd_buf );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Write message to UDP socket
strcpy( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QISEND, cmd_buf );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( ">" );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, MESSAGE_CONTENT, message_len );
gsm2_generic_write ( &gsm2, &ctrl_z, 1 );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Read response
strcpy( cmd_buf, RESPONSE_URC );
strcat( cmd_buf, udp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( cmd_buf );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
// Close TCP socket
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QICLOSE, tcp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
// Close UDP socket
gsm2_send_cmd_with_par( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_QICLOSE, udp_socket_num );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_SMS )
// Check SMS mode
#define CMGF_PDU "+CMGF: 0"
#define CMGF_TXT "+CMGF: 1"
gsm2_send_cmd_check( &gsm2, GSM2_CMD_CMGF );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_PDU ) )
{
// Send SMS in PDU mode
gsm2_send_sms_pdu( &gsm2, SIM_SMSC, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, CMGF_TXT ) )
{
// Send SMS in TXT mode
gsm2_send_sms_text ( &gsm2, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
error_flag = gsm2_rsp_check( GSM2_RSP_OK );
func_error |= error_flag;
gsm2_error_check( error_flag );
}
// 30 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return func_error;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:GSM/LTE