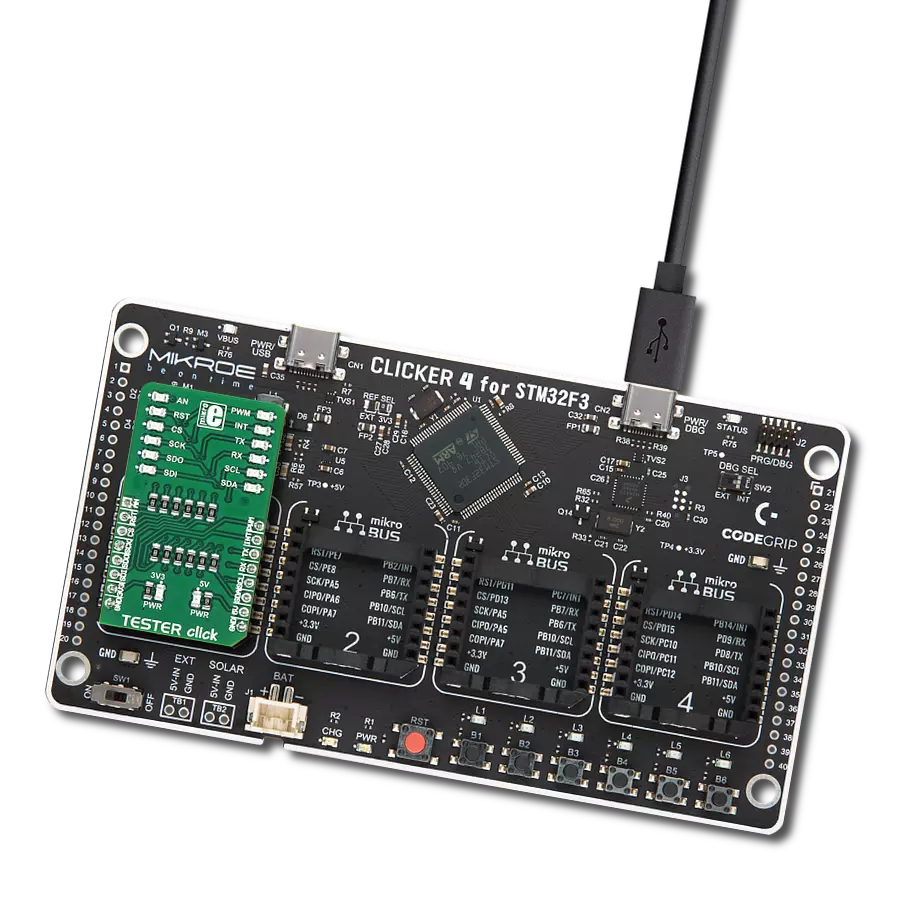
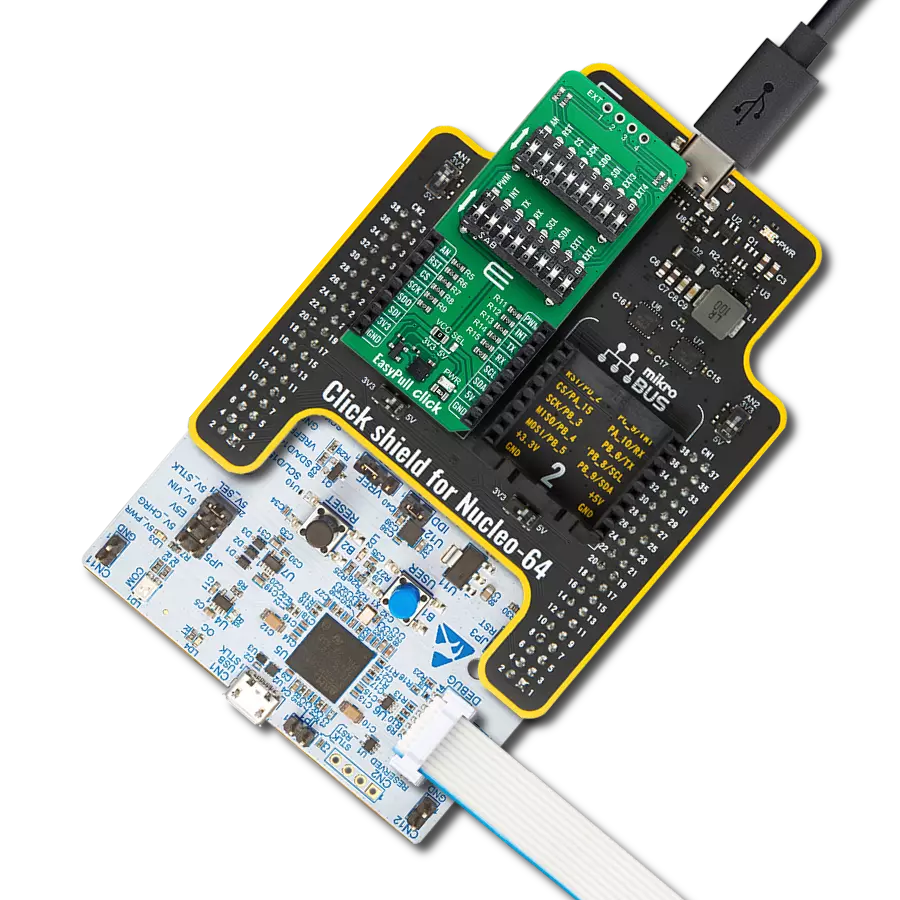
Configure used mikroBUS™ signals within applications to be either in a pull-up or pull-down state
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
EasyPull Click is a compact add-on board designed to empower users to easily configure used mikroBUS™ signals within their applications to be either in a pull-up or pull-down state. This board is equipped with two 8-position switches that enable the pull-up or pull-down configuration for mikroBUS™ signals such as AN, RST, PWM, and INT, as well as for communication protocols like SPI, UART, and I2C. All resistors on the EasyPull Click are set to 4.7kΩ, ensuring consistent performance across various signal lines. Whether for prototyping or final product development, EasyPull Click provides developers with a practical tool for enhancing their projects with reliable signal management capabilities. Configuring the signal lines to the desired state is straightforward, thanks to the clear directional arrows on each switch's left
side. These arrows indicate the direction to toggle the switch to achieve either a pull-up (upward direction) or pull-down (downward direction) state. This feature allows for quick and easy adjustments, enhancing the board's usability and flexibility in different project setups. Additionally, the EasyPull Click board™ offers an unpopulated header marked as EXT, which extends four signals from the switches - two from each - labeled as EXTx. This header can be used as a conventional GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) signal according to the user's requirements. The board also includes two sets of unmarked resistors at the top, connected to the EXT signals, maintaining the 4.7kΩ resistance value consistent with the rest of the board. A unique feature of the EasyPull Click is its low-power mode capability, achieved by cutting
the ID CUT traces on the back of the board. The connection to the lower section of the board, which includes the power (PWR) LED and ID chip, is interrupted by cutting these lines. This action results in significant energy savings, making the EasyPull Click an excellent choice for energy-sensitive applications that require efficient power management. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
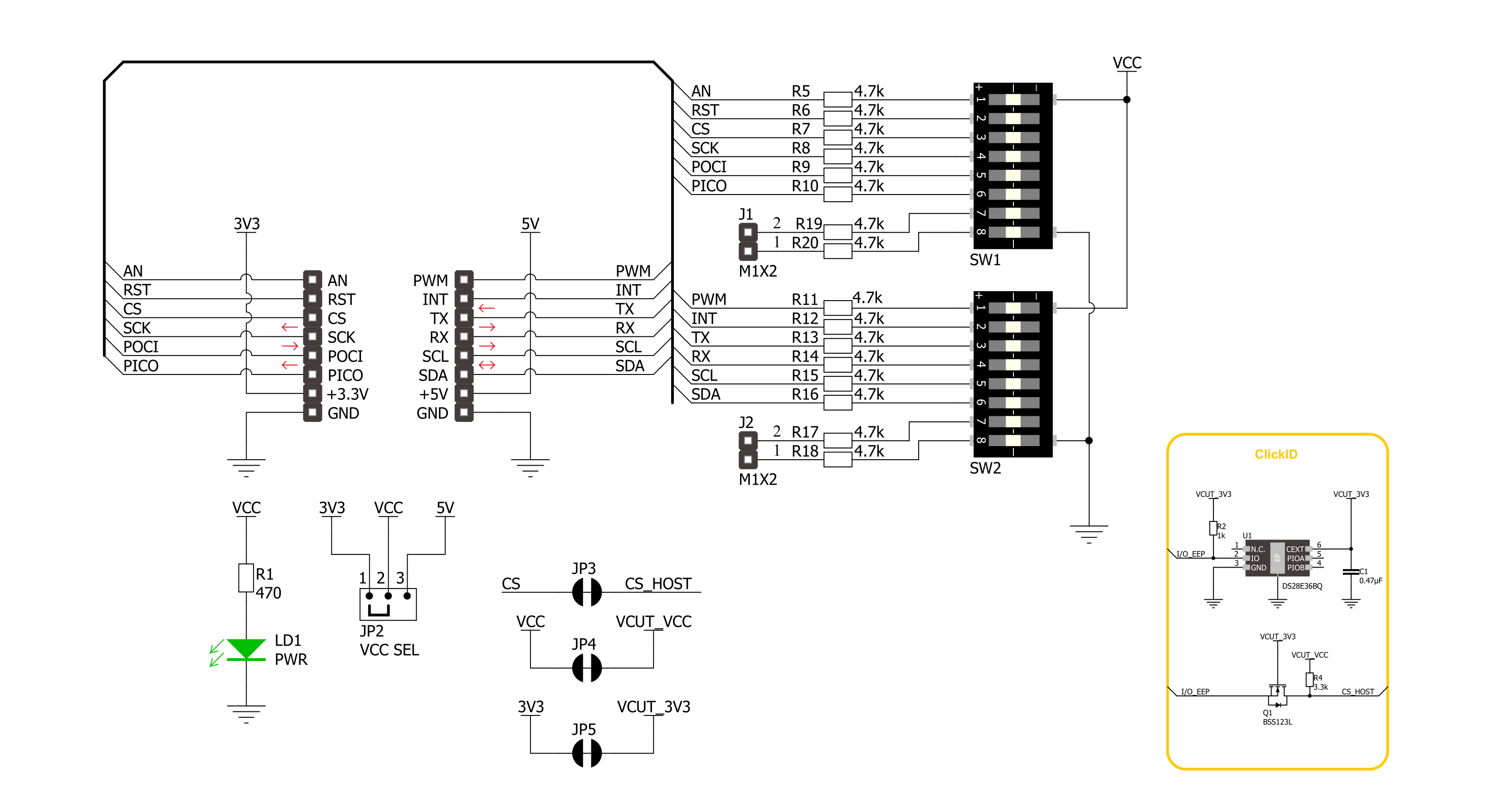
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for EasyPull Click driver.
Key functions:
easypull_get_an_pin- This function reads the state of the AN pin of EasyPull click boardeasypull_get_rst_pin- This function reads the state of the RST pin of EasyPull click boardeasypull_get_cs_pin- This function reads the state of the CS pin of EasyPull click board
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief EasyPull Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of EasyPull Click boards.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and USB UART logger.
*
* ## Application Task
* It checks the state of the pins and displays their state on the USB UART.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "easypull.h"
static easypull_t easypull; /**< EasyPull Click driver object. */
static log_t logger; /**< Logger object. */
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
easypull_cfg_t easypull_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
easypull_cfg_setup( &easypull_cfg );
EASYPULL_MAP_MIKROBUS( easypull_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( DIGITAL_OUT_UNSUPPORTED_PIN == easypull_init( &easypull, &easypull_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
if ( EASYPULL_PIN_STATE_HIGH == easypull_get_an_pin( &easypull ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " AN pin state: HIGH \n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " AN pin state: LOW \n" );
}
if ( EASYPULL_PIN_STATE_HIGH == easypull_get_rst_pin( &easypull ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " RST pin state: HIGH \n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " RST pin state: LOW \n" );
}
if ( EASYPULL_PIN_STATE_HIGH == easypull_get_cs_pin( &easypull ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " CS pin state: HIGH \n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " CS pin state: LOW \n" );
}
if ( EASYPULL_PIN_STATE_HIGH == easypull_get_pwm_pin( &easypull ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " PWM pin state: HIGH \n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " PWM pin state: LOW \n" );
}
if ( EASYPULL_PIN_STATE_HIGH == easypull_get_int_pin( &easypull ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " INT pin state: HIGH \n" );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, " INT pin state: LOW \n" );
}
log_printf( &logger, "- - - - - - - - - - - - - \r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END