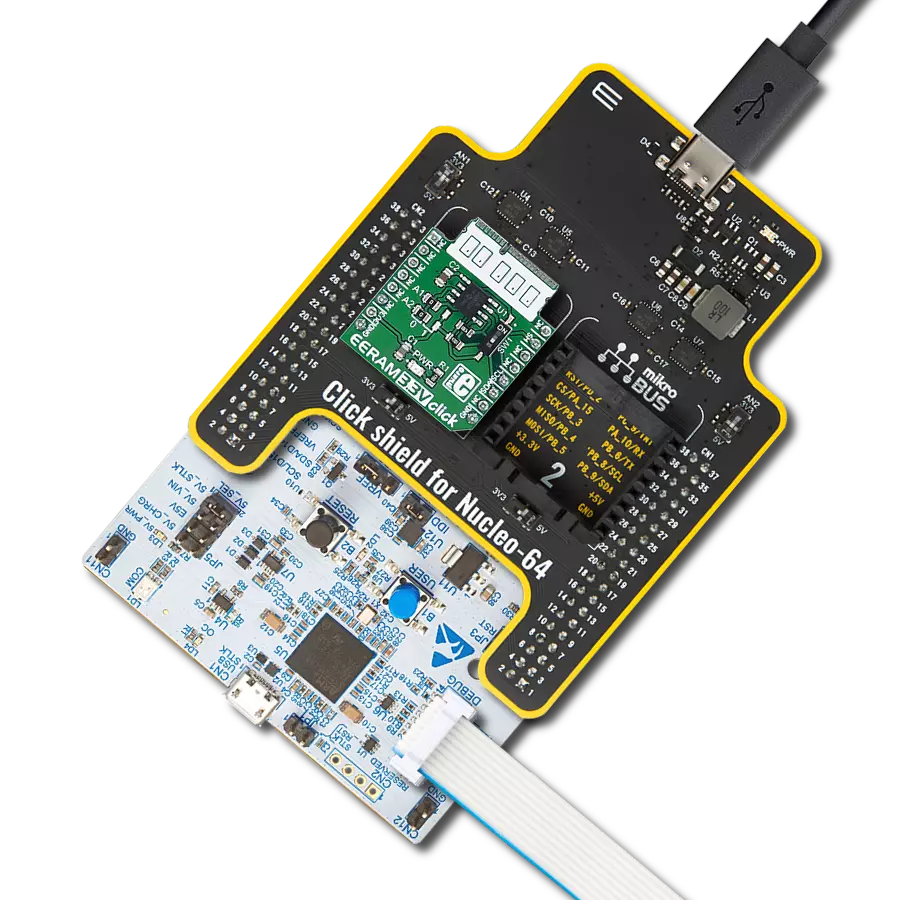
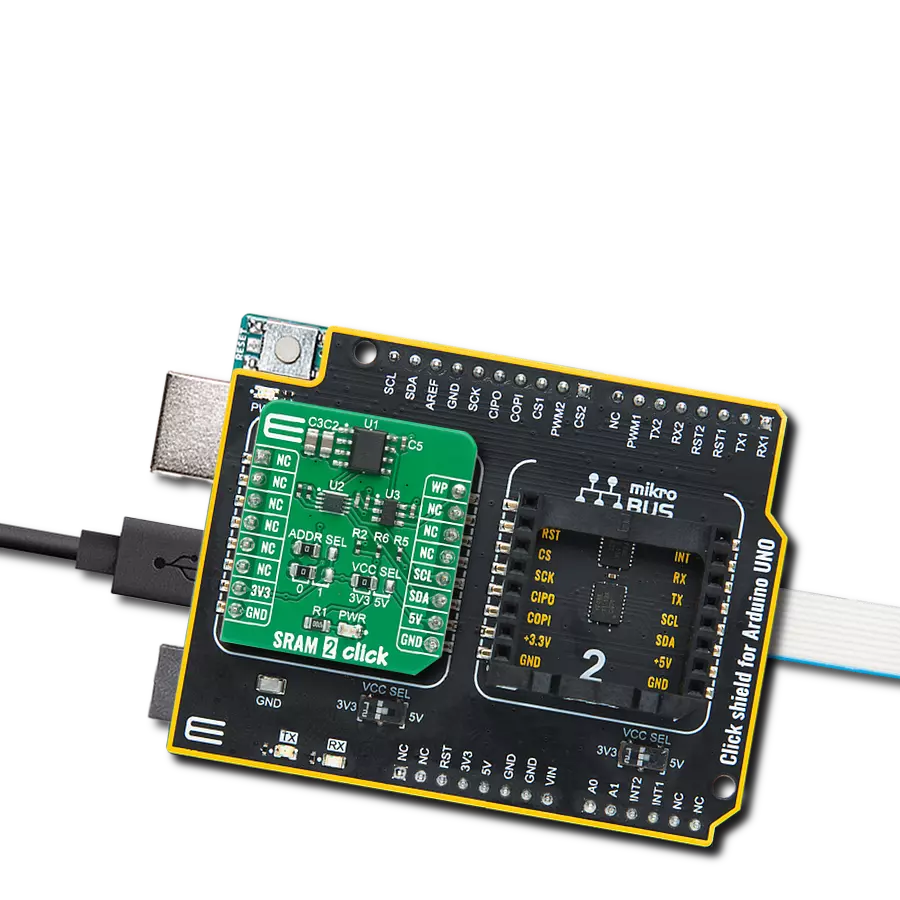
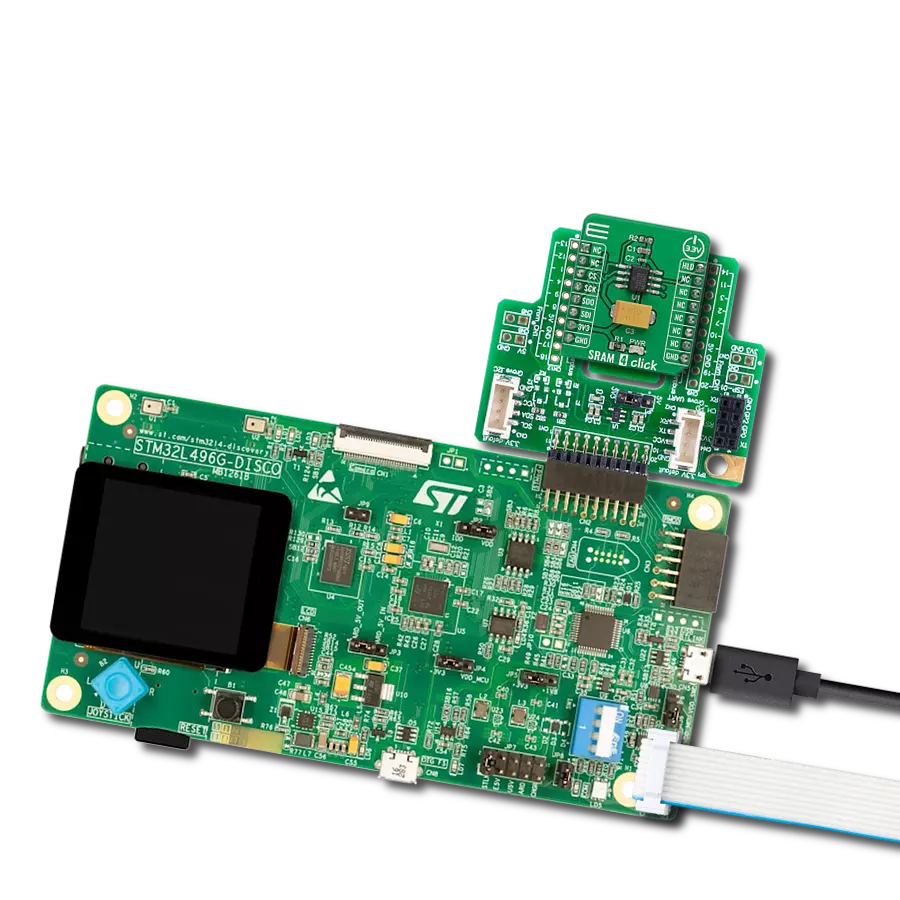
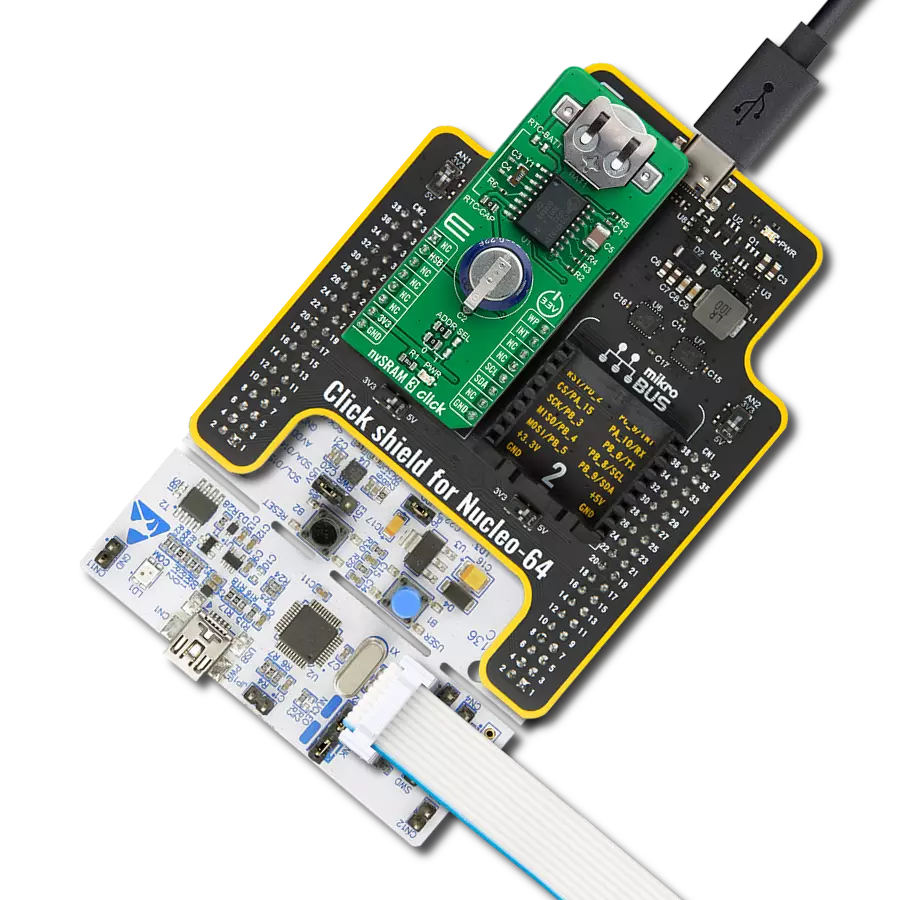
SRAM's combination of speed and power efficiency makes it an essential component in the world of modern electronics
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
SRAM 4 Click is based on the CY14B512Q, a 512Kbit nvSRAM memory organized as 64K words of 8 bits each from Infineon. The nvSRAM specifies one million endurance cycles for nonvolatile cells with data retention of a minimum of 20 years. All the reads and writes to nvSRAM happen to the SRAM, which gives nvSRAM the unique capability to handle infinite writes to the memory. The embedded nonvolatile elements incorporate the QuantumTrap technology, making this Click board™ an ideal choice for secure data storage, creating the world’s most reliable nonvolatile memory. The CY14B512Q communicates with MCU through a standard SPI interface that enables very high clock speeds up to 40MHz with zero cycle
delay read and write cycles. It also supports the two most common modes, SPI Mode 0 and 3, and 104 MHz SPI access speed with special instructions for the read operation. Besides, the SRAM 4 Click also has an additional HOLD signal, routed to the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™ socket labeled as HLD, used to suspend the serial communication without resetting the serial sequence. The CY14B512Q uses the standard SPI opcodes for memory access. In addition to the general SPI instructions for reading and writing, also provide four special instructions: STORE, RECALL, AutoStore Disable, and AutoStore Enable. The significant benefit of this memory over serial EEPROMs is that all reads and writes to nvSRAM
are performed at the speed of the SPI bus with zero cycle delay. Therefore, no wait time is required after any of the memory accesses. Only the STORE and RECALL operations need finite time to complete, and all memory accesses are inhibited during this time. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 4 for STM32F4 is a compact development board designed as a complete solution that you can use to quickly build your own gadgets with unique functionalities. Featuring an STM32F407VGT6 MCU, four mikroBUS™ sockets for Click boards™ connectivity, power management, and more, it represents a perfect solution for the rapid development of many different types of applications. At its core is an STM32F407VGT6 MCU, a powerful microcontroller by STMicroelectronics based on the high-performance
Arm® Cortex®-M4 32-bit processor core operating at up to 168 MHz frequency. It provides sufficient processing power for the most demanding tasks, allowing Clicker 4 to adapt to any specific application requirements. Besides two 1x20 pin headers, four improved mikroBUS™ sockets represent the most distinctive connectivity feature, allowing access to a huge base of Click boards™, growing on a daily basis. Each section of Clicker 4 is clearly marked, offering an intuitive and clean interface. This makes working with the
development board much simpler and, thus, faster. The usability of Clicker 4 doesn’t end with its ability to accelerate the prototyping and application development stages: it is designed as a complete solution that can be implemented directly into any project, with no additional hardware modifications required. Four mounting holes [4.2mm/0.165”] at all four corners allow simple installation by using mounting screws.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
10
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
100
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for SRAM 4 Click driver.
Key functions:
sram4_memory_read- Read data from memory.sram4_memory_write- Write data to memory.sram4_generic_command- Command writing function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief SRAM4 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example application showcases ability of device
* ability to manipulate with memory( writing and reading data ).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of communication modules(SPI, UART) and additional
* pins. Reads ID and checks if it matches with SRAM4_DEVICE_ID to
* check communication. Then clears protection from memory access.
*
* ## Application Task
* Writes 3 times to memory with length of data offset in memory address.
* Then reads 2 times first 2 data written should be read in one read,
* and 3rd write should be read separately.
*
* @author Luka FIlipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "sram4.h"
static sram4_t sram4;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
sram4_cfg_t sram4_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
sram4_cfg_setup( &sram4_cfg );
SRAM4_MAP_MIKROBUS( sram4_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = sram4_init( &sram4, &sram4_cfg );
if ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == init_flag )
{
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( sram4_default_cfg ( &sram4 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
char read_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
char click_name[ ] = "SRAM 4";
char company_name[ ] = "MikroE";
char product_name[ ] = " Click board";
static const uint16_t START_ADR = 0x0001;
uint16_t mem_adr = START_ADR;
//Write Data
sram4_memory_write( &sram4, mem_adr, click_name, strlen( click_name ) );
mem_adr += strlen( click_name );
sram4_memory_write( &sram4, mem_adr, product_name, strlen( product_name ) );
mem_adr += strlen( product_name );
sram4_memory_write( &sram4, mem_adr, company_name, strlen( company_name ) );
//Read Data
mem_adr = START_ADR;
sram4_memory_read( &sram4, mem_adr, read_buf, strlen( click_name ) + strlen( product_name ) );
log_printf( &logger, " > Read Data from 0x%.4X memory address: %s\r\n", mem_adr, read_buf );
memset( read_buf, 0, strlen( read_buf ) );
mem_adr += strlen(click_name) + strlen( product_name );
sram4_memory_read( &sram4, mem_adr, read_buf, strlen( company_name ) );
log_printf( &logger, " > Read Data from 0x%.4X memory address: %s\r\n", mem_adr, read_buf );
log_printf( &logger, "**********************************************************************\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:SRAM