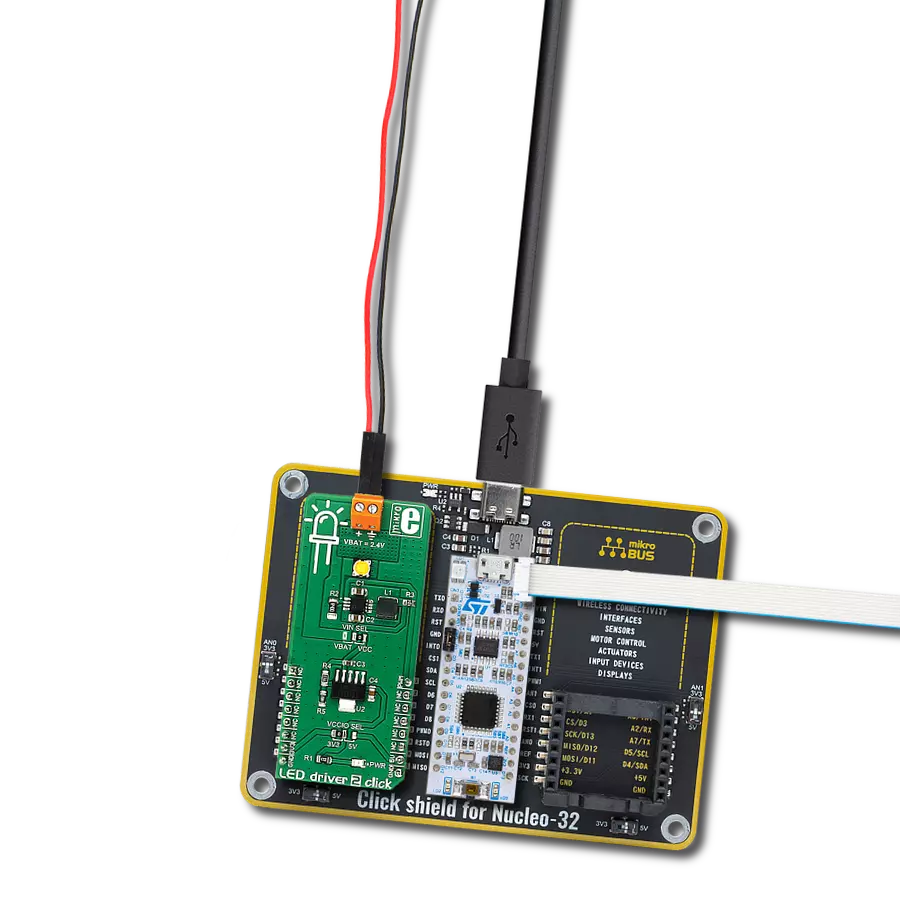
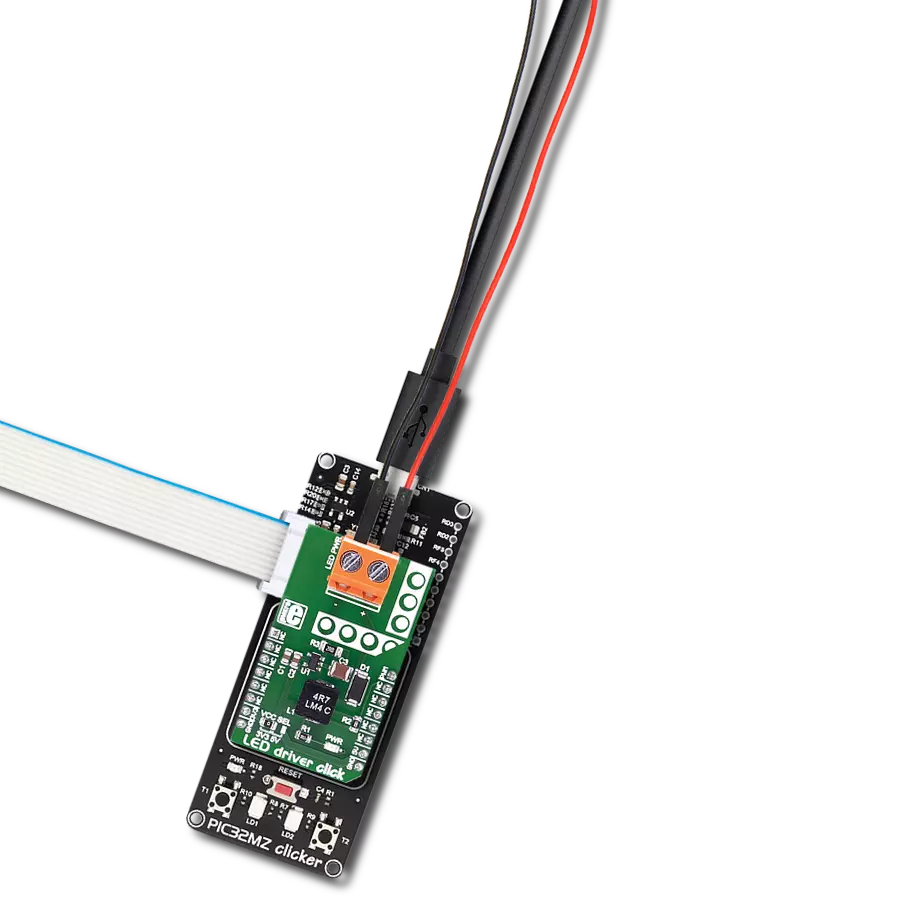
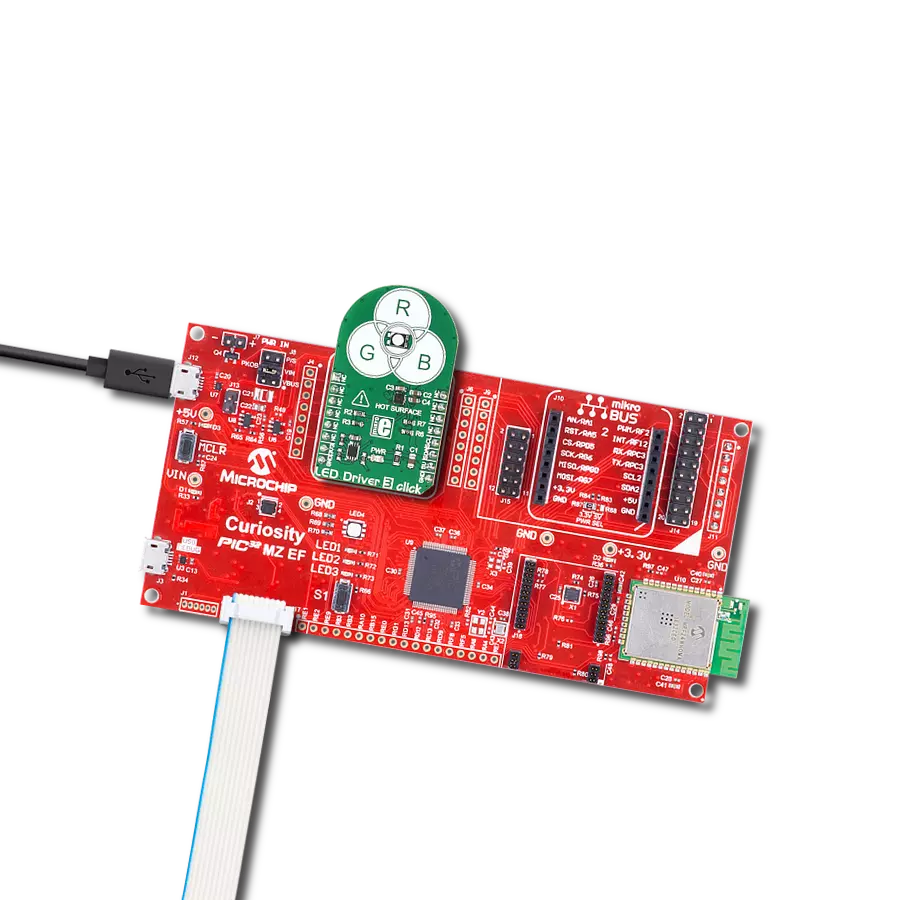
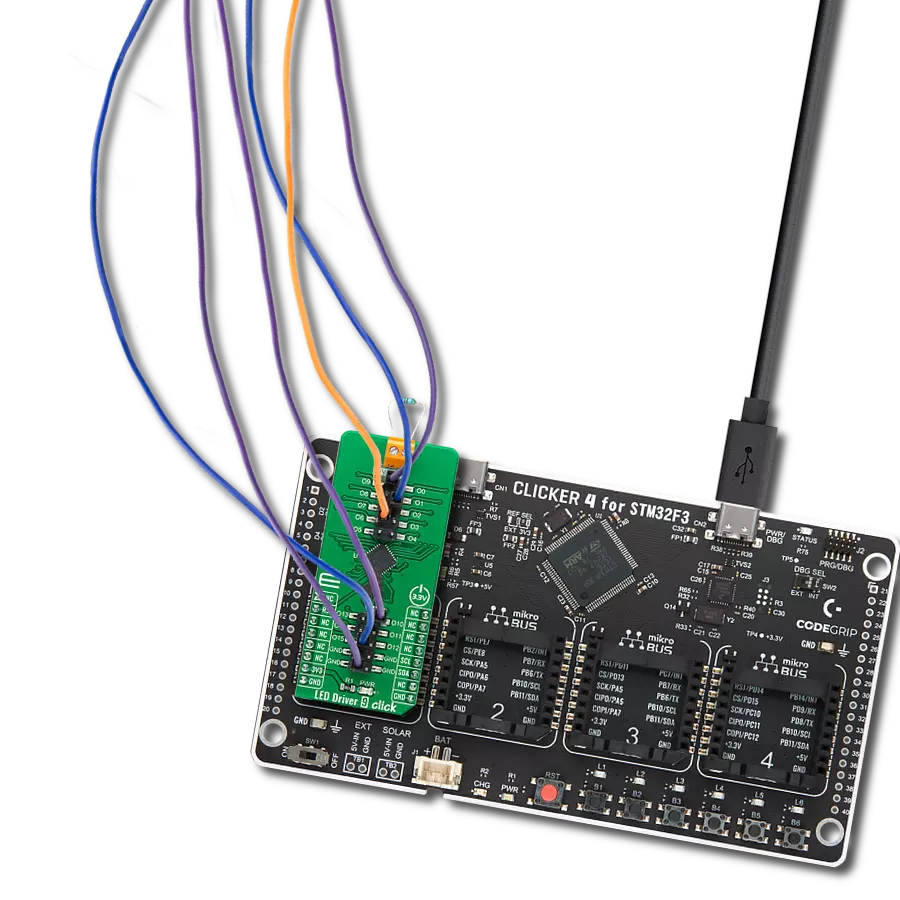
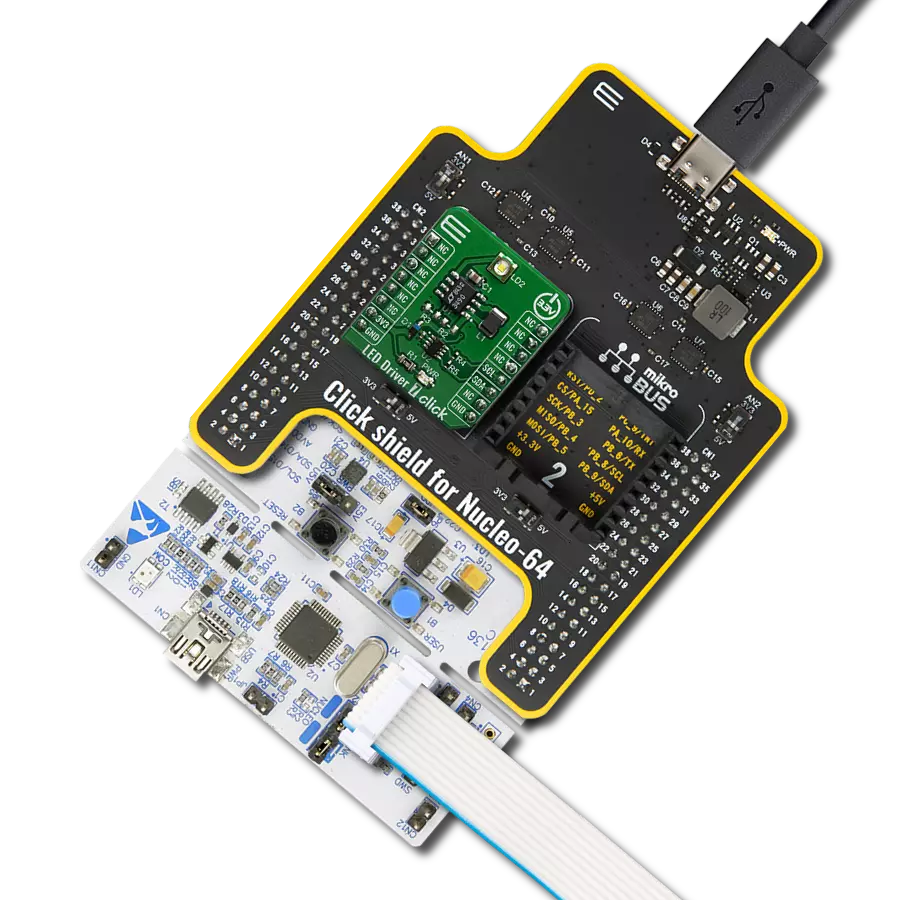
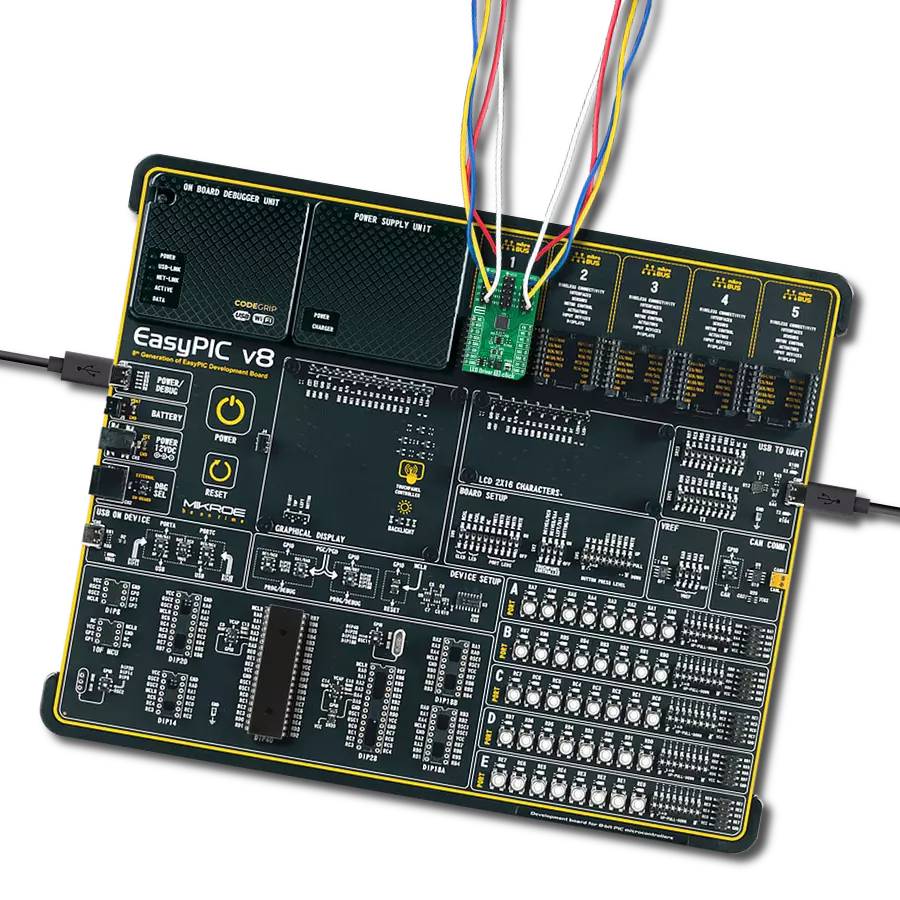
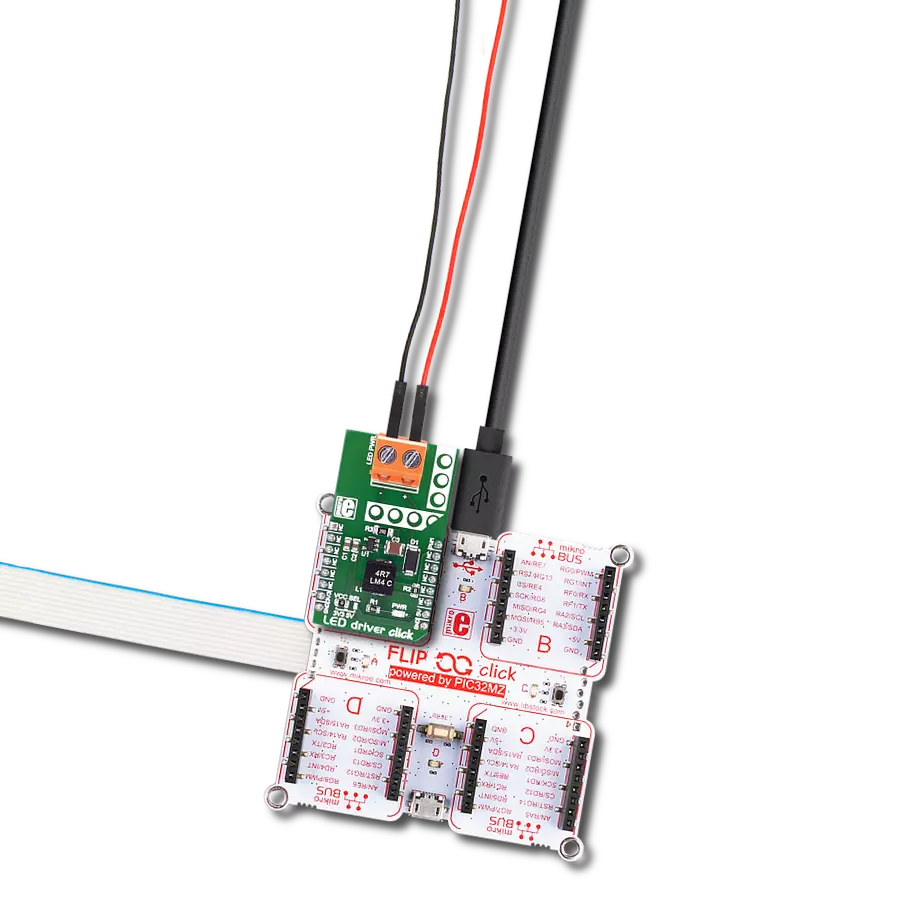
Our white LED driver solution offers easy compatibility with various control systems, making it adaptable for a wide range of lighting applications
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
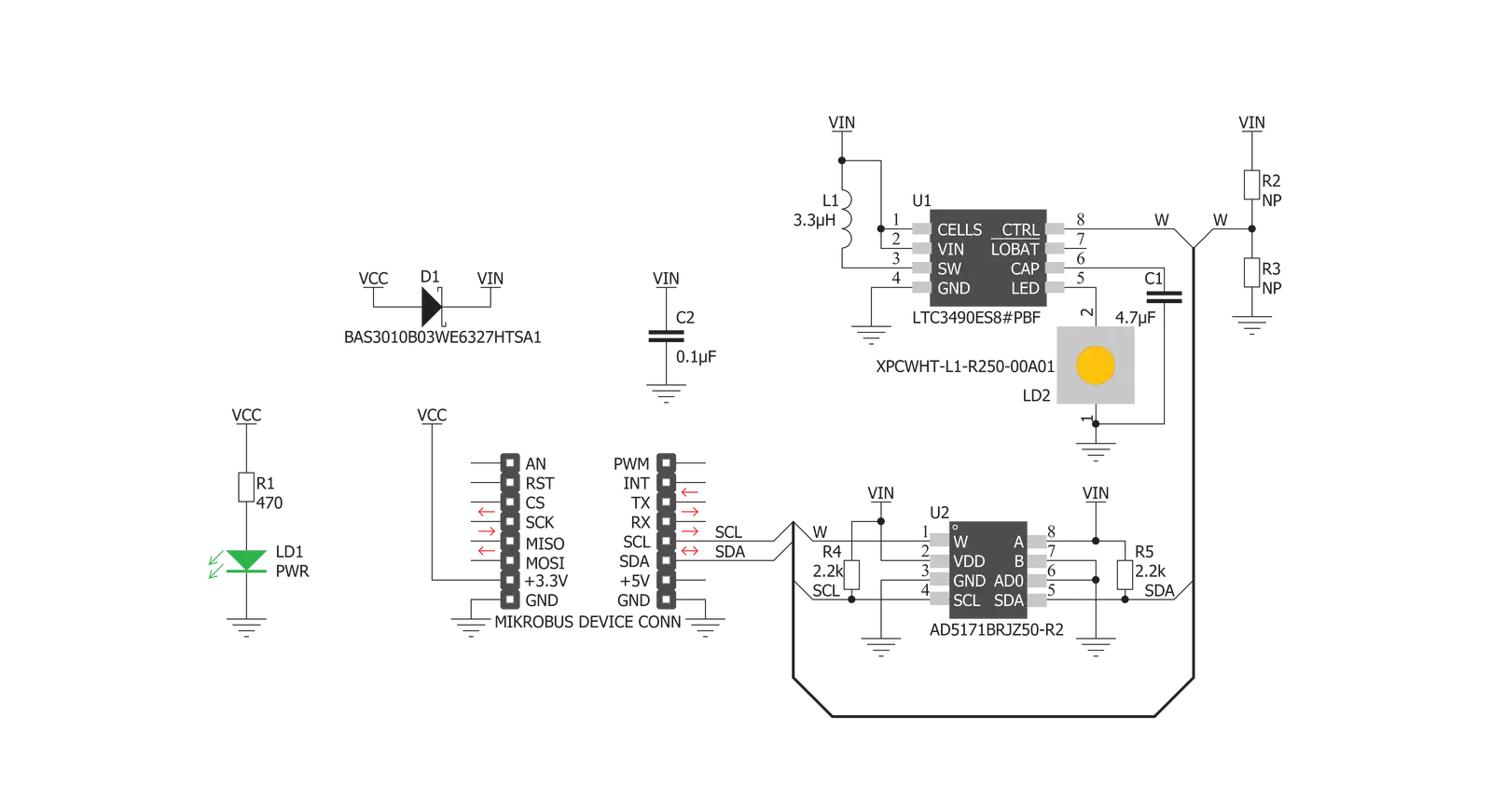
LED Driver 7 Click features the LTC3490, single cell 350mA LED driver from Analog Devices. It provides a constant current drive for 1W LED applications. It is a high-efficiency boost converter. Its key features include the 350mA Constant Current Output, Fixed Frequency Operation: 1.3MHz, Low Quiescent Current: <1mA, and Dimming Control. The LED Driver 7 click also features the AD5171, a 64-position OTP digital potentiometer from Analog Devices. The AD5171 changes the voltage on the CTRL/SHDN pin. This voltage can control the LED drive current from 0mA to 350mA. The AD5171 uses fuse link technology to achieve the memory retention of the resistance setting
function. OTP is a cost-effective alternative over the EEMEM approach for users who do not need to reprogram new memory settings in the digital potentiometer. This device performs the same electronic adjustment function as most mechanical trimmers and variable resistors. The AD5171 is programmed using a 2-wire, I2C compatible digital control. It allows unlimited adjustments before permanently setting the resistance value. During the OTP activation, a permanent fuse blown command is sent after the final value is determined, freezing the wiper position at a given setting (analogous to placing epoxy on a mechanical trimmer). Given the
options its features offer, the LED Driver 7 click is ideally used for Portable lighting, rechargeable flashlights, system calibrations, electronics level settings, automotive electronics adjustments, mechanical trimmers, and potentiometer replacements. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
PIC18F57Q43 Curiosity Nano evaluation kit is a cutting-edge hardware platform designed to evaluate microcontrollers within the PIC18-Q43 family. Central to its design is the inclusion of the powerful PIC18F57Q43 microcontroller (MCU), offering advanced functionalities and robust performance. Key features of this evaluation kit include a yellow user LED and a responsive
mechanical user switch, providing seamless interaction and testing. The provision for a 32.768kHz crystal footprint ensures precision timing capabilities. With an onboard debugger boasting a green power and status LED, programming and debugging become intuitive and efficient. Further enhancing its utility is the Virtual serial port (CDC) and a debug GPIO channel (DGI
GPIO), offering extensive connectivity options. Powered via USB, this kit boasts an adjustable target voltage feature facilitated by the MIC5353 LDO regulator, ensuring stable operation with an output voltage ranging from 1.8V to 5.1V, with a maximum output current of 500mA, subject to ambient temperature and voltage constraints.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC
MCU Memory (KB)
128
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
48
RAM (Bytes)
8196
You complete me!
Accessories
Curiosity Nano Base for Click boards is a versatile hardware extension platform created to streamline the integration between Curiosity Nano kits and extension boards, tailored explicitly for the mikroBUS™-standardized Click boards and Xplained Pro extension boards. This innovative base board (shield) offers seamless connectivity and expansion possibilities, simplifying experimentation and development. Key features include USB power compatibility from the Curiosity Nano kit, alongside an alternative external power input option for enhanced flexibility. The onboard Li-Ion/LiPo charger and management circuit ensure smooth operation for battery-powered applications, simplifying usage and management. Moreover, the base incorporates a fixed 3.3V PSU dedicated to target and mikroBUS™ power rails, alongside a fixed 5.0V boost converter catering to 5V power rails of mikroBUS™ sockets, providing stable power delivery for various connected devices.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for LED Driver 7 Click driver.
Key functions:
leddriver7_generic_write- Generic write functionleddriver7_generic_read- Generic read function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief LedDriver7 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application is portable lighting and rechargeable flashlights.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initalizes I2C driver and writes an initial log.
*
* ## Application Task
* This example demonstrates the use of LED Driver 7 Click board,
* by cycling wiper positions of AD5171 Digital Potentiometer.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "leddriver7.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static leddriver7_t leddriver7;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
leddriver7_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
leddriver7_cfg_setup( &cfg );
LEDDRIVER7_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
leddriver7_init( &leddriver7, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------- \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " LED Driver 7 Click \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "-------------------- \r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
uint8_t n_pos = 0;
uint8_t pos_num = 64;
for ( n_pos = 12; n_pos < pos_num; n_pos++ )
{
leddriver7_generic_write( &leddriver7, LEDDRIVER7_NORM_OP_MODE, &n_pos, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, "Position : %d \r\n", (uint16_t)n_pos );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:LED Drivers