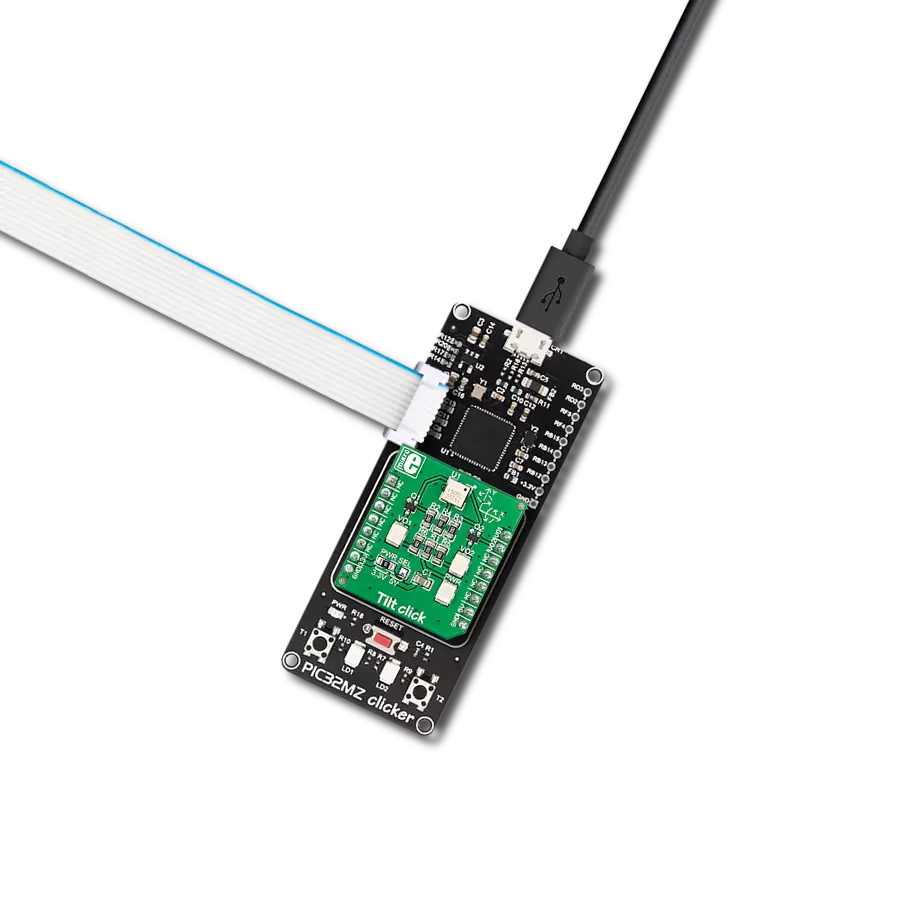
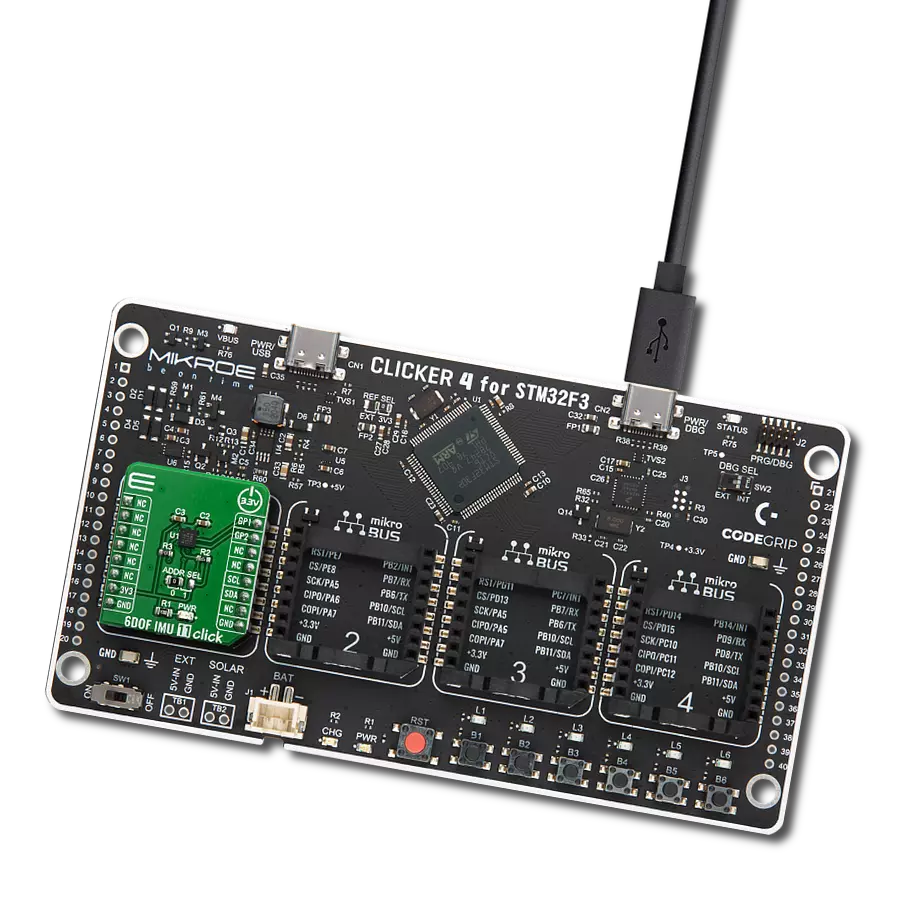
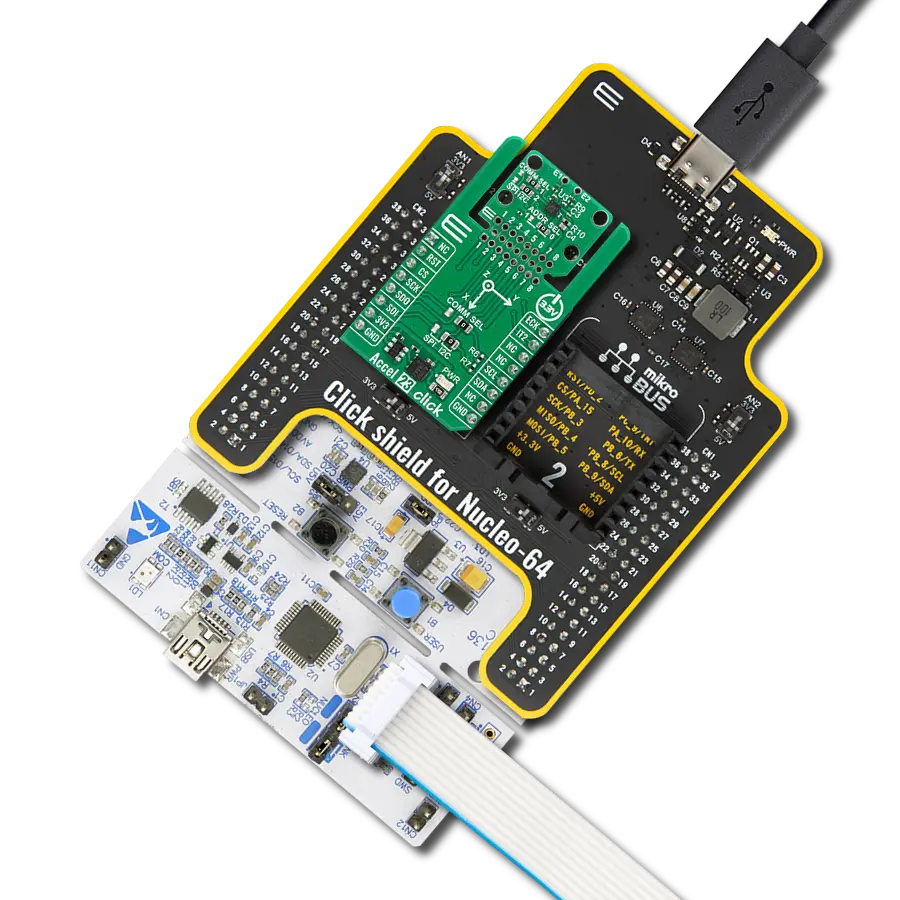
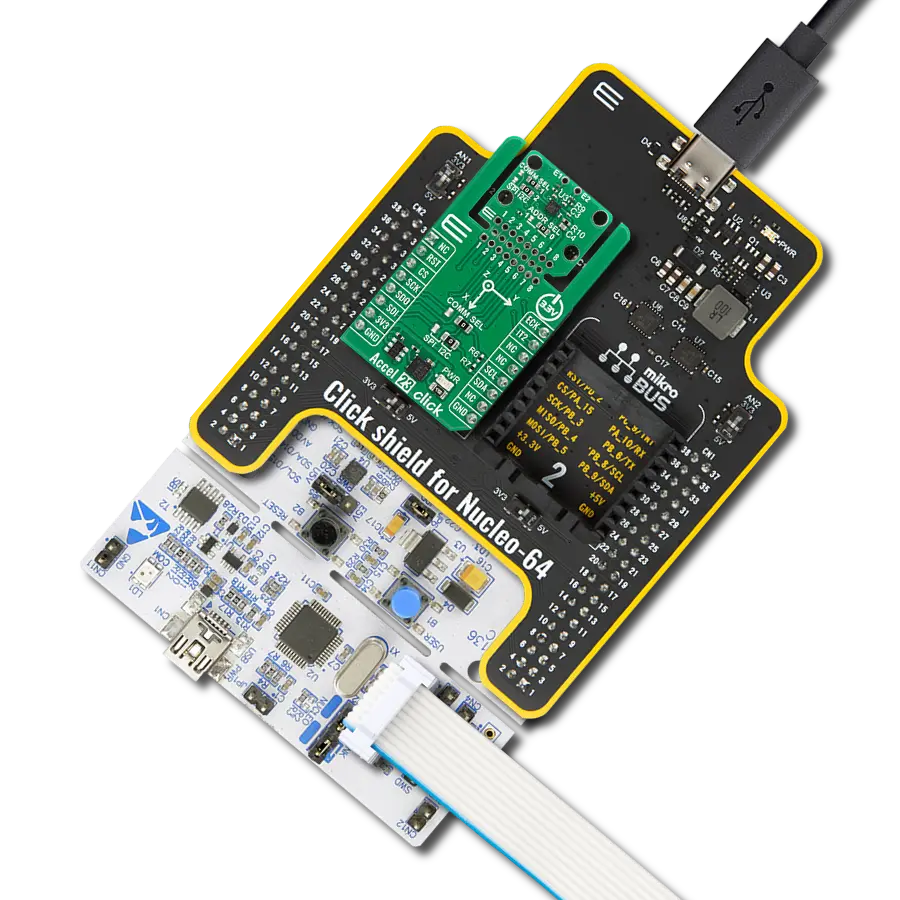
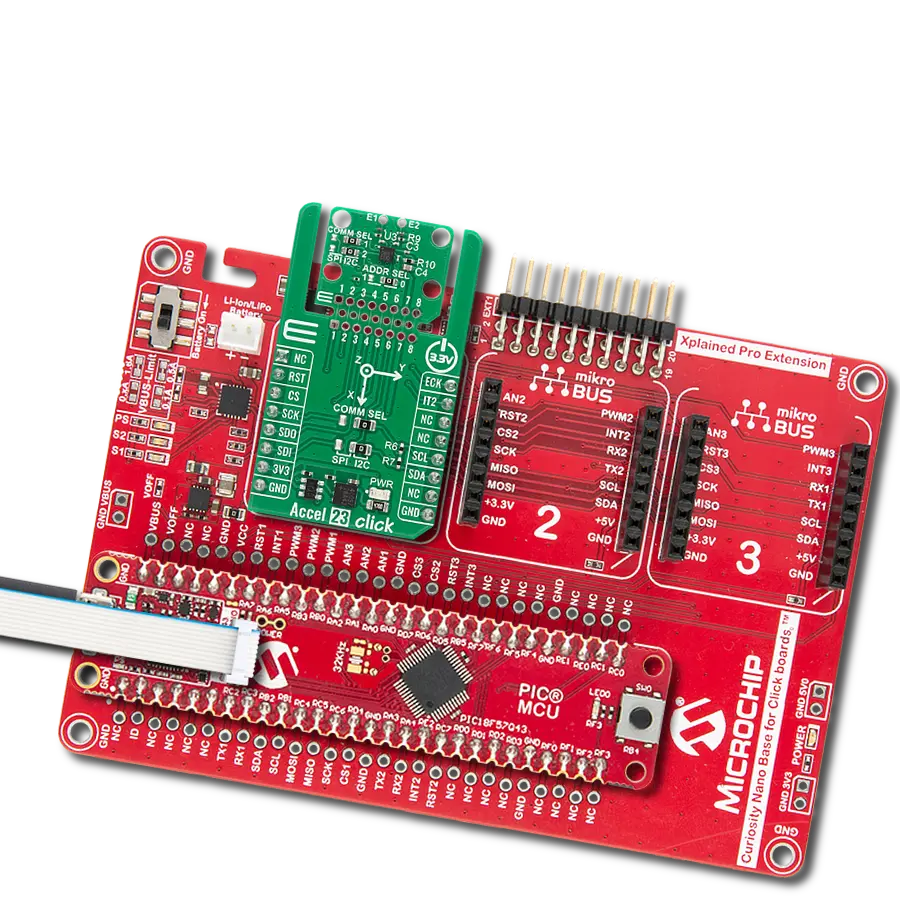
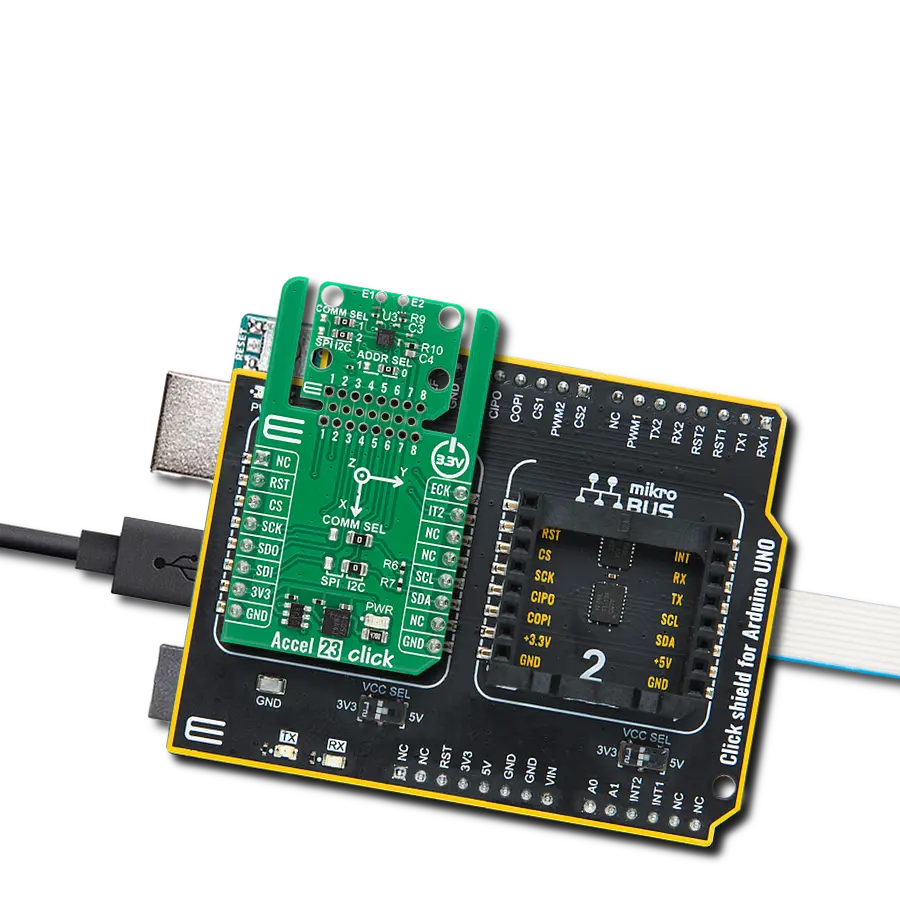
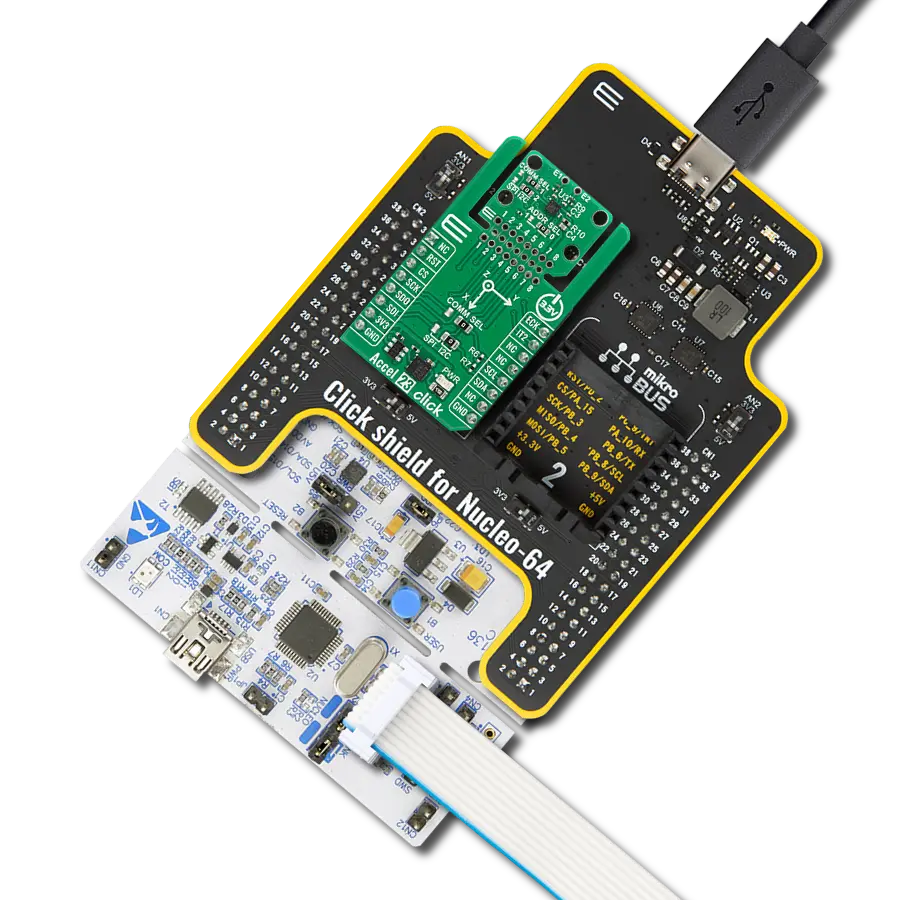
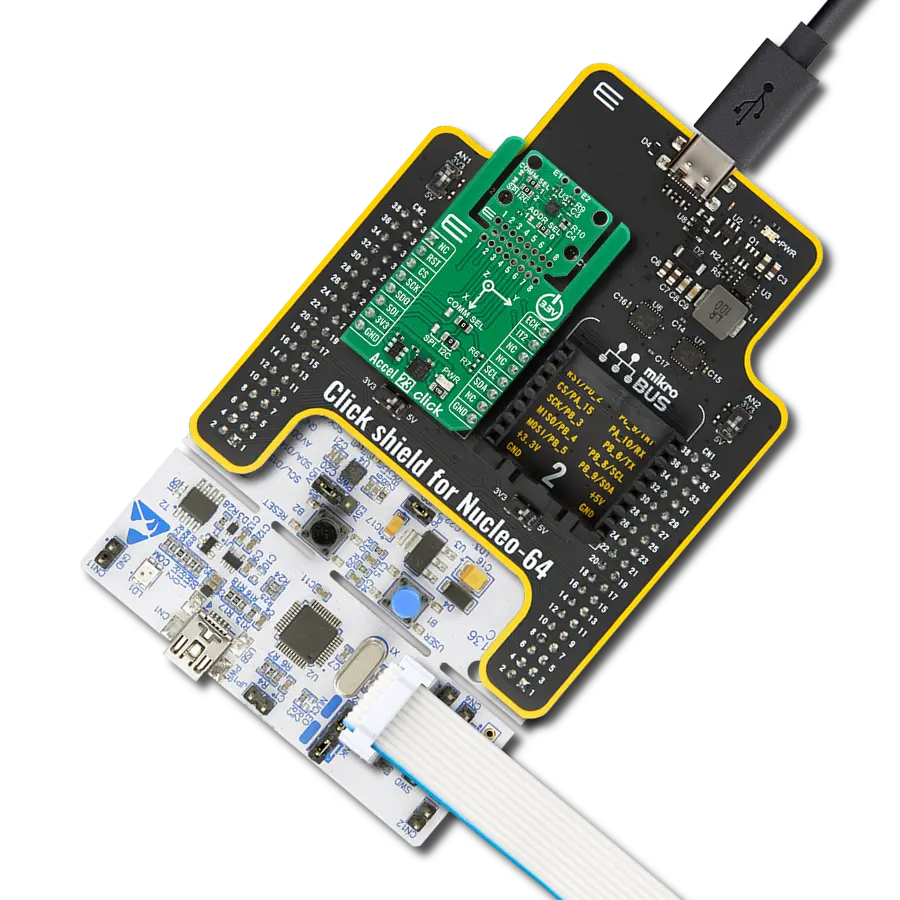
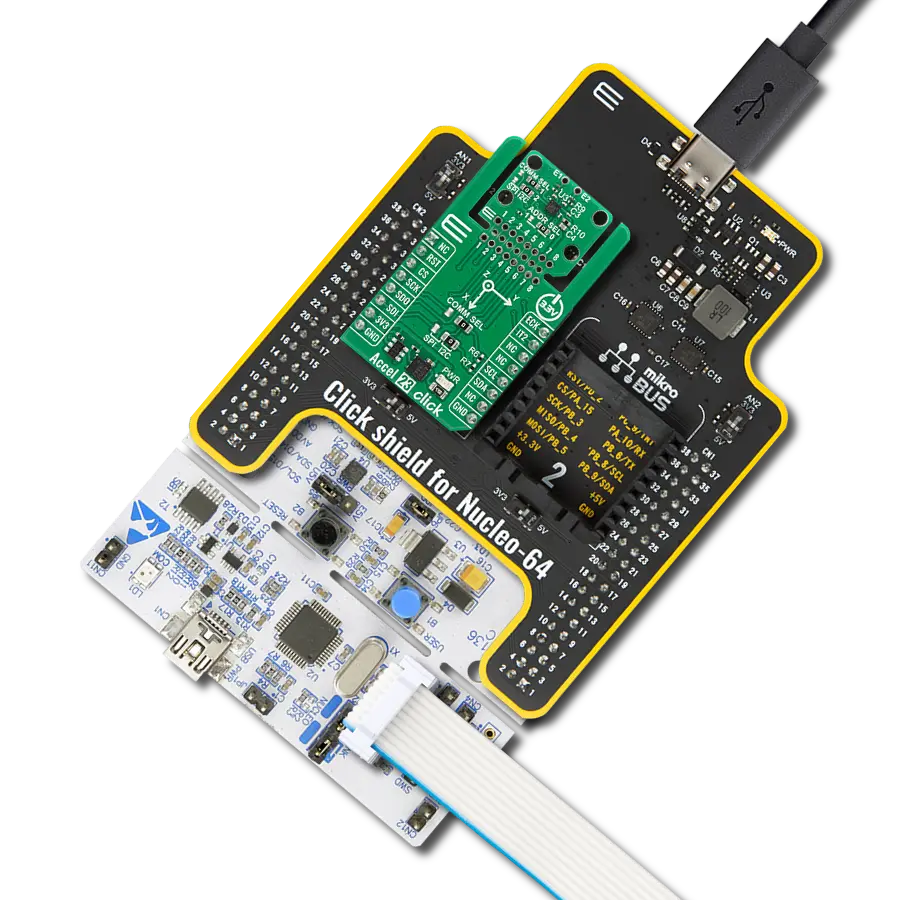
Enhance your projects with accurate motion detection, capturing its speed and direction with precision
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
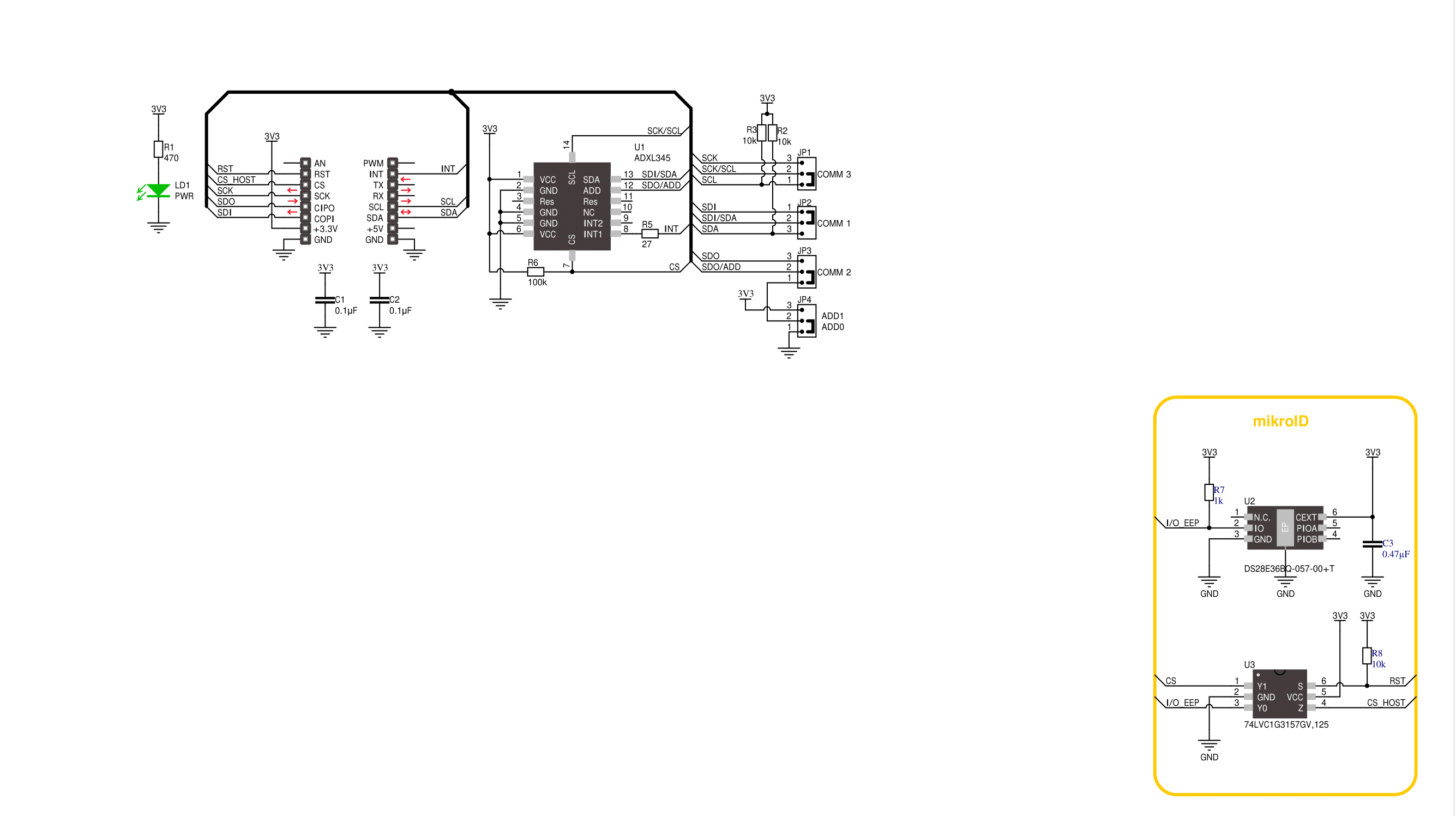
Accel Click is based on the ADXL345, a complete 3-axis acceleration measurement system that operates at low power consumption levels from Analog Devices. It measures both dynamic accelerations, resulting from motion or shock, and static acceleration, such as gravity, and allows selectable full-scale acceleration measurements in ranges of ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, or ±16g with a resolution of 4mg/LSB on the ±2g range. Acceleration is reported digitally, communicating via the SPI or the I2C protocol and providing 16-bit output resolution. Its high resolution also enables the measurement of inclination changes less than 1.0°. The ADXL345 supports several special sensing functions. Activity and inactivity sensing detect the presence or lack
of motion by comparing the acceleration on any axis with user-set thresholds, while tap sensing detects single and double taps in any direction. Besides, a free-fall sensing feature detects if the device is falling. All these functions can be mapped to the interrupt pin routed on the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. Accel Click allows the use of both I2C and SPI interfaces. The selection can be made by positioning SMD jumpers labeled as COMM SEL in an appropriate position. Note that all the jumpers' positions must be on the same side, or the Click board™ may become unresponsive. While the I2C interface is selected, the ADXL345 allows choosing the least significant bit (LSB) of its I2C slave address using the SMD jumper labeled ADDR
SEL. An integrated memory management system with a 32-level first in, first out (FIFO) buffer can store data to minimize host processor activity and lower overall system power consumption. Low power modes enable intelligent motion-based power management with threshold sensing and active acceleration measurement at low power dissipation. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
PIC18F47K42 Curiosity Nano evaluation kit is a cutting-edge hardware platform designed to evaluate the PIC18F47K42 microcontroller (MCU). Central to its design is the inclusion of the powerful PIC18F47K42 microcontroller (MCU), offering advanced functionalities and robust performance. Key features of this evaluation kit include a yellow user LED and a responsive mechanical user switch
providing seamless interaction and testing. The provision for a 32.768kHz crystal footprint ensures precision timing capabilities. With an onboard debugger boasting a green power and status LED, programming and debugging become intuitive and efficient. Further enhancing its utility is the Virtual serial port (CDC) and a debug GPIO channel (DGI GPIO), offering extensive connectivity options.
Powered via USB, this kit boasts an adjustable target voltage feature facilitated by the MIC5353 LDO regulator, ensuring stable operation with an output voltage ranging from 2.3V to 5.1V (limited by USB input voltage), with a maximum output current of 500mA, subject to ambient temperature and voltage constraints.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
40
RAM (Bytes)
8192
You complete me!
Accessories
Curiosity Nano Base for Click boards is a versatile hardware extension platform created to streamline the integration between Curiosity Nano kits and extension boards, tailored explicitly for the mikroBUS™-standardized Click boards and Xplained Pro extension boards. This innovative base board (shield) offers seamless connectivity and expansion possibilities, simplifying experimentation and development. Key features include USB power compatibility from the Curiosity Nano kit, alongside an alternative external power input option for enhanced flexibility. The onboard Li-Ion/LiPo charger and management circuit ensure smooth operation for battery-powered applications, simplifying usage and management. Moreover, the base incorporates a fixed 3.3V PSU dedicated to target and mikroBUS™ power rails, alongside a fixed 5.0V boost converter catering to 5V power rails of mikroBUS™ sockets, providing stable power delivery for various connected devices.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Accel Click driver.
Key functions:
accel_read_x_axis- This function reads X axis value from Accelaccel_read_y_axis- This function reads Y axis value from Accelaccel_read_z_axis- This function reads Z axis value from Accel
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Accel Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Accel Click board by reading and
* displaying the accelerometer data (X, Y, and Z axis).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes SPI/I2C driver and settings data read format,
* power mode, FIFO control and baud rate ( 100Hz default ).
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads X, Y and Z axis and logs on usbuart every 100 ms.
*
* \author Jovan Stajkovic
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "accel.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static accel_t accel;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t tmp;
static int16_t val_x;
static int16_t val_y;
static int16_t val_z;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
accel_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
accel_cfg_setup( &cfg );
ACCEL_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
accel_init( &accel, &cfg );
accel_generic_read( &accel, ACCEL_REG_DEVID, &tmp, 1 );
if ( tmp == ACCEL_DEVID )
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Comunication OK!!! ----\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "---- Comunication ERROR!!! ----\r\n" );
for ( ; ; );
}
accel_default_cfg ( &accel );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
val_x = accel_read_x_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis X : %.3f g\r\n", val_x / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
val_y = accel_read_y_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis Y : %.3f g\r\n", val_y / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
val_z = accel_read_z_axis( &accel );
log_printf( &logger, "Axis Z : %.3f g\r\n", val_z / ACCEL_DATA_RES_LSB_PER_G );
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Motion