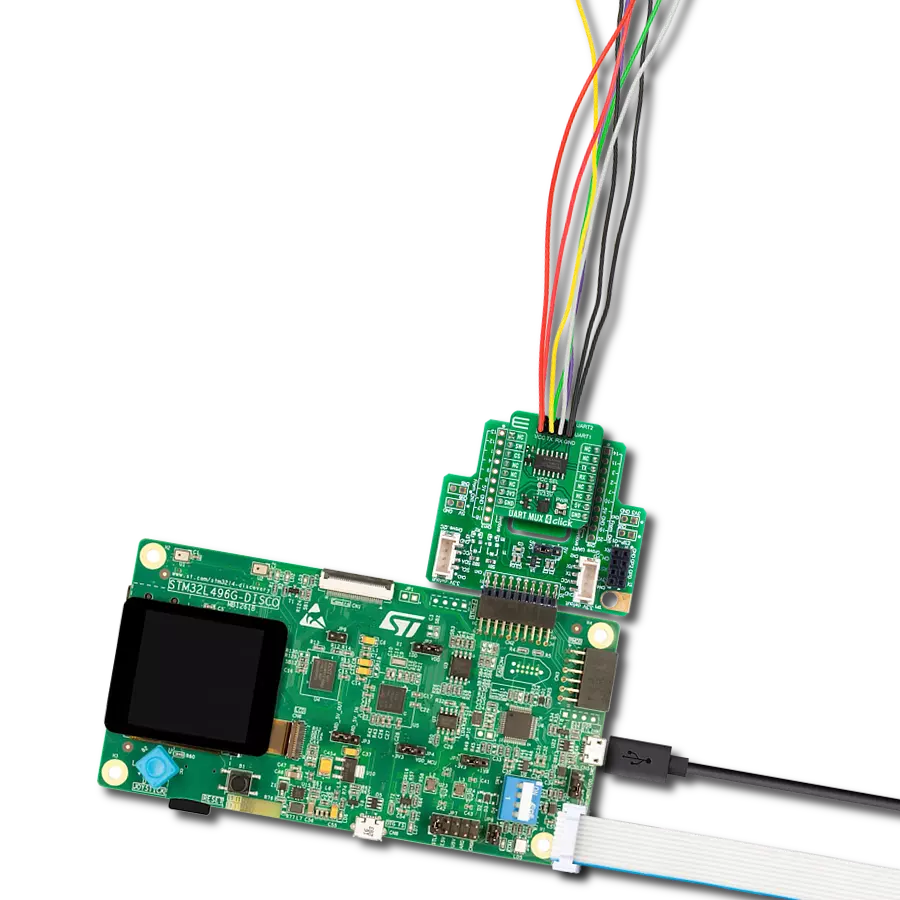
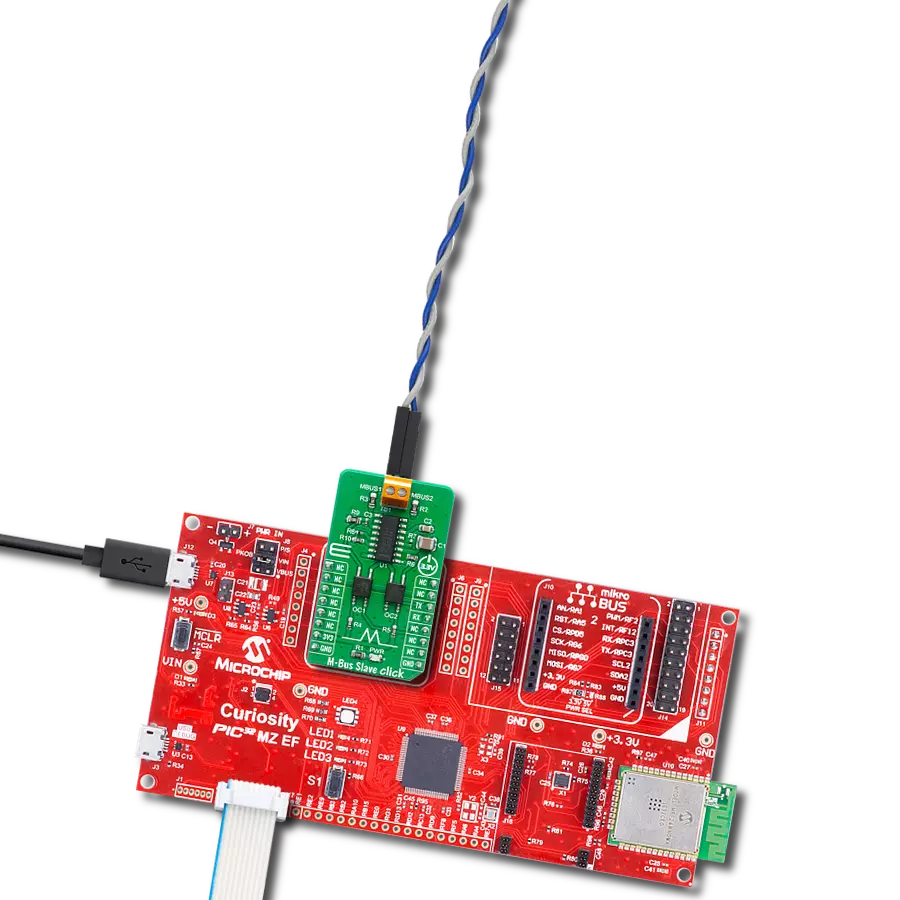
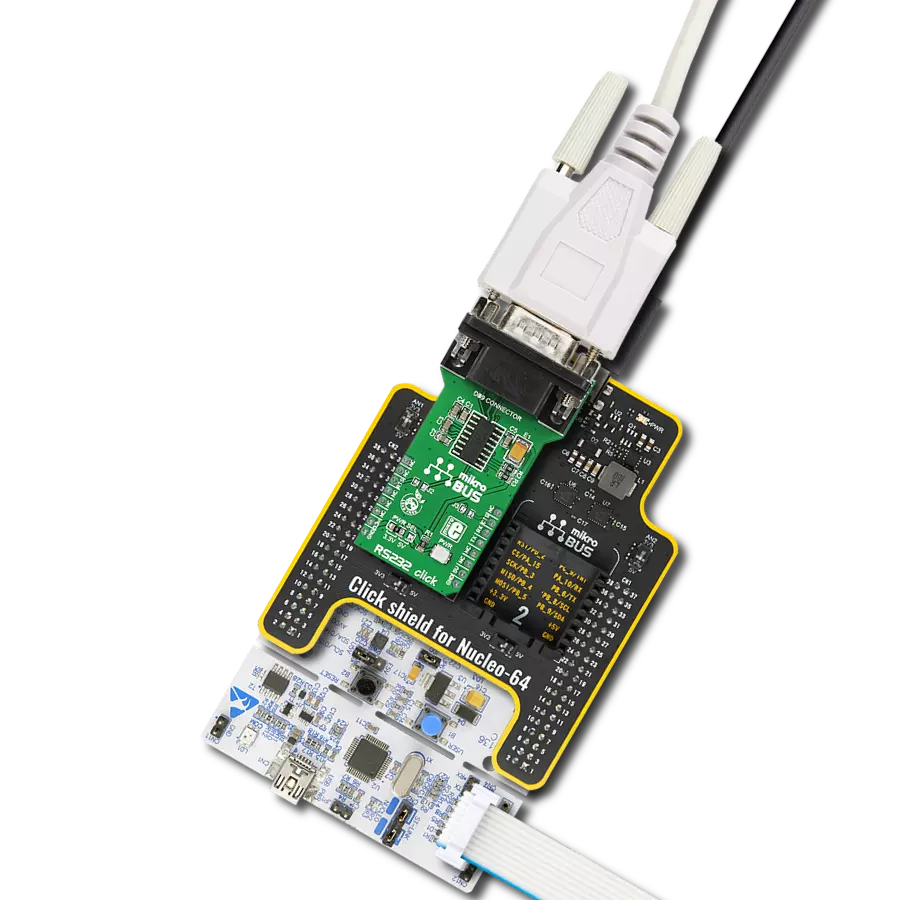
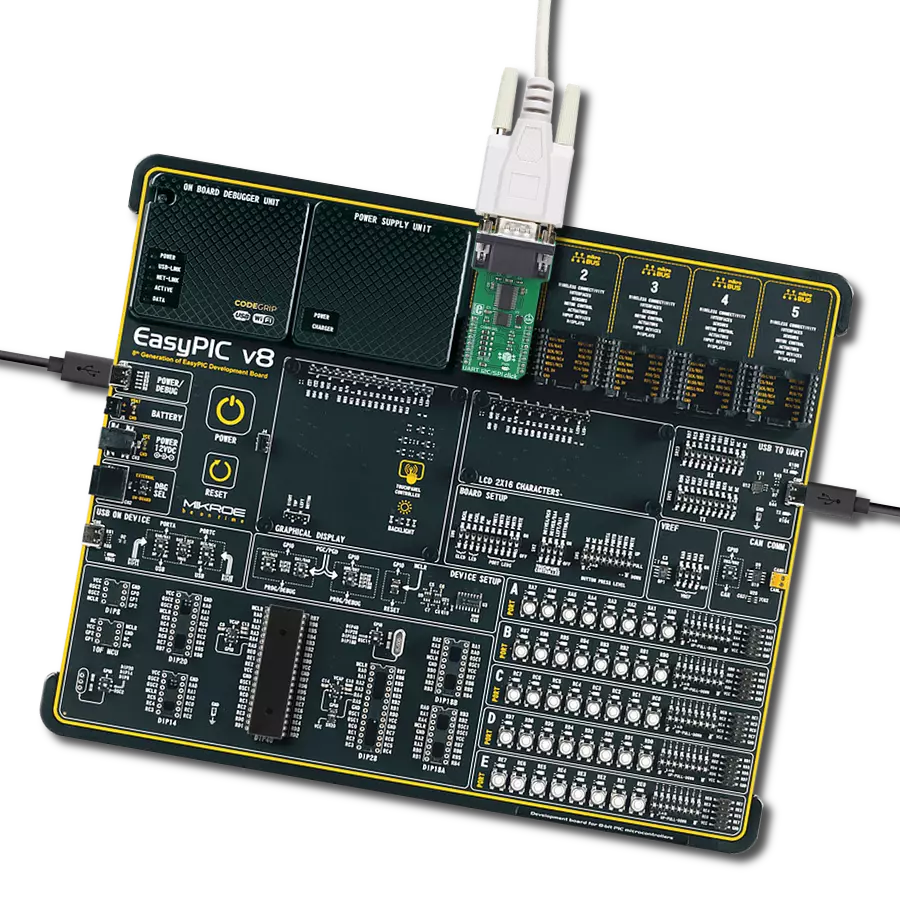
In a world of communication standards, our UART solution acts as a universal translator, enabling smooth dialogue between UART and RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 interfaces
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
RS Transceiver Click is based on the XR34350, an RS-232/RS-422/RS-485 serial transceiver with internal termination and wide output swing from MaxLinear. It is an advanced multiprotocol transceiver with dual protocol serial ports, RS-232 or RS-485/RS-422. The RS-485/RS-422 modes feature one driver and one receiver (1TX/1RX) in both half and full duplex configurations, where high-speed drivers operate up to 20Mbps. The RS-485 and RS-422 are both 2-Wire protocols, where the RS-485 can have multiple commanding devices and listeners. On the other hand, the RS-422 can have only one commander and multiple listeners. The RS-232 mode features three drivers and five receivers (3TX/5RX) and provides full support for all eight signals. In the RS-232 mode, it can achieve data rates up to 1Mbps. All transceiver drivers can be slew limited to 250Kbps in any mode, thus minimizing electromagnetic interference. The XR34350 eliminates the need to design a termination resistor when sharing a single connector or a pair of lines across
multiple serial protocols. It integrates the terminal resistor and switching control, thus allowing it to be switched in and out of the circuit with a single pin. The RS-485/RS-422 receiver inputs are high impedance, while the RS-232 receiver input is pulled down, allowing up to 256 devices on a single communication bus. The RS Transceiver uses a standard UART interface to communicate with the host MCU, with commonly used UART RX and TX. In addition, the UART flow control pins CTS and RTS are available on the mikroBUS™ socket. The transceiver can be reset over the RST pin, and limiting can be activated over the SLW pin. As the mikroBUS™ socket is pin-limited, the RS Transceiver includes the TCA9536, a remote 4-bit IO expander with configuration registers from Texas Instruments, bringing an additional four I/Os to the host MCU. The TCA9536 communicates with the host MCU over the standard I2C serial interface, supporting fast mode up to 1MHz. Using this I/O expander, you can set half-duplex or full-duplex mode over the DIR1 pin of the transceiver.
There are two mode pins, MODE0 and MODE1, that you can use to select one mode between Loopback Mode, Half-Duplex RS-485 Mode #1, RS-232 Mode, and Full-Duplex RS-485/422 Mode #1. The Term pin only applies in the half-duplex and full-duplex RS-485/RS-422 modes as it enables the internal termination resistor. There are two additional headers on this Click board™. The lower one brings GND, L1, L4, L6, and L9 pins from the transceiver, and the RS-485 signals are also available on the upper header for testing purposes of the full and half duplex modes. These signals are also available on the DE-9 connector. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
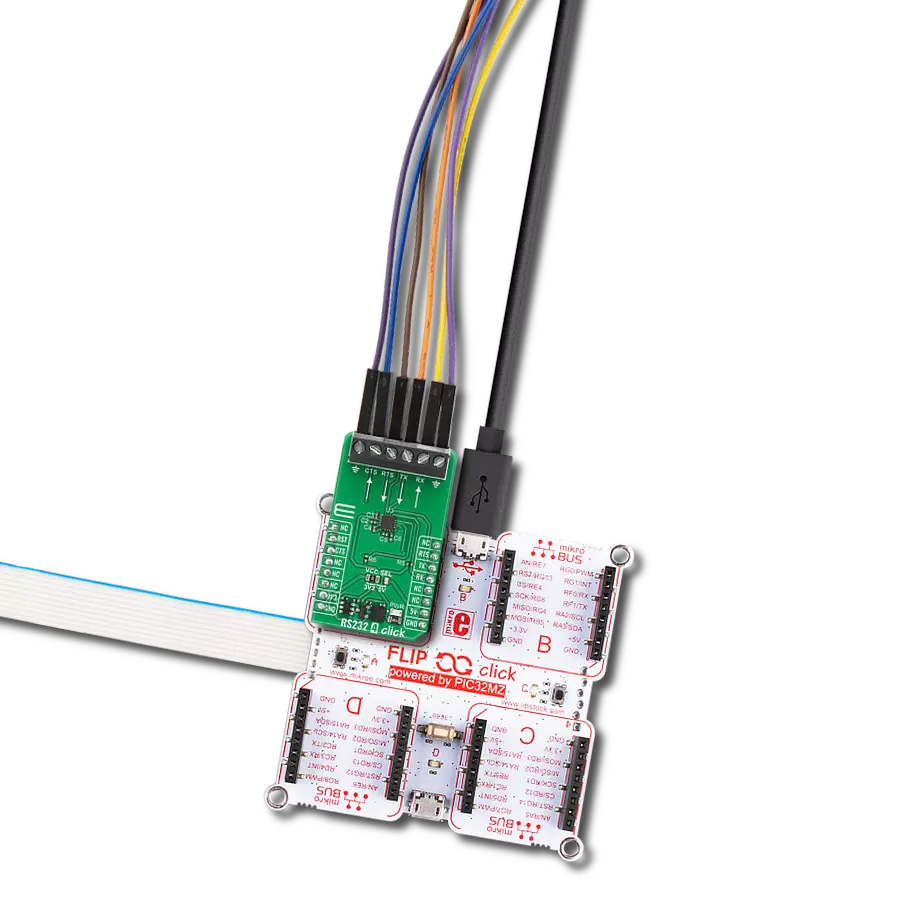
Development board
PIC32MZ Clicker is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit PIC32MZ microcontroller with FPU from Microchip, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a mikroProg connector, and a header for interfacing with external electronics. Thanks to its compact design with clear and easy-recognizable silkscreen markings, it provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere and under
any circumstances. Each part of the PIC32MZ Clicker development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the PIC32MZ Clicker programming method, using USB HID mikroBootloader, or through an external mikroProg connector for PIC, dsPIC, or PIC32 programmer, the Clicker board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. The USB Micro-B connection can provide up to 500mA of current, which is more than enough to operate all onboard
and additional modules. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several buttons and LED indicators. PIC32MZ Clicker is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
524288
You complete me!
Accessories
DB9 Cable Female-to-Female (2m) cable is essential for establishing dependable serial data connections between devices. With its DB9 female connectors on both ends, this cable enables a seamless link between various equipment, such as computers, routers, switches, and other serial devices. Measuring 2 meters in length, it offers flexibility in arranging your setup without compromising data transmission quality. Crafted with precision, this cable ensures consistent and reliable data exchange, making it suitable for industrial applications, office environments, and home setups. Whether configuring networking equipment, accessing console ports, or utilizing serial peripherals, this cable's durable construction and robust connectors guarantee a stable connection. Simplify your data communication needs with the 2m DB9 female-to-female cable, an efficient solution designed to meet your serial connectivity requirements easily and efficiently.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for RS Transceiver Click driver.
Key functions:
rstransceiver_set_op_mode- RS Transceiver sets the operating mode function.rstransceiver_mode_full_duplex- RS Transceiver sets the Full-Duplex mode function.rstransceiver_device_enable- RS Transceiver enables the device function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief RS Transceiver Click example
*
* # Description
* This example reads and processes data from RS Transceiver Click board™.
* The library also includes a function for selecting the desired operating mode,
* enabling/disabling the receiver or driver and data writing or reading.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of I2C and UART module and log UART.
* After driver initialization, default settings turn on the device.
*
* ## Application Task
* This example demonstrates the use of the RS Transceiver Click board™.
* The app shows the device configured in loopback mode,
* sends a "MikroE" message, reads the received data and parses it.
* Results are being sent to the UART Terminal, where you can track their changes.
*
* @author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "rstransceiver.h"
#define DEMO_MESSAGE "\r\nMikroE\r\n"
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 20
static rstransceiver_t rstransceiver;
static log_t logger;
static char app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
rstransceiver_cfg_t rstransceiver_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
rstransceiver_cfg_setup( &rstransceiver_cfg );
RSTRANSCEIVER_MAP_MIKROBUS( rstransceiver_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == rstransceiver_init( &rstransceiver, &rstransceiver_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
if ( RSTRANSCEIVER_ERROR == rstransceiver_default_cfg ( &rstransceiver ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
if ( 0 < rstransceiver_generic_write( &rstransceiver, DEMO_MESSAGE, strlen( DEMO_MESSAGE ) ) )
{
if ( 0 < rstransceiver_generic_read( &rstransceiver, app_buf, strlen( DEMO_MESSAGE ) ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%s", app_buf );
memset( app_buf, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END