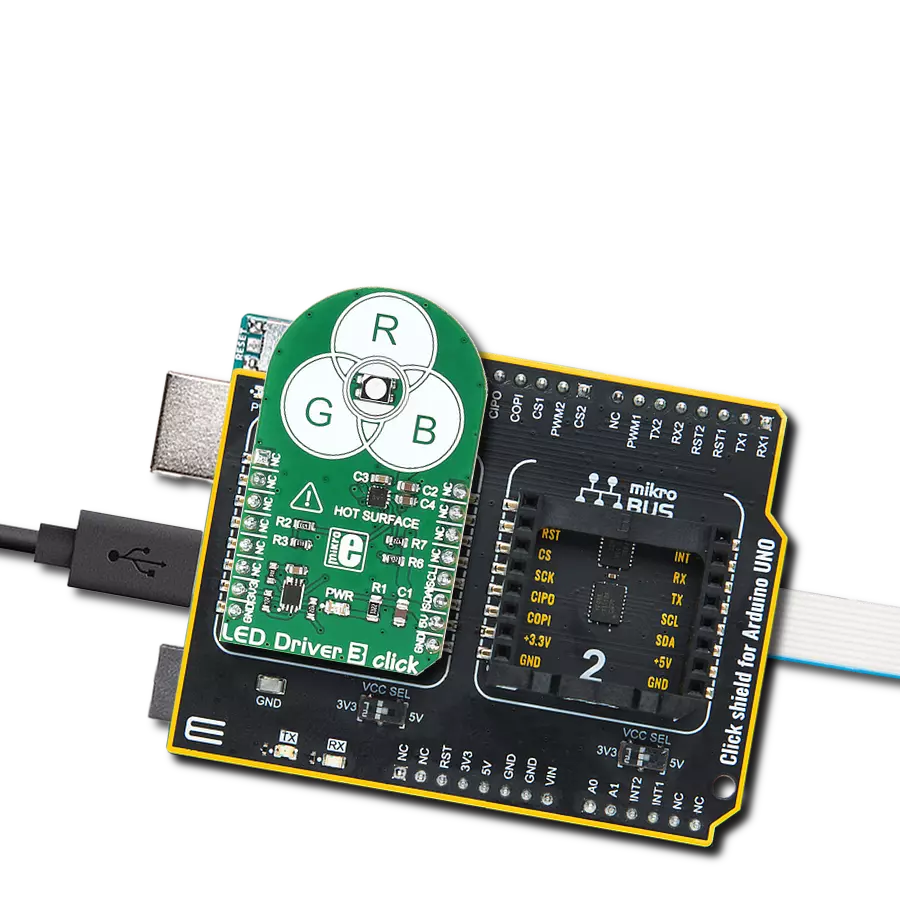
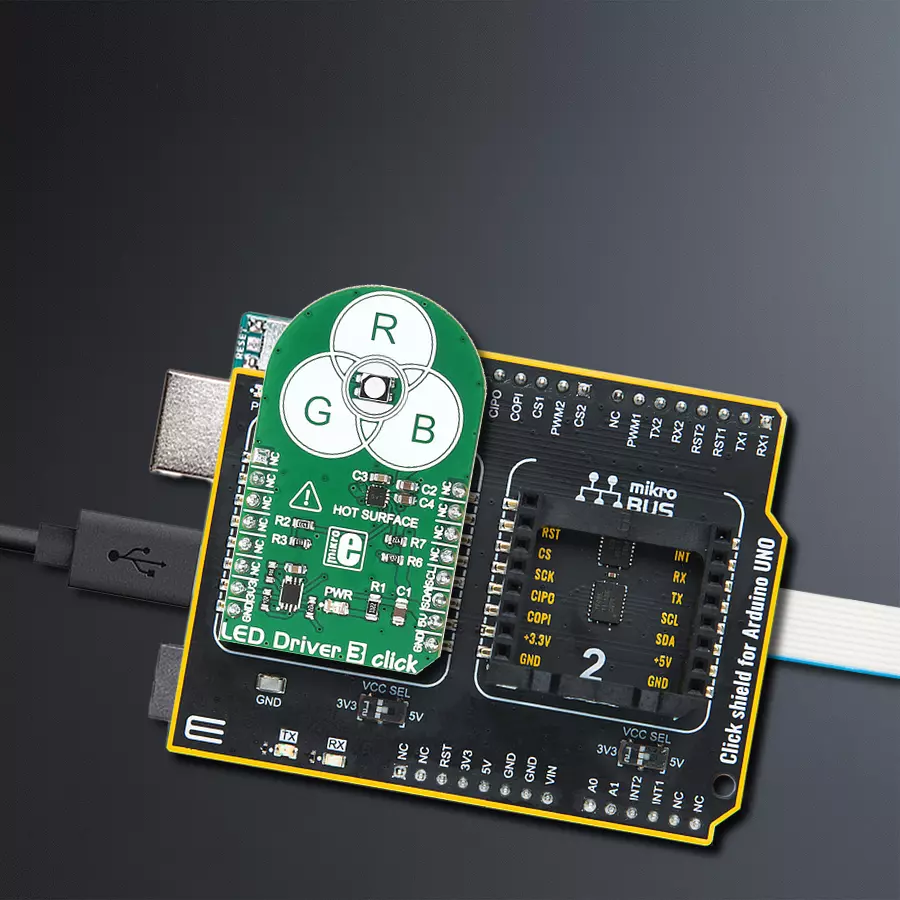
Enhance user experiences in your products with our RGB driver, allowing for customized color schemes and mood-enhancing lighting
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
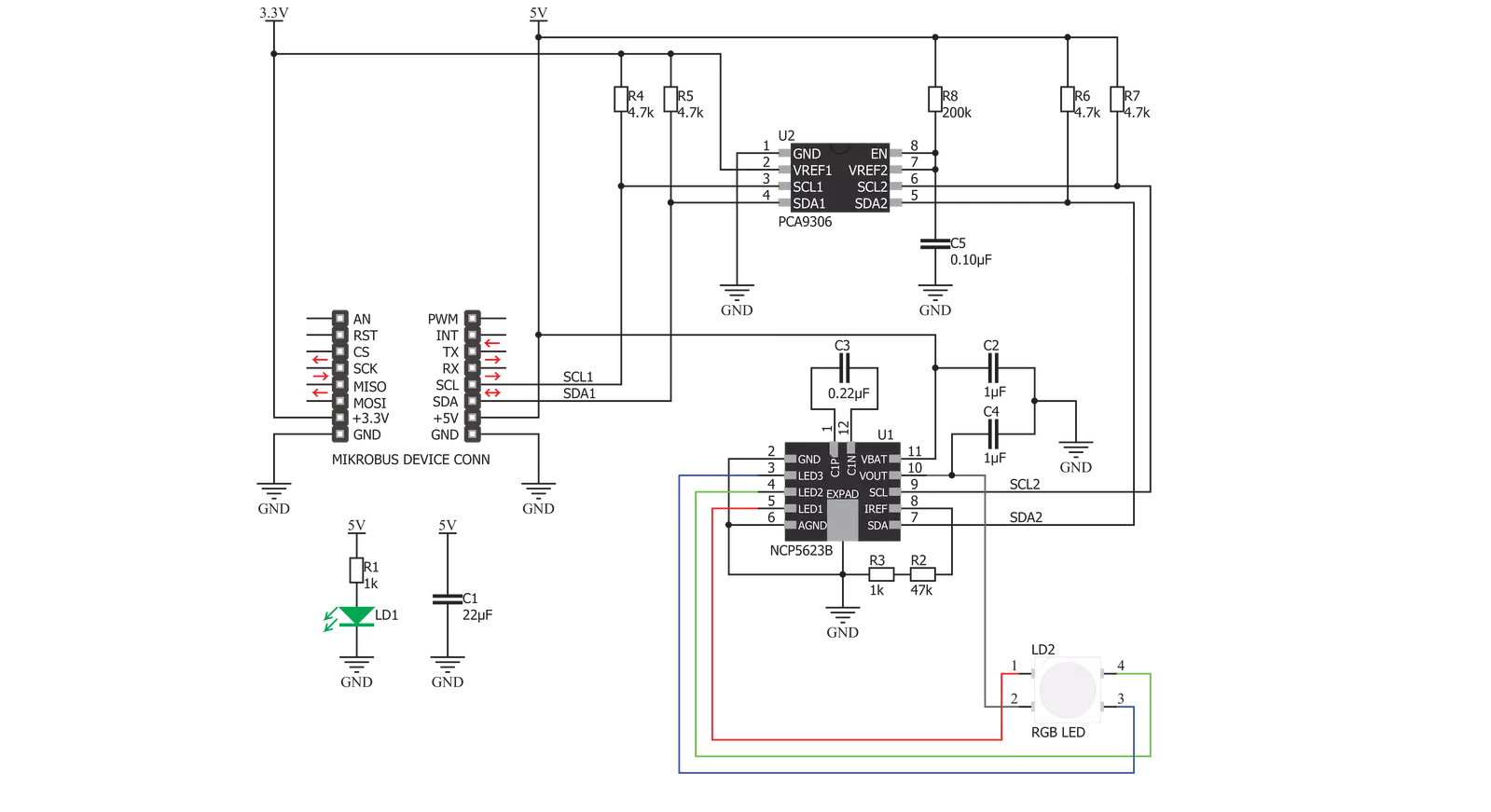
LED Driver 3 Click is based on the NCP5623B, a triple output RGB LED driver controlled through the I2C protocol from ON Semiconductors. This IC has an internal DC/DC converter that works as a high-efficiency charge pump, providing the required DC voltage for all three LED segments. The current flow through each LED segment is regulated by an internal current mirror associated with each channel. The gradual dimming function allows an easy way of dimming RGB LED intensity. With a simple I2C command, it is possible to trigger either upward or downward dimming. Dimming will affect the current through the LED segments, but the internal current limiter does not exceed the maximum allowed current set by the onboard resistor. The integrated PWM operates with five bits, having 32 steps to cover the associated LED channel's full modulation (0 to 100%). A value of 0x00h will turn the associated
LED completely OFF, while 0x1Fh will set the LED to a programmed LED current value. The last three bits (MSB) are used to set the desired command register: PWM1, PWM2, PWM3, dimming direction, gradual dimming, LED current, and more. It should be noted that the gradual dimming function affects the illumination by changing the LED current intensity, while PWM affects the associated LED illumination by changing the pulse width - e.g., it is possible to set the desired color by setting the PWM modulation of each color component, and then gradually dim the brightness of the final color mix up or down by the gradual dimming option - affecting the current through all the LED segments simultaneously. It is also possible to set the fixed value for the current through the LED segments via the I2C interface when gradual dimming is not needed. To allow operation on both 3.3V and 5V MCUs, LED Driver 3
Click employs PCA9306, a dual bidirectional I2C/SMBUS voltage level translator from Texas Instruments. This IC allows the click board to be interfaced with 3.3V and 5V MCUs. The logic voltage level shifting is done automatically, so no SMD jumpers are needed in this case. Both 3.3V and 5V rails are needed for this circuit to be operational. The click board is also equipped with an RGB LED. This is a high-brightness RGB LED with a wide viewing angle that can get very hot and bright while operated with maximum current. For this reason, care must be taken not to touch it or watch directly at the LED. SCL1 and SDA1 lines from the I2C level shifter are routed to the standard mikroBUS™ I2C pins, labeled as SCL and SDA. The click board™ already contains pull-up resistors, so no additional parts are needed to work with the click board.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for LED Driver 3 Click driver.
Key functions:
leddriver3_set_rgb_color- This function sets the color of the rgb LEDs through the parameters for red, green and blueleddriver3_set_color- This function sets colorleddriver3_set_timer- This function sets timer for increase or decrease light
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief LedDriver3 Click example
*
* # Description
* This app changes color and intensity of light.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Driver initialize.
*
* ## Application Task
* Changes color and intensity of light.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "leddriver3.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static leddriver3_t leddriver3;
static log_t logger;
static leddriver3_rgb_t rgb;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
leddriver3_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----\r\n" );
// Click initialization.
leddriver3_cfg_setup( &cfg );
LEDDRIVER3_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( LEDDRIVER3_INIT_ERROR == leddriver3_init( &leddriver3, &cfg ) )
{
log_info( &logger, "---- Init Error ----\r\n" );
log_info( &logger, "---- Run program again ----\r\n" );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, "---- Init Done ----\r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
rgb.red = 0x40;
rgb.green = 0x7F;
rgb.blue = 0x80;
leddriver3_set_intensity( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_INCREMENT | LEDDRIVER3_INTENSITY_8 );
leddriver3_set_timer( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_TIMER_8ms | LEDDRIVER3_TIMER_16ms );
leddriver3_set_color( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_COLOR_RED );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
leddriver3_set_intensity( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_CONSTANT | LEDDRIVER3_INTENSITY_16 );
leddriver3_set_color( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_COLOR_PURPLE );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
leddriver3_set_color( &leddriver3, LEDDRIVER3_COLOR_BLUE );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
leddriver3_set_rgb_color( &leddriver3, &rgb );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:LED Drivers