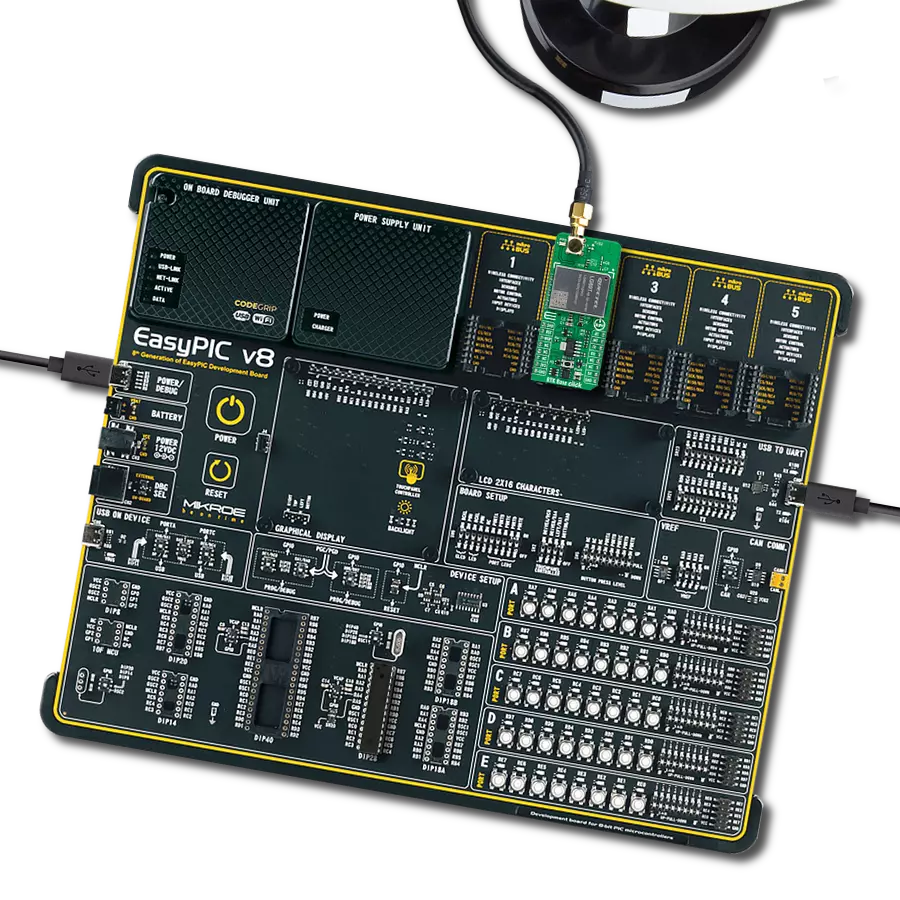
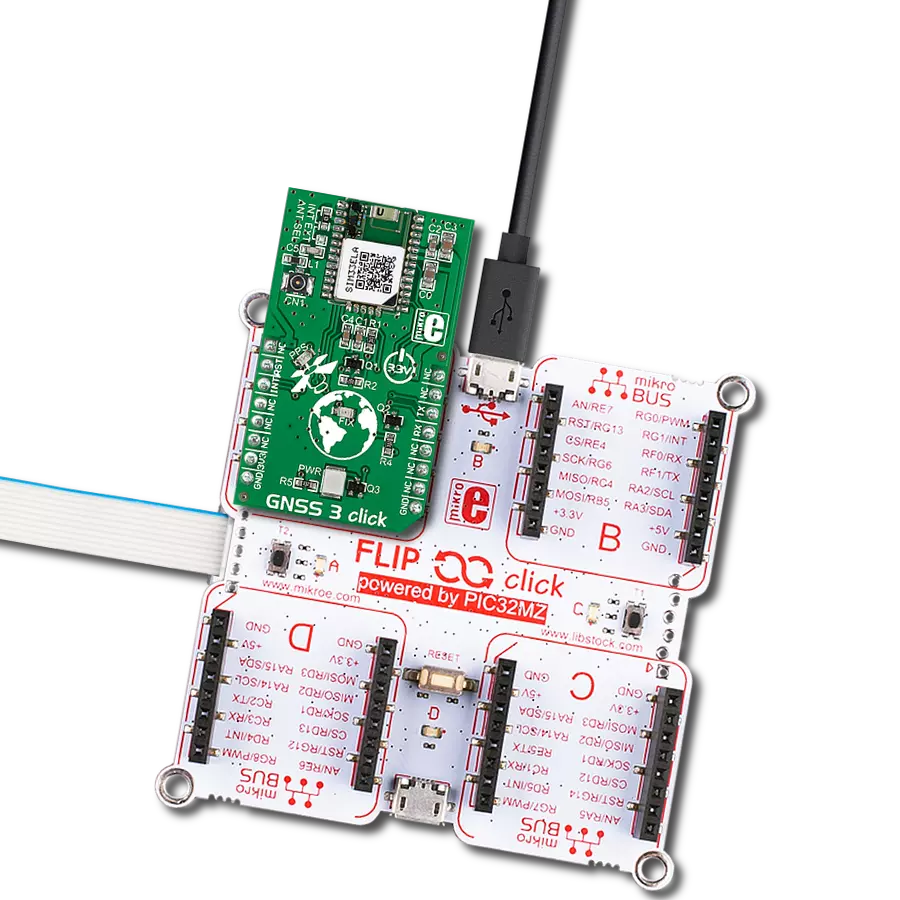
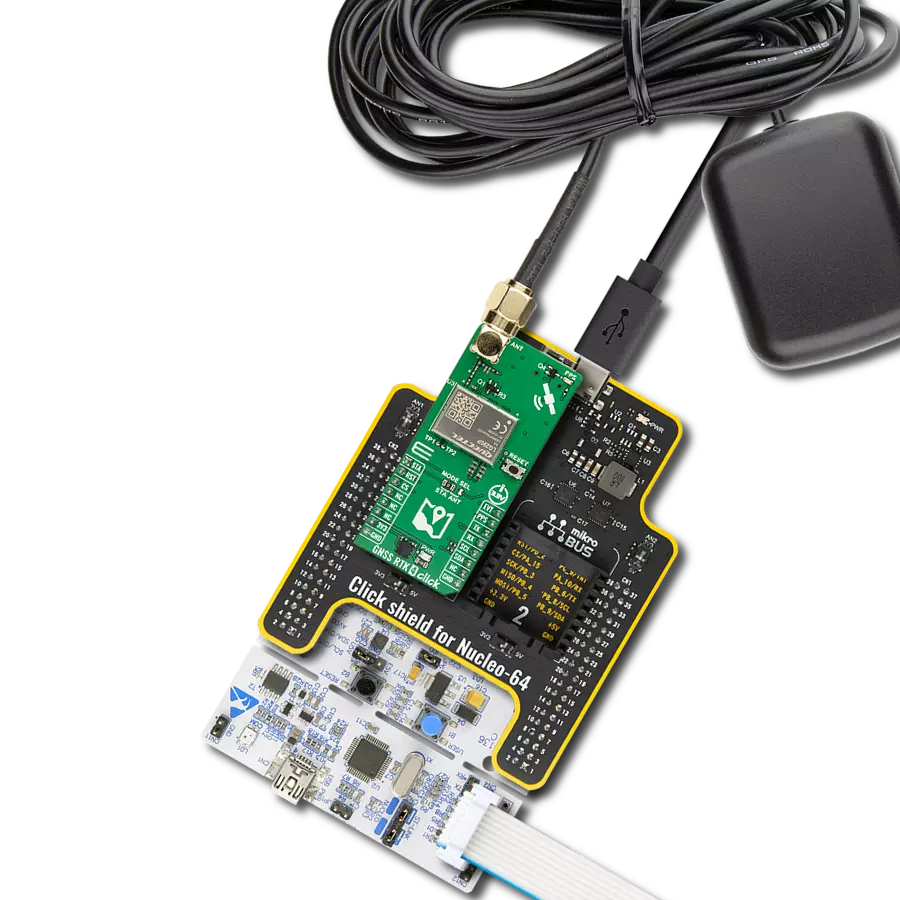
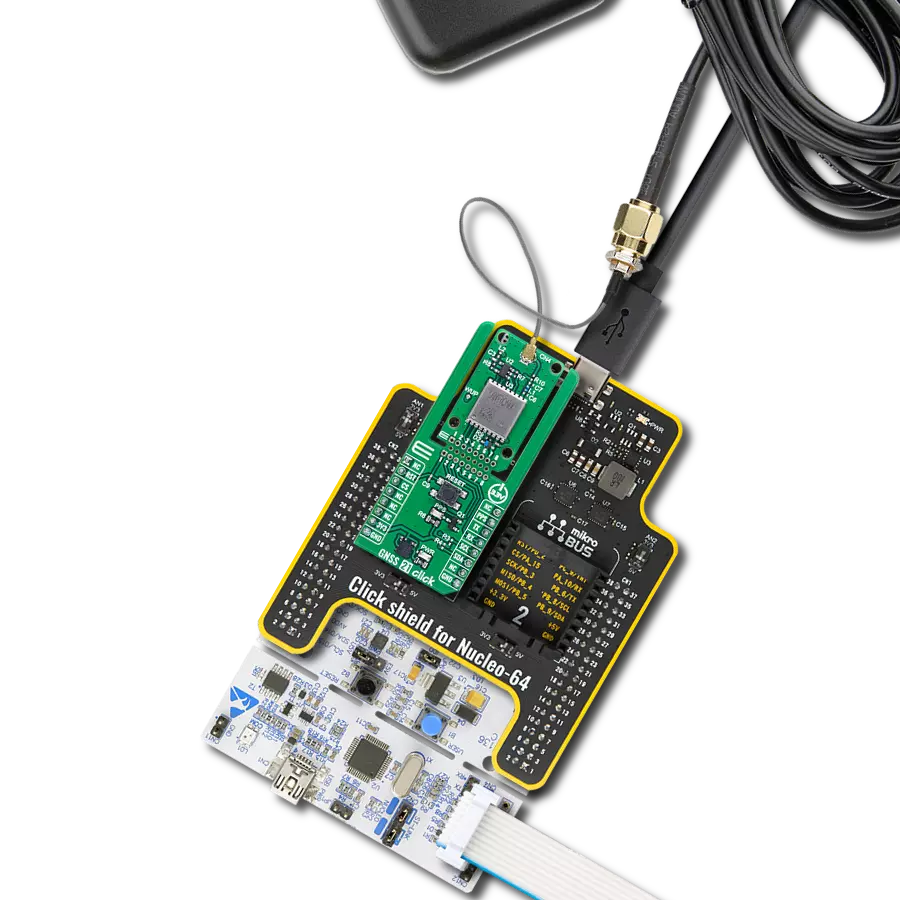
Experience the future of positioning with our GNSS RTK solution, where real-time kinematic capabilities meet cutting-edge innovation to deliver pinpoint accuracy.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
GNSS RTK 3 Click is based on the LC29H(DA/EA), a dual-band, multi-castellation GNSS module from Quectel. With internal LNA and SAW filters, the module achieves better sensitivity and anti-interference capability. Dual frequency support helps the module deliver CEP accuracy values of 1m in autonomous mode and centimeter levels while using the RTK functionality. Integrated RTK (Real-Time Kinetic) position engine provides a sub-meter accuracy with fast convergence time and outstanding performance. This module supports the RTK Rover technique. Before implementing the RTK navigation technique, the module must receive the RTK differential data via its UART port. After validating the differential correction data, the module will enter differential or RTK float mode. The expected accuracy at RTK fixed mode is lower than 20cm. The LC29H(DA/EA) module features an integrated AGNSS, integrated AIC, and jamming function and can receive L1 and L5 GNSS band signals concurrently. The receiver chip is built using 12nm technology and provides advanced power management, which enables low-power GNSS sensing and position fix, which in turn
makes the module ideal for power-sensitive and battery-powered systems. There is a DSEL switch with 0 and 1 positions. By setting it to a 0 position, the UART interface can be used for communication and downloading, while the I2C can only be used for communication. The 1 position sets UART for downloading only, while the I2C interface can be used for communication and downloading. The GNSS RTK 3 Click has an SMA antenna connector for connecting an appropriate antenna, also offered by MIKROE. You can also control the antenna by deactivating it in power-saving mode, lowering power consumption. To interface different voltage levels of the host MCU, GNSS RTK 3 Click is equipped with the TXS0108E, an 8-bit bi-directional level-shifting voltage translator from Texas Instruments. In case of a mains supply failure, the module can use a backup supply voltage from a connected battery. Backup voltage supplies the real-time clock and battery-backed RAM and saves all relevant data in the backup RAM to allow a hot or warm start later. If no battery is present, the backup is powered over the 3.3V rail of the mikroBUS™ socket. As
mentioned, the GNSS RTK 3 Click uses a standard 2-Wire UART interface to communicate with the host MCU with commonly used UART RX and TX pins. The UART 2 interface pins are exposed on a 1.8V DBG header for debugging purposes. The module supports baud rates 9600 up to 3Mbps, while the 115200bps is the default. Besides the UART interface, you can also use a standard 2-Wire I2C interface to communicate with the host MCU with a data rate of up to 400kbps. In both cases, the module will use the NMEA 0183/RTCM 3.x protocols. You can update the LC29H(DA/EA) firmware using any of those interfaces. Using the RST pin, you can reset the module or wake it up using the WUP pin. Besides the 1PPS LED, the one pulse per second can be monitored over the PPS pin. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
GNSS L1/L5 Active External Antenna (YB0017AA) is an active patch antenna from Quectel that supports GNSS L1/L5 BD B1/B2 GLONASS L1, offering excellent performance with its high gain and efficiency for fleet management, navigation, RTK, and many other tracking applications. The magnetic-mounting antenna, with dimensions of 61.5×56.5×23mm, is designed to work with various ground plane sizes or in free space and is connected to the device by a 3m cable with an SMA male connector.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
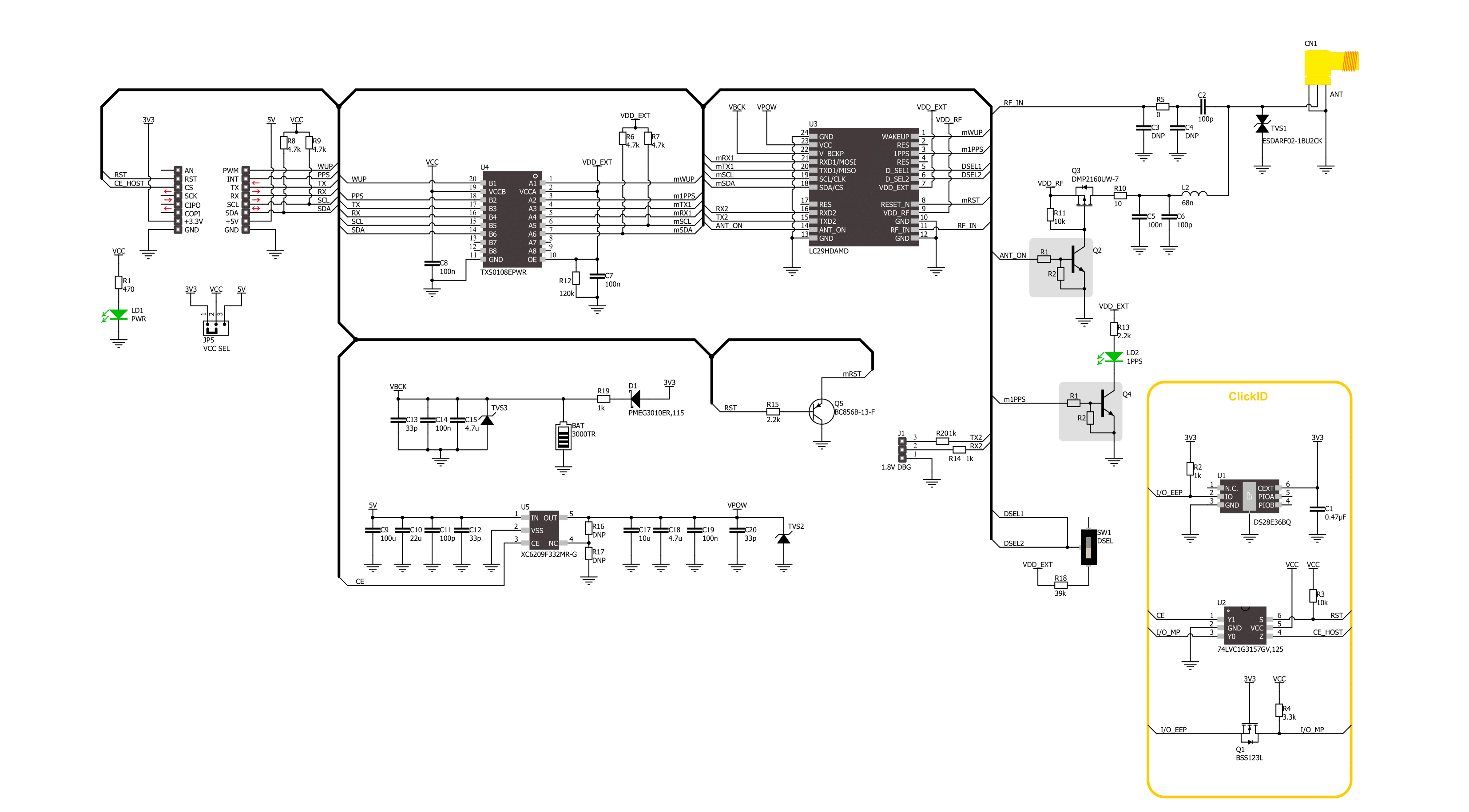
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for GNSS RTK 3 Click driver.
Key functions:
gnssrtk3_enable_device- This function enables the device by setting the CEN pin to high logic state.gnssrtk3_generic_read- This function reads a desired number of data bytes by using UART or I2C serial interface.gnssrtk3_parse_gga- This function parses the GGA data from the read response buffer.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief GNSS RTK 3 DA Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of GNSS RTK 3 DA Click by reading and displaying
* the GNSS coordinates.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and enables the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the received data, parses the NMEA GGA info from it, and once it receives
* the position fix it will start displaying the coordinates on the USB UART.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void gnssrtk3da_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static void gnssrtk3da_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gnssrtk3da_process ( gnssrtk3da_t *ctx )
* - static void gnssrtk3da_parser_application ( uint8_t *rsp )
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gnssrtk3da.h"
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 800
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 200
static gnssrtk3da_t gnssrtk3da;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static uint8_t i2c_data_ready = 0;
/**
* @brief GNSS RTK 3 DA clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length.
* @note None.
*/
static void gnssrtk3da_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief GNSS RTK 3 DA log application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer to USB UART.
* @note None.
*/
static void gnssrtk3da_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief GNSS RTK 3 DA data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #gnssrtk3da_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t gnssrtk3da_process ( gnssrtk3da_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief GNSS RTK 3 DA parser application.
* @param[in] rsp Response buffer.
* @details This function logs GNSS data on the USB UART.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void gnssrtk3da_parser_application ( uint8_t *rsp );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
gnssrtk3da_cfg_t gnssrtk3da_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
gnssrtk3da_cfg_setup( &gnssrtk3da_cfg );
GNSSRTK3DA_MAP_MIKROBUS( gnssrtk3da_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( GNSSRTK3DA_OK != gnssrtk3da_init( &gnssrtk3da, &gnssrtk3da_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
gnssrtk3da_enable_device ( &gnssrtk3da );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
if ( GNSSRTK3DA_OK == gnssrtk3da_process( &gnssrtk3da ) )
{
gnssrtk3da_parser_application( app_buf );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void gnssrtk3da_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static void gnssrtk3da_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t gnssrtk3da_process ( gnssrtk3da_t *ctx )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t overflow_bytes = 0;
int32_t rx_cnt = 0;
int32_t rx_size = 0;
if ( ( GNSSRTK3DA_DRV_SEL_I2C == ctx->drv_sel ) && ( !i2c_data_ready ) )
{
uint16_t pps_wait_log_cnt = 0;
while ( !gnssrtk3da_get_pps_pin ( ctx ) )
{
if ( ++pps_wait_log_cnt > 5000 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Waiting for the position fix (PPS signal)...\r\n\n" );
pps_wait_log_cnt = 0;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
i2c_data_ready = 1;
Delay_ms ( 200 );
}
rx_size = gnssrtk3da_generic_read( ctx, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( ( rx_size > 0 ) && ( rx_size <= APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) )
{
if ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
overflow_bytes = ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE;
app_buf_len = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - rx_size;
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ overflow_bytes ], app_buf_len );
memset ( &app_buf[ app_buf_len ], 0, overflow_bytes );
}
for ( rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ app_buf_len++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
}
}
return GNSSRTK3DA_OK;
}
return GNSSRTK3DA_ERROR;
}
static void gnssrtk3da_parser_application ( uint8_t *rsp )
{
uint8_t element_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
if ( GNSSRTK3DA_OK == gnssrtk3da_parse_gga( rsp, GNSSRTK3DA_GGA_LATITUDE, element_buf ) )
{
static uint8_t wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
if ( strlen( element_buf ) > 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Latitude: %.2s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 2 ] );
memset( element_buf, 0, sizeof( element_buf ) );
gnssrtk3da_parse_gga( rsp, GNSSRTK3DA_GGA_LONGITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Longitude: %.3s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 3 ] );
memset( element_buf, 0, sizeof( element_buf ) );
gnssrtk3da_parse_gga( rsp, GNSSRTK3DA_GGA_ALTITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Altitude: %s m \r\n", element_buf );
wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
}
else
{
if ( wait_for_fix_cnt % 5 == 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Waiting for the position fix...\r\n\n" );
wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
}
wait_for_fix_cnt++;
}
gnssrtk3da_clear_app_buf( );
i2c_data_ready = 0;
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:GPS/GNSS