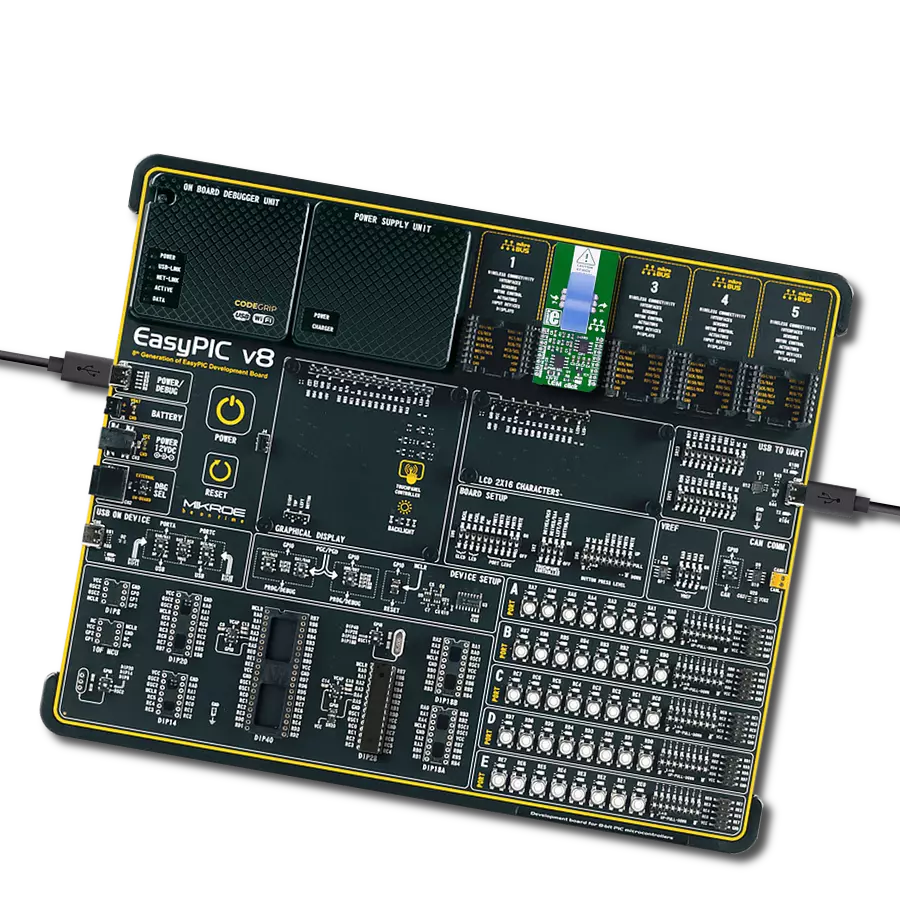
Our voltage-to-frequency technology empowers you to seamlessly convert voltage levels into highly accurate frequency signals, setting a new benchmark for signal synthesis and control
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
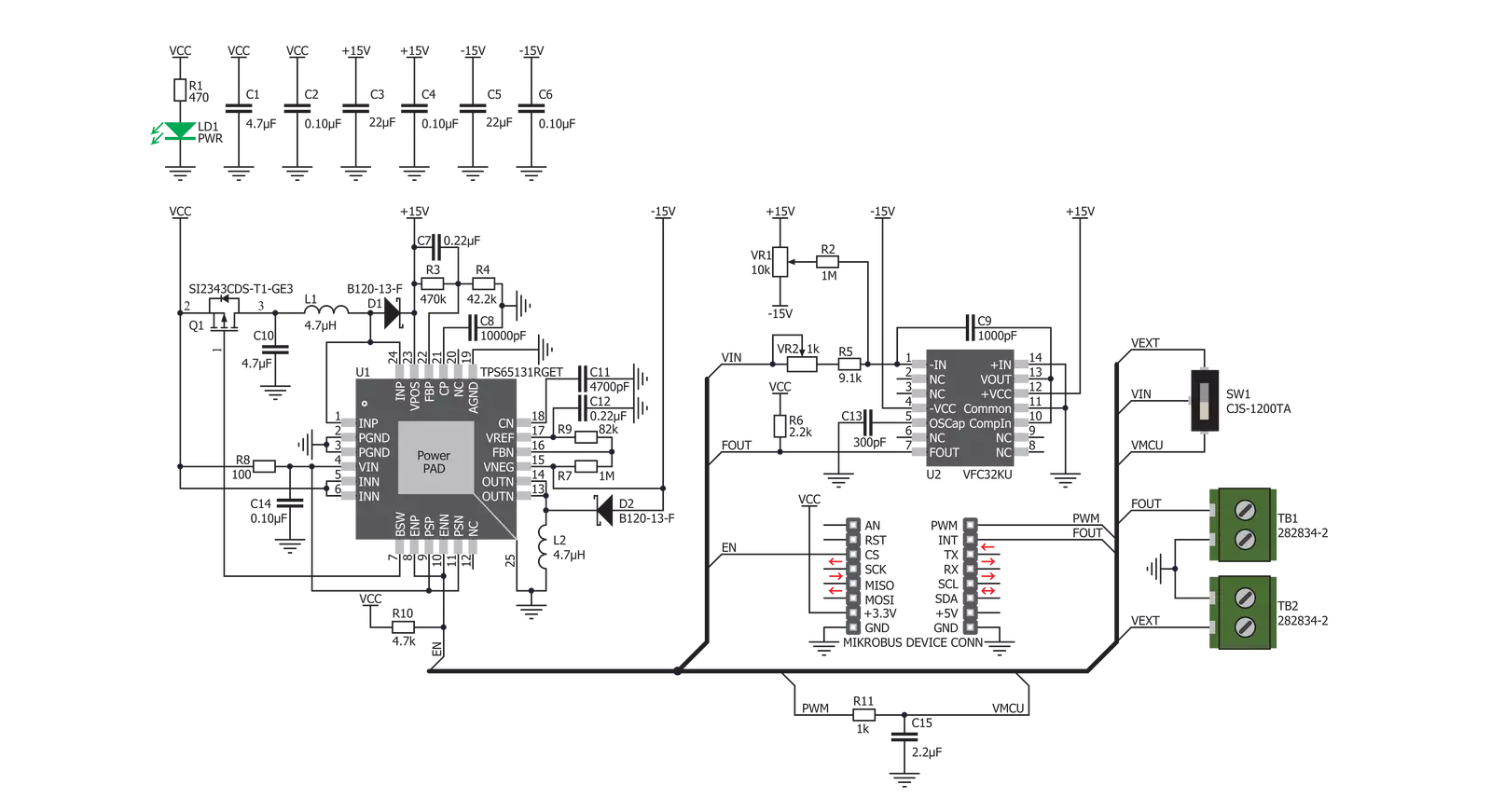
V to Hz 2 Click is based on the VFC32KU, a voltage-to-frequency and frequency-to-voltage converter from Texas Instruments. It accepts voltage at its input and generates a pulse train, with a frequency linearly proportional to the input voltage. The pulse train is routed to a screw terminal labeled as FOUT, as well as the mikroBUS™ INT pin, labeled as FO. The signal can be then further processed by the host MCU. When V to Hz 2 click is operated for the first time, it needs to be calibrated. The click is equipped with two variable resistors for gain and offset fine-tuning. A calibration procedure should be executed before the first use of the Click board™ since even slight variations in the components tolerances could affect the value at the output. It is recommended to correct the offset after longer
time intervals, to compensate for the aging of the passive components on the Click board™. It is done by introducing a known voltage at the input, and adjusting the gain and the offset, until the signal with the expected frequency appears on the output. As already discussed, V to Hz 2 click is equipped with the input voltage terminal (VEXT), which is used to connect the control voltage up to 3.3V. Besides having control voltage input on this terminal, it is possible to select the voltage generated by the MCU as the control voltage input, too. INPUT SEL switch can be set so that the PWM pin from the mikroBUS™ is used as the control voltage input. The PWM signal generated by the MCU is filtered out by the onboard low pass filter so that the control voltage remains constant. The VFC32KU IC requires a dual power supply with
±15V. Therefore, this Click board™ utilizes another IC in order to provide the required voltages. It uses the TPS65131, a positive and negative output DC/DC Converter, from Texas Instruments. This DC/DC converter has already been used in Boost-INV 2 click, so it was tested "on the field" for this purpose. Providing well-stabilized output with the plenty of power headroom, it is a perfect solution for the V to Hz 2 click, also. To enable the conversion circuitry, the EN pin of the TPS65131 boost converter should be pulled to a HIGH logic level. This will activate the boost converter and provide the required power for the VFC32KU IC. This pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ CS pin and it is labeled as EN.
Features overview
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for V To Hz 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
vtohz2_get_freq_out- Function gets the out frequency on mikrobus INT pinvtohz2_enable- Function performs enabling and disabling of the devicevtohz2_pwm_start- This function starts PWM module.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief VToHz2 Click example
*
* # Description
* This appliaction enables usage of a converter for analog voltage input signal into a pulse wave signal of a certain frequency.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes driver and enables the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Sets the output frequency by incrementing the pwm duty cycle from 0 to 100% in an infinite loop.
* Results are being sent to USB UART terminal.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "vtohz2.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static vtohz2_t vtohz2;
static log_t logger;
static float duty_cycle = 0.5;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
vtohz2_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
vtohz2_cfg_setup( &cfg );
VTOHZ2_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
vtohz2_init( &vtohz2, &cfg );
vtohz2_enable( &vtohz2, VTOHZ2_ENABLE );
vtohz2_pwm_start( &vtohz2 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
for ( duty_cycle = 0; duty_cycle <= 1.0; duty_cycle += 0.01 )
{
vtohz2_set_duty_cycle ( &vtohz2, duty_cycle );
log_printf( &logger," PWM Duty: %.2f%%\r\n", duty_cycle * 100 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
log_printf( &logger, "------------------------------\r\n" );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END