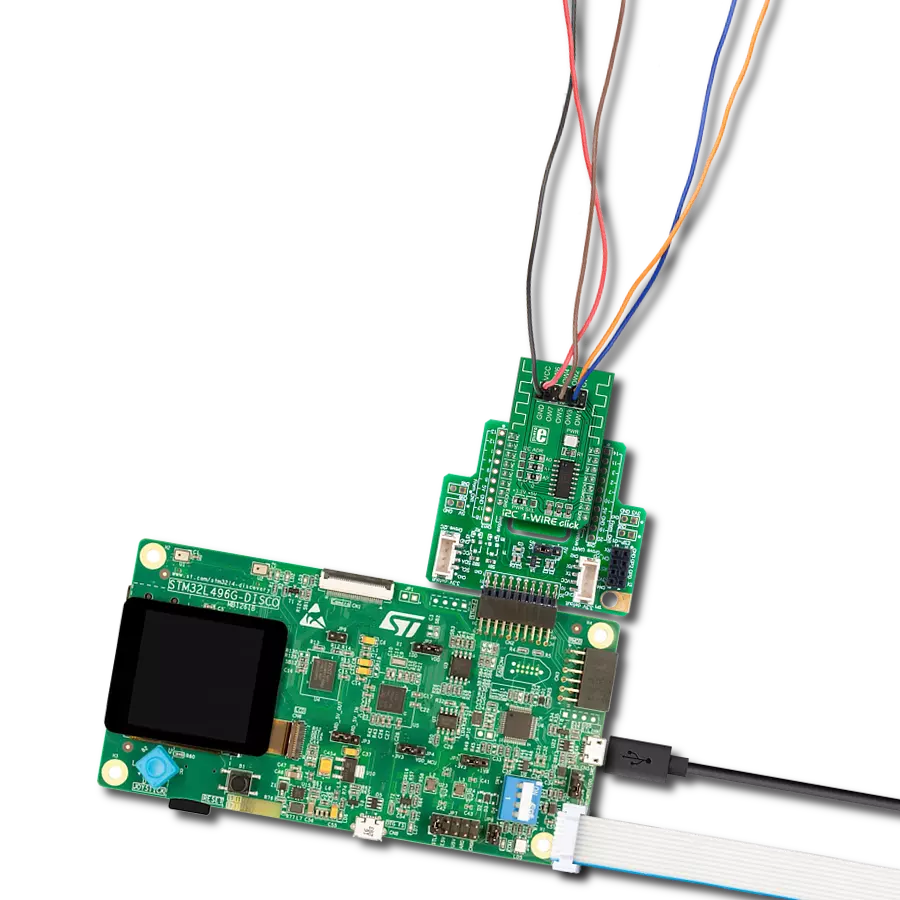
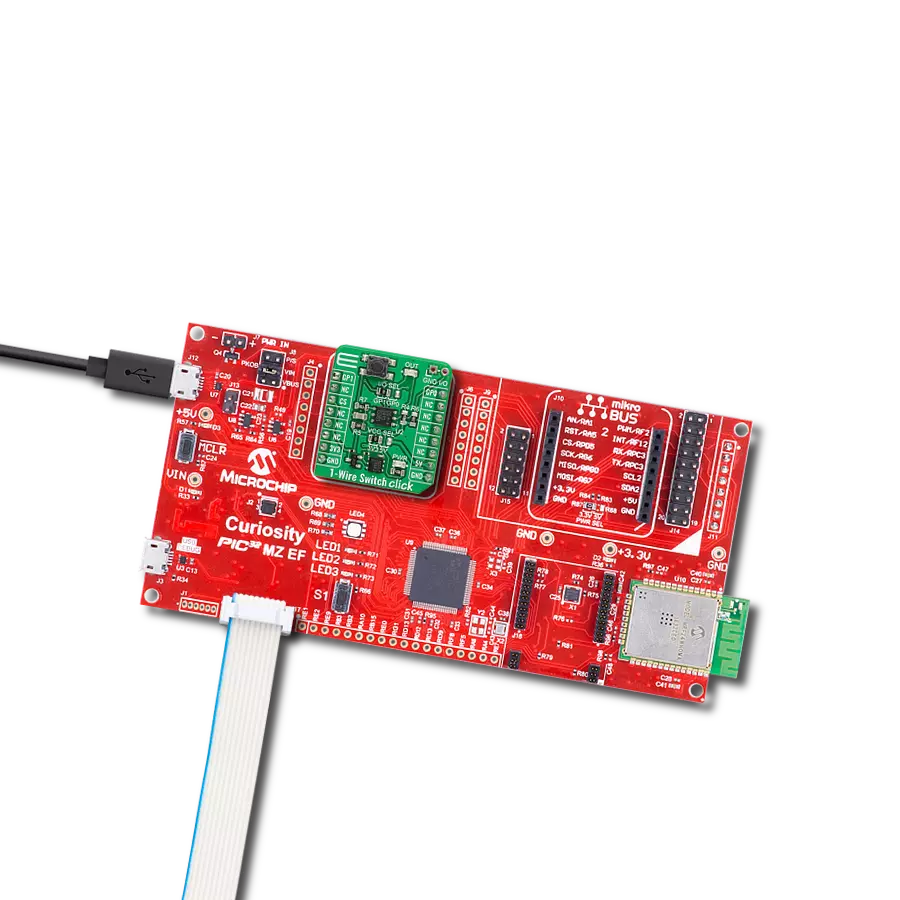
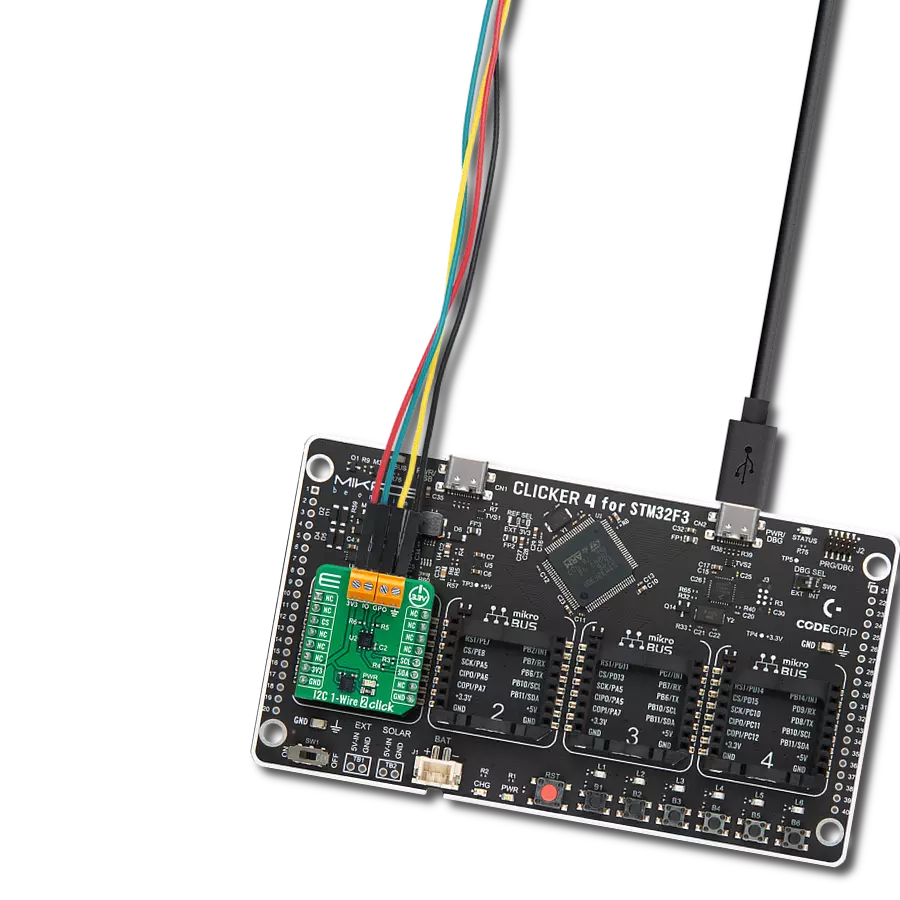
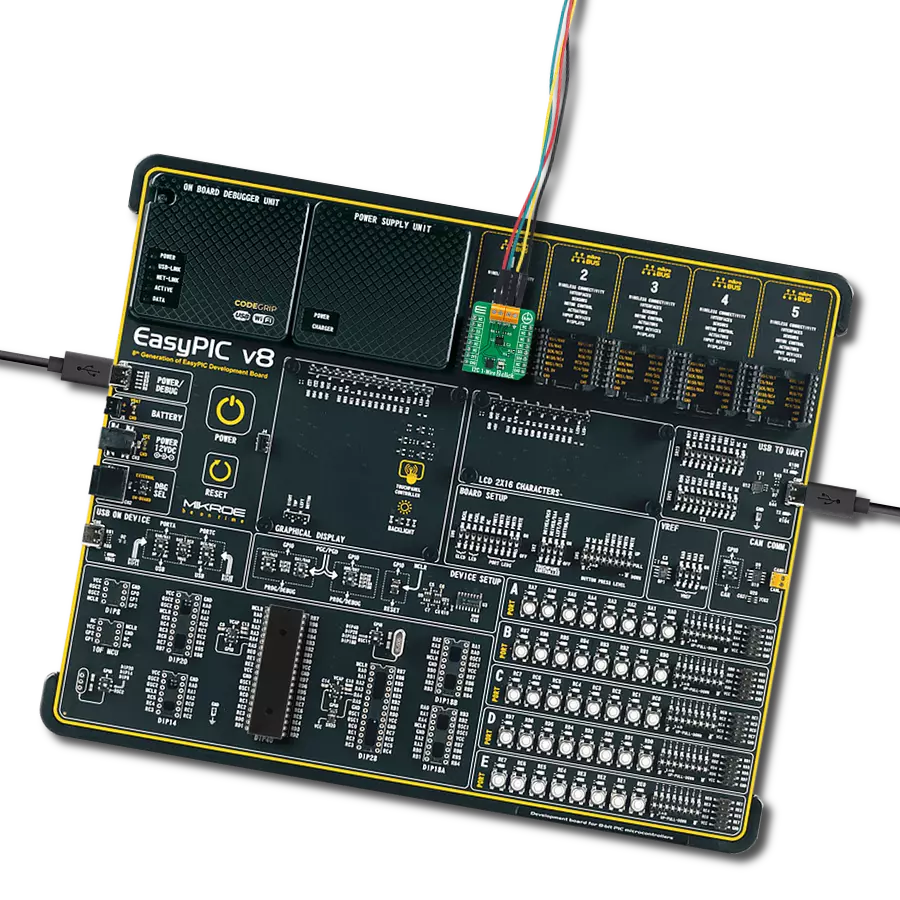
By utilizing a single data line for communication and choosing this type of conversion (1-Wire to UART), you will perform efficient and reliable data transfer without additional wiring
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
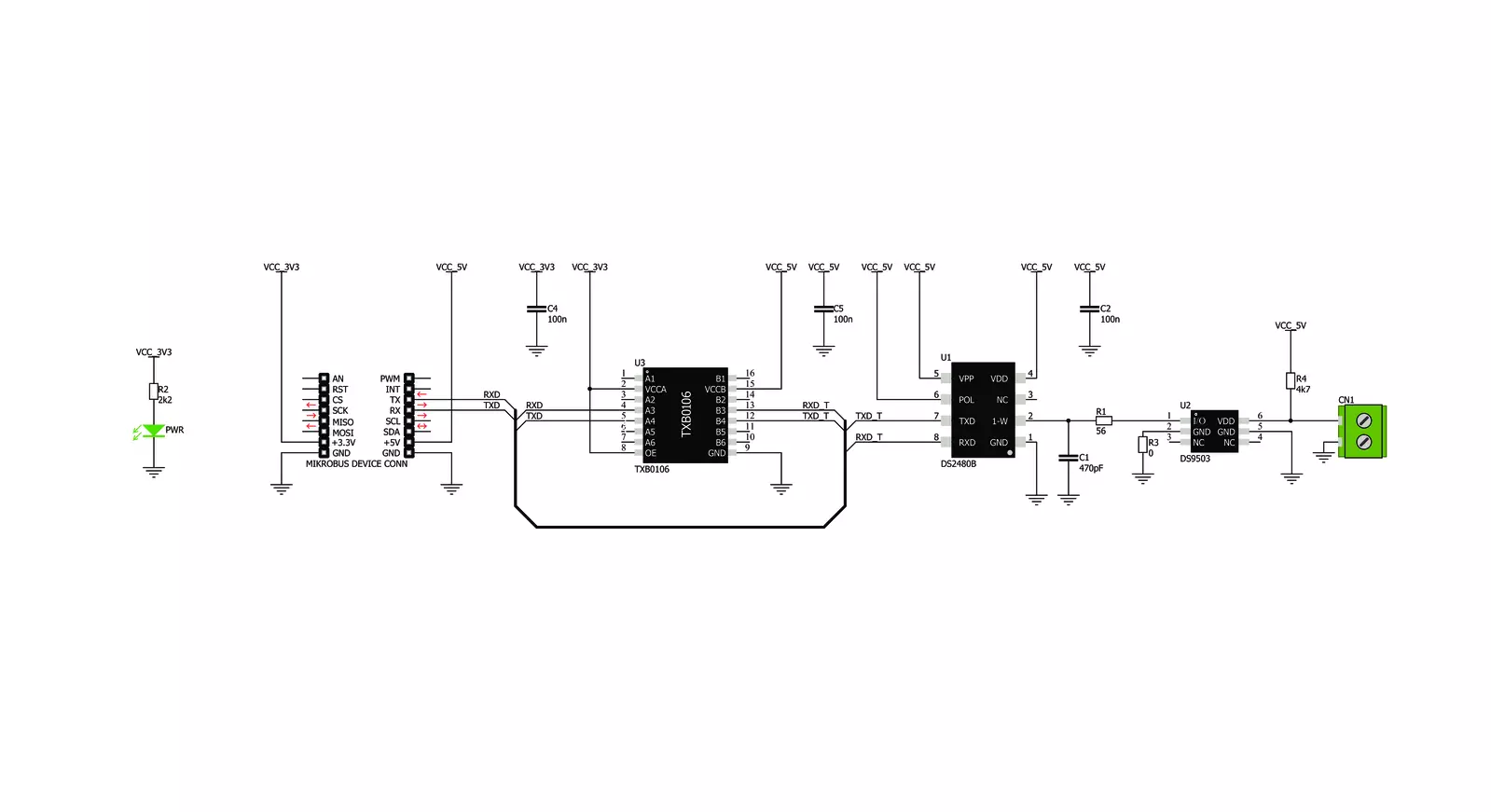
UART 1-Wire Click is based on the DS2480B, a serial to the 1-Wire® driver from Analog Devices. This IC is designed to interface the UART with the 1-Wire® bus directly. It performs data conversion using independent data rates for both interfaces, allowing standard and overdrive communication speeds. Internal timing generators of the DS2480B IC are continuously synchronized with the incoming UART data, which is typically driven by a high-precision crystal oscillator of the host microcontroller (MCU). This allows time-critical 1-Wire® signals to be generated by the DS2480B, significantly reducing the processing load from the host MCU. Many physical parameters of the UART and 1-Wire® buses can be fine-tuned so that the UART 1-Wire click can be accommodated to any UART/RS232 to 1-Wire® signal conversion application. The DS2480B IC can be observed as a complex state machine. UART commands can configure it, so the IC must parse the
incoming data before conversion. The device can be operated in two main operating modes: Command Mode and Data Mode. The Command Mode is the default state after the Power ON event. This mode allows the configuration parameters to be set. However, the DS2480B IC must be initialized before any operation: the 1-Wire® bus reset command should be sent over the TXD line at a fixed rate of 9600 bps. This is used only to calibrate the internal timing generators without performing any action on the 1-Wire® bus. After the initialization, the DS2480B IC can be used normally. The Data Mode converts bytes received at the TXD line into their equivalent 1-Wire® waveforms and reports the responses back to the host MCU through the RXD line. The datasheet of the DS2480B IC illustrates the operating principles of this IC by using the state transition diagram. Along with several examples at the end of the datasheet, it represents a useful starting point for application
development. However, the included mikroSDK-compatible library offers functions that simplify firmware development even more. The DS2480B requires 5V for both the power supply and logic levels. Considering that most MCUs use 3.3V logic levels for UART communication, a level translator had to be added. UART 1-Wire click uses the TXB0106, a bi-directional level translator IC, by Texas Instruments. This IC allows reliable logic voltage level translation, allowing the Click board™ to be used with a wide range of MCUs that use 3.3V logic levels on their UART lines. The 1-Wire® bus can be accessed over the screw terminal on the Click board™. Due to the nature of most 1-Wire® applications, the signal line of the 1-Wire® bus is protected by the DS9503, an integrated ESD Protection Diode with resistors. This IC is specifically designed to be used as Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection in 1-Wire® applications.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for UART 1-Wire Click driver.
Key functions:
uart1wire_write_command- This function sends an 8-bit command to the click module.uart1wire_read_temperature- This function reads the temperature from DALLAS one wire temperature sensors.uart1wire_reset- This function sends a reset pulse signal.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief UART1Wire Click example
*
* # Description
* This example reads and processes data from UART 1-Wire Clicks.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the temperature data from DALLAS temperature sensors and logs the results
* on the USB UART every second.
*
* @note
* Connect only DQ and GND pins to the UART 1-Wire Click connector.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "uart1wire.h"
#include "string.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static uart1wire_t uart1wire;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
uart1wire_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
uart1wire_cfg_setup( &cfg );
UART1WIRE_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
uart1wire_init( &uart1wire, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float temp_f;
uint8_t res_flag;
res_flag = uart1wire_read_temperature ( &uart1wire, &temp_f, UART1WIRE_TEMP_SENSOR_RESOLUTION_9BIT );
if ( res_flag == UART1WIRE_OK )
{
log_printf( &logger, " * Temperature: %.2f C\r\n", temp_f );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:1-Wire