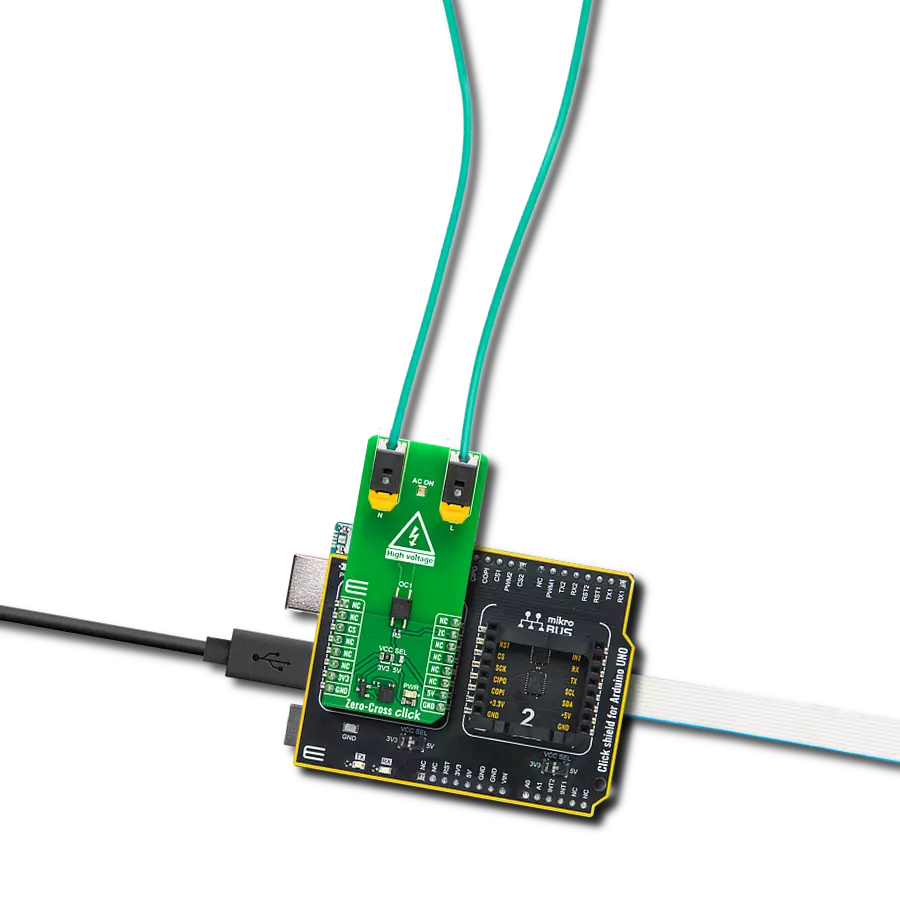
Designed for engineers and innovators, our sinusoidal change detection solution ensures that you capture every shift in your signal, empowering you to respond effectively to dynamic changes in your applications.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
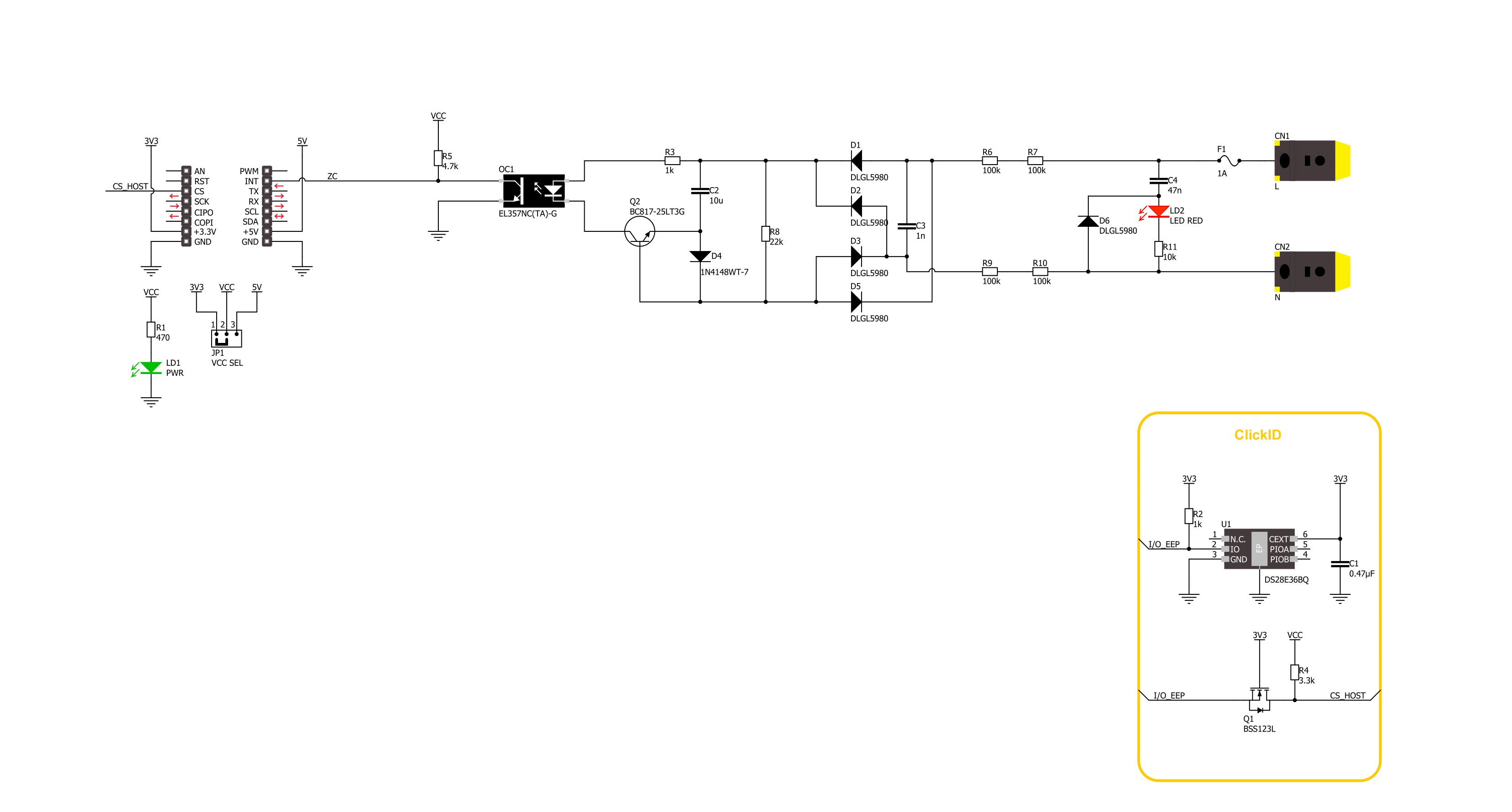
Zero-Cross Click is based on the circuitry that provides Zero Crossing Detection (ZCD). The alternate current can be connected over two block terminals. As it is intended for this Click board™ to work with high voltages, the critical components are placed on the bottom side, but still, take all precautions when working with this Click board™. On the top side is an AC ON LED to present the AC presence visually. All the magic is happening in
the circuitry at the bottom side of this Click board™. The current passes through the Graetz bridge circuitry, consisting of four DLGL5980. The alternate current converts to a direct current, which is necessary for driving an LED in an EL357N-G, a phototransistor photocoupler from Everlight. When activated, the optocoupler sends a LOW logic state to a ZC pin, the pin with which the Zero-Cross Click communicates with the
host MCU. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Fusion for PIC32 v8 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of Microchip's PIC32 microcontrollers regardless of their number of pins and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer over WiFi. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, Fusion for PIC32 v8 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere and under any circumstances at any time. Each part of the
Fusion for PIC32 v8 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module, which offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment, the board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. Communication options such as USB-UART, USB HOST/DEVICE, CAN (on the MCU card, if
supported), and Ethernet is also included. In addition, it also has the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and two display options for the TFT board line of products and character-based LCD. Fusion for PIC32 v8 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
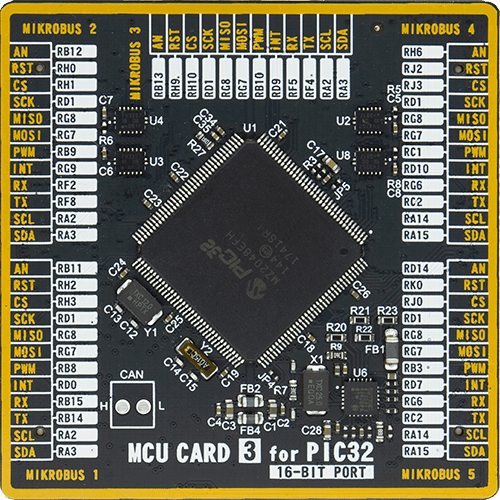
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
144
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Zero-Cross Click driver.
Key functions:
zerocross_pin_read- Zero-Cross pin reading function.zerocross_get_freq- Zero-Cross frequency reading function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Zero-Cross Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of the Zero-Cross Click board.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of the log UART and basic Click initialisation.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reading frequency value approximately once every second.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "zerocross.h"
static zerocross_t zerocross; /**< Zero-Cross Click driver object. */
static log_t logger; /**< Logger object. */
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
zerocross_cfg_t zerocross_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
zerocross_cfg_setup( &zerocross_cfg );
ZEROCROSS_MAP_MIKROBUS( zerocross_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( DIGITAL_OUT_UNSUPPORTED_PIN == zerocross_init( &zerocross, &zerocross_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float freq_val = 0;
zerocross_get_freq( &zerocross, &freq_val );
log_printf( &logger, " Freq %.2f Hz \n\r", freq_val );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END