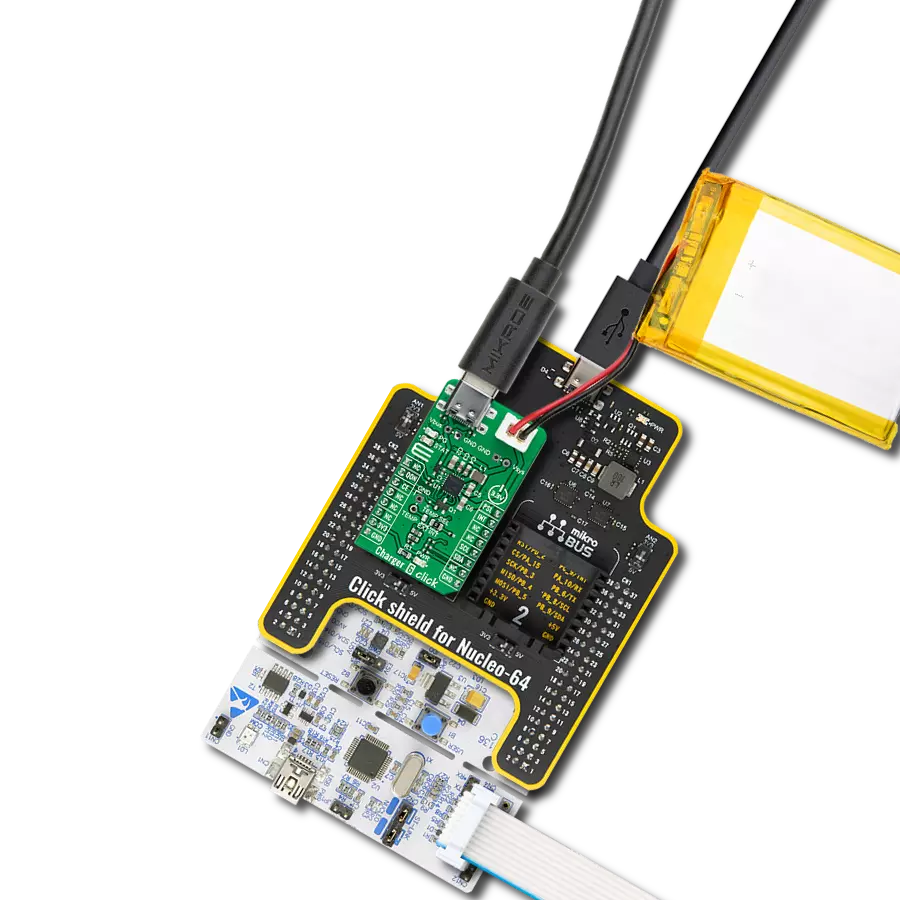
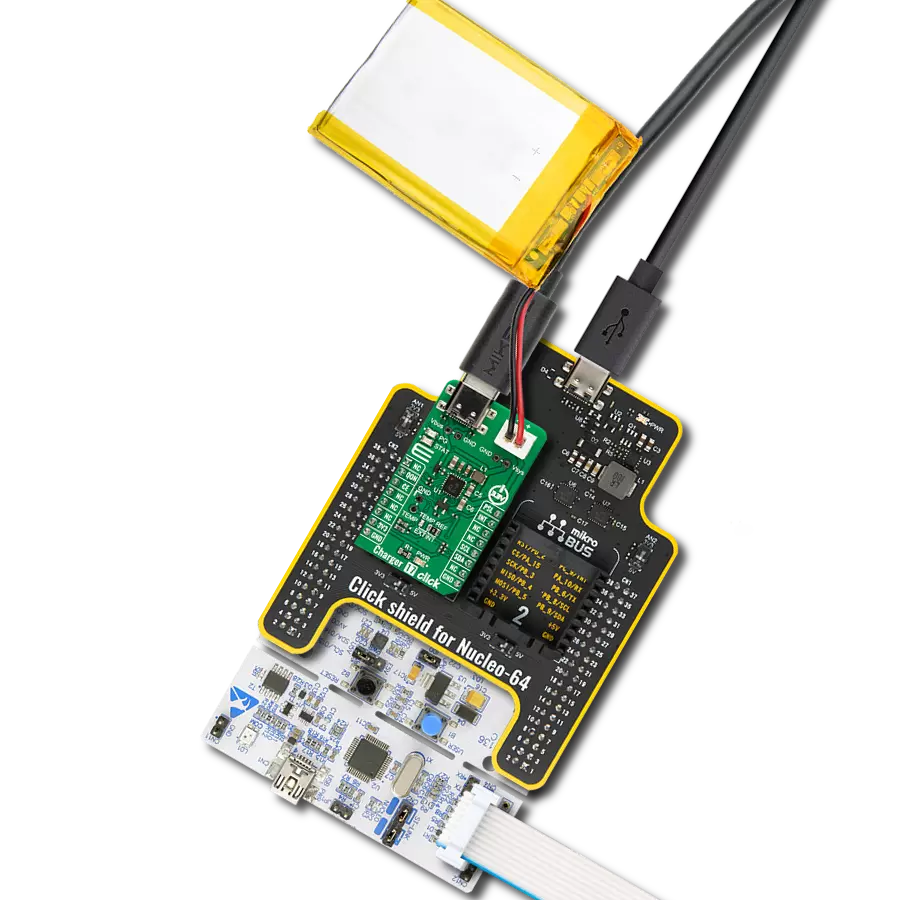
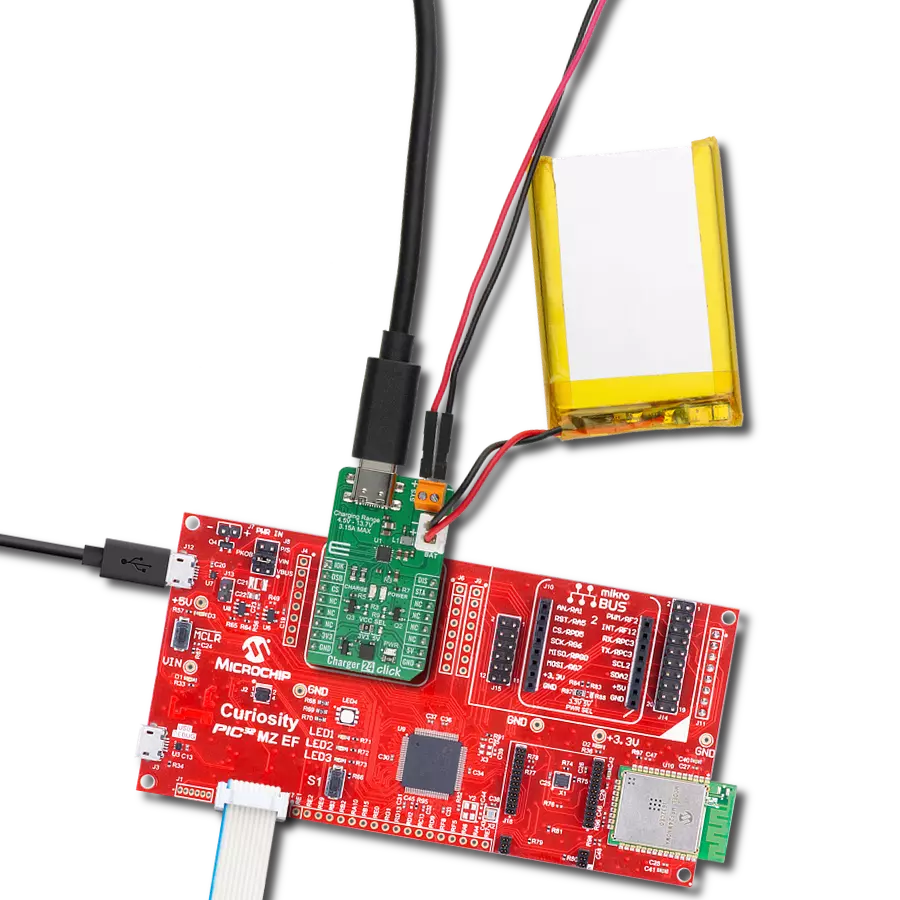
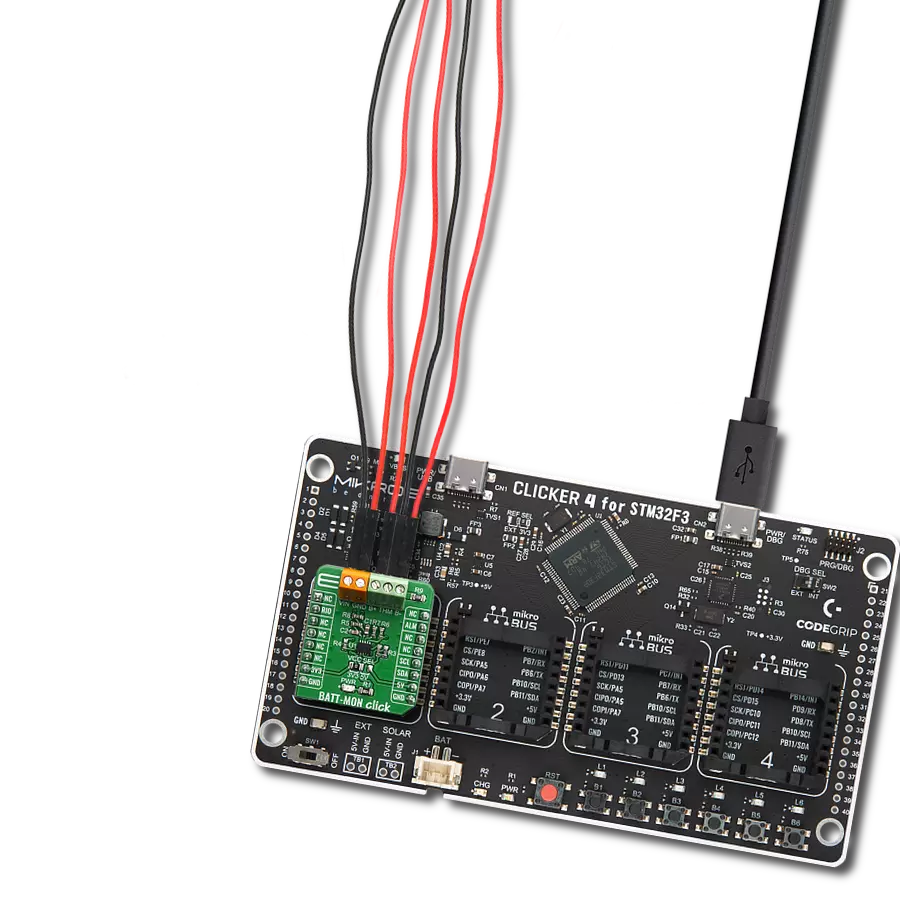
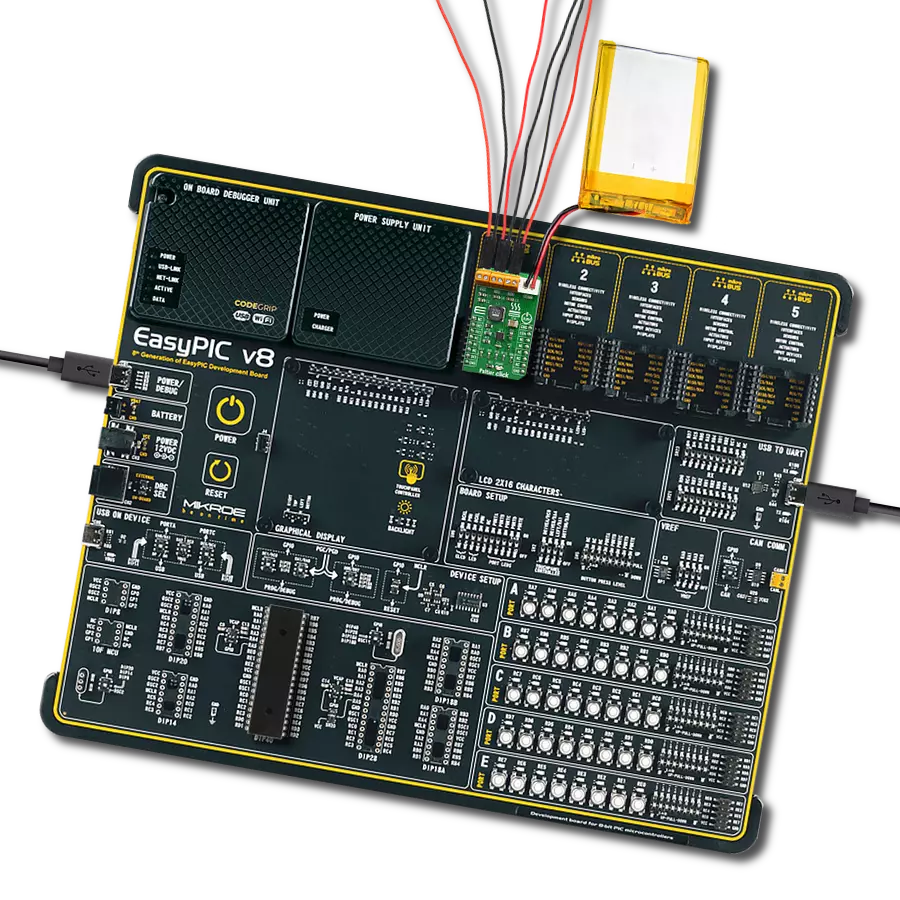
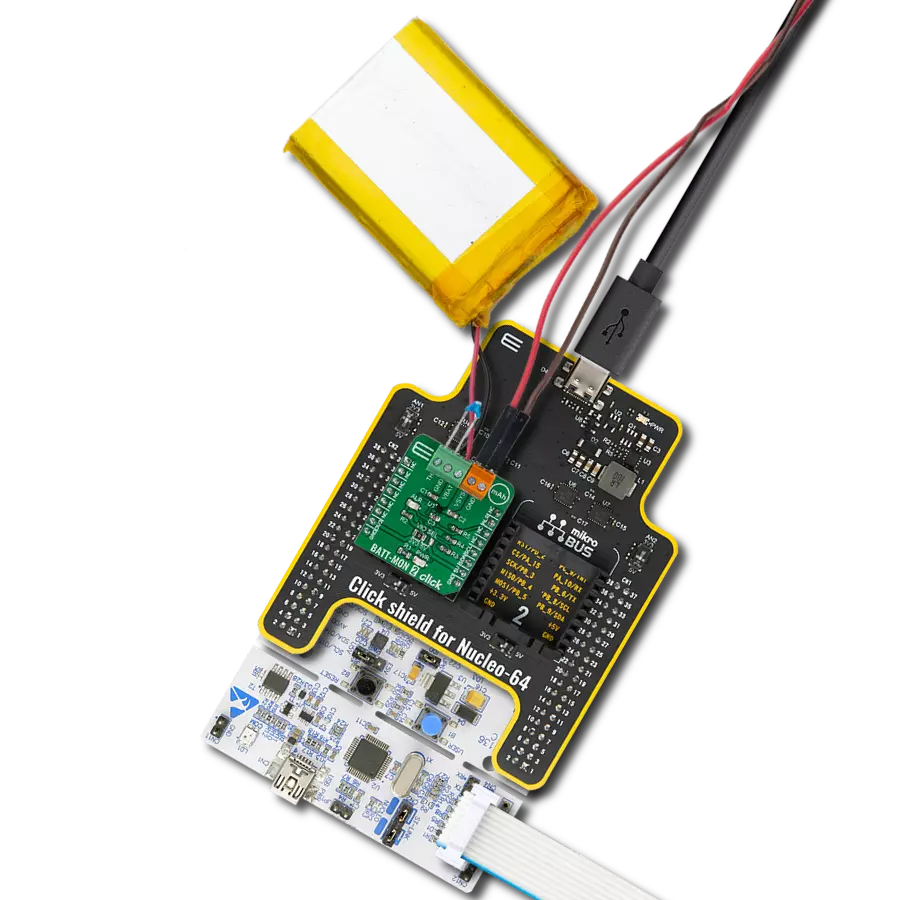
Don't let a low battery ruin your day - add a charger to your solution and keep going strong
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Charger 8 Click is based on two different ICs the MAX8903B, an integrated single-cell Li-Ion/Li-Po battery charger for USB and external power, as well as the MAX17201, a stand-alone battery fuel gauge with SHA-256 authentication, both from Analog Devices. The MAX8903B is labeled as U1, providing most functions for this Click board™. Its primary task is to provide power for the system load and charge a single-cell Li-Ion/Li-Po battery, connected at the standard 2.5mm pitch XS battery connector labeled as BAT. When the USB input is used as a primary power source, the MAX8903B will try to maintain the system current by utilizing the connected battery or the external power supply unit (PSU) at the VIN input. On the other hand, it will try to redirect all the unused power to the battery charging section when the system requires lower current levels. With the help of the Smart Power Selector™ technology, it will always choose the best path to utilize the limited power resources most efficiently. The MAX8903B IC is designed with reliability in mind: the IC prevents draining the battery below the critical level, protects it from overheating (if the thermistor is used), offers prequel charging (for deeply depleted batteries), features overvoltage protection,
charging status monitoring and more. The Click board™ has indicators to monitor the charging process and power distribution. USB LED indicates that there is a valid voltage at the USB input. Instead of the USB connector, the USB power supply input pin of the MAX8903B is connected to the mikroBUS™ 5V power rail. CHARGE LED indicates the charge-in-progress status, while the FAULT LED indicates an error during the charging process. Besides the FAULT LED indicator, the FAULT pin of the MAX8903B is also routed to the mikroBUS™ INT pin, allowing an interrupt to be generated on the host MCU in case of a charging failure. This pin will be pulled to a LOW logic level when the charging timer expires while the charger is still in prequel mode (mode in which only 10% of charging current is applied to the battery while it is deeply discharged) or while the battery stays in fast-charging mode. The DOK pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ AN pin, labeled as DOK. A logic LOW level on this pin indicates a valid power supply at the DC power supply input pin of the MAX8903B. If there is a PSU connected to the VIN terminal, its voltage should stay within the valid range. The undervoltage/overvoltage protection will be activated if the internal voltage threshold is
exceeded. The absolute maximum voltage rating of the MAX8903B is 20V. USB Suspend (USUS) pin from the MAX8903B is routed to the mikroBUS™ PWM pin and labeled as US. It suspends the power source connected to the USB power supply input pin. With no external PSU connected, setting this pin to a HIGH logic level will disable the battery charger and the SYS output, allowing the USB SUSPEND mode. The CEN pin is used to disable the charging circuitry. A resistor pulls it to a LOW logic level, and the MAX8903B should control this pin internally for optimum performance. However, if battery charging is not wanted, pulling this pin to a HIGH logic level can be forced off. It is routed to the mikroBUS™ pin CS and labeled as EN. The MAX17201 offers a battery gauge functionality, allowing monitoring of the performance of the connected battery. It employs a proprietary ModelGauge™ m5 algorithm, which allows very accurate monitoring of all battery parameters, including the predicted aging time, remaining cycles, and more. It has a programmable ALERT function which is signaled over the ALTR1 pin, routed to the mikroBUS™ RST pin, labeled as ALT. The MAX17201 IC uses the I2C interface to communicate with the host MCU.
Features overview
Development board
EasyAVR v7 is the seventh generation of AVR development boards specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of 16-bit AVR microcontrollers from Microchip and has a broad set of unique functions, such as a powerful onboard mikroProg programmer and In-Circuit debugger over USB. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements in one place, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others. With four different connectors for each port, EasyAVR v7 allows you to connect accessory boards, sensors, and custom electronics more
efficiently than ever. Each part of the EasyAVR v7 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An integrated mikroProg, a fast USB 2.0 programmer with mikroICD hardware In-Circuit Debugger, offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides it also includes a clean and regulated power supply block for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including an external 12V power supply, 7-12V AC or 9-15V DC via DC connector/screw terminals, and a power source via the USB Type-B (USB-B)
connector. Communication options such as USB-UART and RS-232 are also included, alongside the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, three display options (7-segment, graphical, and character-based LCD), and several different DIP sockets which cover a wide range of 16-bit AVR MCUs. EasyAVR v7 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
64
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
40
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
Accessories
Li-Polymer Battery is the ideal solution for devices that demand a dependable and long-lasting power supply while emphasizing mobility. Its compatibility with mikromedia boards ensures easy integration without additional modifications. With a voltage output of 3.7V, the battery meets the standard requirements of many electronic devices. Additionally, boasting a capacity of 2000mAh, it can store a substantial amount of energy, providing sustained power for extended periods. This feature minimizes the need for frequent recharging or replacement. Overall, the Li-Polymer Battery is a reliable and autonomous power source, ideally suited for devices requiring a stable and enduring energy solution. You can find a more extensive choice of Li-Polymer batteries in our offer.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Charger 8 Click driver.
Key functions:
charger8_get_temperature- Functions for read Temperature of the chipcharger8_get_capacity- Function for reads the current capacity of the batterycharger8_get_status- Function for reads the Status register
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Charger8 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application is used for charging devices and battery diagnostics
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver init, enable moduele and default configuration,
* disable ALERT and USB suspand mode and sets max battery capacity
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads battery diagnostics and this data logs to USBUART every 1500 ms.
*
* *note:*
* The user can charge a battery internally over mikroBUS or externally by supplying the VIN connectors with 5V.
* For more precise diagnosis and easier tracking of the charging battery status you can set its capacity
* - e.g. if you have a 2000mAh battery you can use the "charger8_setMaxBatteryCapacity()" function and pass the parameter for 2000mAh,
* by doing this you make the readings more precise.
* In the example we used only some possibilities of the diagnostics like temperature of the chip during charging,
* charging current, current battery voltage, current battery capacity and how much the battery is charged in percentage.
* In case of changing the battery to a different one, it is neccessary to reset the device and set the battery's maximum capacity.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "charger8.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static charger8_t charger8;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
charger8_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
charger8_cfg_setup( &cfg );
CHARGER8_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
charger8_init( &charger8, &cfg );
charger8_enable( &charger8, CHARGER8_CHARGER_ENABLE );
charger8_default_cfg( &charger8 );
charger8_reset( &charger8 );
charger8_set_alert( &charger8, CHARGER8_ALERT_DISABLE );
charger8_set_usb_suspend( &charger8, CHARGER8_USB_SUSPAND_MODE_DISABLE );
charger8_set_max_battery_capacity( &charger8, 2000 );
log_printf( &logger, " --- Charger - Start measurement --- \r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
// Task implementation.
float temperature;
float current;
float voltage;
uint8_t soc;
uint16_t capacity;
log_printf( &logger, " - Battery diagnostics - \r\n" );
temperature = charger8_get_temperature( &charger8 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Temperature : %f C\r\n", temperature );
current = charger8_get_current( &charger8 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Current : %f mA\r\n", current);
voltage = charger8_get_voltage( &charger8 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Voltage : %f mV\r\n", voltage);
capacity = charger8_get_capacity( &charger8 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Capacity : %d mAh\r\n", capacity );
soc = charger8_get_soc( &charger8 );
log_printf( &logger, " - SOC : %d %%\r\n", soc );
log_printf( &logger, " -------------------------- \r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END