Our solution is designed to revolutionize mobile operations by seamlessly integrating GPS/GLONASS location tracking with GSM module capability for mobile communication, providing businesses with a versatile tool for precision tracking and seamless connectivity
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
GSM/GNSS Click is based on the MC60, a multi-purpose module that integrates a high-performance GNSS engine and a quad-band GSM/GPRS engine from Quectel Wireless Solutions. The quad-band GSM/GPRS engine can work at 850, 900, 1800, and 1900MHz frequencies. It also features GPRS multi-slot class 12 and supports the GPRS coding schemes CS-1, CS-2, CS-3, and CS-4. The GSM part of the MC60 is integrated with Internet service protocols such as TCP, UDP, PPP, HTTP, and FTP. The excellent positioning performance, low power consumption, and dual μSIM card interfaces make MC60 the best choice for many M2M applications. It also supports EPO™ technology, which provides predicted Extended Prediction Orbit to speed up TTFF without needing an extra server. EASY™ (Embedded Assist System) technology is also supported, enabling the GNSS engine to achieve a swift first fix when there is insufficient satellite information. MC60 also supports working in proven AlwaysLocate™ and GLP (GNSS Low Power) modes, ensuring great positioning accuracy while ultra-low power consumption. The built-in LNA provides the module with improved
RF sensitivity and exceptional acquisition/tracking performance, even in weak signal areas. The Quectel MC60 module has to be powered by a clean and stable power supply. The voltage for the module to work correctly is 4V, derived from the 5V mikroBUS™ power rail through the MCP1826, a 1A low drop output (LDO) regulator. The main 4V power supply is also the power supply for the GSM/GPRS block of the MC60, while the GNSS block is powered with TLV700, a low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator from Texas Instruments, which at its input receives the voltage from MCP1826 LDO (4V) and at its output gives a fixed voltage of 3.3V. Also, activation of the module itself is possible via the RST pin on the mikroBUS™ socket connected to the PWRKEY pin used for turning the module ON and OFF. The MC60 communicates with MCU using the UART interface with commonly used UART RX and TX pins with the hardware flow control pins UART CTS, RTS, RI (Clear to Send, Ready to Send, and Ring Indicator). The GSM/GNSS click also has an onboard MicroSD/MicroSIM card socket with a card detection feature routed to the AN pin on the mikroBUS™ socket, A5839 Bluetooth 3.0 2.4GHz
chip antenna, which only the MC60 module version supports, and an additional header labeled as HD1 for audio interface (channels for connecting speakers and a microphone). In addition to all these features, this Click board™ has a network status yellow LED indicator labeled as NET, indicating if the module is attached to a network. Furthermore, it possesses two SMA antenna connectors with an impedance of 50Ω, labeled as GNSS and GSM, used for connecting the appropriate antenna that MIKROE offers. It can receive GPS coordinates, time, and other information from orbiting satellites when connected to a GPS antenna. The Click board™ can be used for all GSM functions: calls, messages (SMS, MMS), and mobile internet. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via an onboard jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
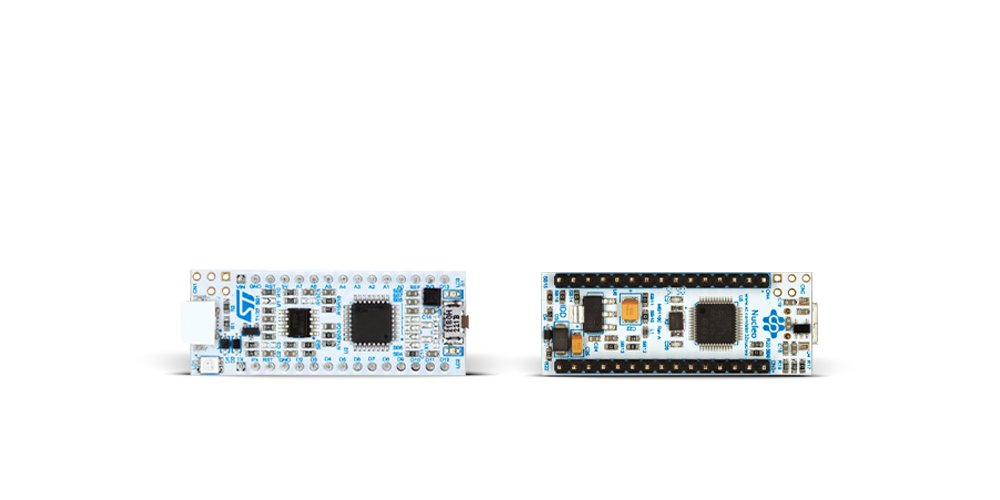
Development board
Nucleo 32 with STM32F031K6 MCU board provides an affordable and flexible platform for experimenting with STM32 microcontrollers in 32-pin packages. Featuring Arduino™ Nano connectivity, it allows easy expansion with specialized shields, while being mbed-enabled for seamless integration with online resources. The
board includes an on-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer, supporting USB reenumeration with three interfaces: Virtual Com port, mass storage, and debug port. It offers a flexible power supply through either USB VBUS or an external source. Additionally, it includes three LEDs (LD1 for USB communication, LD2 for power,
and LD3 as a user LED) and a reset push button. The STM32 Nucleo-32 board is supported by various Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IAR™, Keil®, and GCC-based IDEs like AC6 SW4STM32, making it a versatile tool for developers.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is the perfect way to expand your development board's functionalities with STM32 Nucleo-32 pinout. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 provides two mikroBUS™ sockets to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™. We are fully stocked with everything, from sensors and WiFi transceivers to motor control and audio amplifiers. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is compatible with the STM32 Nucleo-32 board, providing an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new ideas and quickly create prototypes with any STM32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The STM32 Nucleo-32 boards do not require any separate probe as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer and come with the STM32 comprehensive software HAL library and various packaged software examples. This development platform provides users with an effortless and common way to combine the STM32 Nucleo-32 footprint compatible board with their favorite Click boards™ in their upcoming projects.
Rubber Antenna GSM/GPRS Right Angle is the perfect companion for all GSM Click boards™ in our extensive lineup. This specialized antenna is designed to optimize your wireless connectivity with impressive features. With a wide frequency range spanning 824-894/1710-1990MHz or 890-960/1710-1890MHz, it can handle various frequency bands, ensuring a seamless and reliable connection. The antenna boasts an impedance of 50 Ohms and a gain of 2dB, enhancing signal reception and transmission. Its 70/180MHz bandwidth provides flexibility for diverse applications. The vertical polarization further enhances its performance. With a maximum input power capacity of 50W, this antenna ensures robust communication even under demanding conditions. Measuring a compact 50mm in length and featuring an SMA male connector, the Rubber Antenna GSM/GPRS Right Angle is a versatile and compact solution for your wireless communication needs.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for GSM/GNSS Click driver.
Key functions:
gsmgnss_send_cmd- Send command functiongsmgnss_set_sim_apn- Set sim card APNgsmgnss_send_sms_pdu- GSM GNSS send SMS in PDU mode.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief GSMGNSS Click example
*
* # Description
* This example reads and processes data from GSM/GNSS Click.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and powers up the module, then sets default configuration
* for connecting the device to network.
*
* ## Application Task
* Waits for the device to connect to network, then waits for the GNSS position fix. Once it get a fix,
* it sends an SMS with GNSS info to the selected phone number approximately every 40 seconds.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void gsmgnss_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static void gsmgnss_error_check( err_t error_flag )
* - static void gsmgnss_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static void gsmgnss_check_connection( void )
* - static err_t gsmgnss_rsp_check ( void )
* - static err_t gsmgnss_process ( void )
* - static void gnss_parser_application ( void )
*
* @note
* A passive GPS antenna is required for the GNSS to receive the position fix. It may take several minutes
* for the module to receive the fix.
* In order for the example to work, user needs to set the phone number to which he wants
* to send an SMS, and also will need to set an APN and SMSC (required for PDU mode only) of entered SIM card.
* Enter valid data for the following macros: SIM_APN, SIM_SMSC and PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE.
* E.g.
SIM_APN "vipmobile"
SIM_SMSC "+381610401"
PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "+381659999999"
*
* @author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gsmgnss.h"
#include "string.h"
#define APP_OK 0
#define APP_ERROR_DRIVER -1
#define APP_ERROR_OVERFLOW -2
#define APP_ERROR_TIMEOUT -3
#define RSP_OK "OK"
#define RSP_ERROR "ERROR"
#define SIM_APN "" // Set valid SIM APN
#define SIM_SMSC "" // Set valid SMS Service Center Address - only in PDU mode
#define PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE "" // Set Phone number to message
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 256
#define WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION 0
#define CONNECTED_TO_NETWORK 1
static gsmgnss_t gsmgnss;
static log_t logger;
static char app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static int32_t app_buf_cnt = 0;
static uint8_t app_connection_status = WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
static err_t app_error_flag;
static uint8_t gnss_parser_flag = 0;
static uint8_t gnss_info_message[ 200 ] = { 0 };
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length and counter.
* @note None.
*/
static void gsmgnss_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concats data to application buffer.
*
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* @li @c -2 - Application buffer overflow.
*
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t gsmgnss_process ( void );
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS check for errors.
* @details This function checks for different types of errors and logs them on UART.
* @note None.
*/
static void gsmgnss_error_check( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS logs application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer.
* @note None.
*/
static void gsmgnss_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS response check.
* @details This function checks for response and returns the status of response.
*
* @return application status.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t gsmgnss_rsp_check ( void );
/**
* @brief GSM/GNSS check connection.
* @details This function checks connection to the network and
* logs that status to UART.
*
* @note None.
*/
static void gsmgnss_check_connection( void );
/**
* @brief GNSS parser application.
* @param rsp Response buffer.
* @details This function logs GNSS data on the USB UART and stores data in gnss_info_message buffer.
*
* @note None.
*/
static void gnss_parser_application ( char *rsp );
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
gsmgnss_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
gsmgnss_cfg_setup( &cfg );
GSMGNSS_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
gsmgnss_init( &gsmgnss, &cfg );
gsmgnss_module_power( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_MODULE_POWER_ON );
// dummy read
gsmgnss_process( );
gsmgnss_clear_app_buf( );
// AT
gsmgnss_send_cmd( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_AT );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// ATI - product information
gsmgnss_send_cmd( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_ATI );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// CGMR - firmware version
gsmgnss_send_cmd( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CGMR );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// CMEE - Report Mobile Equipment Error
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CMEE, "2" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// COPS - deregister from network
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_COPS, "2" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// CGDCONT - set sim apn
gsmgnss_set_sim_apn( &gsmgnss, SIM_APN );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// CFUN - full funtionality
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CFUN, "1" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// COPS - automatic mode
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_COPS, "0" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
// CREG - network registration status
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CREG, "1" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// QGNSSC - power ON GNSS
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_QGNSSC, "1" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
app_buf_len = 0;
app_buf_cnt = 0;
app_connection_status = WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
if ( app_connection_status == WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION )
{
// CREG - network registration status
gsmgnss_send_cmd_check( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CREG );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
// CSQ - signal quality
gsmgnss_send_cmd( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CSQ );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
else
{
log_info( &logger, "CONNECTED TO NETWORK" );
// SMS message format - PDU mode
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_CMGF, "0" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
for( ; ; )
{
// Get GNSS info
gnss_parser_flag = 1;
gsmgnss_send_cmd_with_parameter( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_QGNSSRD, "\"NMEA/GGA\"" );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
if ( gnss_parser_flag == 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "> Sending message to phone number...\r\n" );
gsmgnss_send_sms_pdu ( &gsmgnss, SIM_SMSC, PHONE_NUMBER_TO_MESSAGE, gnss_info_message );
app_error_flag = gsmgnss_rsp_check( );
gsmgnss_error_check( app_error_flag );
// 30 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void gsmgnss_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
app_buf_cnt = 0;
}
static err_t gsmgnss_process ( void )
{
err_t return_flag = APP_ERROR_DRIVER;
int32_t rx_size;
char rx_buff[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
rx_size = gsmgnss_generic_read( &gsmgnss, rx_buff, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = 0;
return_flag = APP_OK;
if ( app_buf_len + rx_size >= PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
gsmgnss_clear_app_buf( );
return_flag = APP_ERROR_OVERFLOW;
}
else
{
buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
app_buf_len += rx_size;
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buff[ rx_cnt ] != 0 )
{
app_buf[ ( buf_cnt + rx_cnt ) ] = rx_buff[ rx_cnt ];
}
else
{
app_buf_len--;
buf_cnt--;
}
}
}
return return_flag;
}
static err_t gsmgnss_rsp_check ( void )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 100000;
err_t error_flag = gsmgnss_process( );
if ( ( error_flag != 0 ) && ( error_flag != -1 ) )
{
return error_flag;
}
while ( ( strstr( app_buf, RSP_OK ) == 0 ) && ( strstr( app_buf, RSP_ERROR ) == 0 ) )
{
error_flag = gsmgnss_process( );
if ( ( error_flag != 0 ) && ( error_flag != -1 ) )
{
return error_flag;
}
timeout_cnt++;
if ( timeout_cnt > timeout )
{
while ( ( strstr( app_buf, RSP_OK ) == 0 ) && ( strstr( app_buf, RSP_ERROR ) == 0 ) )
{
gsmgnss_send_cmd( &gsmgnss, GSMGNSS_CMD_AT );
gsmgnss_process( );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
gsmgnss_clear_app_buf( );
return APP_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
gsmgnss_check_connection();
gsmgnss_log_app_buf();
return APP_OK;
}
static void gsmgnss_error_check( err_t error_flag )
{
if ( ( error_flag != 0 ) && ( error_flag != -1 ) )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case -2:
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
case -3:
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
static void gsmgnss_log_app_buf ( void )
{
if ( gnss_parser_flag == 1 )
{
gnss_parser_application( app_buf );
}
else
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n-----------------------------------\r\n" );
}
gsmgnss_clear_app_buf( );
}
static void gsmgnss_check_connection( void )
{
#define CONNECTED "+CREG: 1,1"
if ( strstr( app_buf, CONNECTED ) != 0 )
{
app_connection_status = CONNECTED_TO_NETWORK;
}
}
static void gnss_parser_application ( char *rsp )
{
char element_buf[ 200 ] = { 0 };
memset( gnss_info_message, 0, 200 );
gsmgnss_generic_parser( rsp, GSMGNSS_NMEA_GNGGA, GSMGNSS_GNGGA_LATITUDE, element_buf );
if ( strlen( element_buf ) )
{
strcpy( gnss_info_message, "GNSS info\n" );
strcat( gnss_info_message, "Latitude: " );
strncat( gnss_info_message, element_buf, 2 );
strcat( gnss_info_message, " deg, " );
strcat( gnss_info_message, &element_buf[ 2 ] );
strcat( gnss_info_message, " min" );
gsmgnss_generic_parser( rsp, GSMGNSS_NMEA_GNGGA, GSMGNSS_GNGGA_LONGITUDE, element_buf );
strcat( gnss_info_message, "\nLongitude: " );
strncat( gnss_info_message, element_buf, 3 );
strcat( gnss_info_message, " deg, " );
strcat( gnss_info_message, &element_buf[ 3 ] );
strcat( gnss_info_message, " min" );
memset( element_buf, 0, sizeof( element_buf ) );
gsmgnss_generic_parser( rsp, GSMGNSS_NMEA_GNGGA, GSMGNSS_GNGGA_ALTITUDE, element_buf );
strcat( gnss_info_message, "\nAltitude: " );
strcat( gnss_info_message, element_buf );
strcat( gnss_info_message, " m" );
log_printf( &logger, "%s", gnss_info_message );
gnss_parser_flag = 0;
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "Waiting for the position fix..." );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n-----------------------------------\r\n" );
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END