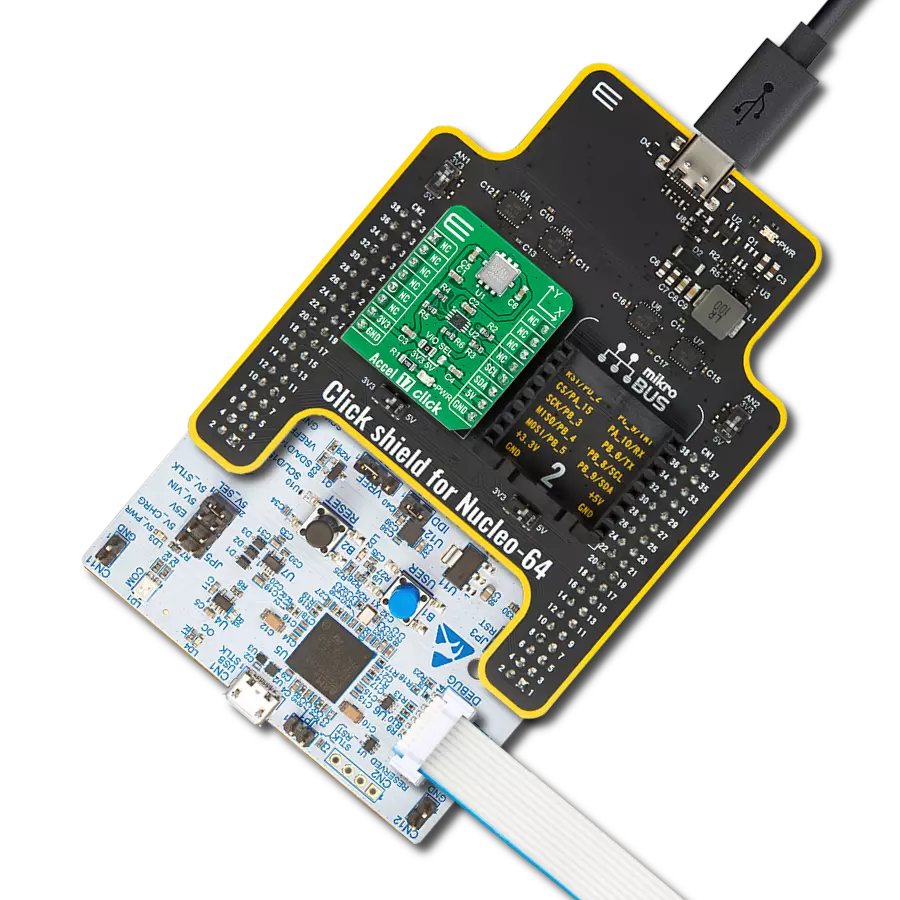
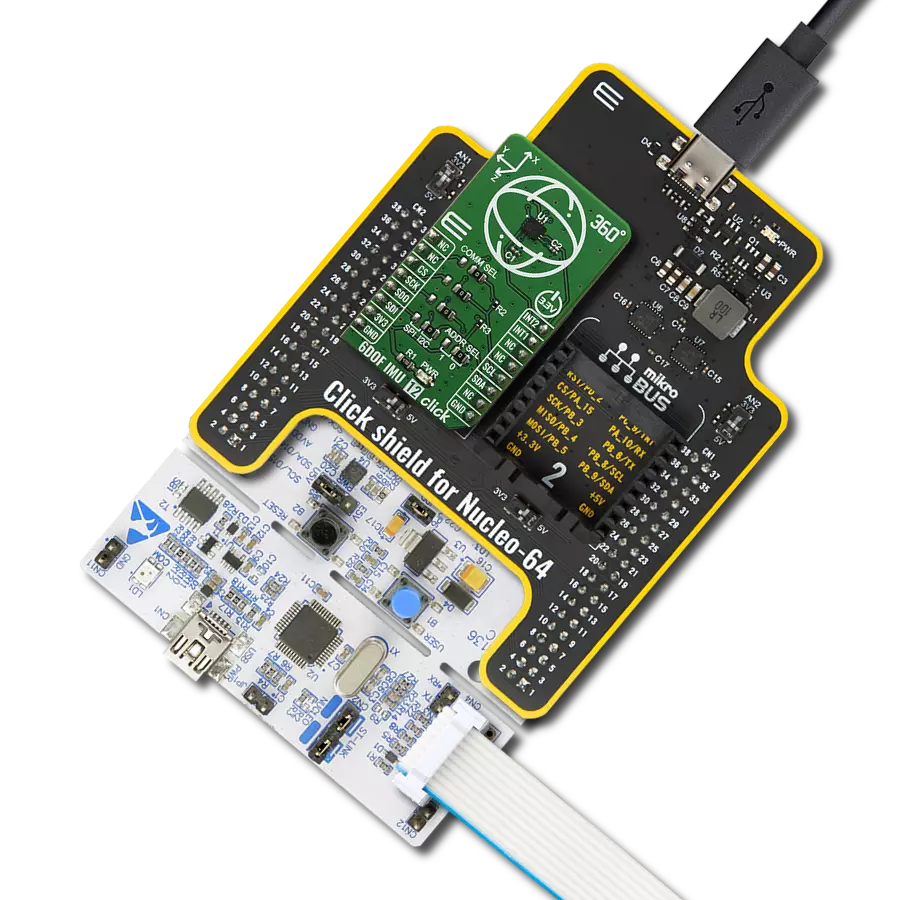
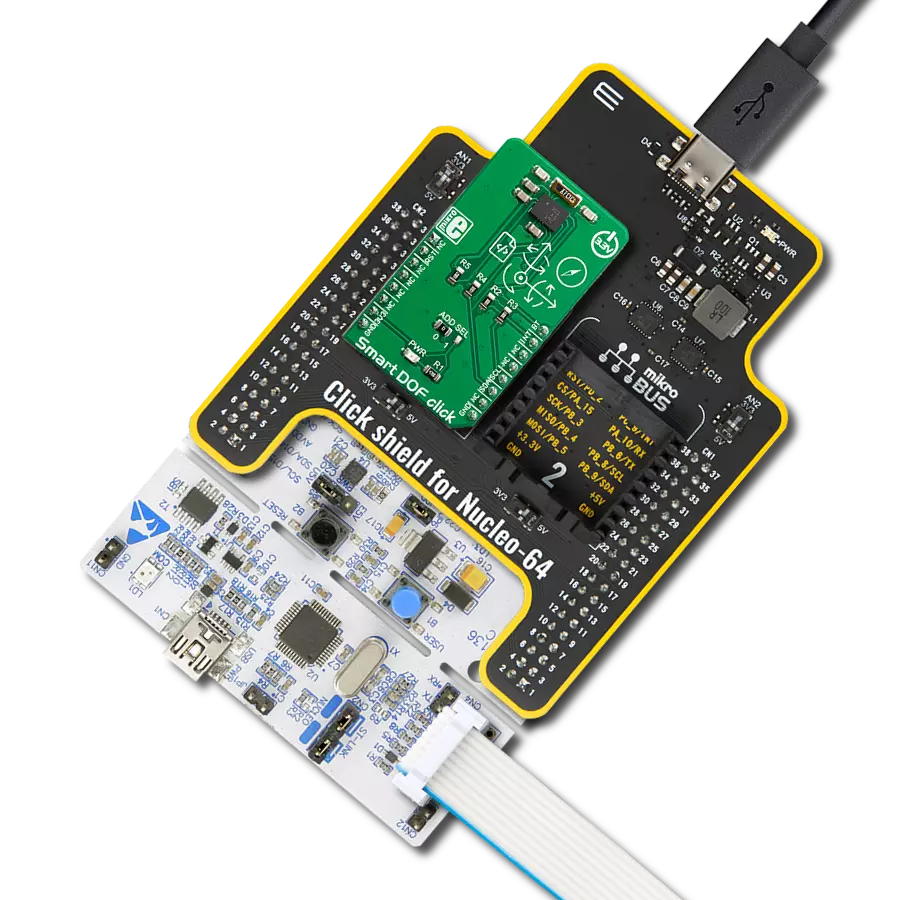
This solution precisely measures and records changes in an object's velocity, making them invaluable in fields like robotics, automotive safety, and more
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Accel 7 Click is based on the KXTJ3-1057, ±2g / ±4g / ±8g / ±16g tri-axis digital accelerometer from Rohm Semiconductor. This sensor utilizes an advanced acceleration sensing method, based on the differential capacitance. The integrated MEMS, produced with the proprietary Kionix technology, is composed of two plates. One is fixed to the substrate, while the other can move freely along a single axis. The acceleration causes the change in the capacitance between these plates, which is then processed by an integrated ASIC. The ASIC incorporates a capacitance-to-voltage amplifier which converts the differential capacitance of the MEMS sensor into an analog voltage, used as the input for the low-noise A/D converter (ADC). The integrated ASIC also contains the logic section used to set all the operational parameters of the KXTJ3-1057, such as the data rate, filter settings, interrupts, ADC resolution, and more. The ASIC also incorporates an OTP memory that contains the calibration parameters and other device-specific settings used on each power-on reset (POR) cycle. The ADC can be operated with the resolution of 8, 12, or 14 bits. This allows power consumption to be managed, as the lower resolution typically allows less power consumption. The power consumption is also affected by the output data rate value (ODR). The ODR value above 400Hz forces the high-resolution mode (14-bits) so the power consumption rises
exponentially as the ODR changes from 0.781Hz to 1600Hz. The ADC resolution, as well as the other operating parameters of the KXTJ3-1057 IC can be adjusted by using two configuration registers. Some options can only be altered while the IC operates in the Stand-by mode. The acceleration range can be selected from ±2g to ±16g. The choice of the ADC resolution is directly related with the number of counts for a certain acceleration range. For example, using ±2g range with the 8-bit ADC resolution means that the whole range between -2g and +2g will be covered by 255 values, from -127 to +127. Therefore, the output of 127 will be equivalent of 2g acceleration (more precisely, 1.984g). The datasheet of the KXTJ3-1057 offers a comprehensive set of tables with these settings. However, the Accel 7 click comes with the library that contains simple to use functions which simplify the acceleration measurements. The interrupt engine allows interrupt reporting on a dedicated INT pin. There are multiple interrupt status registers, allowing both combined and individual events to be read. This allows the INT pin to be used more flexible. Depending on the settings, it is possible to pulse and latch this pin. When latched, it will stay asserted until the specific register is read (INT_REL in the datasheet). Pulsed operation will produce a short pulse on this pin, but the status bits will remain set, until the INT_REL register is read.
Un-latched mode allows the status bits to be cleared automatically, so there is no need to read the INT_REL register. One distinctive feature of the KXTJ3-1057 is that it can generate a Wake-up (motion detection) interrupt, when the acceleration measurement exceeds the value stored in the Wake-up threshold registers. In this case, a bit in the interrupt status register will indicate that a Wake-up event occurred. The Wake-up interrupt features a debouncing counter: if an acceleration value has exceeded the threshold and remained above this threshold during a programmed number of counts, an interrupt event will be reported. To distinguish between two successive movement events, there is yet another countdown timer, which sets the non-activity time interval before another Wake-up event can be reported. Note that the thresholds use fixed g-range and resolution, regardless of user settings. Each KXTJ3-1057 device is factory calibrated, and its calibration parameters are stored in the one-time programmable memory (OTP). These parameters include the gain corrections and offset calibration. After each POR cycle, these calibration values are automatically applied, reducing the output error. Along with the used MEMS differential sensing technology, this reduces the measurement error to a virtually unmeasurable value. A built-in self-test function allows reliable operation of the Accel 7 click.
Features overview
Development board
Nucleo-64 with STM32F091RC MCU offers a cost-effective and adaptable platform for developers to explore new ideas and prototype their designs. This board harnesses the versatility of the STM32 microcontroller, enabling users to select the optimal balance of performance and power consumption for their projects. It accommodates the STM32 microcontroller in the LQFP64 package and includes essential components such as a user LED, which doubles as an ARDUINO® signal, alongside user and reset push-buttons, and a 32.768kHz crystal oscillator for precise timing operations. Designed with expansion and flexibility in mind, the Nucleo-64 board features an ARDUINO® Uno V3 expansion connector and ST morpho extension pin
headers, granting complete access to the STM32's I/Os for comprehensive project integration. Power supply options are adaptable, supporting ST-LINK USB VBUS or external power sources, ensuring adaptability in various development environments. The board also has an on-board ST-LINK debugger/programmer with USB re-enumeration capability, simplifying the programming and debugging process. Moreover, the board is designed to simplify advanced development with its external SMPS for efficient Vcore logic supply, support for USB Device full speed or USB SNK/UFP full speed, and built-in cryptographic features, enhancing both the power efficiency and security of projects. Additional connectivity is
provided through dedicated connectors for external SMPS experimentation, a USB connector for the ST-LINK, and a MIPI® debug connector, expanding the possibilities for hardware interfacing and experimentation. Developers will find extensive support through comprehensive free software libraries and examples, courtesy of the STM32Cube MCU Package. This, combined with compatibility with a wide array of Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), including IAR Embedded Workbench®, MDK-ARM, and STM32CubeIDE, ensures a smooth and efficient development experience, allowing users to fully leverage the capabilities of the Nucleo-64 board in their projects.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
32768
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-64 comes equipped with two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with no effort. This way, Mikroe allows its users to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™, such as WiFi, GSM, GPS, Bluetooth, ZigBee, environmental sensors, LEDs, speech recognition, motor control, movement sensors, and many more. More than 1537 Click boards™, which can be stacked and integrated, are at your disposal. The STM32 Nucleo-64 boards are based on the microcontrollers in 64-pin packages, a 32-bit MCU with an ARM Cortex M4 processor operating at 84MHz, 512Kb Flash, and 96KB SRAM, divided into two regions where the top section represents the ST-Link/V2 debugger and programmer while the bottom section of the board is an actual development board. These boards are controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and efficiently debug the Nucleo-64 board out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB mini port on the board. Most of the STM32 microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the STM32 Nucleo-64 board with our Click Shield for Nucleo-64, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
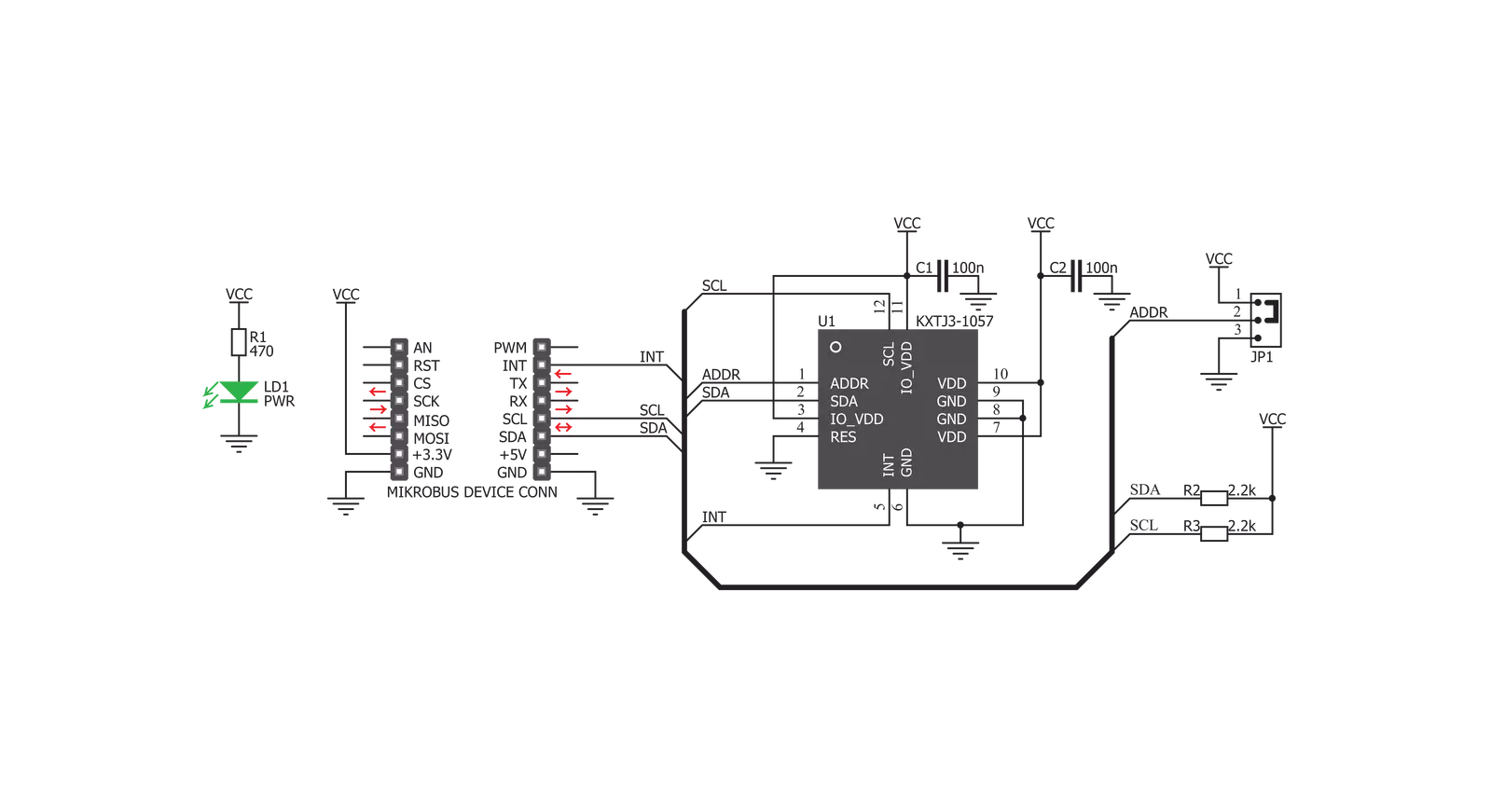
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Accel 7 Click driver.
Key functions:
accel7_get_axis- This function reads two bytes of data from the desired axis registeraccel7_res_range_cfg- This function calculates the resolution and range values which are used in the default_cfg() functionaccel7_get_interrupt_state- This function reads the state of the interrupt pin
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Accel7 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example shows how data from all three axes is collected, processed and later
* displayed in the logger module.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* This is where the logger and the Click modules get initialised and configured.
*
* ## Application Task
* This is where the data gets collected, processed and printed out.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "accel7.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static accel7_t accel7;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
accel7_cfg_t cfg;
uint8_t resolution = ACCEL7_DATA_RESP_14bit;
uint8_t range = ACCEL7_RANGE_8g;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
accel7_cfg_setup( &cfg );
ACCEL7_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
accel7_init( &accel7, &cfg );
accel7_default_cfg( &accel7, resolution, range );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( )
{
int16_t x_axis;
int16_t y_axis;
int16_t z_axis;
x_axis = accel7_get_axis( &accel7, ACCEL7_AXIS_X );
y_axis = accel7_get_axis( &accel7, ACCEL7_AXIS_Y );
z_axis = accel7_get_axis( &accel7, ACCEL7_AXIS_Z );
log_printf( &logger, "X axis: %d\r\n", x_axis );
log_printf( &logger, "Y axis: %d\r\n", y_axis );
log_printf( &logger, "Z axis: %d\r\n", z_axis );
log_printf( &logger, "------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Motion