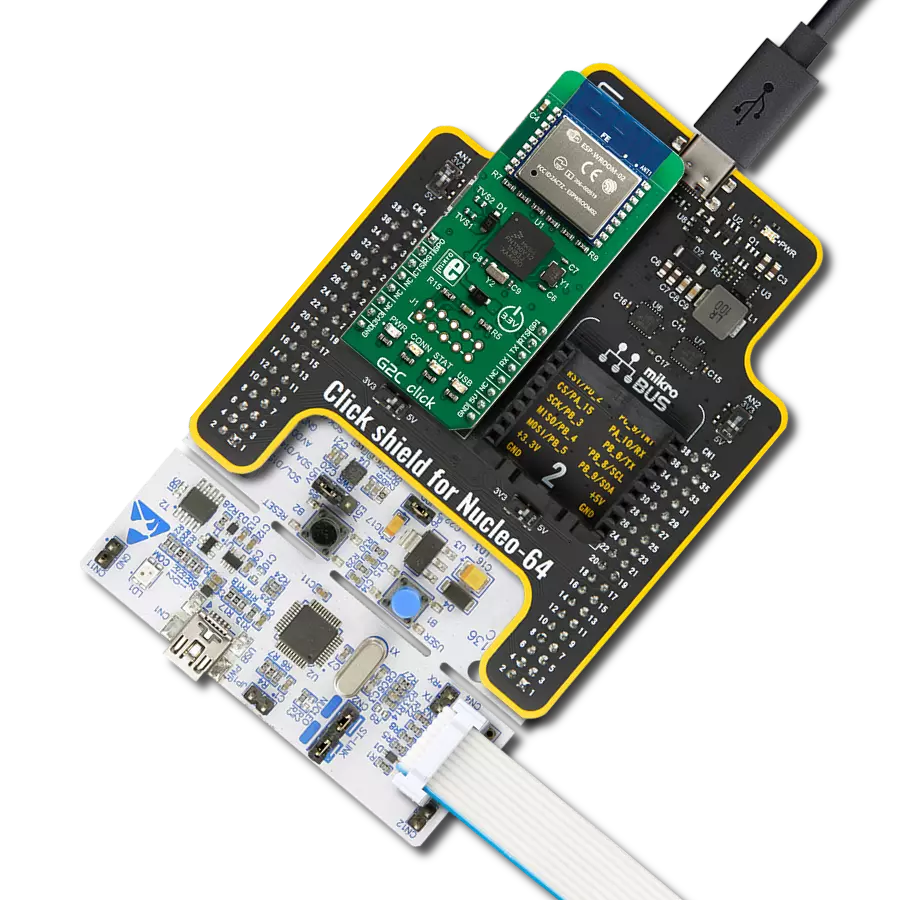
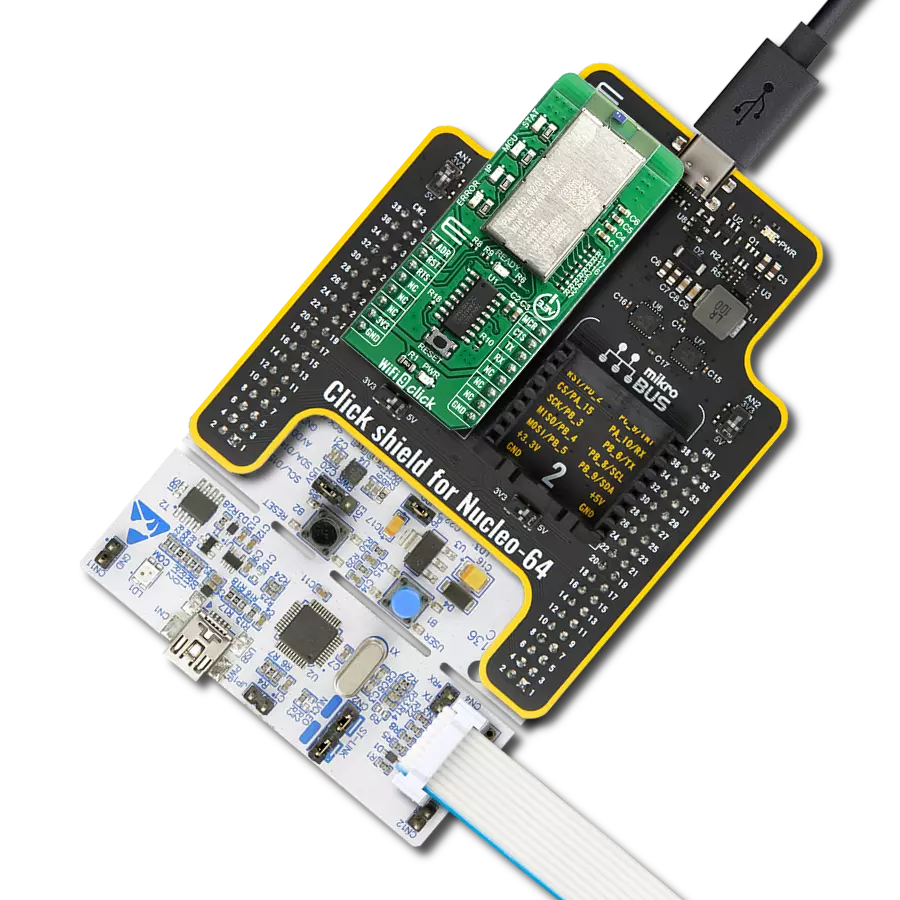
Boost your projects with dual-band WiFi and BLE connectivity for secure and reliable communication
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
WiFi NORA Click is based on the NORA-W366-00B6-00B, a dual-band WiFi and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) module from u-blox, based on a Realtek RTL8720DF chip designed to enhance wireless connectivity in professional-grade applications. This module supports WiFi 4 (802.11a/b/g/n) in both 2.4 and 5GHz bands, enabling it to function as either a WiFi station or an access point. Additionally, it offers Bluetooth v5.3 capabilities, allowing it to operate as a peripheral, central, or both, with the flexibility to act as a GATT client or server. Designed for a wide range of applications, WiFi NORA Click is ideal for industrial automation, smart buildings and homes, smart cities, metering and utilities, healthcare, and EV charging. The module comes globally certified and equipped with an internal PCB antenna that delivers high performance and an extensive range. Pre-flashed with u-connectXpress software, the NORA-W366-00B module simplifies end-product integration and accelerates time-to-market. It includes a TCP/IP stack for both point-to-point and
point-to-multipoint use cases and ensures secure communication with cloud-based services through support for TLS encryption and MQTT protocols. The module also offers robust security features, including WPA2/WPA3, WiFi enterprise security, and Bluetooth LE secure connections. This Click board™ establishes communication between the NORA-W366-00B6-00B module and the host MCU through a UART interface, using standard UART RX and TX pins along with hardware flow control pins (CTS/RTS). The default communication speed is set at 115200bps, ensuring efficient data exchange. The host MCU configures wireless communication and various other features using high-level AT commands, eliminating the need for in-depth expertise in WiFi and Bluetooth protocol stacks. Besides interface pins, the module also uses some other mikroBUS™ pins like the WKP pin, which serves as an output for the host MCU wake-up function, and the WHS pin, which is used as the module wake-up signal to bring the module out of deep sleep mode. The board also features
an RST pin and a RESET button, providing functionality for resetting the module. WiFi NORA Click features two buttons, SW1 and SW2, to enter bootloader mode. When both buttons are pressed simultaneously, the module enters bootloader mode. If this state is maintained for more than 10 seconds without sending commands to the bootloader via UART, the u-connectXpress application will automatically boot, and the module settings will be restored to factory default values. Pressing only the SW1 button triggers the booting of the u-connectXpress application. Additionally, the Click board™ includes one user-configurable RGB LED indicator labeled LD2, which is used to indicate various module statuses. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
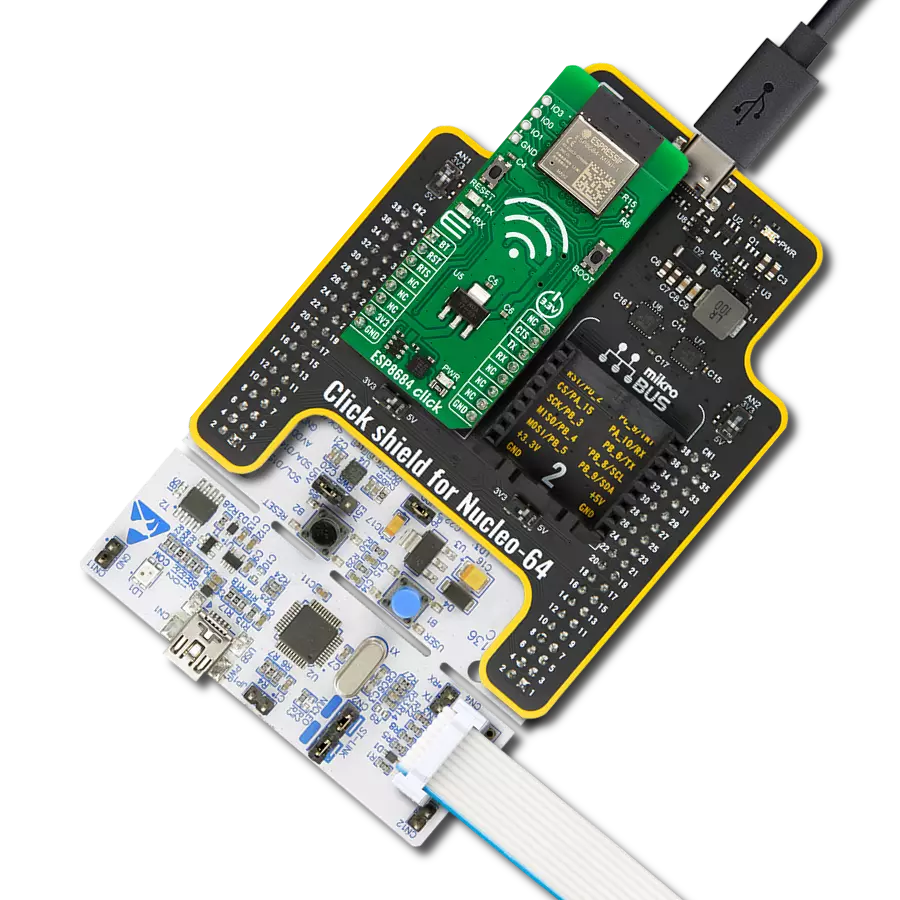
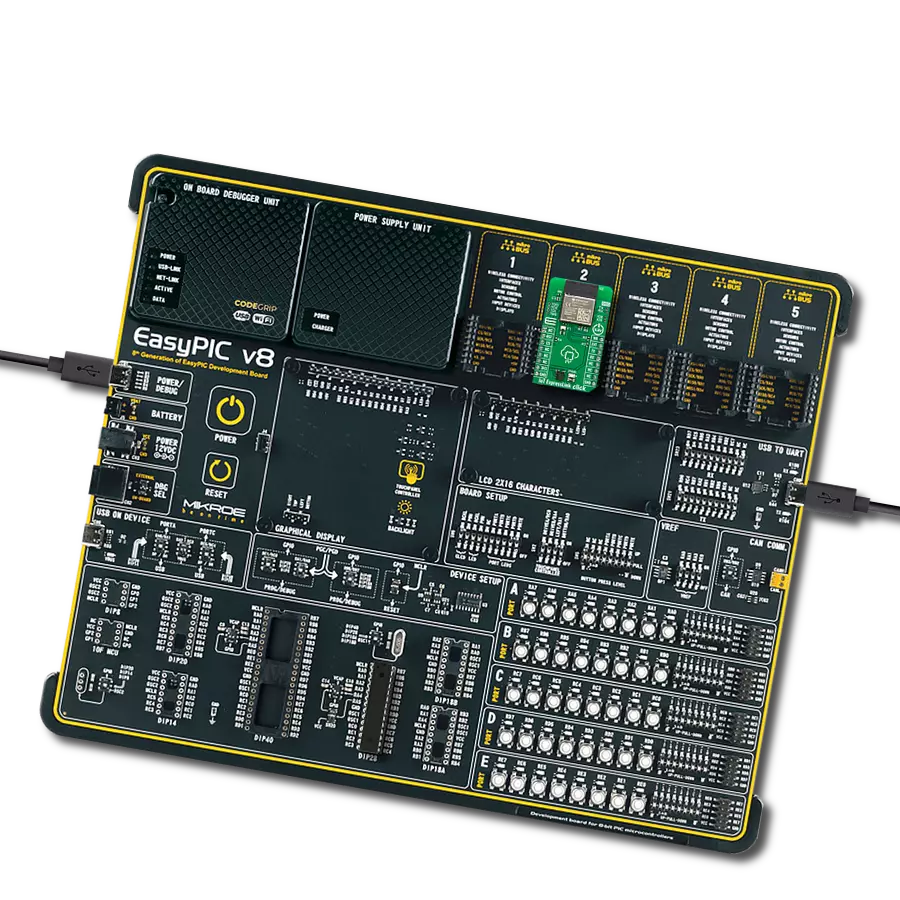
Development board
Nucleo 32 with STM32F031K6 MCU board provides an affordable and flexible platform for experimenting with STM32 microcontrollers in 32-pin packages. Featuring Arduino™ Nano connectivity, it allows easy expansion with specialized shields, while being mbed-enabled for seamless integration with online resources. The
board includes an on-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer, supporting USB reenumeration with three interfaces: Virtual Com port, mass storage, and debug port. It offers a flexible power supply through either USB VBUS or an external source. Additionally, it includes three LEDs (LD1 for USB communication, LD2 for power,
and LD3 as a user LED) and a reset push button. The STM32 Nucleo-32 board is supported by various Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IAR™, Keil®, and GCC-based IDEs like AC6 SW4STM32, making it a versatile tool for developers.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
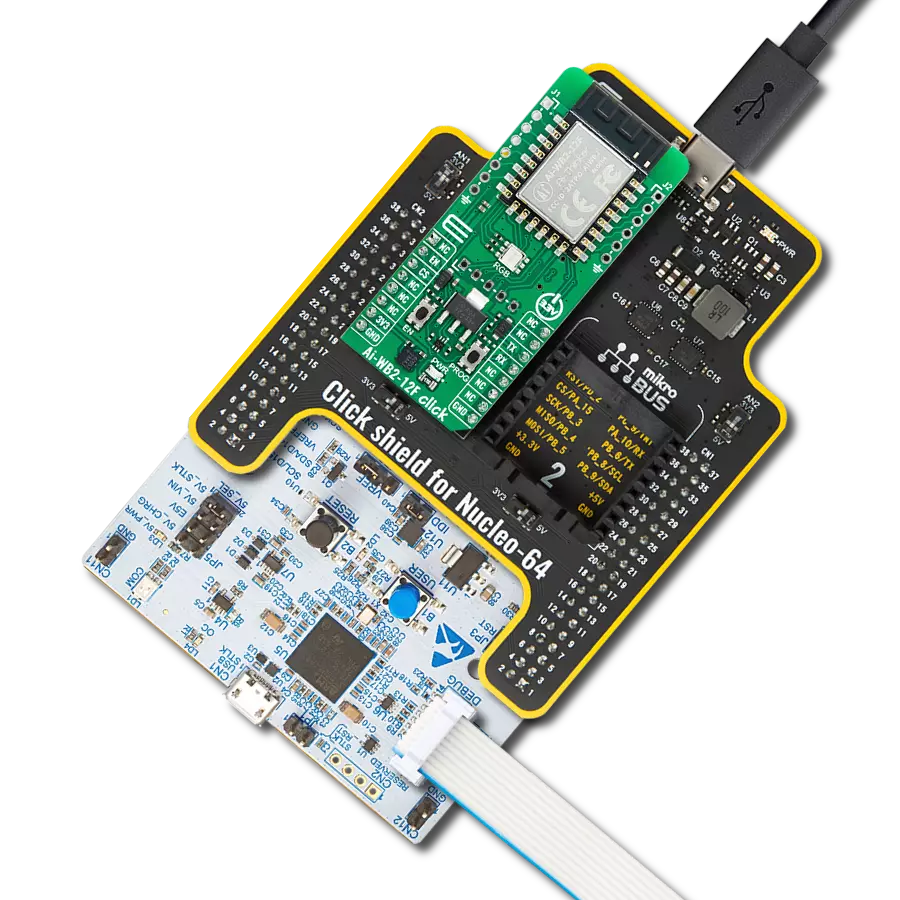
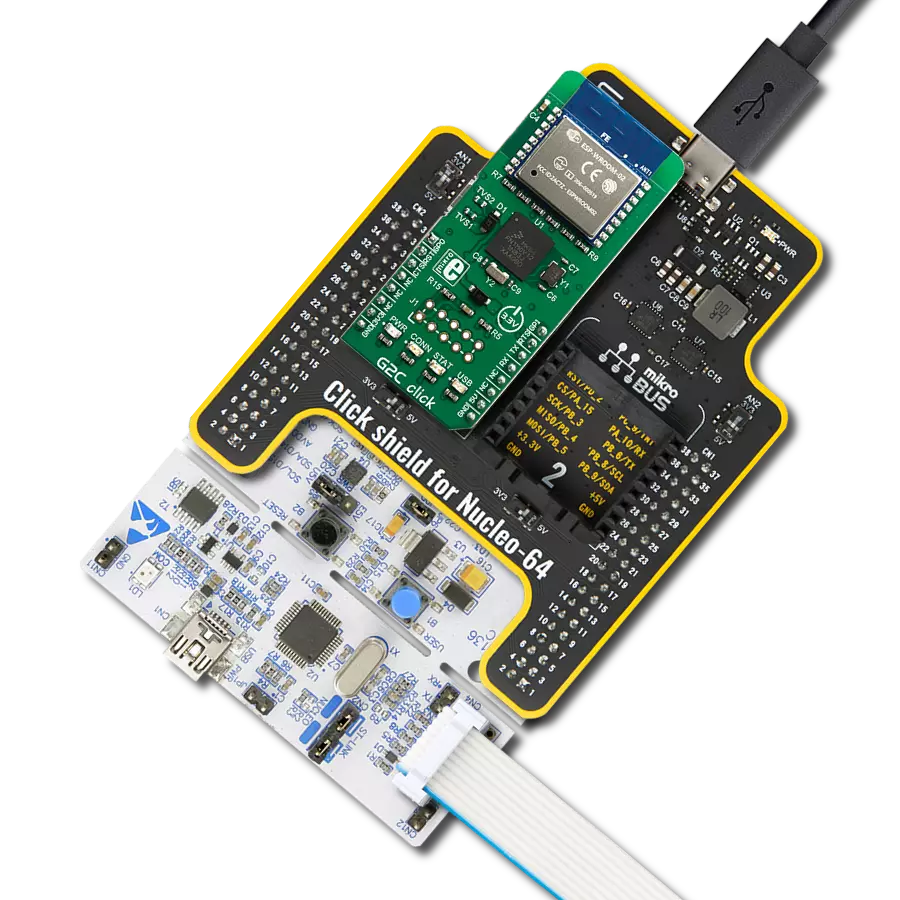
Accessories
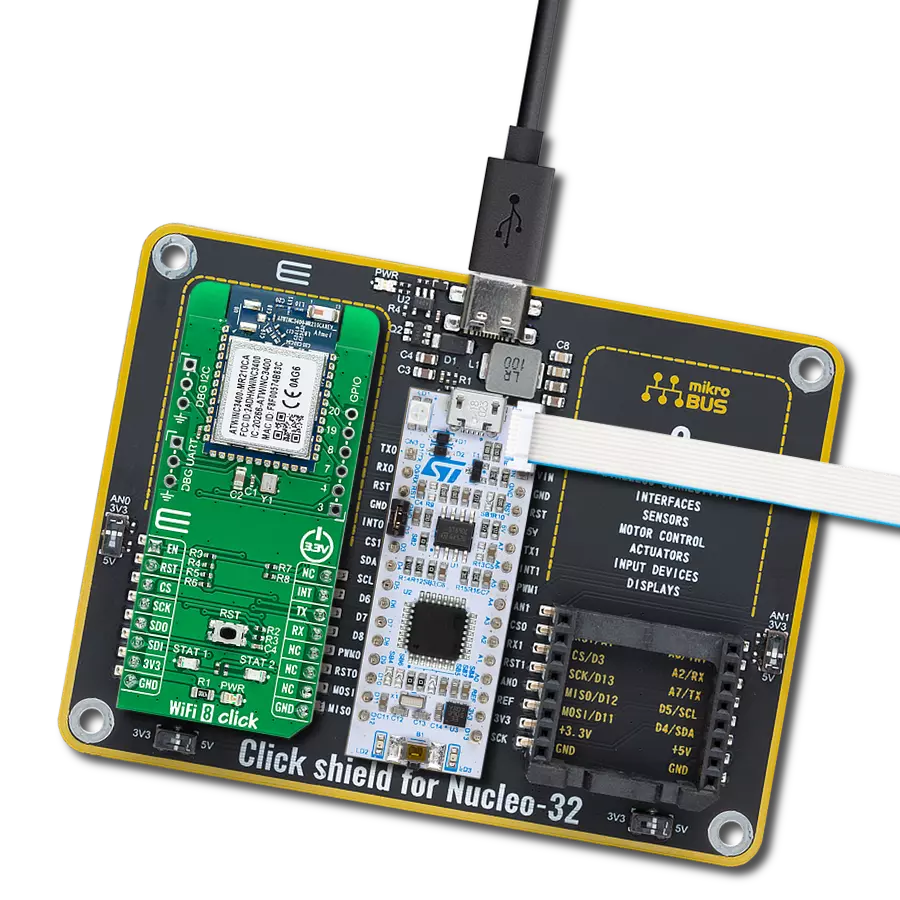
Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is the perfect way to expand your development board's functionalities with STM32 Nucleo-32 pinout. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 provides two mikroBUS™ sockets to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™. We are fully stocked with everything, from sensors and WiFi transceivers to motor control and audio amplifiers. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is compatible with the STM32 Nucleo-32 board, providing an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new ideas and quickly create prototypes with any STM32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The STM32 Nucleo-32 boards do not require any separate probe as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer and come with the STM32 comprehensive software HAL library and various packaged software examples. This development platform provides users with an effortless and common way to combine the STM32 Nucleo-32 footprint compatible board with their favorite Click boards™ in their upcoming projects.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for WiFi NORA Click driver.
Key functions:
wifinora_hw_reset- This function is used to perform HW reset.wifinora_send_cmd- This function is used to send a desired command.wifinora_send_cmd_with_par- This function sends a desired command with the parameter.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief WiFi NORA Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of WiFi NORA Click board by processing
* the incoming data and displaying them on the USB UART.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver, tests the communication, and after that restarts the device, and performs example configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* It creates a connection to the TCP-UDP echo server, sends a message to it reads it back, displaces it on the UART terminal, and then closes the connection.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void wifinora_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static void wifinora_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t wifinora_process ( wifinora_t *ctx )
* - static err_t wifinora_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
* - static void wifinora_configure_for_example ( void )
* - static void wifinora_configure_for_example ( void )
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "wifinora.h"
// Message content
#define MESSAGE_CONTENT "WiFi NORA Click board - demo example."
// TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
// WiFi parameters
#define WIFI_SSID "MikroE Public"
#define WIFI_PWD "mikroe.guest"
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 200
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 200
static wifinora_t wifinora;
static log_t logger;
static err_t error_flag;
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
/**
* @brief WiFi NORA clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length.
* @note None.
*/
static void wifinora_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief WiFi NORA log application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer to USB UART.
* @note None.
*/
static void wifinora_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief WiFi NORA data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t wifinora_process ( void );
/**
* @brief Response check.
* @details This function checks for response and
* returns the status of response.
* @param[in] rsp Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -1 - Error response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
*/
static err_t wifinora_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp );
/**
* @brief Check for errors.
* @details This function checks for different types of
* errors and logs them on UART or logs the response if no errors occured.
* @param[in] error_flag Error flag to check.
*/
static void wifinora_error_check ( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief WiFi NORA configure for example function.
* @details This function is used to configure device for example.
*/
static void wifinora_configure_for_example ( void );
/**
* @brief WiFi NORA execute example function.
* @details This function executes TCP/UDP Example.
*/
static void wifinora_example ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
wifinora_cfg_t wifinora_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
wifinora_cfg_setup( &wifinora_cfg );
WIFINORA_MAP_MIKROBUS( wifinora_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == wifinora_init( &wifinora, &wifinora_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
wifinora_process( );
wifinora_clear_app_buf( );
// Hardware reset
wifinora_hw_reset( &wifinora );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_READY );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
// Communication check
wifinora_send_cmd( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
// Factory reset
wifinora_send_cmd( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USYFR );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
// Software reset
wifinora_send_cmd( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_SW_RESET );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_READY );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
wifinora_send_cmd( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_GMM );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
wifinora_configure_for_example( );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
wifinora_example( );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void wifinora_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static void wifinora_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t wifinora_process ( void )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t overflow_bytes = 0;
int32_t rx_cnt = 0;
int32_t rx_size = wifinora_generic_read( &wifinora, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( ( rx_size > 0 ) && ( rx_size <= APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) )
{
if ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
overflow_bytes = ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE;
app_buf_len = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - rx_size;
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ overflow_bytes ], app_buf_len );
memset ( &app_buf[ app_buf_len ], 0, overflow_bytes );
}
for ( rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ app_buf_len++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
}
}
return WIFINORA_OK;
}
return WIFINORA_ERROR;
}
static err_t wifinora_rsp_check ( uint8_t *rsp )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 120000;
wifinora_clear_app_buf( );
wifinora_process( );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, rsp ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, WIFINORA_RSP_ERROR ) ) )
{
wifinora_process( );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > timeout )
{
wifinora_clear_app_buf( );
return WIFINORA_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
wifinora_process( );
if ( strstr( app_buf, rsp ) )
{
return WIFINORA_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, WIFINORA_RSP_ERROR ) )
{
return WIFINORA_ERROR_CMD;
}
else
{
return WIFINORA_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
}
static void wifinora_error_check ( err_t error_flag )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case WIFINORA_OK:
{
wifinora_log_app_buf( );
break;
}
case WIFINORA_ERROR:
{
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
}
case WIFINORA_ERROR_TIMEOUT:
{
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
}
case WIFINORA_ERROR_CMD:
{
log_error( &logger, " ERROR Response!" );
break;
}
case WIFINORA_ERROR_UNKNOWN:
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " Unknown!" );
break;
}
}
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
static void wifinora_configure_for_example ( void )
{
uint8_t command_data[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
#define WLAN_HANDLE "0"
strcpy( command_data, WLAN_HANDLE );
strcat( command_data, ",\"" );
strcat( command_data, WIFI_SSID );
strcat( command_data, "\"" );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_UWSCP, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_UWSIPD, "0" );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
#define WPA_THRESHILD "0"
strcpy( command_data, WLAN_HANDLE );
strcat( command_data, ",\"" );
strcat( command_data, WIFI_PWD );
strcat( command_data, "\"," );
strcat( command_data, WPA_THRESHILD );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_UWSSW, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_UWSC, "0" );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
#define CONNECTED "+UENEU"
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( CONNECTED );
}
static void wifinora_example ( void )
{
uint8_t command_data[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
#define TCP_CLIENT "0"
#define UDP_CLIENT "1"
#define READ_LEN "255"
log_printf( &logger, " TCP Example \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
#define TCP_PROTOCOL "6"
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOCR, TCP_PROTOCOL );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
strcpy( command_data, TCP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, REMOTE_PORT );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOC, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, " Send data \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
strcpy( command_data, TCP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, ",\"" );
strcat( command_data, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
strcat( command_data, "\"" );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOWS, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, " Read data \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
strcpy( command_data, TCP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, READ_LEN );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USORS, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
// 10 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " UDP Example \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
#define UDP_PROTOCOL "17"
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOCR, UDP_PROTOCOL );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
strcpy( command_data, UDP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, REMOTE_IP );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, REMOTE_PORT );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOC, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, " Send data \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
strcpy( command_data, UDP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, ",\"" );
strcat( command_data, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
strcat( command_data, "\"" );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOWS, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, " Read data \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
strcpy( command_data, UDP_CLIENT );
strcat( command_data, "," );
strcat( command_data, READ_LEN );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USORS, command_data );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
log_printf( &logger, " Close sockets \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -\r\n" );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOCL, UDP_CLIENT );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
wifinora_send_cmd_with_par( &wifinora, WIFINORA_CMD_AT_USOCL, TCP_CLIENT );
error_flag = wifinora_rsp_check( WIFINORA_RSP_OK );
wifinora_error_check( error_flag );
// 10 seconds delay
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:WiFi