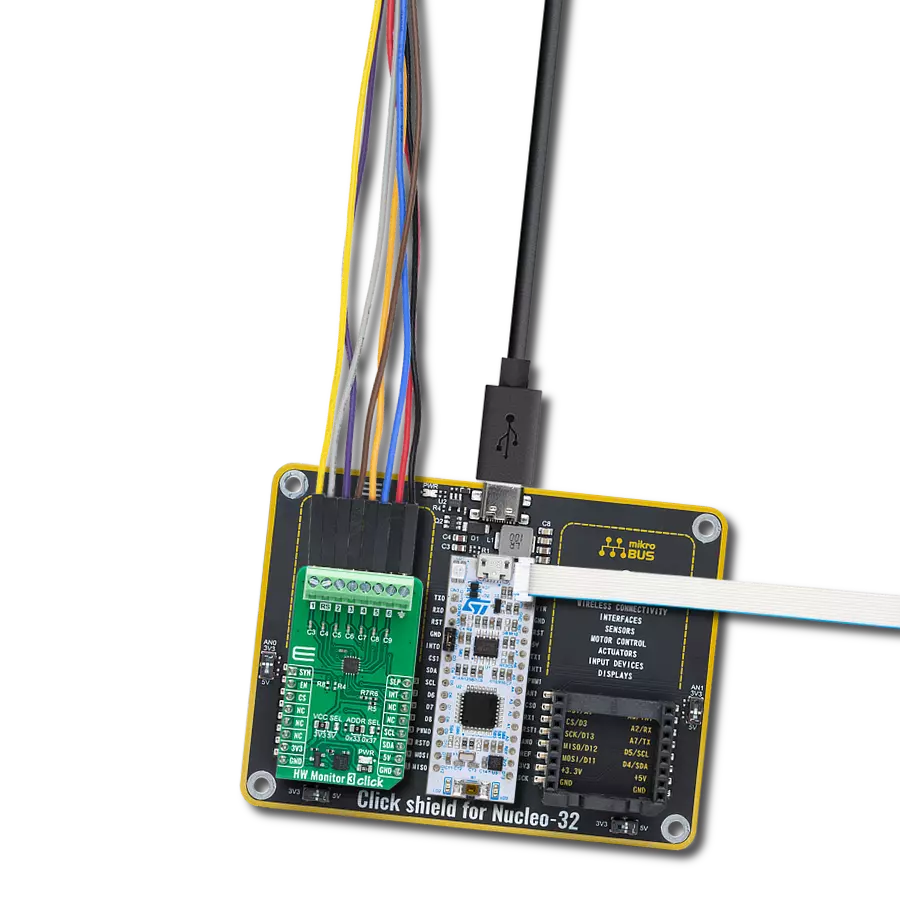
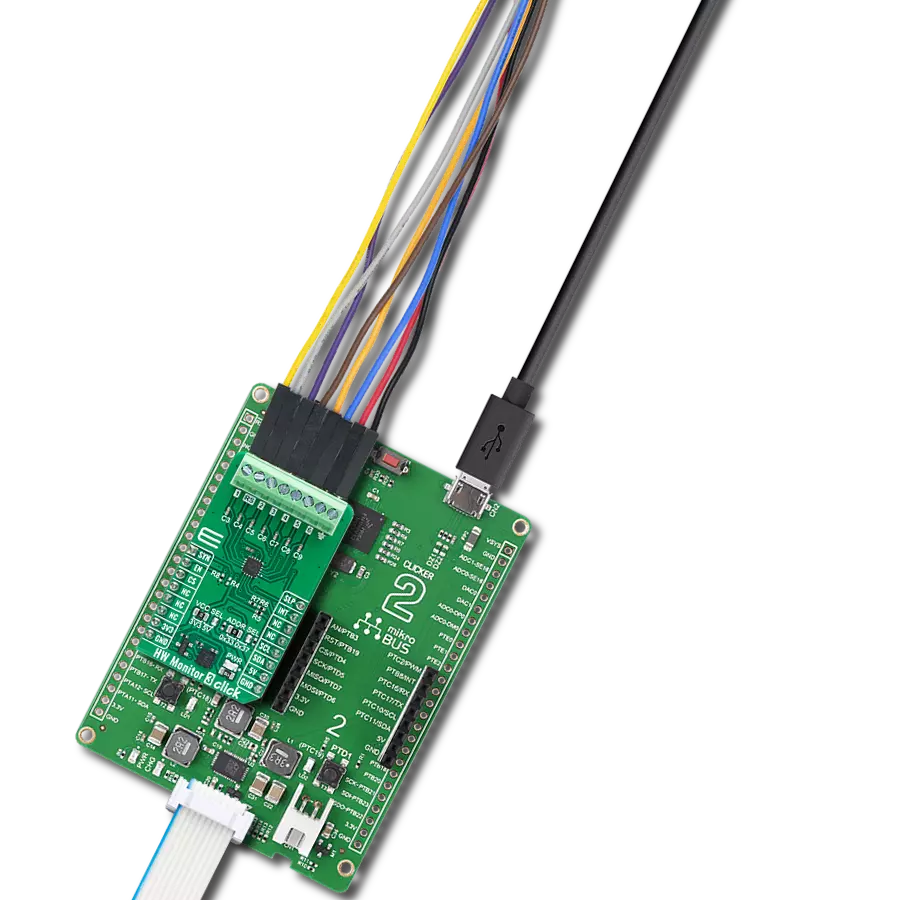
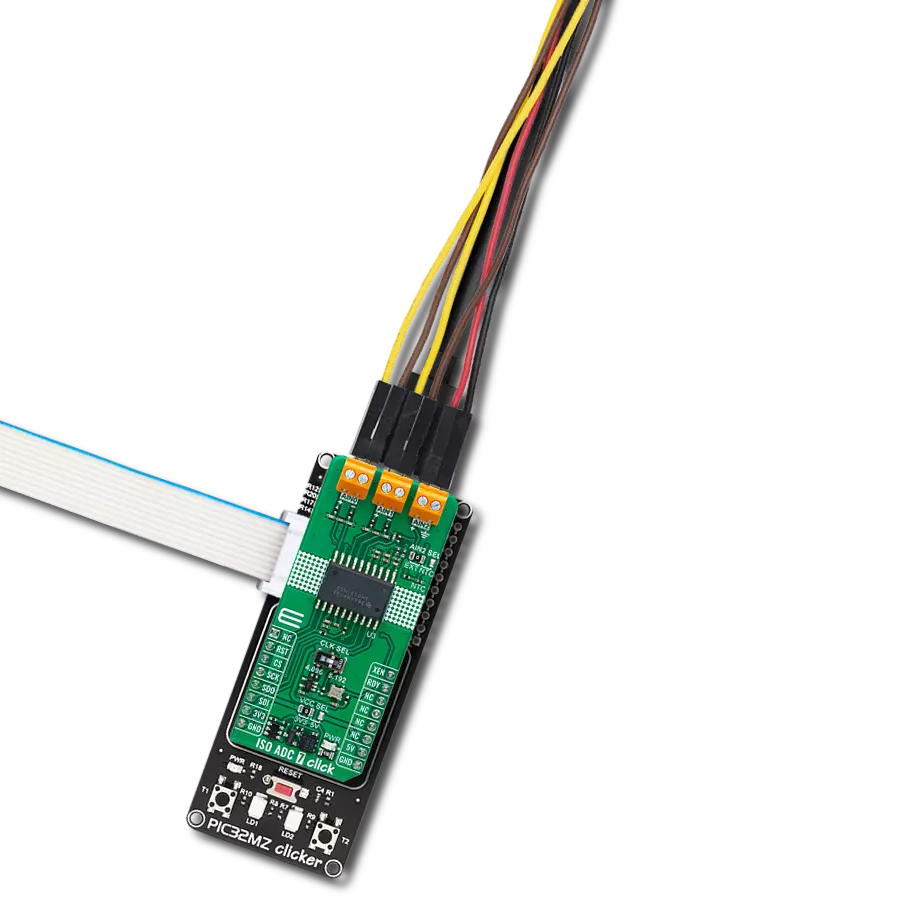
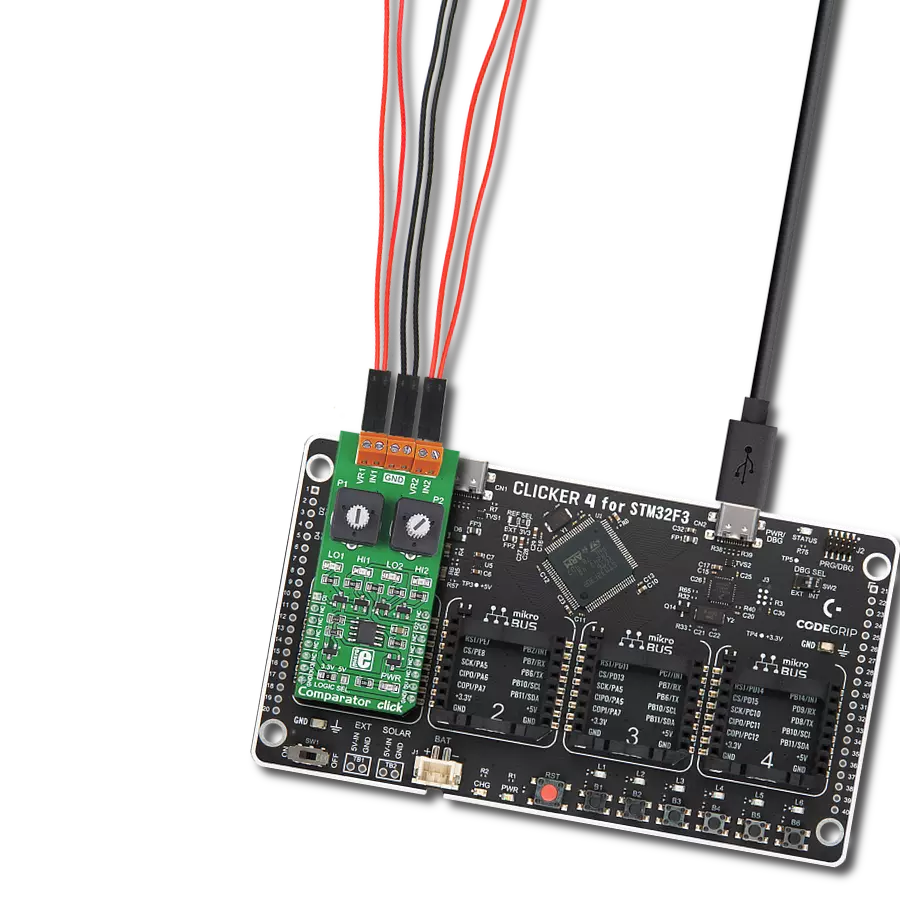
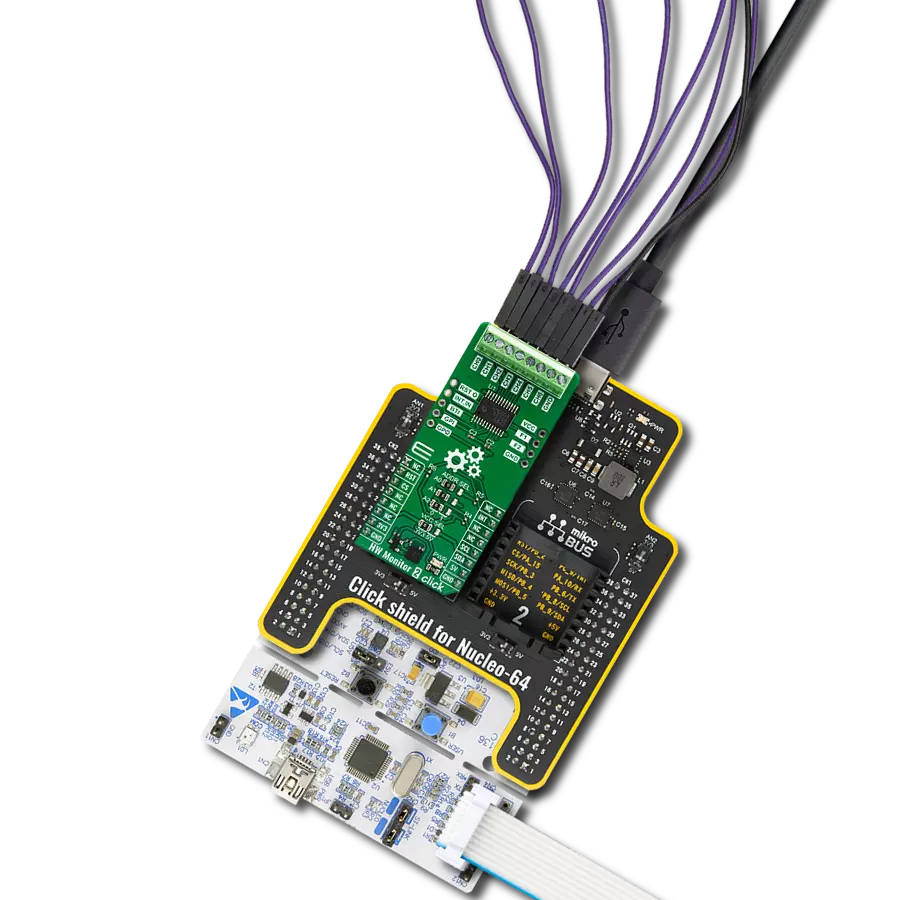
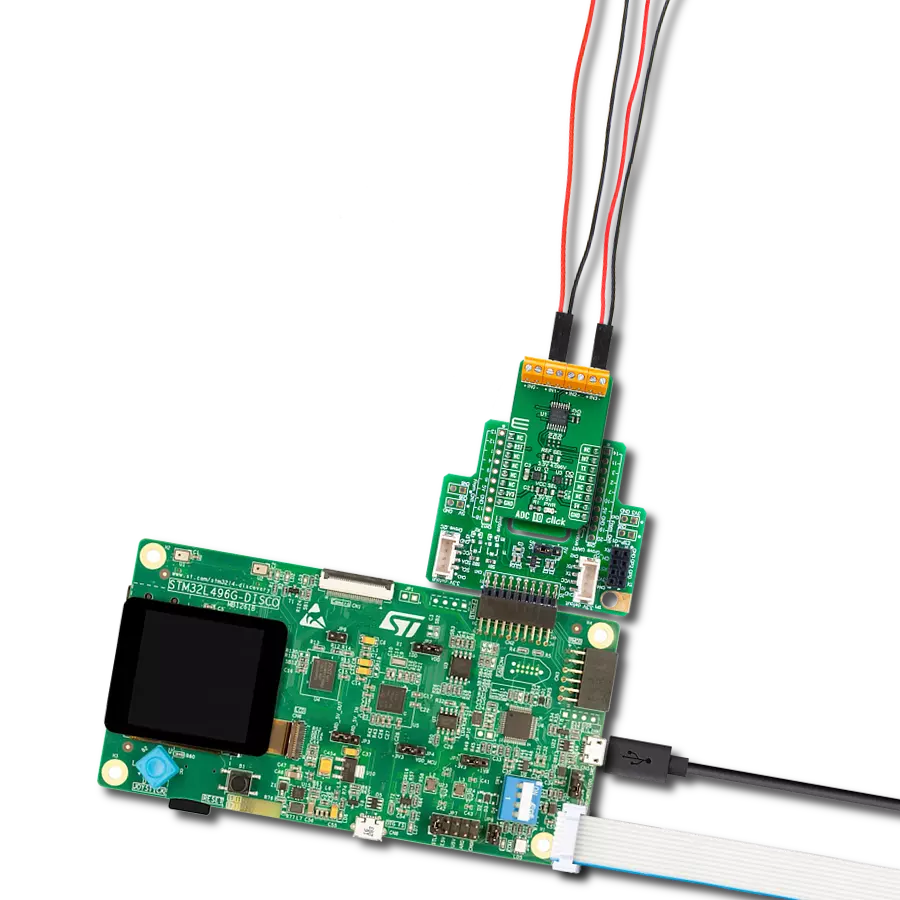
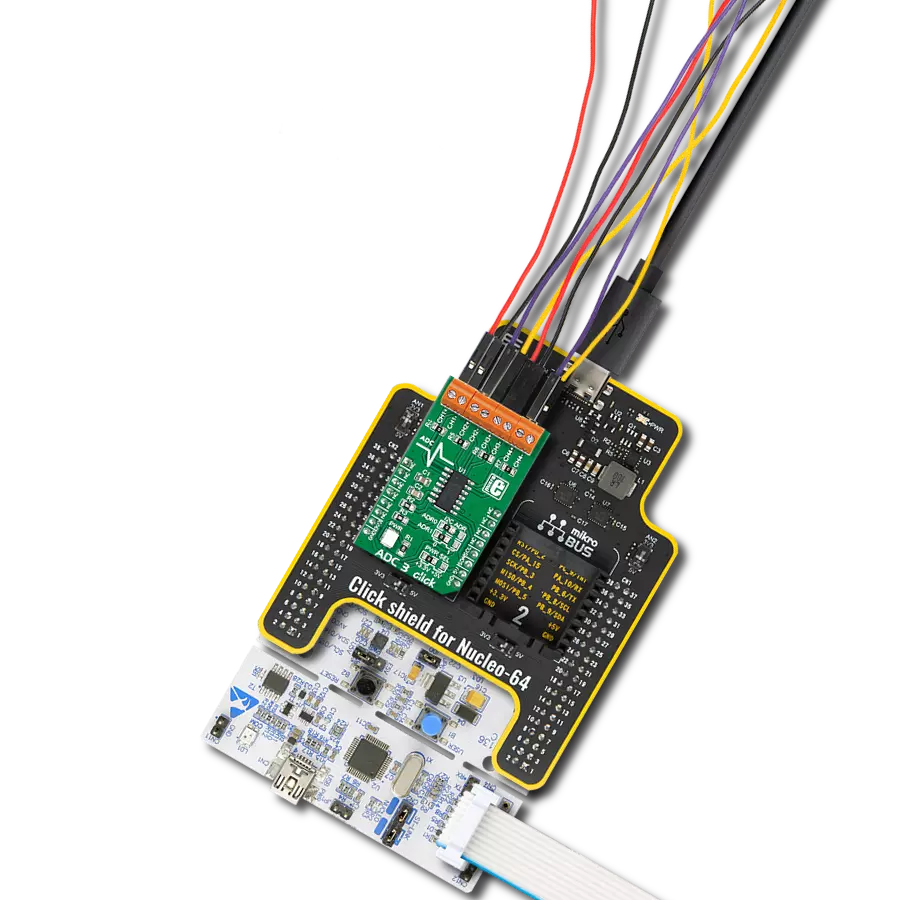
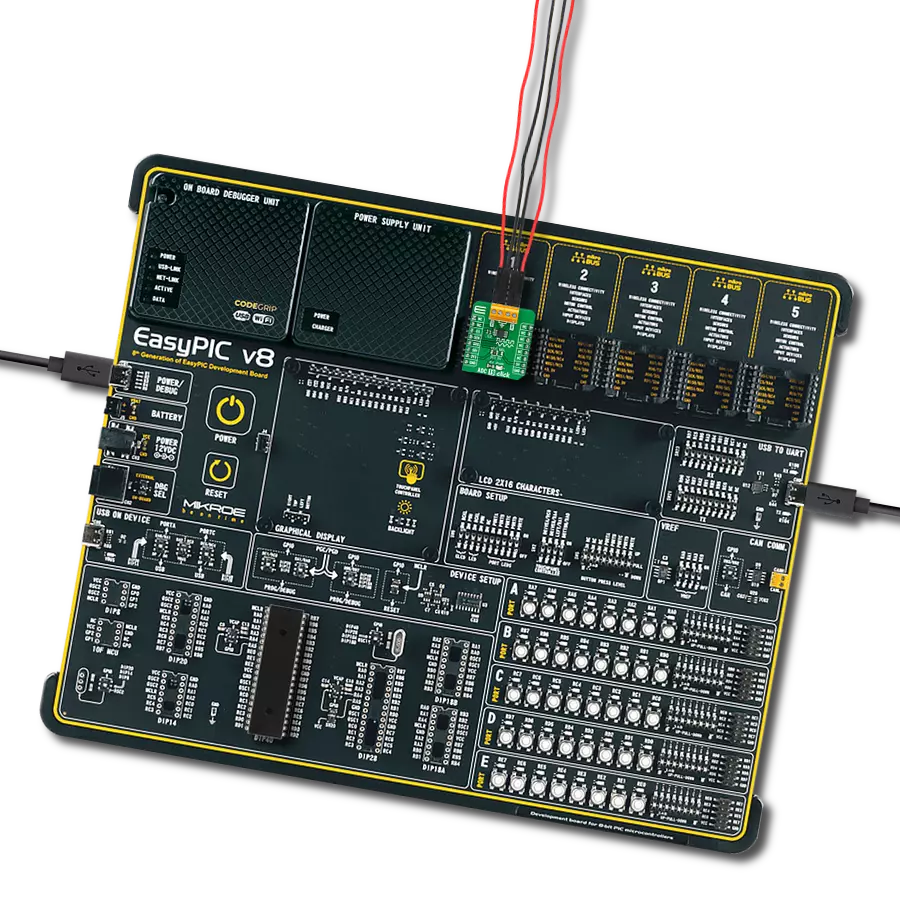
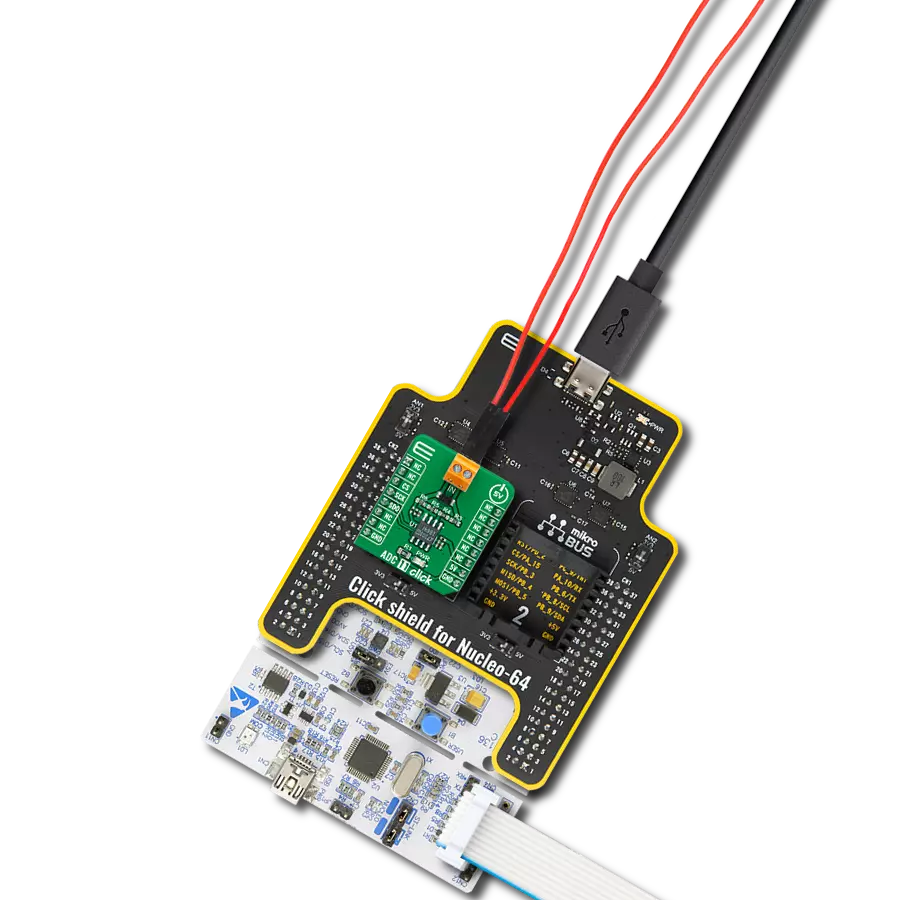
Multi-channel data acquisition with robust 5000-VRMS isolation and advanced filtering for electricity meters and battery management
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
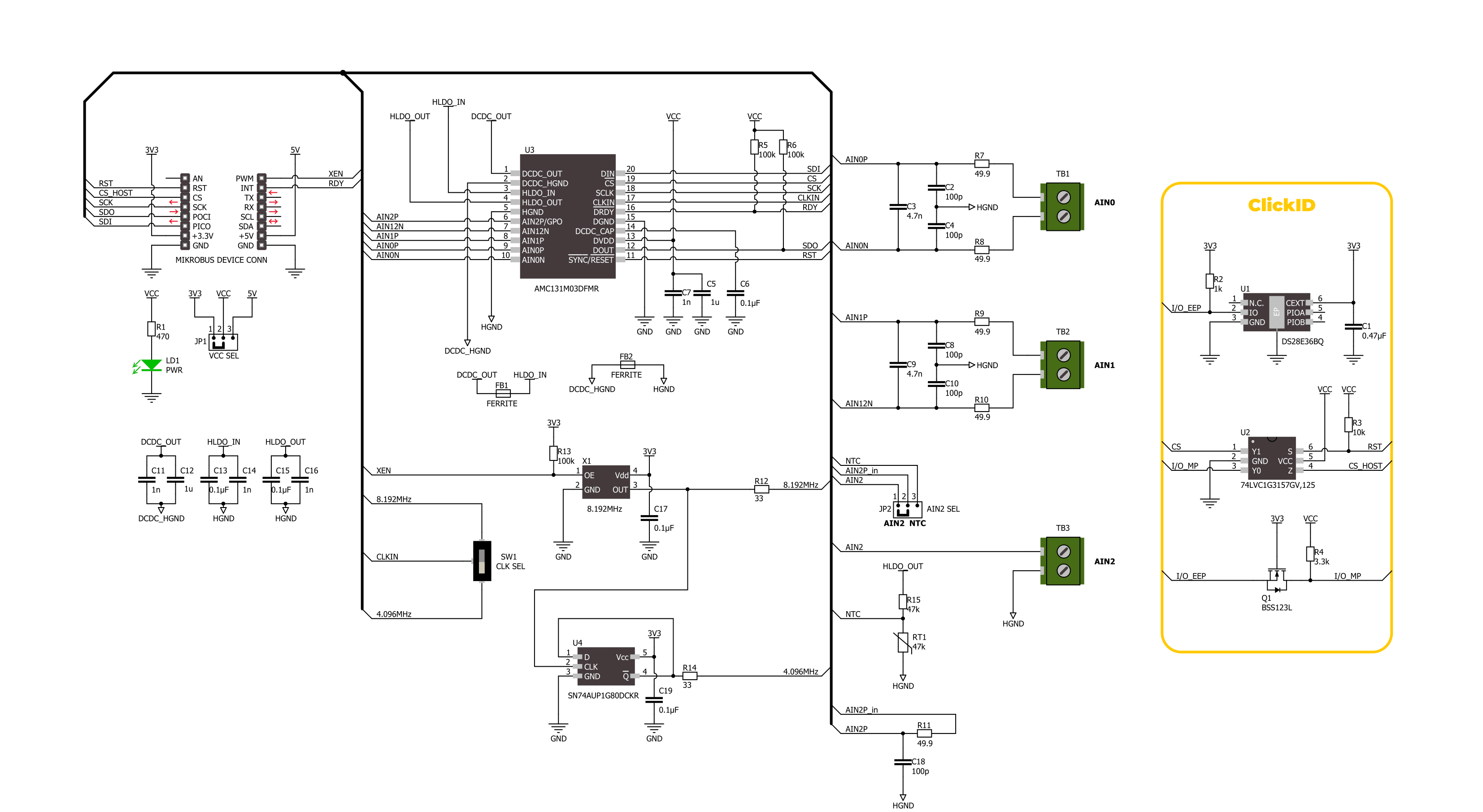
ISO ADC 7 Click is based on the AMC131M03, a three-channel, 24-bit delta-sigma (ΔΣ) ADC with simultaneous sampling capabilities from Texas Instruments, designed for applications requiring precise multi-channel data acquisition, such as electricity meters, battery management systems, EV charging stations, and circuit breakers. The AMC131M03 includes a silicon-dioxide (SiO2)-based capacitive isolation barrier that provides 5000-VRMS isolation (certified by UL1577) for 1 minute, offering excellent immunity to magnetic fields and enhanced safety for use in industrial and high-voltage applications. Additionally, the AMC131M03 meets low EMI standards (CISPR-11 and CISPR-25), ensuring reliable performance in environments with stringent electromagnetic compatibility requirements. Each of the three channels (AIN0-AIN2) of the AMC131M03 includes a built-in digital decimation filter that demodulates the output of the ΔΣ modulator, enabling data rates up to 64kSPS per channel in high-resolution mode. This filter significantly reduces quantization noise, providing a wide dynamic range. The relative phase of the samples between channels can also be adjusted, compensating for any phase delay in sensor responses. Additionally, the modulator's
frequency is derived from a user-selectable clock source, which can be configured via the CLK SEL switch, allowing the choice between 4.096 MHz and 8.192 MHz. The main clock is activated using the XEN pin. A programmable clock divider provides flexibility in setting the modulator's frequency to match specific application needs, further optimizing the device's performance. Thus, as mentioned, the digital decimation filter enhances the signal-to-noise ratio by filtering out-of-band noise, resulting in improved accuracy and efficiency. The AMC131M03 also integrates a low-drift internal voltage reference and a high-precision programmable gain amplifier (PGA), offering gains up to 128. Its integrated precharge buffer ensures high input impedance when the PGA gain exceeds 4, enabling accurate measurements of signals with small amplitudes. The ADC also incorporates a negative charge pump, allowing absolute input voltages as low as 1.3V, making it ideal for single-ended power supply systems measuring signals close to ground. This Click board™ communicates with the host MCU via a standard SPI interface. Additional control pins include the RST pin, which can be used both as a reset and for synchronization across multiple AMC131M03-
based devices, and the RDY pin, which serves as a data-ready interrupt signal. These features allow for flexible and synchronized multi-channel data acquisition, ensuring precise timing and data integrity. A key feature of the AMC131M03 is its integrated temperature sensor, which supports both internal and external temperature measurements. The AIN2 input channel is multiplexed with the temperature sensor, and users can select between internal and external sensing modes through register settings. The AIN2 SEL jumper on the Click board™ allows for selecting the type of external temperature coefficient (TC) element. In the "EXT" position, the jumper enables the use of an external positive (PTC) or negative temperature coefficient (NTC) element, while the "NTC" position activates the onboard NTC sensor for direct temperature measurement. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ISO ADC 7 Click driver.
Key functions:
isoadc7_read_voltage- This function reads the voltage measurements of all three channels.isoadc7_read_data- This function reads the status register and raw data of all three channels.isoadc7_set_gain- This function sets the gain level for all channels.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief ISO ADC 7 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of ISO ADC 7 Click board by reading and displaying
* the voltage levels from 3 isolated analog input channels.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration.
* The full-scale voltage input range is set to +-1.2V for all channels.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the voltage levels from all 3 isolated analog input channels and displays
* the results on the USB UART once per second approximately.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "isoadc7.h"
static isoadc7_t isoadc7;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
isoadc7_cfg_t isoadc7_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
isoadc7_cfg_setup( &isoadc7_cfg );
ISOADC7_MAP_MIKROBUS( isoadc7_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == isoadc7_init( &isoadc7, &isoadc7_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( ISOADC7_ERROR == isoadc7_default_cfg ( &isoadc7 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float ch0 = 0;
float ch1 = 0;
float ch2 = 0;
if ( ISOADC7_OK == isoadc7_read_voltage ( &isoadc7, &ch0, &ch1, &ch2 ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " CH0: %.1f mV\r\n", ch0 );
log_printf ( &logger, " CH1: %.1f mV\r\n", ch1 );
log_printf ( &logger, " CH2: %.1f mV\r\n\n", ch2 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:ADC