Unleash the full potential of your audio with this compact and high-performance amplifier
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
AudioAMP 11 Click is based on the NAU8224, a stereo Class-D audio amplifier from Nuvoton Technology. Besides an excellent quantity performance, such as high efficiency, the NAU8224 is also characterized by high output power and low quiescent current. It can drive a 4Ω load with up to 3.1W output power. This audio amplifier is designed to reduce high-frequency emissions with the ferrite bead filters on its outputs (speaker channels). The ferrite beads have a low impedance in the audio range, and because of that, they act as a pass-through filter in the audio frequency range. Furthermore, the NAU8224 has several
protection features like thermal overload, short circuit, and supply under-voltage protection allowing a reliable operation. This Click board™ communicates with MCU using the standard I2C 2-Wire interface to read data and configure settings, supporting a Fast Mode operation up to 400kHz. The NAU8224 can be enabled or disabled using the EN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, offering a switch operation to turn ON/OFF the audio amplifier. In addition to its possible digital control, the NAU8224 also has several gain settings, such as 6dB, 12dB, 18dB, and 24dB, selectable via onboard switches labeled as GAIN SEL.
This audio amplifier also provides register-programmable volume control next to the hardware gain selection. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
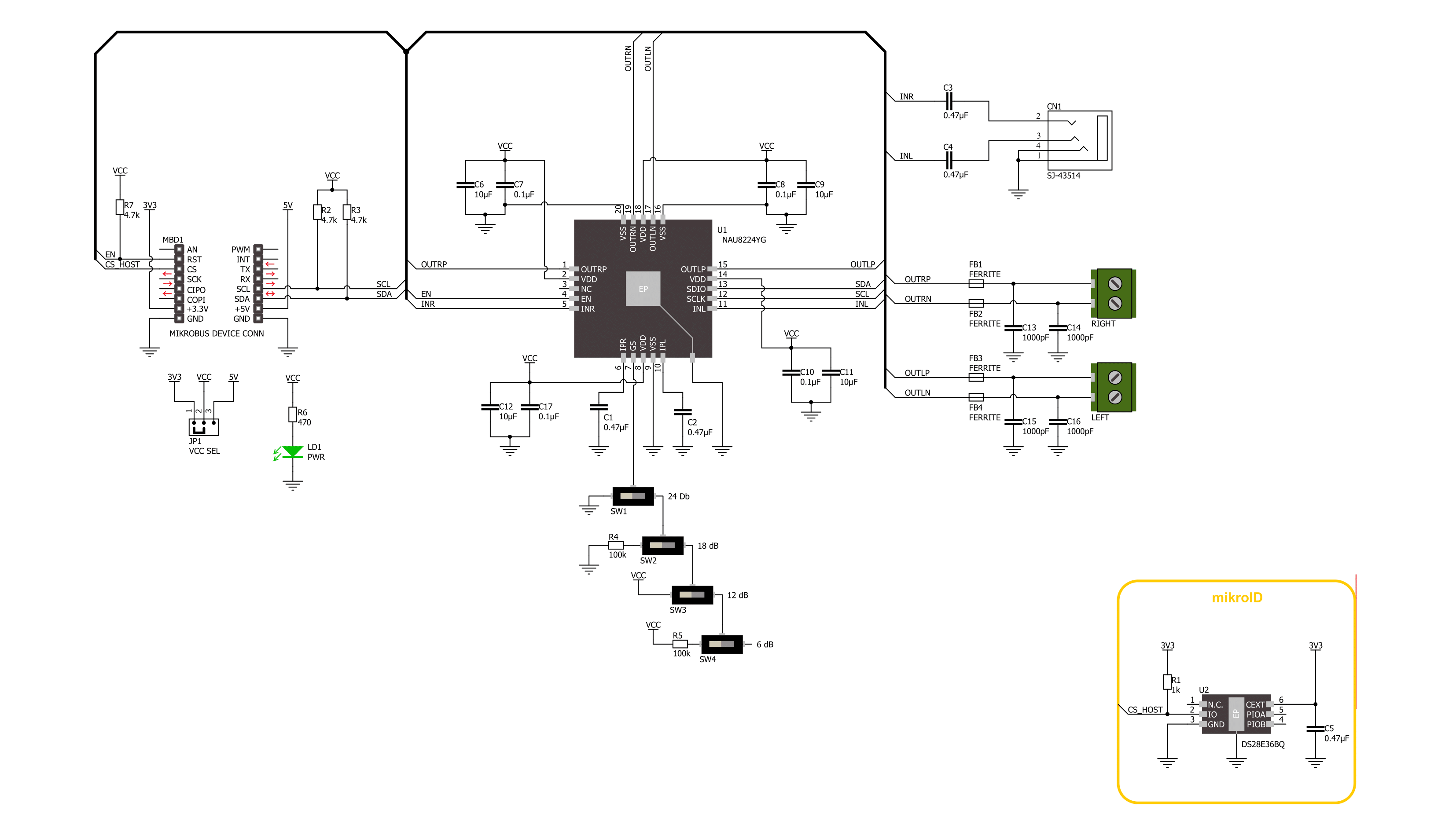
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for AudioAMP 11 Click driver.
Key functions:
audioamp11_enable_deviceAudioAMP 11 enable device function.audioamp11_check_gainAudioAMP 11 check gain function.audioamp11_set_output_volume_levelAudioAMP 11 set output volume level function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief AudioAMP 11 Click example
*
* # Description
* This library contains API for the AudioAMP 11 click driver.
* This demo application shows use of a AudioAMP 11 click board™.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of I2C module and log UART.
* After driver initialization the app set default settings,
* performs power-up sequence, sets the volume level to 0.
*
* ## Application Task
* This example demonstrates the use of the AudioAMP 11 click board™.
* If GAIN SEL switches are set to 12dB, the app performs circles
* switching the volume from -20.5 dB to 12 dB.
* If the GAIN SEL switches are different, the app sets the volume level to 31 (maximum).
* Results are being sent to the UART Terminal, where you can track their changes.
*
* @author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "audioamp11.h"
static audioamp11_t audioamp11;
static log_t logger;
uint8_t vol_ctrl = AUDIOAMP11_GS_12dB_VOLCTRL_m20_5dB;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
audioamp11_cfg_t audioamp11_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
audioamp11_cfg_setup( &audioamp11_cfg );
AUDIOAMP11_MAP_MIKROBUS( audioamp11_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == audioamp11_init( &audioamp11, &audioamp11_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( AUDIOAMP11_ERROR == audioamp11_default_cfg ( &audioamp11 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
log_printf( &logger, "----------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
uint8_t gain_level = 0;
uint8_t volume_level = 0;
audioamp11_check_gain( &audioamp11, &gain_level );
log_printf( &logger, " Gain set to %d dB\r\n", AUDIOAMP11_CALC_GAIN_CONFIG( gain_level ) );
if ( AUDIOAMP11_GAINDEC_12dB == gain_level )
{
float volume_table[ 32 ] = { OUTPUT_VOLUME_12dB };
audioamp11_set_output_volume_level( &audioamp11, vol_ctrl );
Delay_ms( 100 );
if ( vol_ctrl > AUDIOAMP11_GS_12dB_VOLCTRL_12dB )
{
vol_ctrl--;
}
else
{
vol_ctrl = AUDIOAMP11_GS_12dB_VOLCTRL_m20_5dB;
}
audioamp11_get_output_volume_level( &audioamp11, &volume_level );
log_printf( &logger, " Volume set to %.1f dB\r\n", volume_table[ volume_level ] );
}
else
{
audioamp11_set_output_volume_level( &audioamp11, AUDIOAMP11_VOLUME_LEVEL_31 );
audioamp11_get_output_volume_level( &audioamp11, &volume_level );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Volume Level %d: ", ( uint16_t ) ( AUDIOAMP11_VOLUME_LEVEL_0 - volume_level ) );
for ( uint8_t n_cnt = 0; n_cnt < ( AUDIOAMP11_VOLUME_LEVEL_0 - volume_level ); n_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "|" );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n----------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms( 1000 );
}
void main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Amplifier