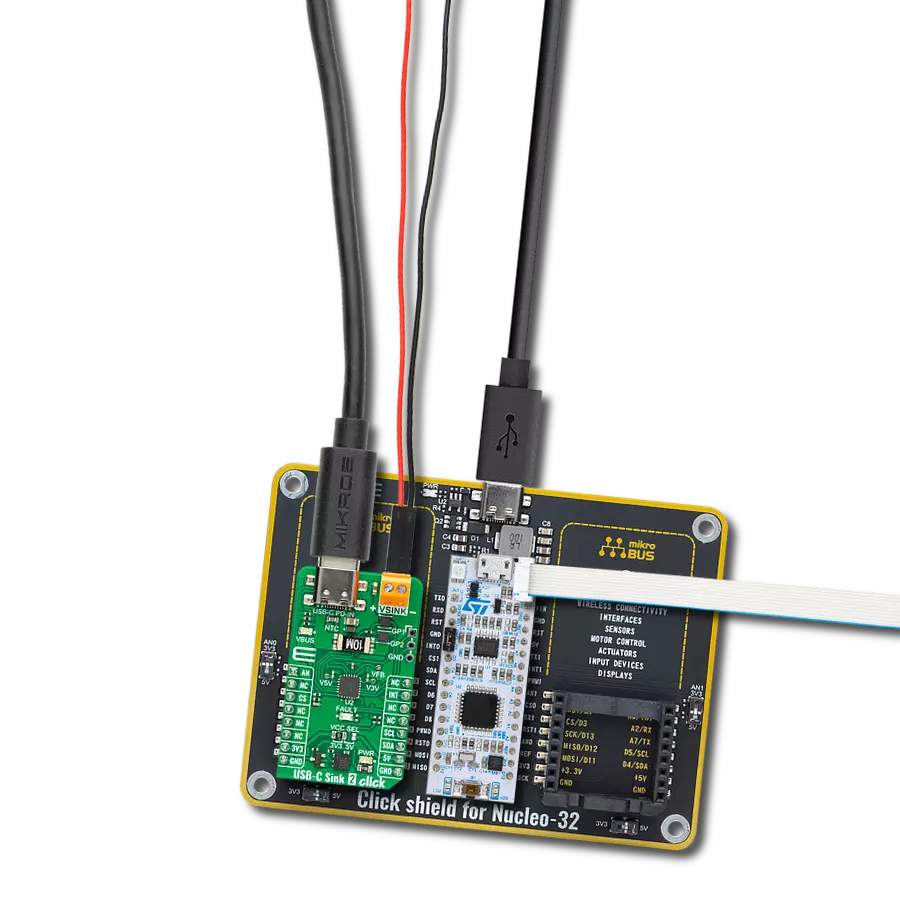
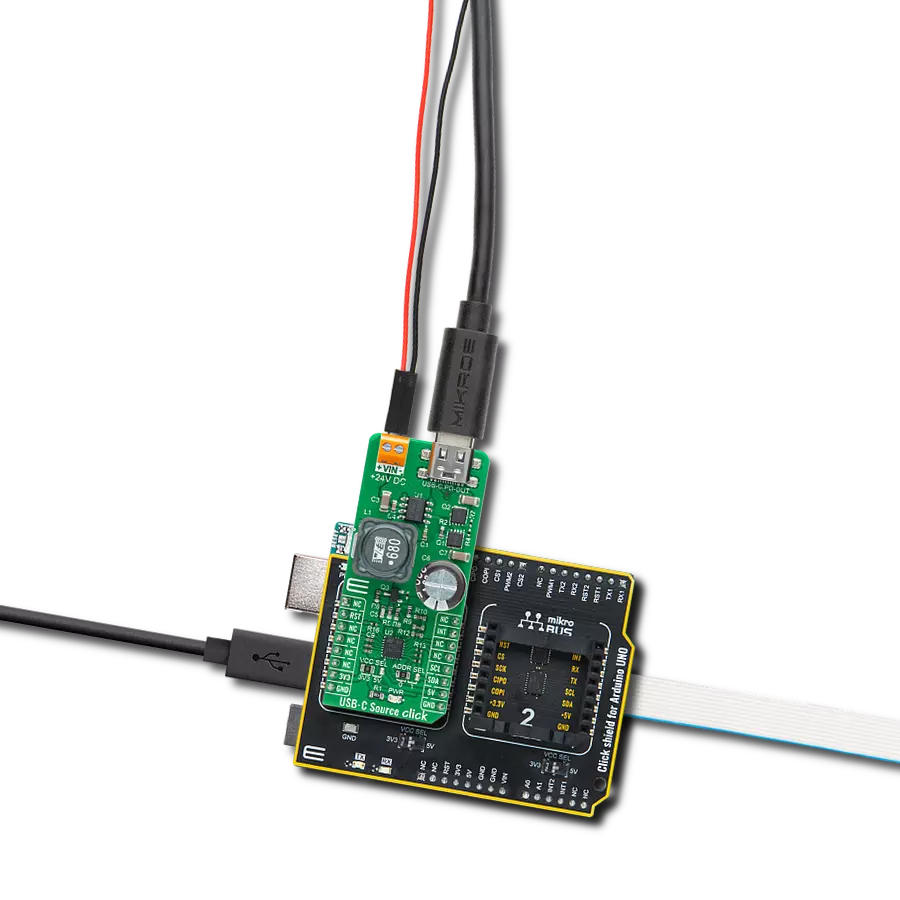
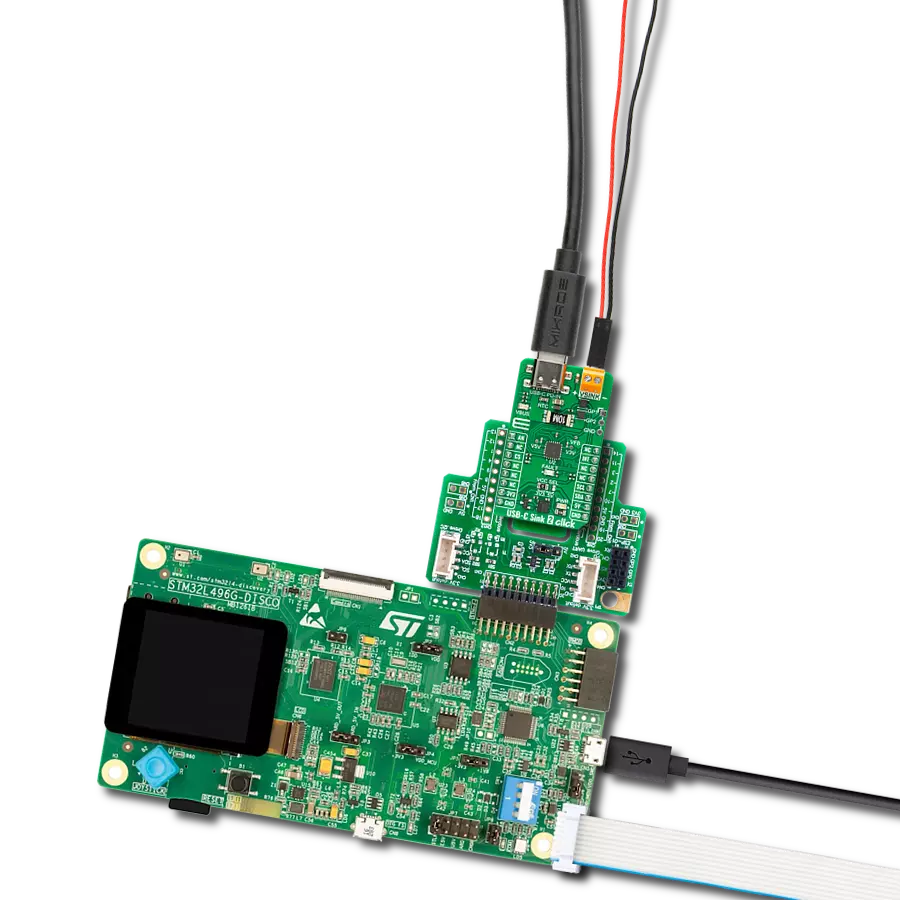
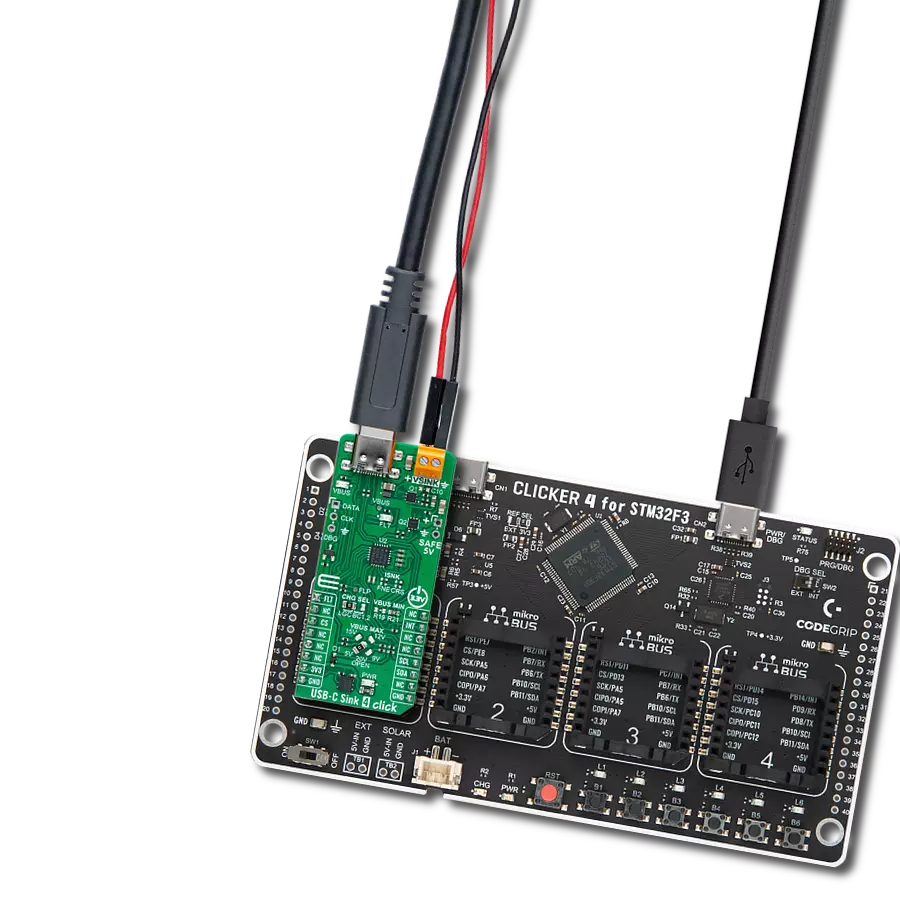
Say goodbye to low battery anxiety – our USB-C Sink guarantees your devices stay charged and ready for action.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
USB-C Sink Click is based on the STUSB4500, a USB-C sink-only controller compatible with Power-Delivery (PD) from STMicroelectronics. Based on the default power profiles (PDO) configuration stored in internal non-volatile memory, the stand-alone controller STUSB4500 implements proprietary algorithms to negotiate a Power Delivery contract with a source without any internal or external software support (Auto-Run Mode), making it the ideal device for automatic High Power Profile charging, especially from a Dead Battery Power state. This Click board™ has the VBUS monitoring block that supervises from the VBUS_VS_DISCH input pin the VBUS voltage on the USB Type-C receptacle side. It is used to check that VBUS is within a valid voltage range to establish a correct Source-to-Sink connection and to enable a safe VBUS power path through the VBUS_EN_SNK pin. It detects unexpected VBUS voltage conditions, such as undervoltage or
overvoltage, relative to the valid VBUS voltage range. The STUSB4500 also has a pin that is asserted when a valid Source-to-Sink connection is established and when a connection to a debug accessory device is detected, presented visually with a blue LED labeled ATTACH. The STUSB4500 communicates with MCU using the standard I2C interface that supports transfers up to 400 Kbit/s (Fast Mode) to configure, control, and read the device's status. It also has the possibility of the USB Power Delivery communication over CC1 and CC2 configuration channel pins used for connection and attachment detection, plug orientation determination, and system configuration management across USB Type-C cables. Four 7-bit device address is available by default (0x28, 0x29, 0x2A, or 0x2B) depending on the setting of the address pin ADDR0 and ADDR1. The user programs these pins and determines the LSBs of the slave address, and it can be selected
by positioning the onboard SMD jumpers labeled as ADDR SEL. Additional functionality, such as Reset and 'Alert' interrupt, is provided and routed at RST and INT pins of the mikroBUS™ socket. The RST pin resets all analog signals, states machine, and reloads configuration, while an interrupt output labeled INT represents alarm output. Also, there are two additional green diodes associated with two pins on the mikroBUS™ socket (labeled as PO2 and PO3) that report by default the status of the USB power delivery contract negotiation with the source labeled as PDO2 and PDO3. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for USB-C Sink Click driver.
Key functions:
usbcsink_hw_reset- HW reset function.usbcsink_get_pdo2- Get PO2 pin state function.usbcsink_write_byte- Write byte function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief USBCSink Click example
*
* # Description
* This is an example which demonstrates the use of USB-C Sink Click board.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver enables - I2C,
* set hw reset, set PDO2 profile and current value for PDO2 1.5A,
* upload new data and reset device to write NVM settings to the STUSB450,
* also write log.
*
* ## Application Task
* USB-C Sink Click board can be used to read the Power Data Objects (PDO)
* highest priority profile:
* PDO1 : 5V,
* PDO2 : 12V,
* PDO3 : 20V.
* All data logs write on USB uart changes for every 5 sec.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "usbcsink.h"
static usbcsink_t usbcsink;
static log_t logger;
uint8_t sel_profile;
float demo_data;
void application_init ( void ) {
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
usbcsink_cfg_t usbcsink_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
usbcsink_cfg_setup( &usbcsink_cfg );
USBCSINK_MAP_MIKROBUS( usbcsink_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = usbcsink_init( &usbcsink, &usbcsink_cfg );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == init_flag ) {
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
usbcsink_hw_reset( &usbcsink );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
usbcsink_set_pdo_num( USBCSINK_SET_PDO_2 );
usbcsink_set_current( USBCSINK_SET_PDO_2, 1.5 );
sel_profile = usbcsink_get_pdo_num( );
log_printf( &logger , "- - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger , " Setting PDO ~ PDO%d \r\n", ( uint16_t ) sel_profile );
log_printf( &logger , "- - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
usbcsink_upload_new_data( &usbcsink, USBCSINK_UPLOAD_NEW_DATA_VAL );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
usbcsink_hw_reset( &usbcsink );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void ) {
usbcsink_load_data( &usbcsink );
log_printf( &logger , " New Parameters \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger , "------------------------\r\n" );
sel_profile = usbcsink_get_pdo_num( );
log_printf( &logger , " PDO Number ~ PDO%d\r\n", ( uint16_t ) sel_profile );
log_printf( &logger , "- - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
demo_data = usbcsink_get_voltage( sel_profile );
log_printf( &logger , " Voltage : %.2f V\r\n", demo_data );
demo_data = usbcsink_get_current( sel_profile );
log_printf( &logger , " Current : %.2f A\r\n", demo_data );
log_printf( &logger , "------------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:USB-C PD