Upgrade your IoT projects with an IEEE802.15.4-compliant 2.4GHz RF transceiver, offering ZigBee, MiWi, MiWi P2P, and proprietary wireless networking for seamless connectivity and endless innovation
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
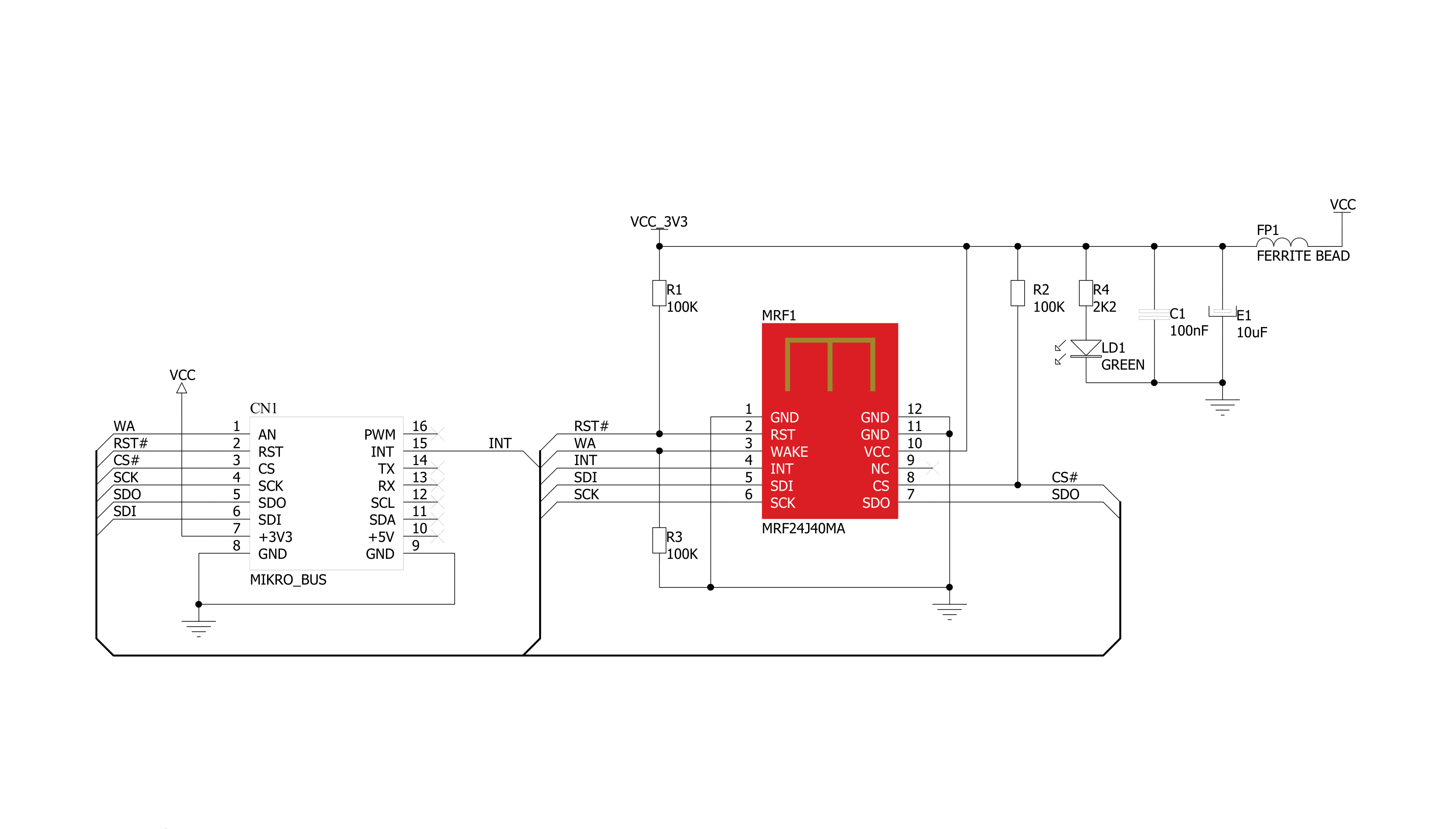
BEE Click is based on the MRF24J40MA, a 2.4GHz RF transceiver module from Microchip. It operates at ISM Band from 2.405 to 2.48GHz over an integrated PCB antenna and matching circuitry. You can set one of the 16 channels in the frequency range. With up to 36dB of TX power control range, it can achieve data rates of up to 250Kbps. The module integrates the PHY and MAC functionality and can create a low-cost, low-power, and low-data-rate Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN). To reduce the load on the host MCU, the module
features automatic packet retransmission, automatic acknowledgment, energy detection, CSMA-CA algorithm, three CCA modes, security encryption and decryption, and more. To communicate with the host MCU, the BEE Click uses a standard 4-Wire SPI serial interface and supports SPI mode 0 only, which requires that SCK idles in a low state. In addition, BEE Click features other functionalities, such as the RST pin for resetting the module with active Low. The WA pin is an external wake-up trigger disabled by default
and should be enabled in the software. This pin is in conjunction with the sleep mode. In addition, the module can signal one of eight interrupt events over the INT pin. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
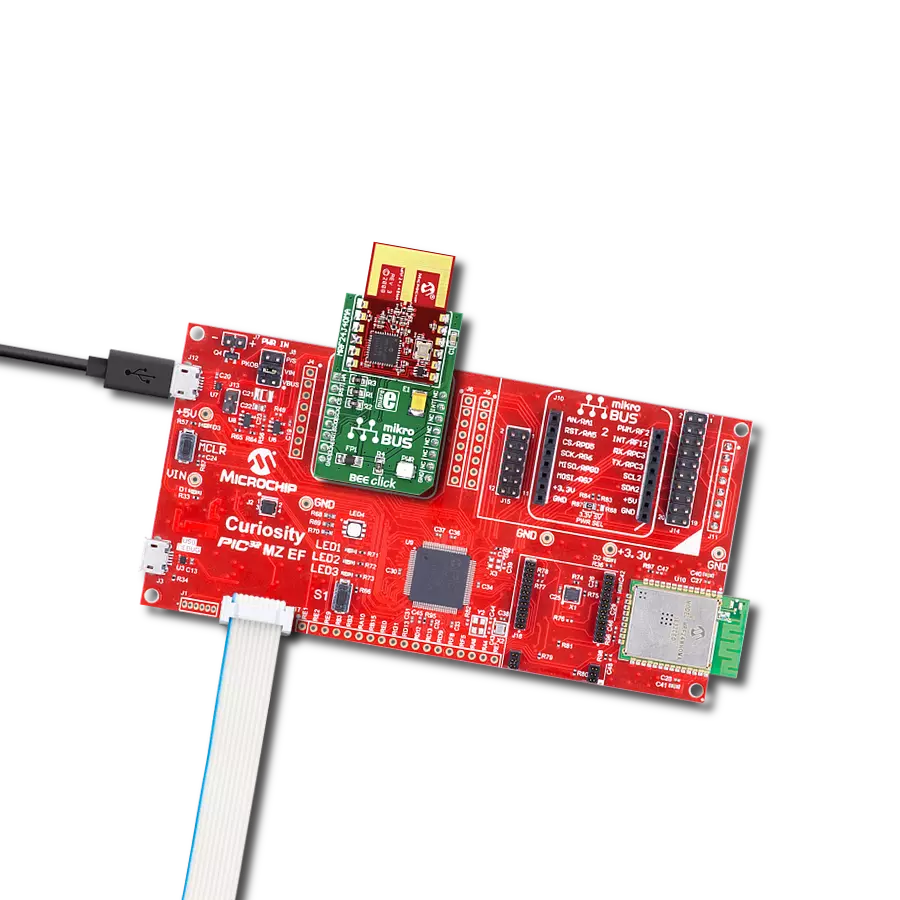
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for BEE Click driver.
Key functions:
bee_read_rx_fifo- Read RX FIFO functionbee_write_tx_normal_fifo- Write TX normal FIFO function
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Bee Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of an BEE Click board by showing
* the communication between the two Click boards.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and configures the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Depending on the selected application mode, it reads all the received data or
* sends the desired message every 3 seconds.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "bee.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
// Comment out the line below in order to switch the application mode to receiver
#define DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
static bee_t bee;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t short_address1[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t short_address2[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t long_address1[ 8 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t long_address2[ 8 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t pan_id1[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t pan_id2[ 2 ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t rx_data_fifo[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t rx_data_fifo_old[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT ] = { 0 };
static uint8_t data_tx1[] = { 'M', 'i', 'k', 'r', 'o', 'E', 0 };
static uint8_t data_tx2[] = { 'B', 'E', 'E', ' ', ' ', ' ', 0 };
static uint8_t tx_data_fifo[ BEE_DATA_LENGHT + BEE_HEADER_LENGHT + 2 ] = { 0 };
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
bee_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
bee_cfg_setup( &cfg );
BEE_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
bee_init( &bee, &cfg );
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 2; cnt++ )
{
short_address1[ cnt ] = 1;
short_address2[ cnt ] = 2;
pan_id1[ cnt ] = 3;
pan_id2[ cnt ] = 3;
}
for ( uint8_t cnt = 0; cnt < 8; cnt++ )
{
long_address1[ cnt ] = 1;
long_address2[ cnt ] = 2;
}
log_printf( &logger, " Reset and WakeUp \r\n" );
bee_hw_reset( &bee );
bee_soft_reset( &bee );
bee_rf_reset( &bee );
bee_enable_immediate_wake_up( &bee );
#ifdef DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
// Transmitter mode
log_printf( &logger, " Application Mode: Transmitter\r\n" );
tx_data_fifo[0] = BEE_HEADER_LENGHT;
tx_data_fifo[1] = BEE_HEADER_LENGHT + BEE_DATA_LENGHT;
tx_data_fifo[2] = 0x01; // control frame
tx_data_fifo[3] = 0x88;
tx_data_fifo[4] = 0x23; // sequence number
tx_data_fifo[5] = pan_id2[1]; // destinatoin pan
tx_data_fifo[6] = pan_id2[0];
tx_data_fifo[7] = short_address2[0]; // destination address
tx_data_fifo[8] = short_address2[1];
tx_data_fifo[9] = pan_id1[0]; // source pan
tx_data_fifo[10] = pan_id1[1];
tx_data_fifo[11] = short_address1[0]; // source address
tx_data_fifo[12] = short_address1[1];
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx1[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
log_printf( &logger, " Set address and PAN ID \r\n" );
bee_set_long_address( &bee, &long_address1 );
bee_set_short_address( &bee, &short_address1 );
bee_set_pan_id( &bee, &pan_id1 );
#else
log_printf( &logger, " Application Mode: Receiver\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " Set address and PAN ID \r\n" );
bee_set_long_address( &bee, &long_address2 );
bee_set_short_address( &bee, &short_address2 );
bee_set_pan_id( &bee, &pan_id2 );
#endif
log_printf( &logger, " Init ZigBee module: \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set nonbeacon-enabled \r\n" );
bee_nonbeacon_init( &bee );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set as PAN coordinator\r\n" );
bee_nonbeacon_pan_coordinator_device( &bee );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set max TX power\r\n" );
bee_set_tx_power( &bee, 31 );
log_printf( &logger, " - All frames 3, data frame\r\n" );
bee_set_frame_format_filter( &bee, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Set normal mode\r\n" );
bee_set_reception_mode( &bee, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - Device Wake Up\r\n" );
bee_hw_wake_up( &bee );
bee_read_byte_short( &bee, BEE_INTSTAT ); // clears status register
Delay_1sec( );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
#ifdef DEMO_APP_TRANSMITTER
// Transmitter mode
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx1[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT);
bee_write_tx_normal_fifo( &bee, 0, &tx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " - Sent data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", data_tx1 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
memcpy( &tx_data_fifo[ 13 ], &data_tx2[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
bee_write_tx_normal_fifo( &bee, 0, &tx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
log_printf( &logger, " - Sent data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", data_tx2 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#else
// Receiver mode
bee_read_rx_fifo( &bee, &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ] );
if ( memcmp( &rx_data_fifo_old[ 0 ], &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT ) )
{
memcpy( &rx_data_fifo_old [ 0 ], &rx_data_fifo[ 0 ], BEE_DATA_LENGHT );
log_printf( &logger, " - Received data : " );
log_printf( &logger, "%.6s \r\n", rx_data_fifo );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
Delay_ms ( 500 );
#endif
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:ZigBee