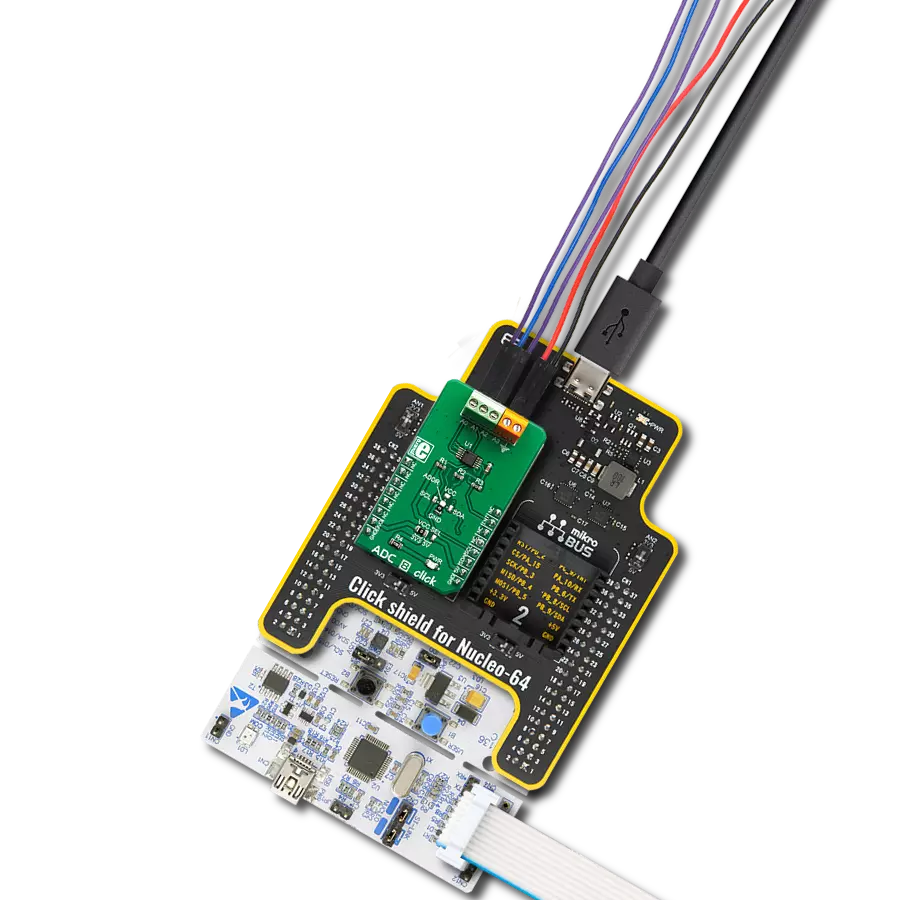
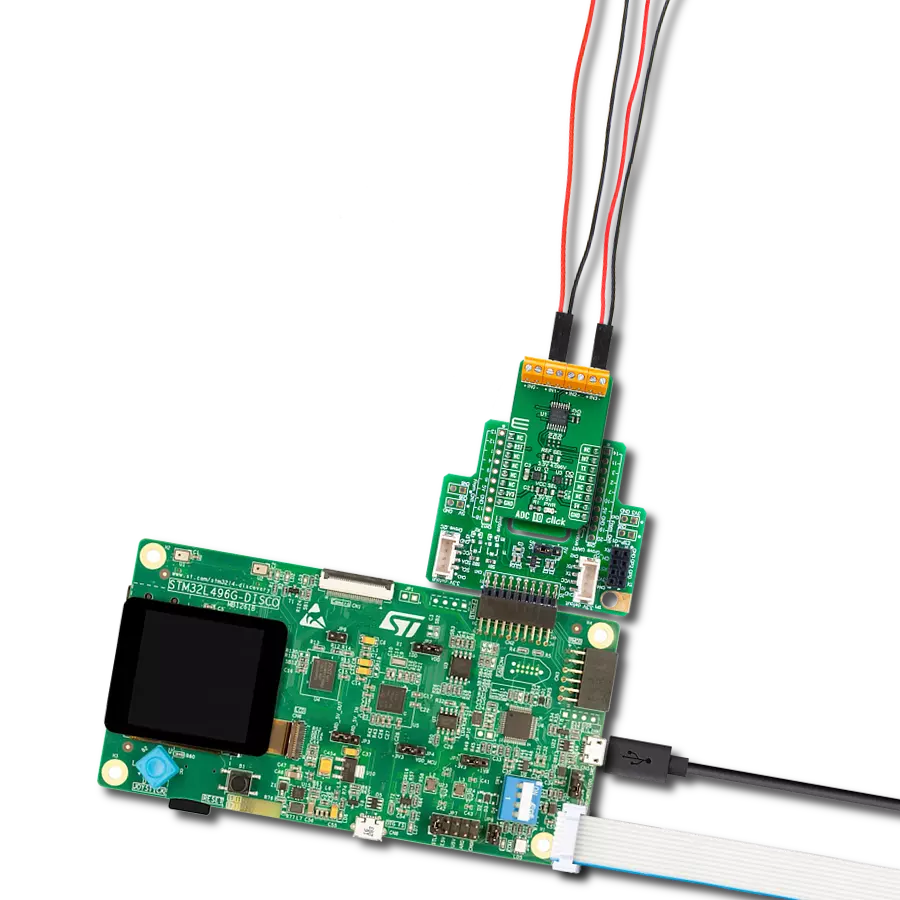
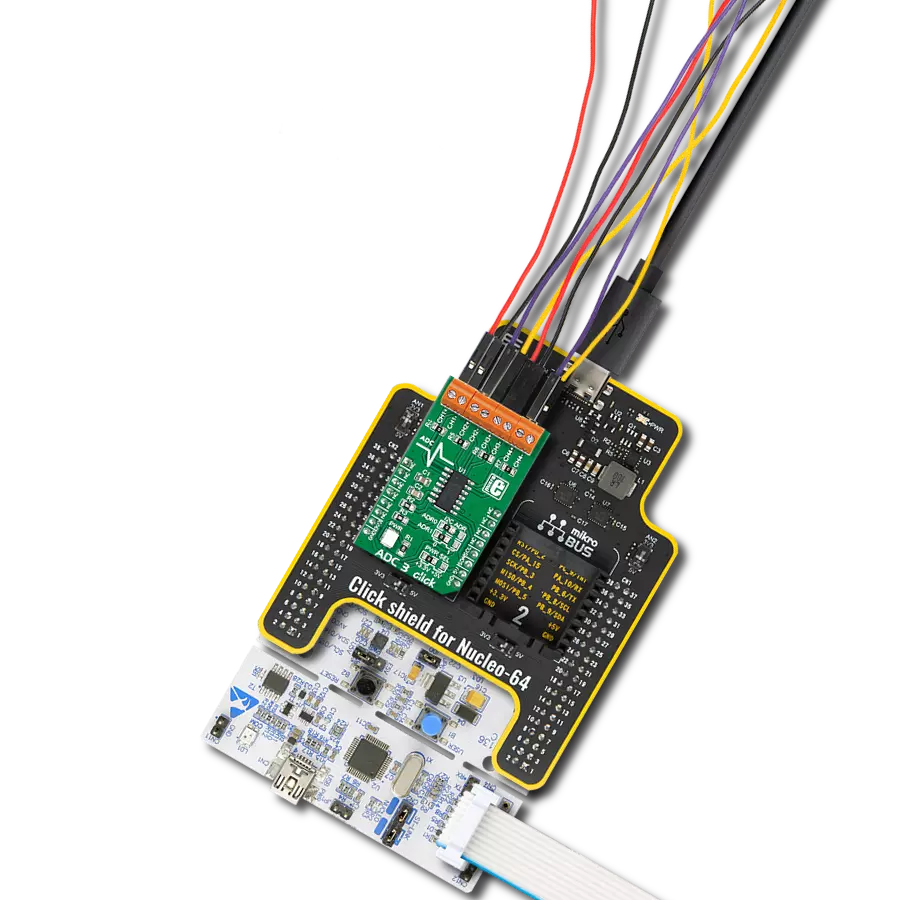
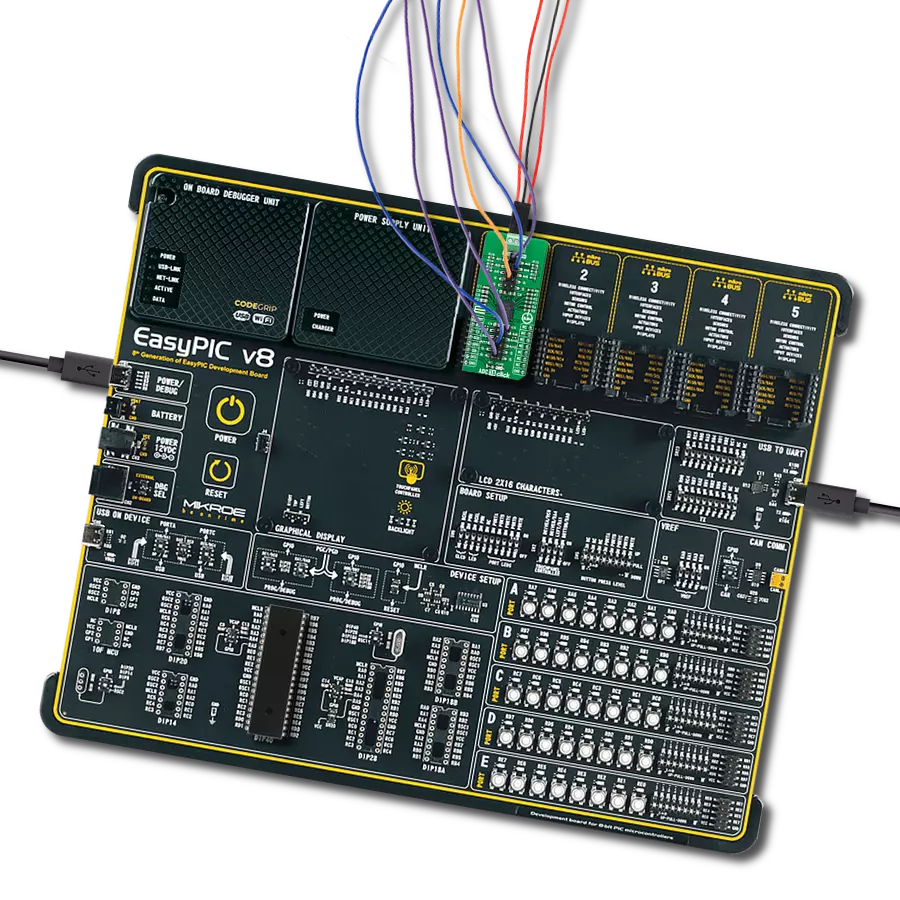
Unleash the power of isolation with our cutting-edge A/D converter!
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
ISO ADC 2 Click is based on the AD7091R, a 12-bit successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an isolated DC-DC converter from Analog Devices. This Click board™ allows single-supply operation and consists of active Analog Devices components: AD8616, a level shifting circuit; AD7091R, an ADC stage; and ADuM5401, an output isolation stage. The AD8616 is chosen for this application because of its low offset voltage, low bias current, and low noise. The output of the OpAmp is 0.1V to 2.4V, which matches the input range of the ADC (0V to 2.5V) with a 100mV safety margin to maintain linearity. A single-pole RC filter (R2/C9) follows the OpAmp output stage to reduce the out-of-band noise. The next part of the circuit is the AD7091R, ADC chosen because of its
ultralow power, which is significantly lower than any competitive A/D converter. It features a power-down option, implemented across the serial interface to save power between conversions, described in the Modes of Operation section in the datasheet. After a successful conversion, the ADC sends the data to the MCU through galvanic isolation provided by the ADuM5401 quad-channel digital isolator with an integrated DC-DC converter. The isolator has a secondary side controller architecture with isolated pulse-width modulation (PWM) feedback, and it works on the principle common to most switching power supplies. The ISO ADC 2 Click communicates with MCU using the 3-wire SPI serial interface that operates at clock rates up to 50MHz used for accessing data from the result register
and controlling the device's modes of operation. The CONVST signal of the AD7091R routed to the RST pin on the mikroBUS™ is used to initiate the conversion process, data acquisition, and select the operation mode. This ADC requires the user to initiate a software reset upon Power-Up, and it should be noted that failure to apply the correct software reset command may result in a device malfunction. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
Features overview
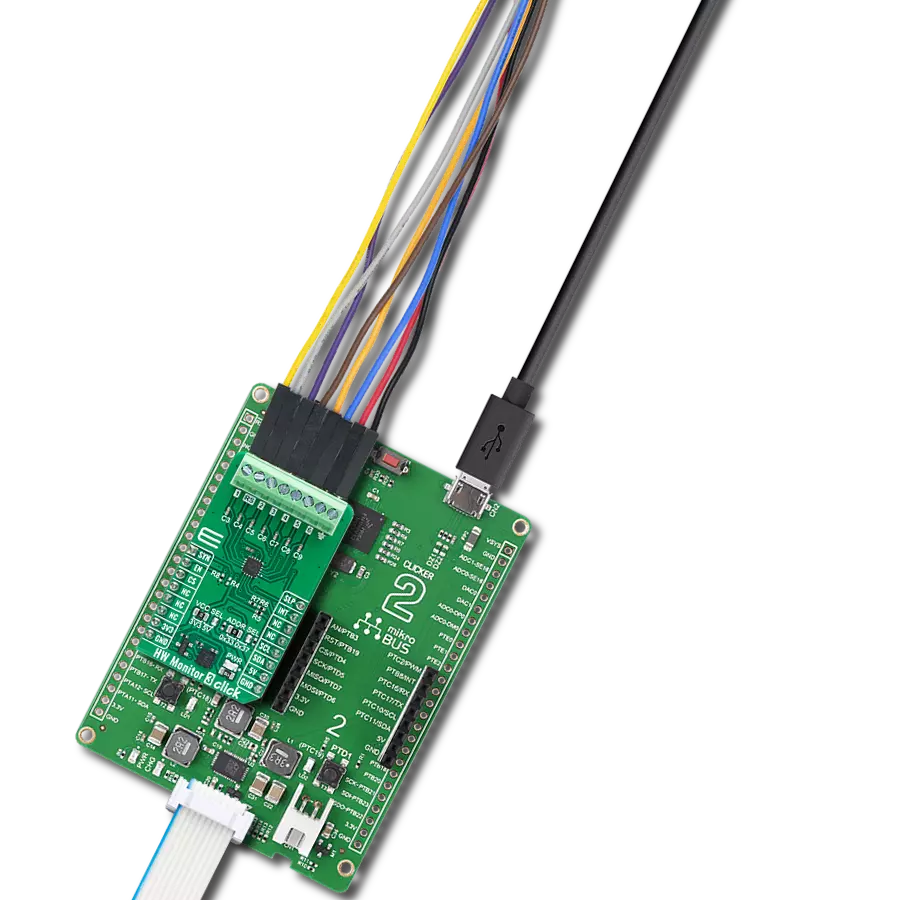
Development board
Kinetis Clicker is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 microcontroller, the MK22FN512VLH12 from NXP Semiconductor, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a mikroProg connector, and a header for interfacing with external electronics. Thanks to its compact design with clear and easy-recognizable silkscreen markings, it provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access
anywhere and under any circumstances. Each part of the Kinetis Clicker development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Kinetis Clicker programming method, using USB HID mikroBootloader, or through an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. The USB-MiniAB connection provides up to 500mA of current, which is more than enough to operate all
onboard and additional modules. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several buttons and LED indicators. Kinetis Clicker is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
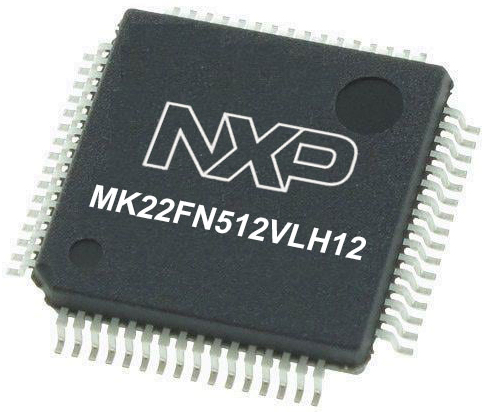

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
512
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
64
RAM (Bytes)
131072
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

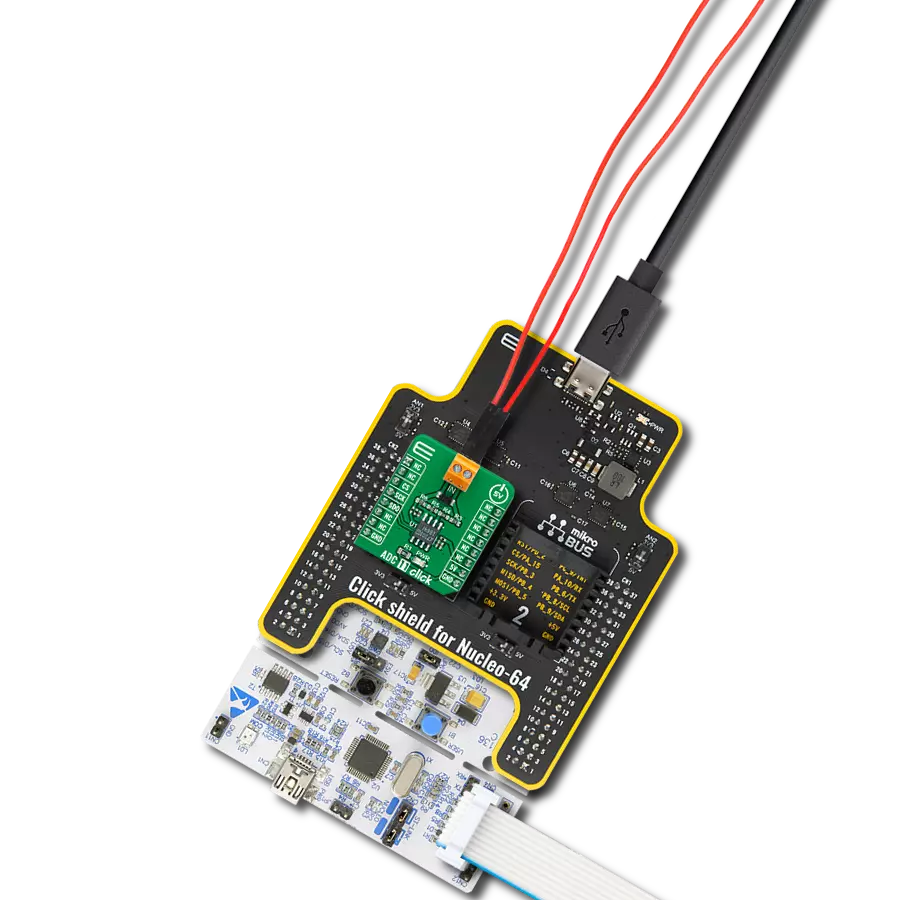
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ISO ADC 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
uint16_t isoadc2_read_adc ( void )Function for reading 12bit ADC datauint16_t isoadc2_get_mv ( uint16_t adc_data )Function for converting ADC to mV data
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief IsoAdc2 Click example
*
* # Description
* This is an example that demonstrates the use of the ISO ADC 2 Click board.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of SPI module and additional GPIO pins.
*
* ## Application Task
* Every second reads ADC data and voltage in mV and logs result.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "isoadc2.h"
static isoadc2_t isoadc2;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void ) {
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
isoadc2_cfg_t isoadc2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
isoadc2_cfg_setup( &isoadc2_cfg );
ISOADC2_MAP_MIKROBUS( isoadc2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = isoadc2_init( &isoadc2, &isoadc2_cfg );
if ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == init_flag ) {
log_error( &logger, " Application Init Error. " );
log_info( &logger, " Please, run program again... " );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void ) {
uint16_t rx_data;
uint16_t mv_data;
isoadc2_read_adc( &isoadc2, &rx_data );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
isoadc2_get_mv( &isoadc2, &mv_data );
log_printf( &logger, " ADC: %d \r\n", rx_data );
log_printf( &logger, " VIN: %d mV\r\n", mv_data );
log_printf( &logger, "---------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END