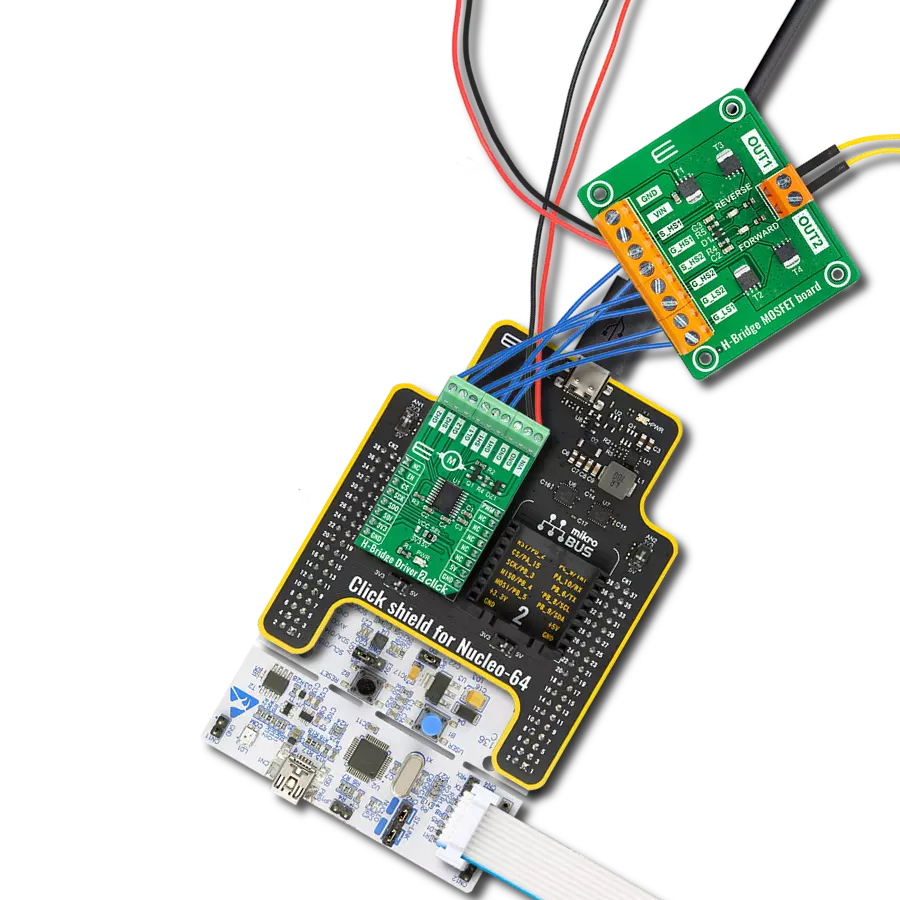
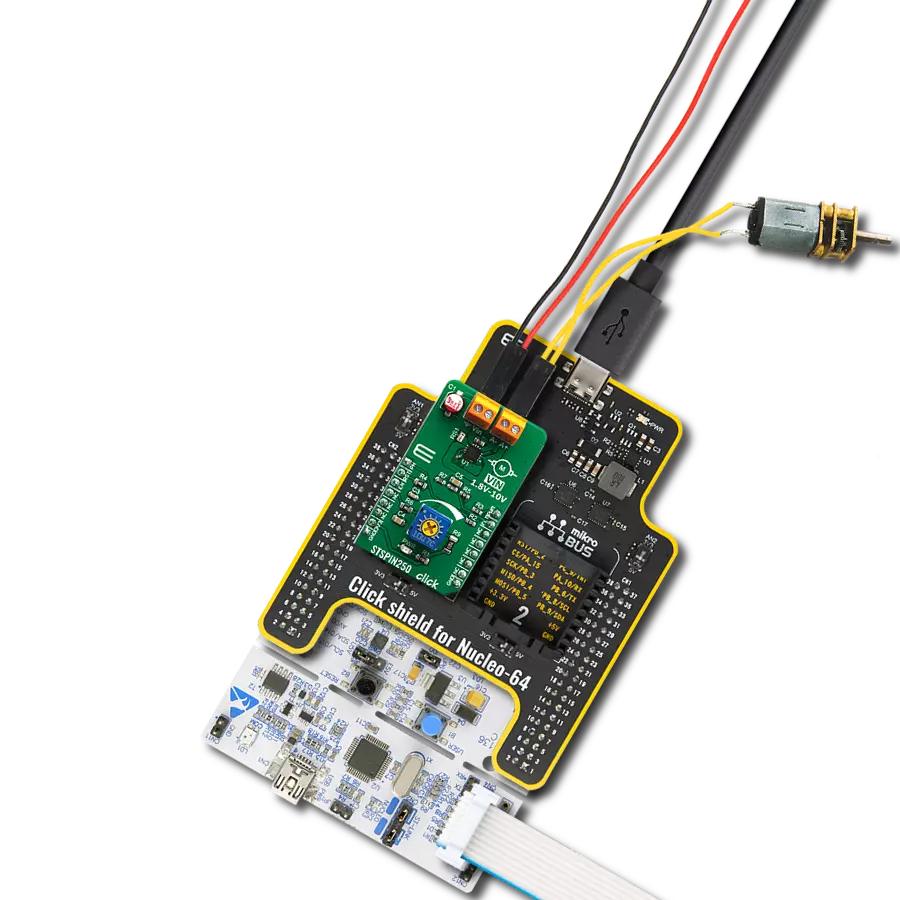
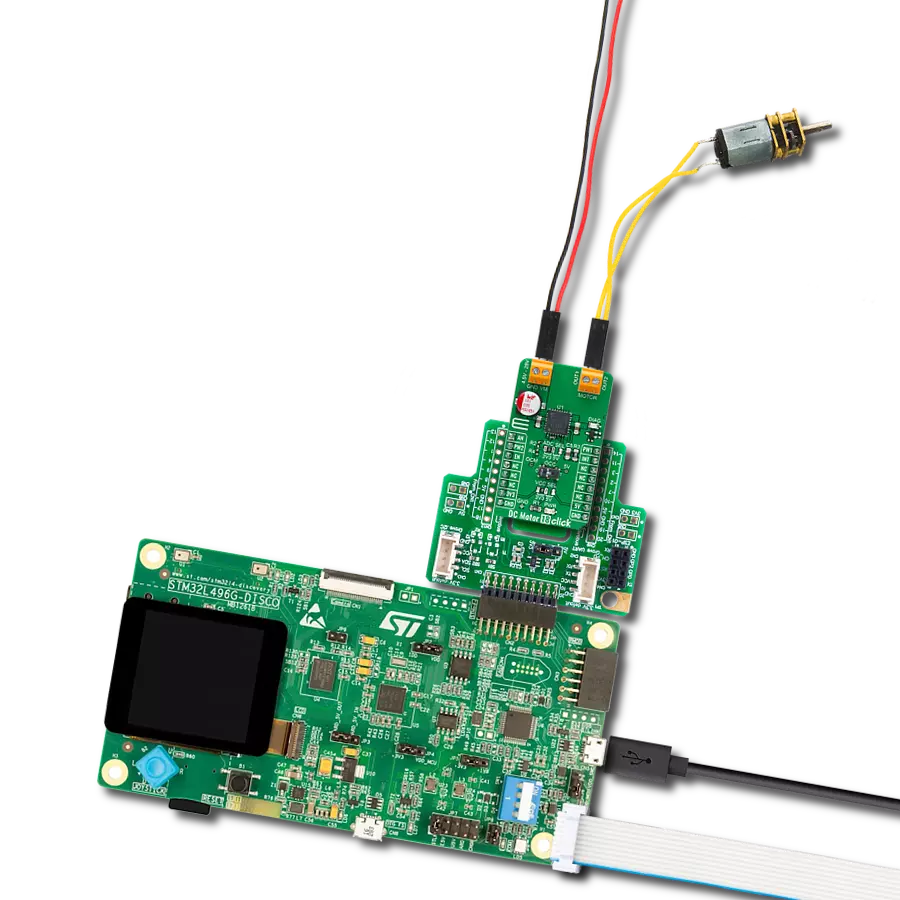
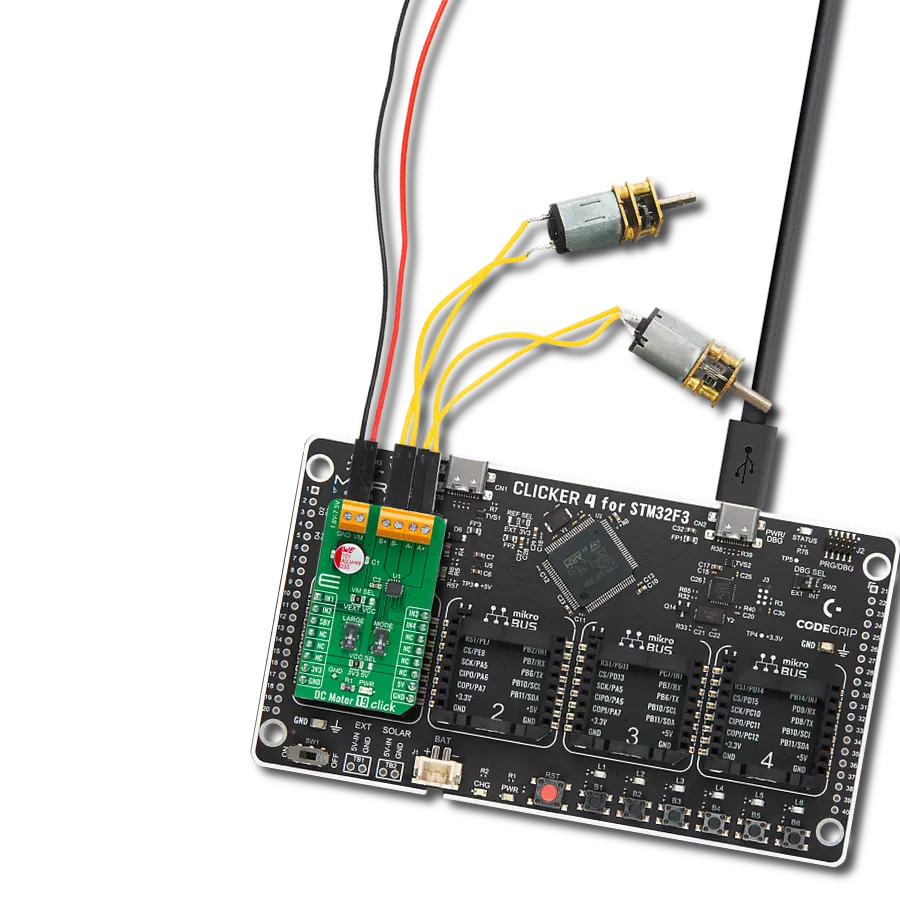
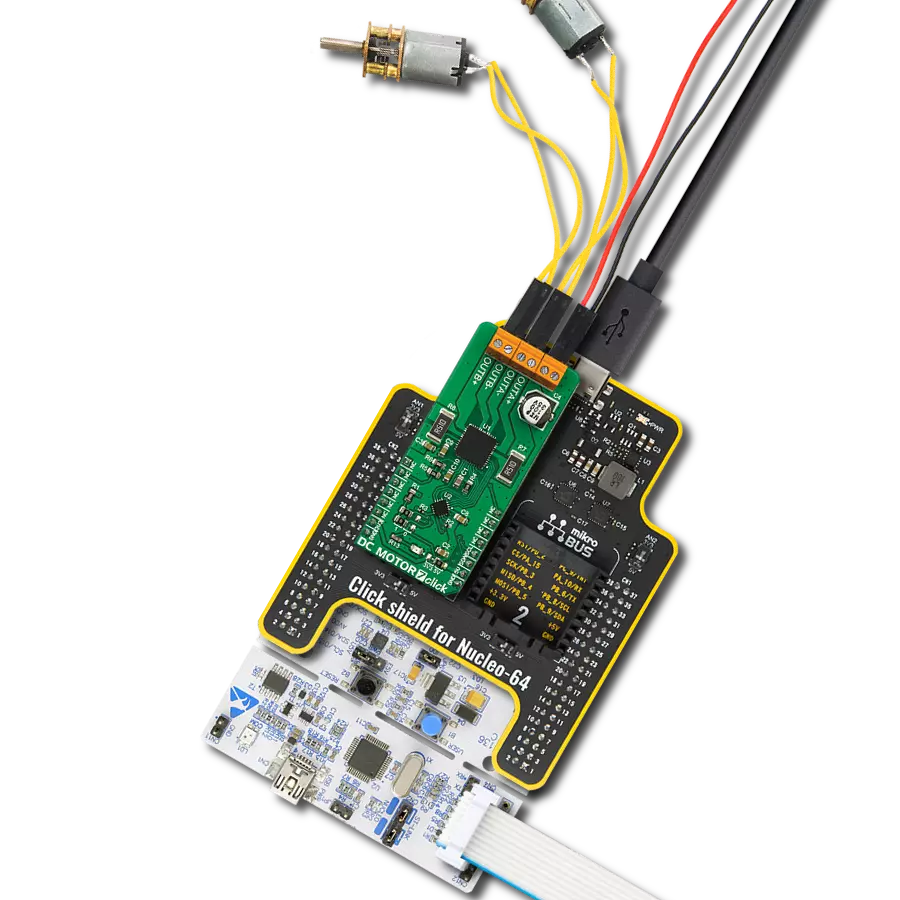
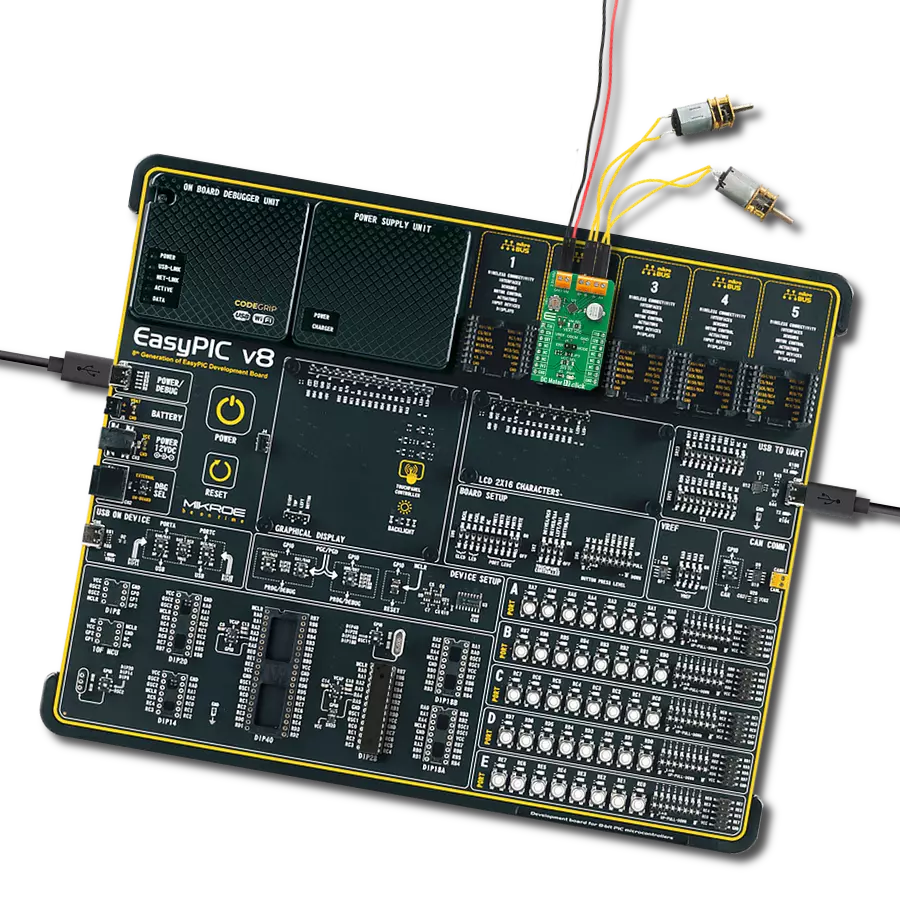
Unlock speed control possibilities with our PWM-controlled DC motor solution
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
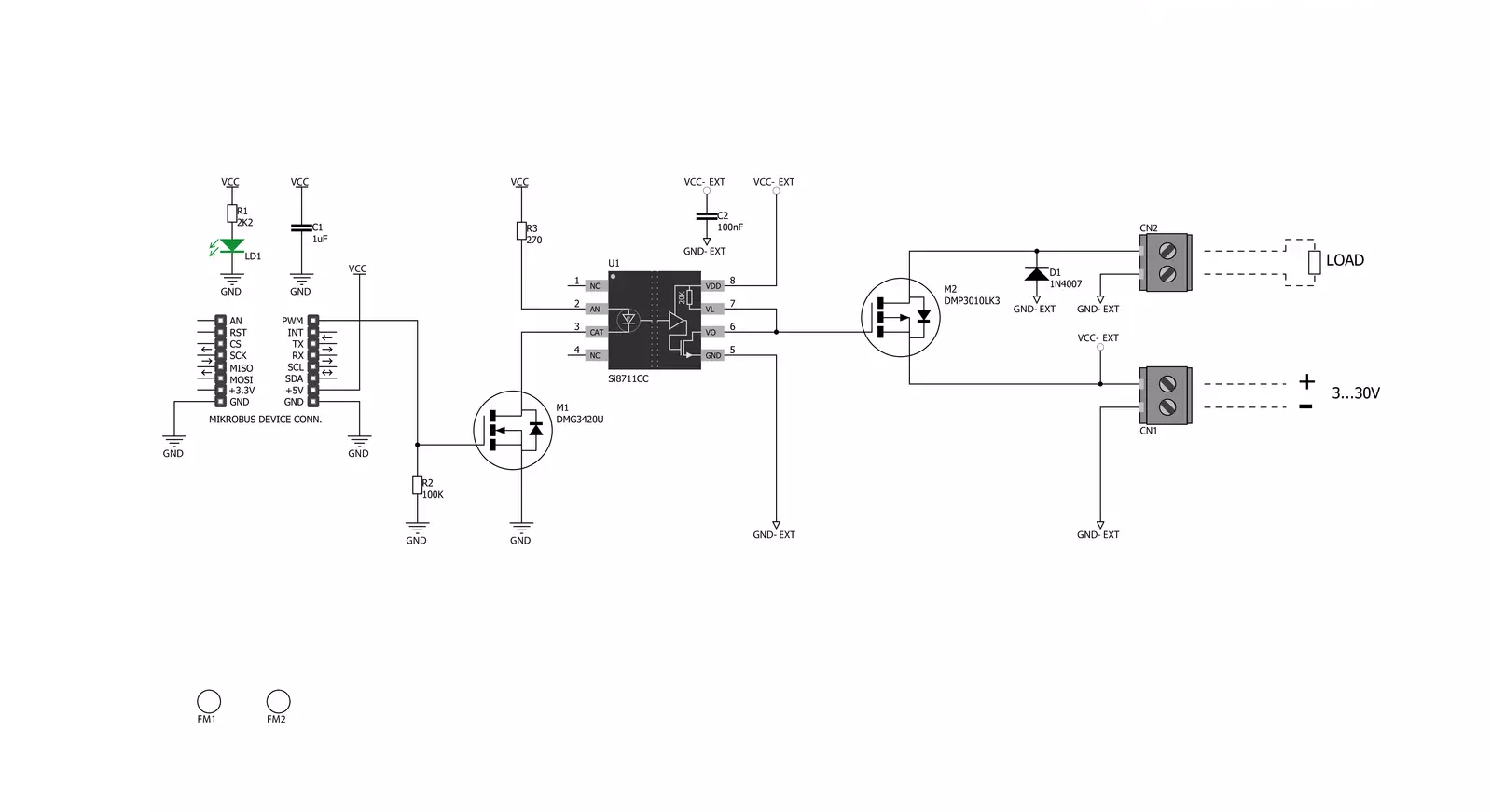
PWM driver Click is based on the Si8711CC, a 5kV LED emulator input, open collector output isolator from Skyworks. Compared to the optocouplers, the Si8711CC is more resistant to temperature, age, and forward current effects. It has a longer service life, higher common-mode transient immunity, and more. The Si8711CC is based on proprietary CMOS isolation technology for low-power, high-speed operation and is resistant to wear-out effects that, in the case of optocouplers, degrade the performance. The Si8711CC features up to 5000VRMS isolation and 10kV surge protection, making it a perfect isolator. For controlling the devices, it is capable of data rates DC of up to 15Mbps, with a propagation delay of 30ns. The Si8711CC controls the loads over the DMP3010LK3,
a P-channel enhancement mode MOSFET from Diodes Incorporated. This fast-switching diode has ESD protected gate, low input capacitance, and low on-resistance, designed to maintain superior switching performance, making it ideal for high-efficiency power management applications. The PWM Driver Click comes with the screw terminals labeled LOAD (+END, -END) to connect the load, which the Si7811CC controls over the DMP3010LK3 diode, and EXT for external power supply. It is not recommended to use this Click board™ with loads over 50W as the MOSFET can get overheated; this, however, does not apply if the Click board™ is used as an ON/OFF switch. The PWM Driver Click is controlled by the host MCU by PWM pulses over the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. The PWM
pin does not have direct control over the Si8711CC but rather through the DMG3420U, an N-channel enhancement mode MOSFET from Diodes Incorporated. This diode shares many features with the one mentioned above, such as low on-resistance, low input capacitance, fast switching speed, and more. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 5V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for PWM driver Click driver.
Key functions:
pwmdriver_set_duty_cycle- Generic sets PWM duty cyclepwmdriver_pwm_stop- Stop PWM modulepwmdriver_pwm_start- Start PWM module
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file
* @brief PwmDriver Click example
*
* # Description
* This application is controls the speed DC motors.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver enables - GPIO, PWM initialization set PWM duty cycle and PWM frequency,
* start PWM, enable the engine, and start to write log.
*
* ## Application Task
* This is an example that demonstrates the use of the PWM driver Click board.
* This example shows the automatic control of PWM,
* the first increases duty cycle and then the duty cycle is falling.
* Results are being sent to the Usart Terminal where you can track their changes.
*
* *note:*
* EXT PWR 3-30VDC
*
* @author Nikola Peric
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "pwmdriver.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static pwmdriver_t pwmdriver;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
pwmdriver_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
pwmdriver_cfg_setup( &cfg );
PWMDRIVER_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
pwmdriver_init( &pwmdriver, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " Initialization PWM \r\n " );
pwmdriver_set_duty_cycle( &pwmdriver, 0.0 );
pwmdriver_pwm_start( &pwmdriver );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Task ----" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
static int8_t duty_cnt = 1;
static int8_t duty_inc = 1;
float duty = duty_cnt / 10.0;
pwmdriver_set_duty_cycle ( &pwmdriver, duty );
log_printf( &logger, "Duty: %d%%\r\n", ( uint16_t )( duty_cnt * 10 ) );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
if ( 10 == duty_cnt )
{
duty_inc = -1;
}
else if ( 0 == duty_cnt )
{
duty_inc = 1;
}
duty_cnt += duty_inc;
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END