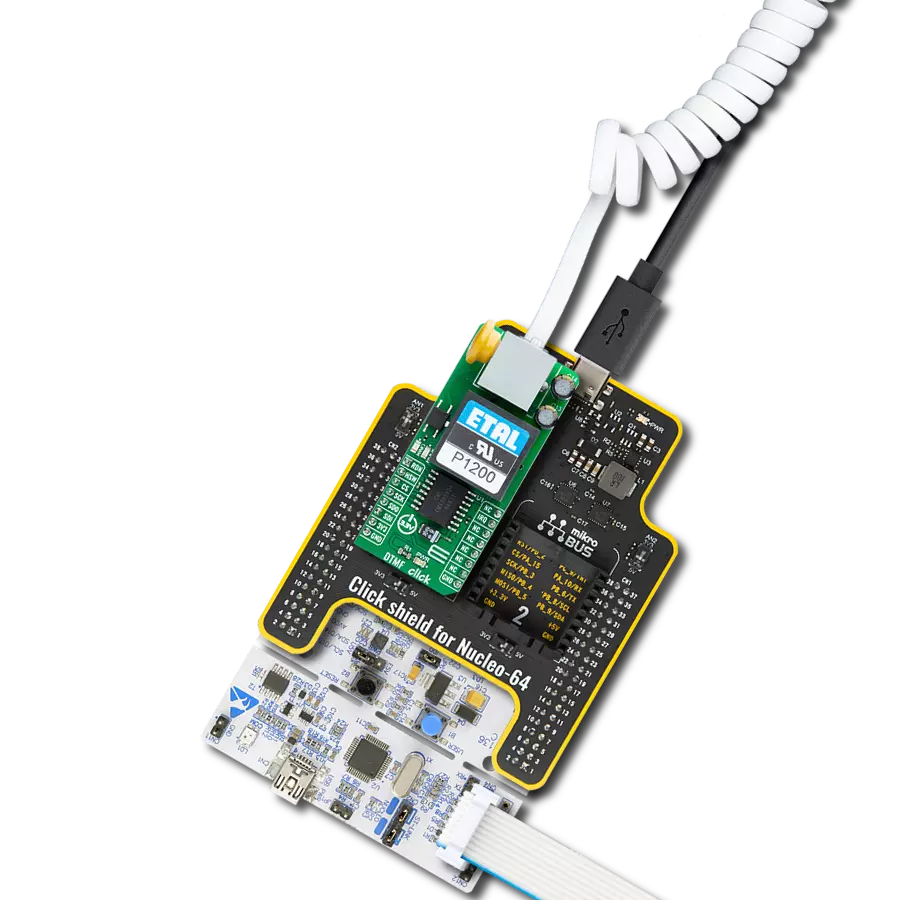
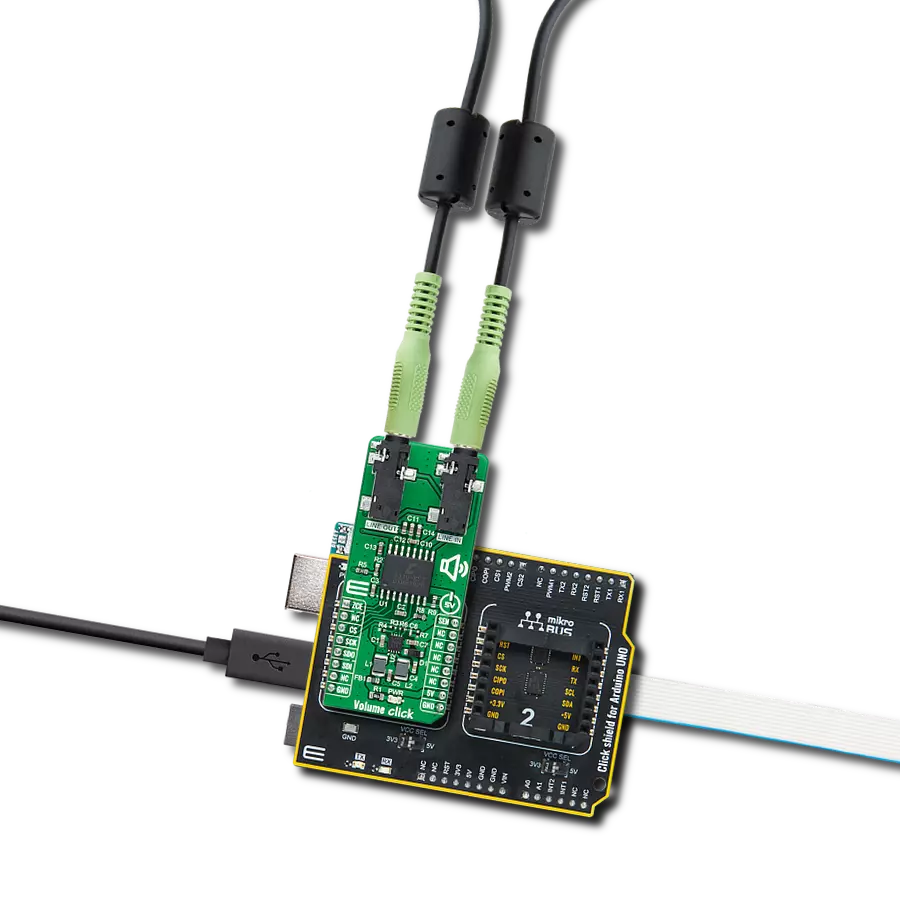
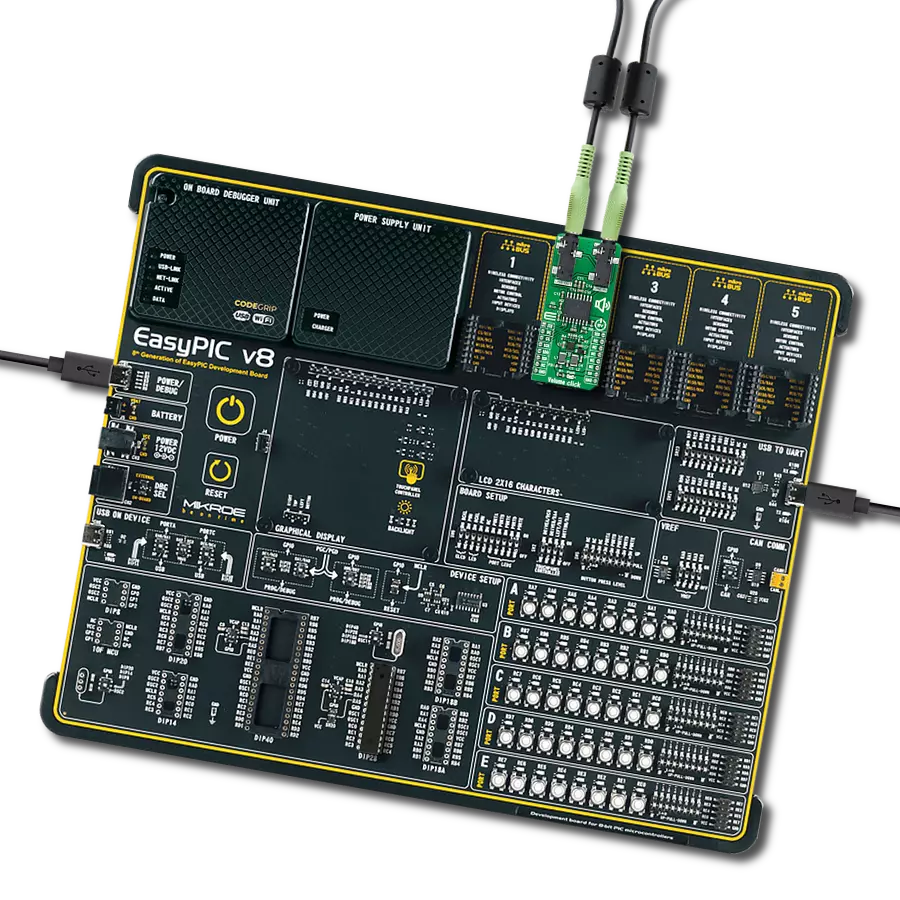
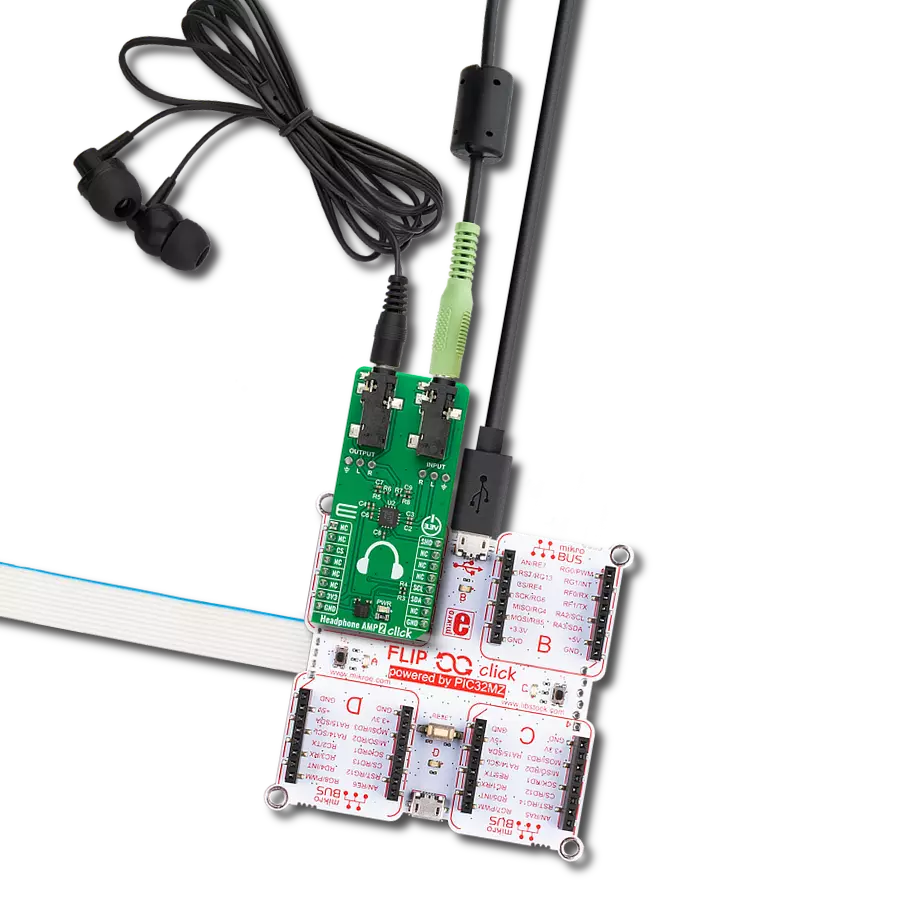
Our stereo digital volume control device is designed to give you unparalleled control over your audio, allowing you to fine-tune your sound to perfection
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Volume Click is based on the CS3310, a complete stereo digital volume control designed specifically for audio systems from Cirrus Logic. It features a 16-bit serial interface that controls two independent, low-distortion audio channels. The left and right levels of the analog input channels are set by a 16-bit serial data word (the first 8 bits address the right while the remaining 8 bits address the left channel). The CS3310 includes an array of well-matched resistors and a low-noise active output stage capable of driving a 600Ω load. A total adjustable range of 127dB, in 0.5dB steps, is achieved through 95.5dB of attenuation and 31.5dB of gain. The digital section power supply of the Volume Click is achieved through a 5V pin from a mikroBUS™ socket while the device itself is powered by ±5V from the LT3032, a dual 150mA positive and negative low noise low dropout linear
regulator with micropower quiescent current from Analog Devices. Volume Click communicates with MCU using the standard SPI serial interface with two additional GPIO pins that accept 16-bit data and enable users to read the current volume setting. Those two GPIO pins brought with this Click board™ are used for Zero Crossing Enable and Hardware MUTE functions. Once in operation, the CS3310 can be brought to a muted state with the MUTE pin labeled as SEN routed on the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™ socket or by writing zeros to the volume control registers. A volume control change occurs after the CS pin latches the data in the volume control data register, and two zero crossings are detected. The zero-crossing enable pin, labeled as ZCE routed on the AN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, turns on or off the zero-crossing detection function and the 18ms
time-out circuit. If two zero crossings are not detected within 18ms of the change in the CS pin, the new volume setting is implemented. Upon initial application of power, the SEN pin of the CS3310 should be set to LOW to initiate a Power-Up sequence. This sequence sets the serial shift register and the volume control register to zero and performs an offset calibration. The device should remain muted until the supply voltages have settled to ensure accurate calibration. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 5V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
PIC18F57Q43 Curiosity Nano evaluation kit is a cutting-edge hardware platform designed to evaluate microcontrollers within the PIC18-Q43 family. Central to its design is the inclusion of the powerful PIC18F57Q43 microcontroller (MCU), offering advanced functionalities and robust performance. Key features of this evaluation kit include a yellow user LED and a responsive
mechanical user switch, providing seamless interaction and testing. The provision for a 32.768kHz crystal footprint ensures precision timing capabilities. With an onboard debugger boasting a green power and status LED, programming and debugging become intuitive and efficient. Further enhancing its utility is the Virtual serial port (CDC) and a debug GPIO channel (DGI
GPIO), offering extensive connectivity options. Powered via USB, this kit boasts an adjustable target voltage feature facilitated by the MIC5353 LDO regulator, ensuring stable operation with an output voltage ranging from 1.8V to 5.1V, with a maximum output current of 500mA, subject to ambient temperature and voltage constraints.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
48
RAM (Bytes)
8196
You complete me!
Accessories
Curiosity Nano Base for Click boards is a versatile hardware extension platform created to streamline the integration between Curiosity Nano kits and extension boards, tailored explicitly for the mikroBUS™-standardized Click boards and Xplained Pro extension boards. This innovative base board (shield) offers seamless connectivity and expansion possibilities, simplifying experimentation and development. Key features include USB power compatibility from the Curiosity Nano kit, alongside an alternative external power input option for enhanced flexibility. The onboard Li-Ion/LiPo charger and management circuit ensure smooth operation for battery-powered applications, simplifying usage and management. Moreover, the base incorporates a fixed 3.3V PSU dedicated to target and mikroBUS™ power rails, alongside a fixed 5.0V boost converter catering to 5V power rails of mikroBUS™ sockets, providing stable power delivery for various connected devices.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Volume Click driver.
Key functions:
volume_set_vol_gain- Set volume gain functionvolume_power_up- Power Up functionvolume_hw_mute- Hardware MUTE function
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Volume Click example
*
* # Description
* This example sets up the device and performs volume turn up and down.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes drivers and powers up the device.
*
* ## Application Task
* Circles the volume from -40 [dB] to 10 [dB] back and forth.
*
* @author Stefan Nikolic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "volume.h"
float left_speaker_gain;
float right_speaker_gain;
uint8_t one_circle;
static volume_t volume;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void ) {
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
volume_cfg_t volume_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
volume_cfg_setup( &volume_cfg );
VOLUME_MAP_MIKROBUS( volume_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = volume_init( &volume, &volume_cfg );
if ( init_flag == SPI_MASTER_ERROR ) {
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
volume_default_cfg ( &volume );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void ) {
left_speaker_gain = -40;
right_speaker_gain = -40;
one_circle = 0;
log_printf( &logger, " Turning volume up.\r\n" );
while ( one_circle < 2 ) {
if ( one_circle == 0 ) {
if ( left_speaker_gain <= 10 || right_speaker_gain <= 10 ) {
volume_set_vol_gain( &volume, left_speaker_gain, right_speaker_gain );
left_speaker_gain += 0.5;
right_speaker_gain += 0.5;
Delay_ms ( 50 );
} else {
one_circle++;
log_printf( &logger, " Turning volume down.\r\n" );
}
} else if ( left_speaker_gain >= -40 || right_speaker_gain >= -40 ) {
volume_set_vol_gain( &volume, left_speaker_gain, right_speaker_gain );
left_speaker_gain -= 0.5;
right_speaker_gain -= 0.5;
Delay_ms ( 50 );
} else one_circle++;
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Signal Processing