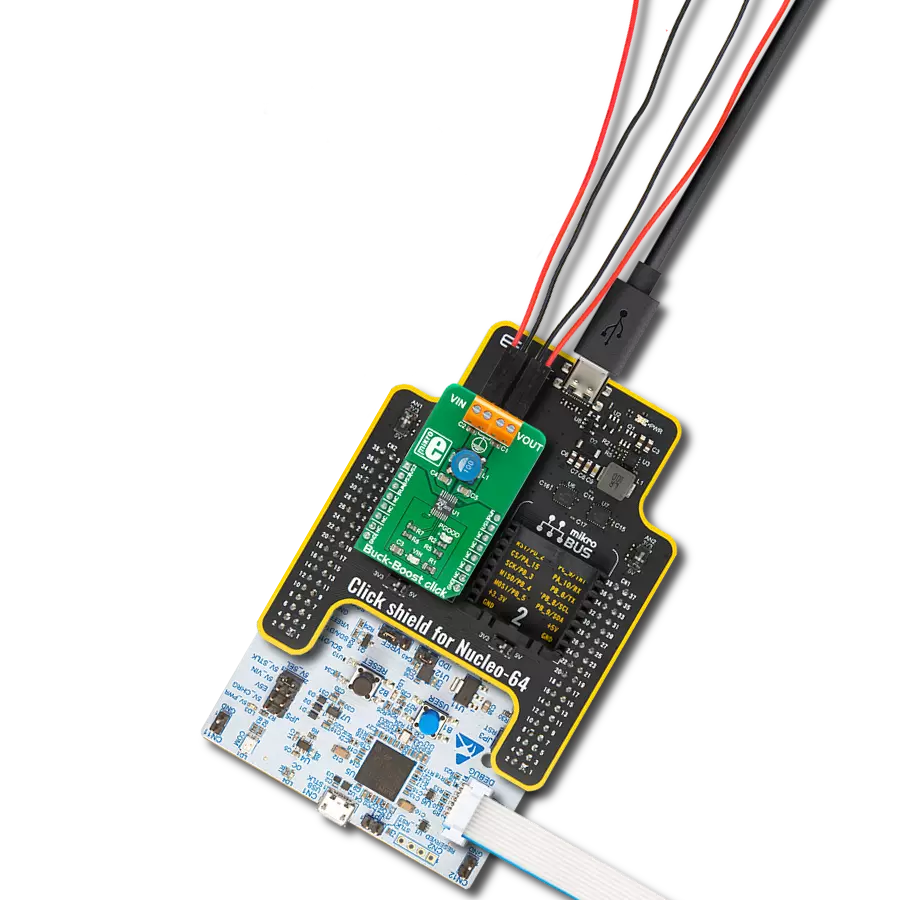
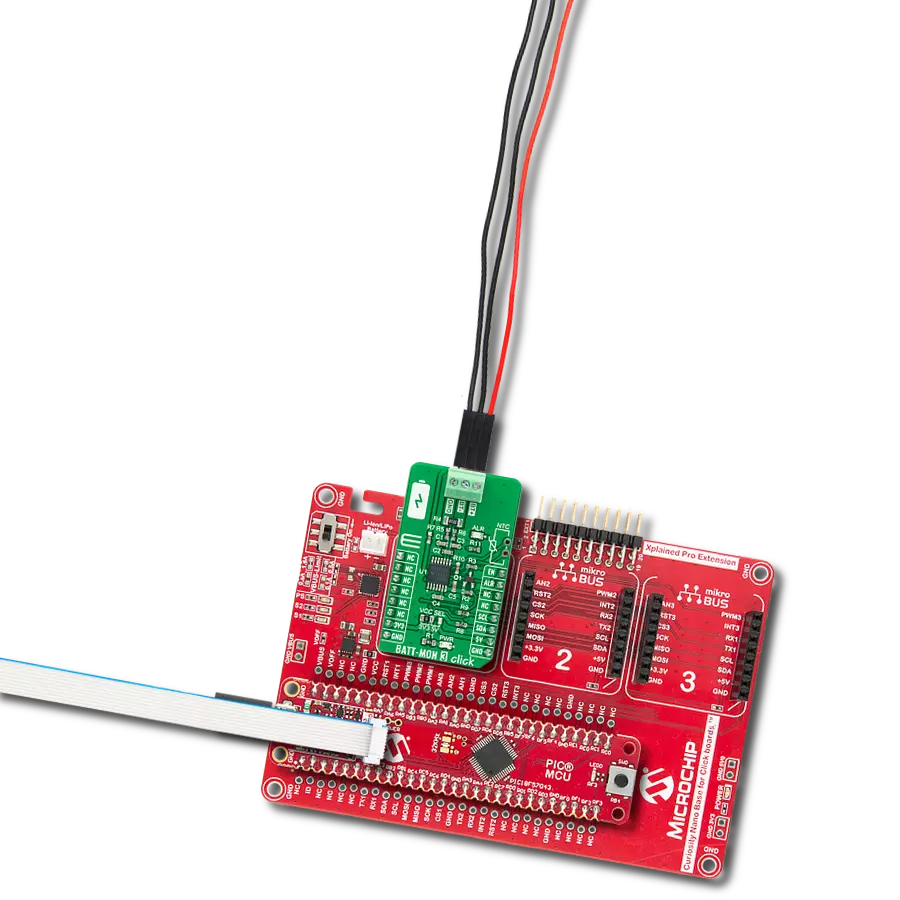
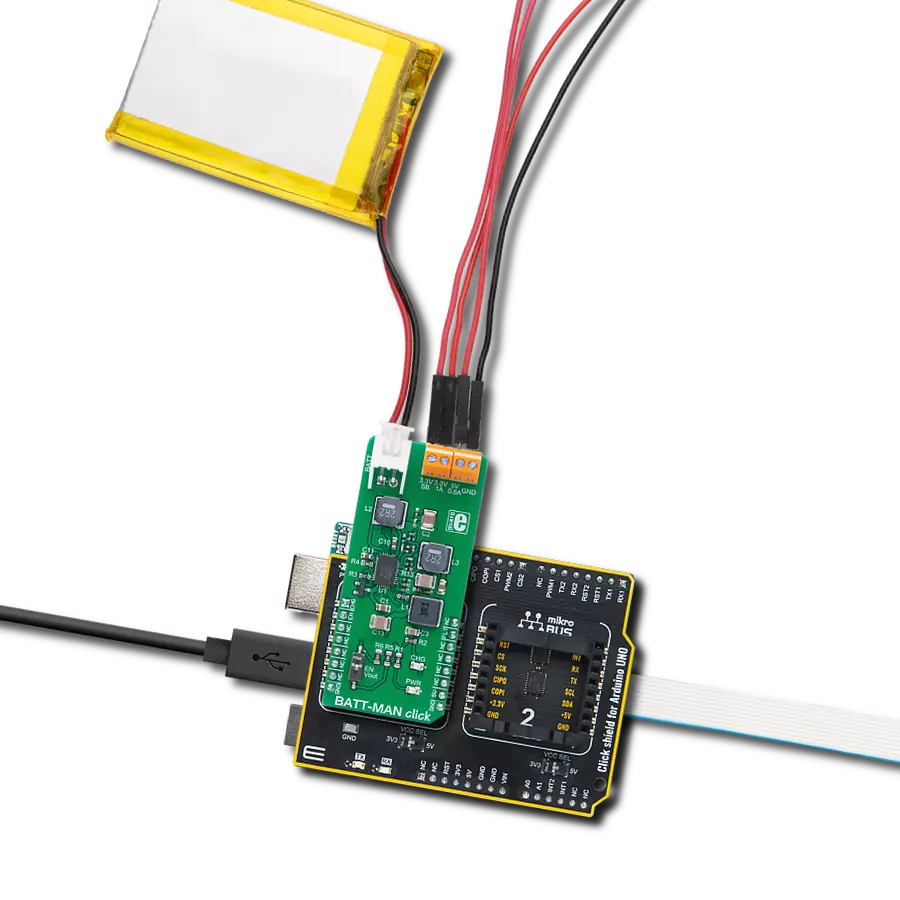
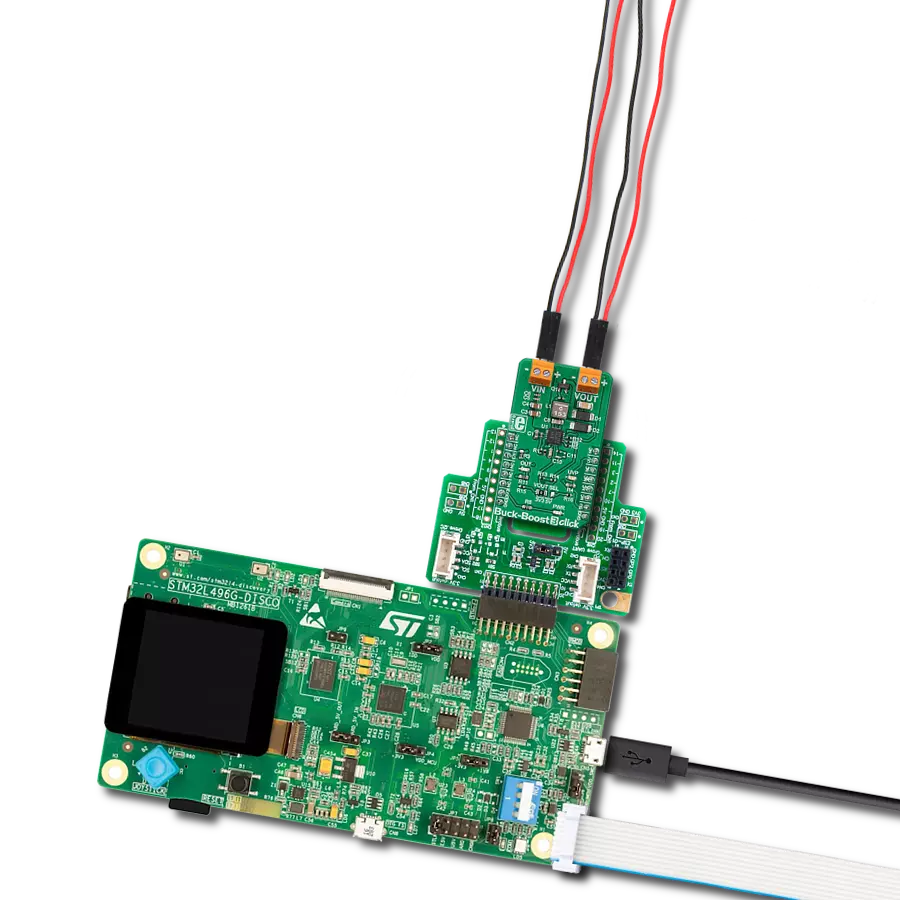
Revolutionize your energy management with our avant-garde Buck-Boost combo at your side
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
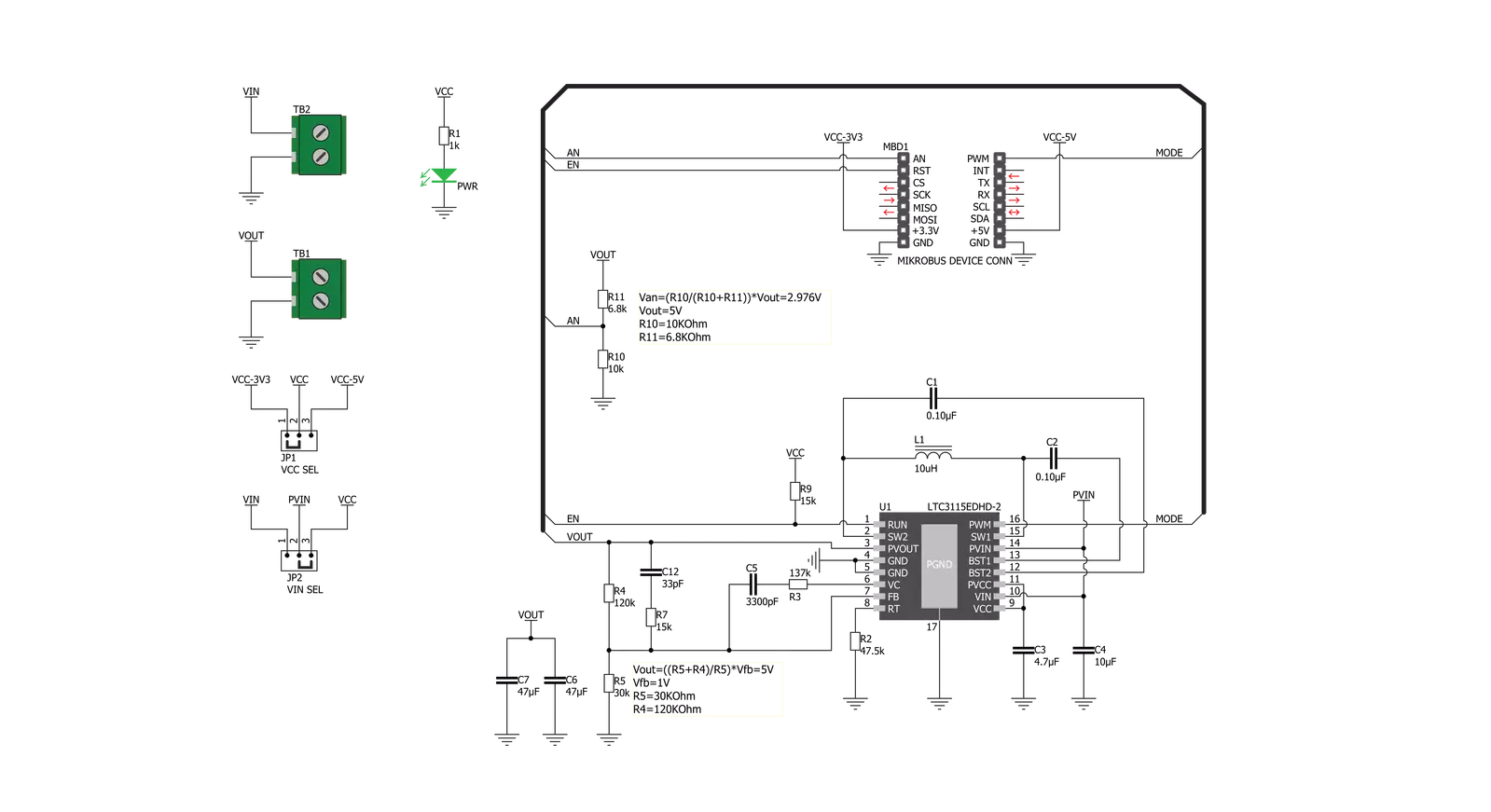
Buck-Boost 2 Click is based on the LTC3115-2, a 40V, 2A synchronous buck-boost DC/DC converter from Analog Devices. This IC relies on the advanced four MOSFET switch topology, so it can sustain the regulation when the input voltage is lower and higher than the output voltage, set by the feedback network to 5V. A proprietary switching algorithm ensures a transparent, continuous transition between operating modes. The LTC3115-2 features both forward and reverse current limiting sections. The maximum current available on the output depends on the mode of operation: If the output voltage is greater than the input voltage, the device works in boost mode, and the maximum current is about 0.6A. If the output voltage exceeds the input voltage, the device works in buck mode, and the maximum current available is about 1.4A. Also, the maximum output current is affected by the switching mode, selectable by the MODE pin, routed to the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™. There are two modes available: fixed frequency PWM mode and burst mode. While working in PWM mode, the LTC3115-2 IC uses a fixed frequency determined by the onboard resistor - in the case of the Buck-Boost 2 click, it is fixed at 750kHz. The PWM mode is used when a heavier load is connected to the output
terminal. This mode is set when the PWM/SYNC pin is pulled to a HIGH logic level. This mode allows the maximum current on the output and results in the lowest amount of switching noise and output voltage ripple. This mode provides power for the connected devices while they work in the active mode. The burst mode is used for maintained efficiency when light output loads are used. When the PWM/SYNC pin is pulled to a LOW logic level, the device will work in burst mode. While in burst mode, the variable frequency switching algorithm is used, resulting in a low quiescent current, which allows lowered power consumption - e.g., when the external voltage input is taken from a battery. The error amplifier is powered down in this mode, and the output current should not be greater than allowed, else the output voltage will lose regulation. This mode is perfectly suited to power up various devices while they work in standby mode. When using the synchronization function of the PWM/SYNC pin, the device works in the fixed frequency PWM mode, but the external clock source of the internal PLL section regulates its frequency. This can be useful when special power supply noise requirements must be met. Since the internal PLL can only increase the internal clock frequency, the
external clock signal should be above the frequency set by the onboard resistor (750kHz), taking the sufficient error margin into account. The RUN pin of the LTC3115-2 IC is routed to the mikroBUS™ RST pin and is used to activate the internal logic and switching circuitry. Setting this pin to a HIGH logic level (above 1.21V) will enable both the logic and the switching sections of the LTC3115-2 IC. It is possible to measure and monitor the output voltage of the Buck-Boost 2 by utilizing the voltage divider, with its middle point routed to the AN pin of the mikroBUS™. By applying the calculation from the formula below, it is possible to determine the exact value of the output voltage. It can monitor the output to take appropriate action when the voltage drops or loses regulation. This board allows operation with both 3.3V and 5V MCUs. There is an onboard SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL, which is used to set the logic voltage (e.g., for the RUN pin) and the input voltage for the LTC3115-2 IC. Another SMD jumper, labeled VIN SEL, selects the voltage chosen by the VCC SEL and the external source connected to the input terminal. The output load should be connected to the output terminal. Two screw terminals allow easy and secure connection of the input and output lines.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Buck-Boost 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
buckboost2_set_mode- This function sets the working modebuckboost2_power_off- This function powers OFF the chipbuckboost2_power_on- This function powers on the chip
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Buck Boost 2 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application enables use of DC-DC step-down/step-up regulator (buck/boost).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes Driver init and turn ON chip and settings mode with improvement current.
*
* ## Application Task
* The Click has a constant output voltage of 5V, no additional settings are required.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "buckboost2.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static buckboost2_t buckboost2;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
buckboost2_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info(&logger, "---- Application Init ----");
// Click initialization.
buckboost2_cfg_setup( &cfg );
BUCKBOOST2_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
buckboost2_init( &buckboost2, &cfg );
buckboost2_power_on( &buckboost2 );
buckboost2_set_mode( &buckboost2, BUCKBOOST2_WITH_IMPROVEMENT );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
// Task implementation.
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Buck-Boost