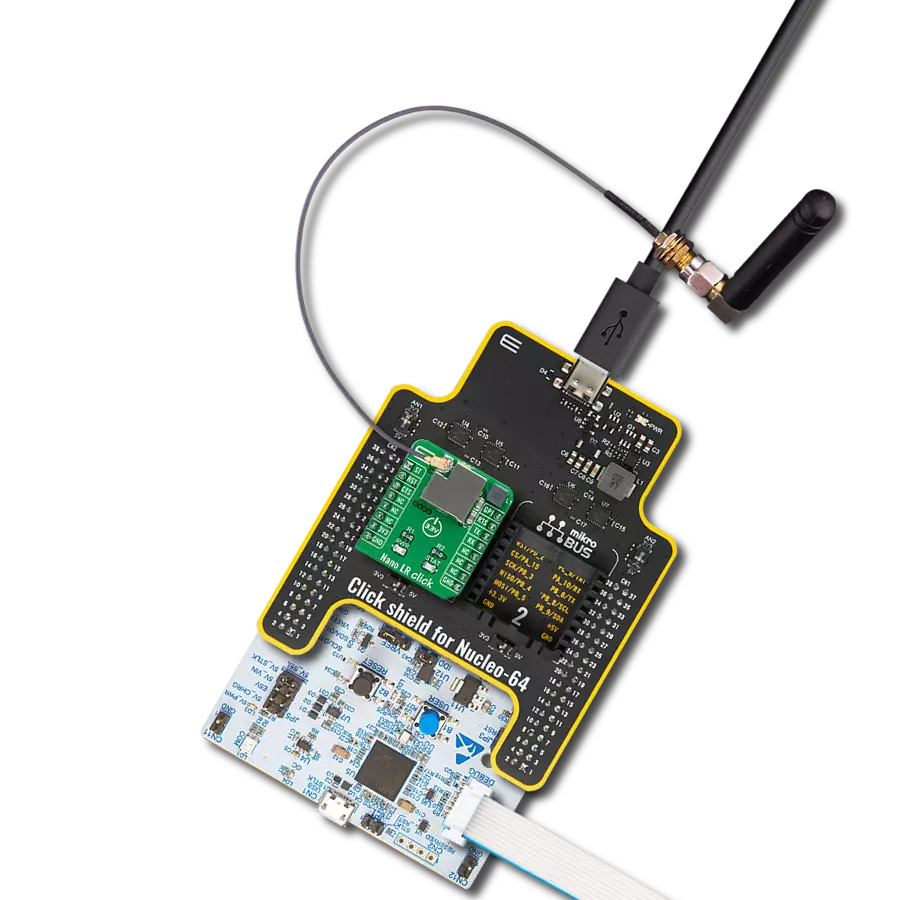
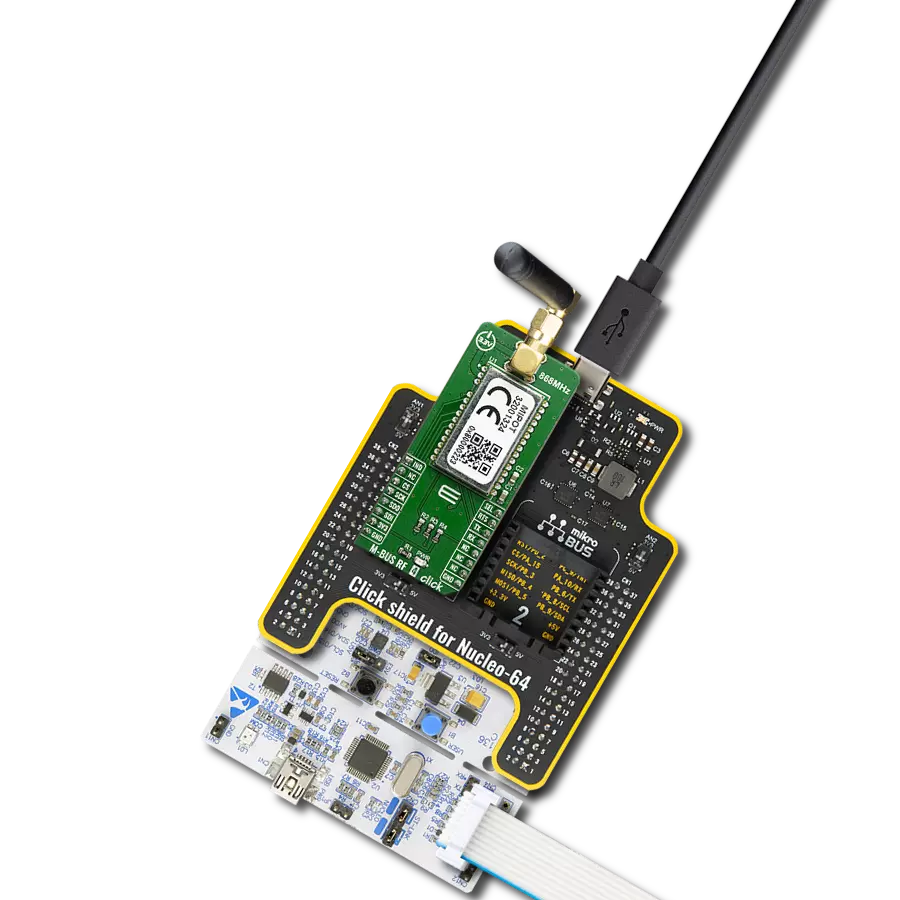
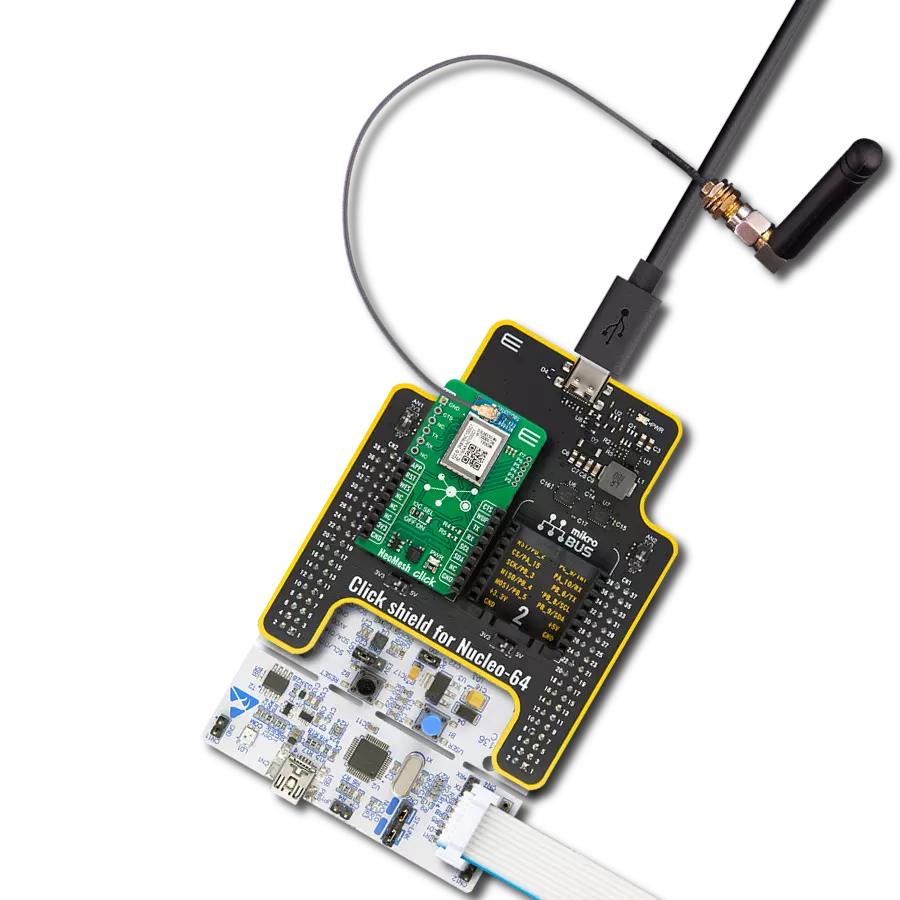
Compact yet robust wireless module solution engineered for the seamless creation of wireless mesh network nodes
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
NeoMesh Click - 868MHz is based on the NC1000C-8, a wireless Mesh network module from NeoCortec. Besides being controlled by the host MCU, NeoMesh Click can be used as a standalone device. You can configure the module over the System API (SAPI), a UART-based interface with hardware flow control. This interface is configured to ensure direct compatibility with the FTDI serial to USB cable. When using the NeoMesh Click as a standalone board, the application interface of the NeoMesh module can be easily accessed through the pin header located at the side of the module. There are eight pins, six in the header labeled P2-7, which allows you to use up to 6 channels of 12-bit ADC, GPIOs, I2C sensors, and UART application APIs. Specific pins of this header can be used to interface with an external microcontroller through UART. The module also can be configured wirelessly. At the bottom side, there is an unconnected WES jumper. You can use the Wireless Encrypted Setup by connecting it, but only if it is already configured through the WES
procedure. Every WES channel has a specified AES 128 encryption key. Just beside is another jumper, VCC, this one connected. The NeoMesh is optimized for ultra-low power operation and allows operation on small batteries for several years. If you want to make an ultra-low power node, consider using the NeoMesh Click with some low-power development board with battery management, such as the Clicker 2 series or similar. This scenario is ideal where the node can send data infrequently, and the payload size is small. NeoMesh is a wireless system designed with versatility in mind, allowing users to build products in many different application areas. This system can handle data transmission, lost neighbor nodes, moving nodes, and more. Data transmission through the network is done sequentially from node to node until the data reaches its destination. There are three types of NeoMesh devices: coordinator, router, and end device. You can configure your device according to your needs. NeoMesh uses a standard UART serial interface to communicate
with the host MCU, with commonly used UART RX and TX pins and a transfer speed of 115200bps. Hardware control flow is available through the CTS pin. You can also use an I2C interface as a virtual UART. There are unpopulated pull-up resistors on I2C lines. The I2C interface can be enabled over the I2C SEL jumper. While disabled, you can use the WUP pin to indicate the WakeUp activity state of the module; otherwise, the WUP function is unavailable. The module can be reset over the RST pin. The generic application activity is indicated over the APP pin with a logic LOW state when active. If the Wireless Encrypted Setup JP2 jumper is closed, you can enable the WES client over the WES pin. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
UNI Clicker is a compact development board designed as a complete solution that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It supports a wide range of microcontrollers, such as different ARM, PIC32, dsPIC, PIC, and AVR from various vendors like Microchip, ST, NXP, and TI (regardless of their number of pins), four mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a debugger/programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, it allows you to build
gadgets with unique functionalities and features quickly. Each part of the UNI Clicker development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the UNI Clicker programming method, using a third-party programmer or CODEGRIP/mikroProg connected to onboard JTAG/SWD header, the UNI Clicker board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or using a Li-Po/Li
Ion battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board (plus USB HOST/DEVICE), including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. UNI Clicker is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
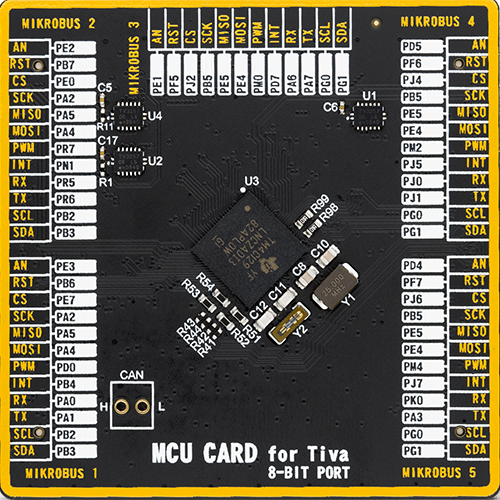
MCU Card / MCU
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
Texas Instruments
Pin count
212
RAM (Bytes)
262144
You complete me!
Accessories
868MHz right-angle rubber antenna is a compact and versatile solution for wireless communication. Operating within the frequency range of 868-915MHz, it ensures optimal signal reception and transmission. With a 50-ohm impedance, it's compatible with various devices and systems. This antenna boasts a 2dB gain, enhancing signal strength and extending communication range. Its vertical polarization further contributes to signal clarity. Designed to handle up to 50W of input power, it's a robust choice for various applications. Measuring just 48mm in length, this antenna is both discreet and practical. Its SMA male connector ensures a secure and reliable connection to your equipment. Whether you're working with IoT devices, remote sensors, or other wireless technologies, the 868MHz right-angle antenna offers the performance and flexibility you need for seamless communication.
IPEX-SMA cable is a type of RF (radio frequency) cable assembly. "IPEX" refers to the IPEX connector, a miniature coaxial connector commonly used in small electronic devices. "SMA" stands for SubMiniature Version A and is another coaxial connector commonly used in RF applications. An IPEX-SMA cable assembly has an IPEX connector on one end and an SMA connector on the other, allowing it to connect devices or components that use these specific connectors. These cables are often used in applications like WiFi or cellular antennas, GPS modules, and other RF communication systems where a reliable and low-loss connection is required.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for NeoMesh Click - 868MHz driver.
Key functions:
neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame- This function sends a desired AAPI frame by using UART serial interface.neomesh868mhz_read_aapi_frame- This function reads an AAPI frame by using UART serial interface.neomesh868mhz_send_sapi_frame- This function sends a desired SAPI frame by using UART serial interface.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief NeoMesh 868MHz Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of NeoMesh 868MHz Click board by showing
* the communication between the two Click boards.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and configures the Click board for the selected
* application mode.
*
* ## Application Task
* One Click board should be set to originator mode and the others to receiver 1 or 2.
* If the SINGLE_RECEIVER_MODE is enabled, the originator device sends a desired message
* to RECEIVER_1 node and waits for an acknowledge response, otherwise it sends the same
* message to both RECEIVER_1 and RECEIVER_2 nodes. The receiver devices reads and parses
* all incoming AAPI frames and displays them on the USB UART.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "neomesh868mhz.h"
// Comment out the line below to add the APP_RECEIVER_2 to the APP_ORIGINATOR example.
#define SINGLE_RECEIVER_MODE
// Demo aplication selection macros
#define APP_ORIGINATOR 0
#define APP_RECEIVER_1 1
#define APP_RECEIVER_2 2
#define DEMO_APP APP_ORIGINATOR
// Text message to send in the originator mode
#define DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE "MIKROE-NeoMesh"
#define DEFAULT_PORT 0
// Node ID macros
#define NODE_ID_ORIGINATOR 0x0100u
#define NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 0x0020u
#define NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 0x0021u
static neomesh868mhz_t neomesh868mhz;
static log_t logger;
static neomesh868mhz_aapi_frame_t aapi_frame;
static neomesh868mhz_sapi_frame_t sapi_frame;
/**
* @brief NeoMesh 868MHz parse aapi rsp function.
* @details This function reads and parses AAPI responses until an expected response is received.
* @param[in] exp_rsp : Expected AAPI response.
* @return @li @c 0 - Success,
* @li @c -1 - Error, no expected response is received,
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( uint8_t exp_rsp );
/**
* @brief NeoMesh 868MHz parse sapi rsp function.
* @details This function reads and parses SAPI responses until an expected response is received.
* @param[in] exp_rsp : Expected SAPI response.
* @return @li @c 0 - Success,
* @li @c -1 - Error, no expected response is received,
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( uint16_t exp_rsp );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
neomesh868mhz_cfg_t neomesh868mhz_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
neomesh868mhz_cfg_setup( &neomesh868mhz_cfg );
NEOMESH868MHZ_MAP_MIKROBUS( neomesh868mhz_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == neomesh868mhz_init( &neomesh868mhz, &neomesh868mhz_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Enable SAPI over AAPI\r\n" );
aapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_CMD_SAPI_TO_AAPI;
aapi_frame.len = 0;
neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_BOOTLOADER_START );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Login with password\r\n" );
sapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_CMD_LOGIN;
sapi_frame.len = 5;
sapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_LOGIN_PASSWORD_0;
sapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_LOGIN_PASSWORD_1;
sapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_LOGIN_PASSWORD_2;
sapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_LOGIN_PASSWORD_3;
sapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_LOGIN_PASSWORD_4;
neomesh868mhz_send_sapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &sapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Set NODE ID to: " );
sapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_CMD_SET_SETTING;
sapi_frame.len = 3;
sapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_SETTINGS_ID_NODE_ID;
#if ( DEMO_APP == APP_RECEIVER_1 )
log_printf( &logger, "%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 );
sapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
sapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 & 0xFF );
#elif ( DEMO_APP == APP_RECEIVER_2 )
log_printf( &logger, "%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 );
sapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
sapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 & 0xFF );
#elif ( DEMO_APP == APP_ORIGINATOR )
log_printf( &logger, "%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) NODE_ID_ORIGINATOR );
sapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( NODE_ID_ORIGINATOR >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
sapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( NODE_ID_ORIGINATOR & 0xFF );
#endif
neomesh868mhz_send_sapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &sapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Commit settings\r\n" );
sapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_CMD_COMMIT_SETTINGS;
sapi_frame.len = 0;
neomesh868mhz_send_sapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &sapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Start protocol stack\r\n" );
sapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_CMD_START_PROTOCOL_STACK;
sapi_frame.len = 0;
neomesh868mhz_send_sapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &sapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_PROTOCOL_STACK_START );
// Wait for the device to actually switch back to application layer
while ( !neomesh868mhz_get_cts_pin ( &neomesh868mhz ) );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Get NODE info\r\n" );
aapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_CMD_NODE_INFO;
aapi_frame.len = 0;
neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NODE_INFO );
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Get neighbour list\r\n" );
aapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_CMD_NEIGHBOUR_LIST;
aapi_frame.len = 0;
neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame );
neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NEIGHBOUR_LIST );
#if ( DEMO_APP == APP_RECEIVER_1 )
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Application Mode: Receiver 1\r\n" );
#elif ( DEMO_APP == APP_RECEIVER_2 )
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Application Mode: Receiver 2\r\n" );
#elif ( DEMO_APP == APP_ORIGINATOR )
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Application Mode: Originator\r\n" );
#else
#error "Selected application mode is not supported!"
#endif
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
#if ( DEMO_APP == APP_ORIGINATOR )
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Send message to node: %.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 );
aapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_CMD_ACK_SEND;
aapi_frame.len = 3 + strlen ( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE );
aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_1 & 0xFF );
aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = DEFAULT_PORT;
strcpy ( &aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ], DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE );
if ( NEOMESH868MHZ_OK == neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame ) )
{
neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ACK );
}
#ifndef SINGLE_RECEIVER_MODE
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Send message to node: %.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 );
aapi_frame.cmd = NEOMESH868MHZ_CMD_ACK_SEND;
aapi_frame.len = 3 + strlen ( DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE );
aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 >> 8 ) & 0xFF );
aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] = ( uint8_t ) ( NODE_ID_RECEIVER_2 & 0xFF );
aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] = DEFAULT_PORT;
strcpy ( &aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ], DEMO_TEXT_MESSAGE );
if ( NEOMESH868MHZ_OK == neomesh868mhz_send_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame ) )
{
neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ACK );
}
#endif
#else
neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( NULL );
#endif
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static err_t neomesh868mhz_parse_aapi_rsp ( uint8_t exp_rsp )
{
while ( NEOMESH868MHZ_OK == neomesh868mhz_read_aapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &aapi_frame ) )
{
switch ( aapi_frame.cmd )
{
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ACK:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ACK ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NACK:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NACK ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ACK_HOST:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ACK HOST DATA ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Packet Age: %.3f sec\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] ) * 0.125f );
log_printf( &logger, " Port: %u\r\n", aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 5; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
aapi_frame.payload[ aapi_frame.len ] = 0;
log_printf( &logger, " Payload (string): %s\r\n\n", &aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ACK_HOST_HAPA:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ACK HOST DATA HAPA ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Packet Age: %.3f sec\r\n",
( ( ( uint32_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 24 ) |
( ( uint32_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] << 16 ) |
( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ] ) * pow ( 2, -19 ) );
log_printf( &logger, " Port: %u\r\n", aapi_frame.payload[ 6 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 7; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NACK_HOST:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NACK HOST DATA ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Packet Age: %.3f sec\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] ) * 0.125f );
log_printf( &logger, " Port: %u\r\n", aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Sequence number: %u\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 6 ] ) & 0x0FFFu );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 7; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NACK_HOST_HAPA:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NACK HOST DATA HAPA ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Originator ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Packet Age: %.3f sec\r\n",
( ( ( uint32_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 24 ) |
( ( uint32_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] << 16 ) |
( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ] ) * pow ( 2, -19 ) );
log_printf( &logger, " Port: %u\r\n", aapi_frame.payload[ 6 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Sequence number: %u\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 7 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 8 ] ) & 0x0FFFu );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 9; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NACK_SEND:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NACK SEND ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Destination ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Sequence number: %u\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] ) & 0x0FFFu );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NACK_DROP:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NACK DROP ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Destination ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Sequence number: %u\r\n",
( ( ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] << 8 ) |
aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ] ) & 0x0FFFu );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NODE_INFO:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NODE INFO ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Node ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Unique ID: %.2X%.2X%.2X%.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 6 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Type: %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 7 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NEIGHBOUR_LIST:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NEIGHBOUR LIST ----\r\n" );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt += 3 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " %u# -> ", ( uint16_t ) ( ( cnt / 3 ) + 1 ) );
if ( ( 0xFF != aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] ) &&
( 0xFF != aapi_frame.payload[ cnt + 1 ] ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, "Node ID: %.2X%.2X, RSSI: -%u dBm\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt + 1 ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt + 2 ] );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "N/A\r\n" );
}
}
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_NETWORK_COMMAND:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- NETWORK COMMAND ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Node ID: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Command: %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 3; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ROUTE_INFO:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ROUTE INFO ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Bit Mask: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_WES_STATUS:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- WES STATUS ----\r\n" );
if ( !aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, " WES stopped\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " WES server running\r\n" );
}
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_WES_SETUP:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- WES SETUP ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Unique ID: %.2X%.2X%.2X%.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ],
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Type: %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 5 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_GET_SW_VERSION:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- SW VERSION ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " HW/SW Type: %.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " NeoMesh Version: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 1 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 2 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " Bootloader Version: %.2X%.2X\r\n",
( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 3 ], ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ 4 ] );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_RSP_ALT_MODE:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ALT MODE ----\r\n" );
if ( !aapi_frame.payload[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Network in Normal mode\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " Network in Alternate mode\r\n" );
}
break;
}
default:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- RESPONSE ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " CMD: 0x%.2X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.cmd );
log_printf( &logger, " LEN: %u\r\n", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.len );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < aapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) aapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
}
if ( exp_rsp == aapi_frame.cmd )
{
return NEOMESH868MHZ_OK;
}
}
return NEOMESH868MHZ_ERROR;
}
static err_t neomesh868mhz_parse_sapi_rsp ( uint16_t exp_rsp )
{
while ( NEOMESH868MHZ_OK == neomesh868mhz_read_sapi_frame ( &neomesh868mhz, &sapi_frame ) )
{
switch ( sapi_frame.cmd )
{
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_OK:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- OK ----\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_ERROR:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- ERROR ----\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_BOOTLOADER_START:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Bootloader STARTED ----\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_PROTOCOL_STACK_START:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Protocol Stack STARTED ----\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_PROTOCOL_STACK_ERROR:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Protocol Stack ERROR ----\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_SETTINGS_LIST_OUTPUT:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Settings List Output ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < sapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) sapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_SETTINGS_VALUE:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Settings Value ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < sapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) sapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
break;
}
case NEOMESH868MHZ_SAPI_RSP_RESET:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Reset EVENT ----\r\n" );
break;
}
default:
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- RESPONSE ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " CMD: 0x%.4X\r\n", ( uint16_t ) sapi_frame.cmd );
log_printf( &logger, " PLEN: %u\r\n", ( uint16_t ) sapi_frame.len );
if ( sapi_frame.len )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Payload: " );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < sapi_frame.len; cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%.2X ", ( uint16_t ) sapi_frame.payload[ cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
break;
}
}
if ( exp_rsp == sapi_frame.cmd )
{
return NEOMESH868MHZ_OK;
}
}
return NEOMESH868MHZ_ERROR;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Sub-1 GHz Transceievers