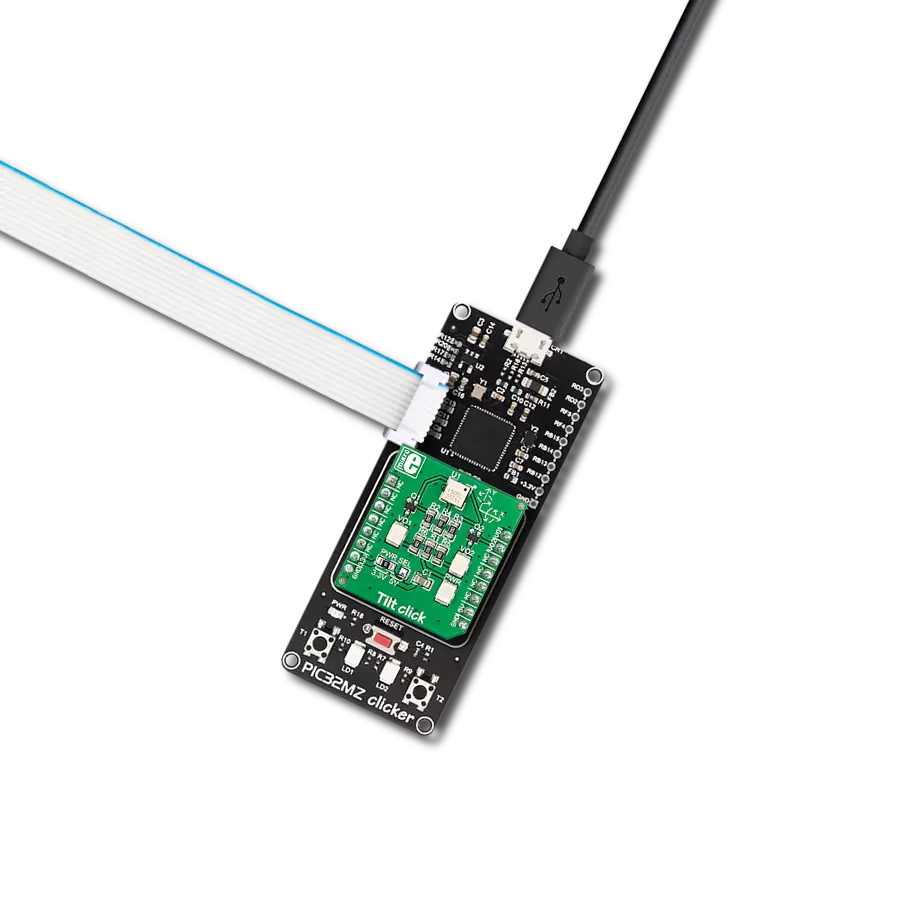
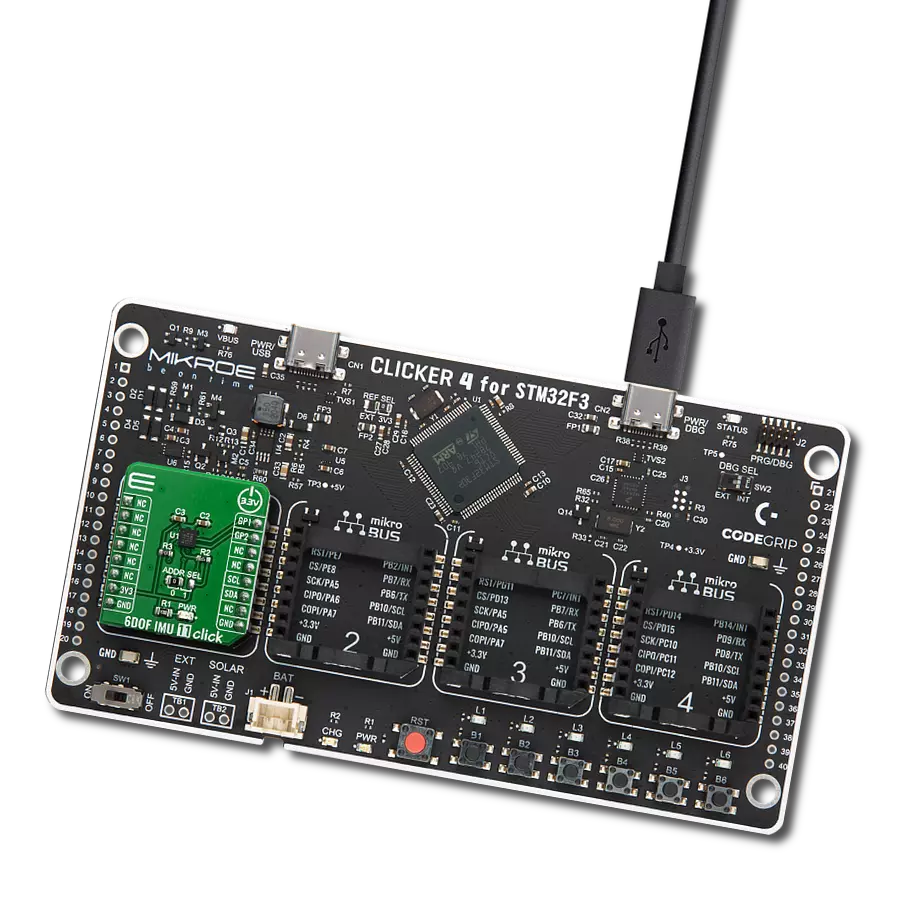
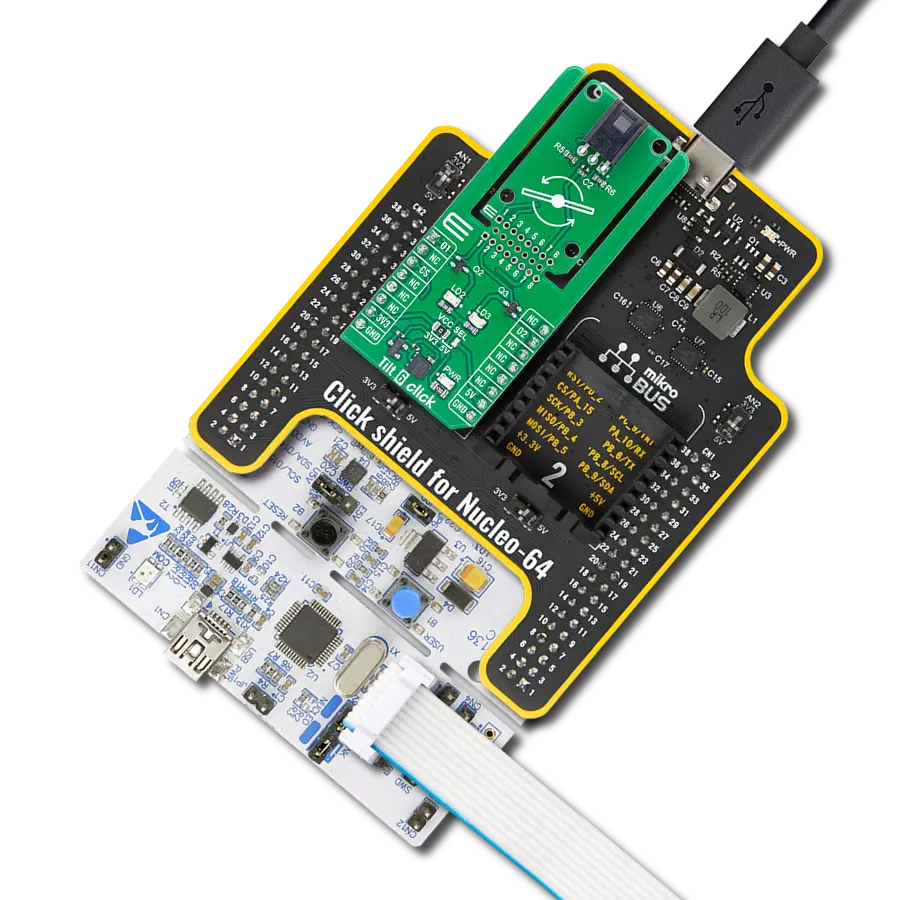
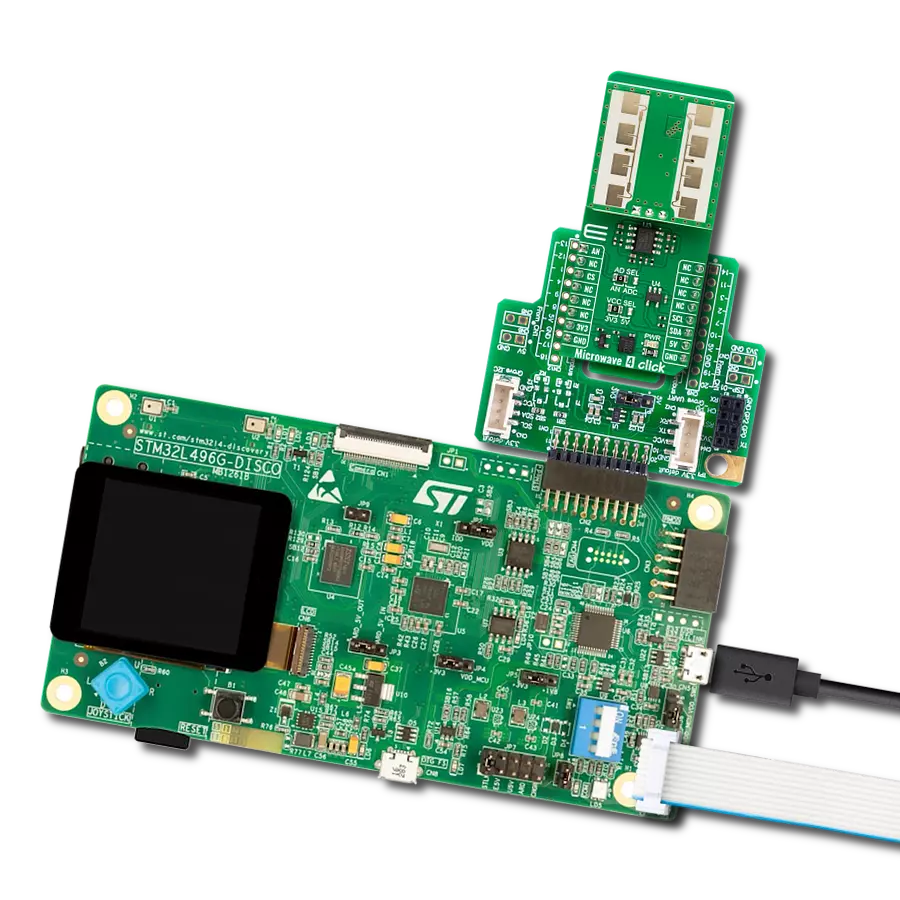
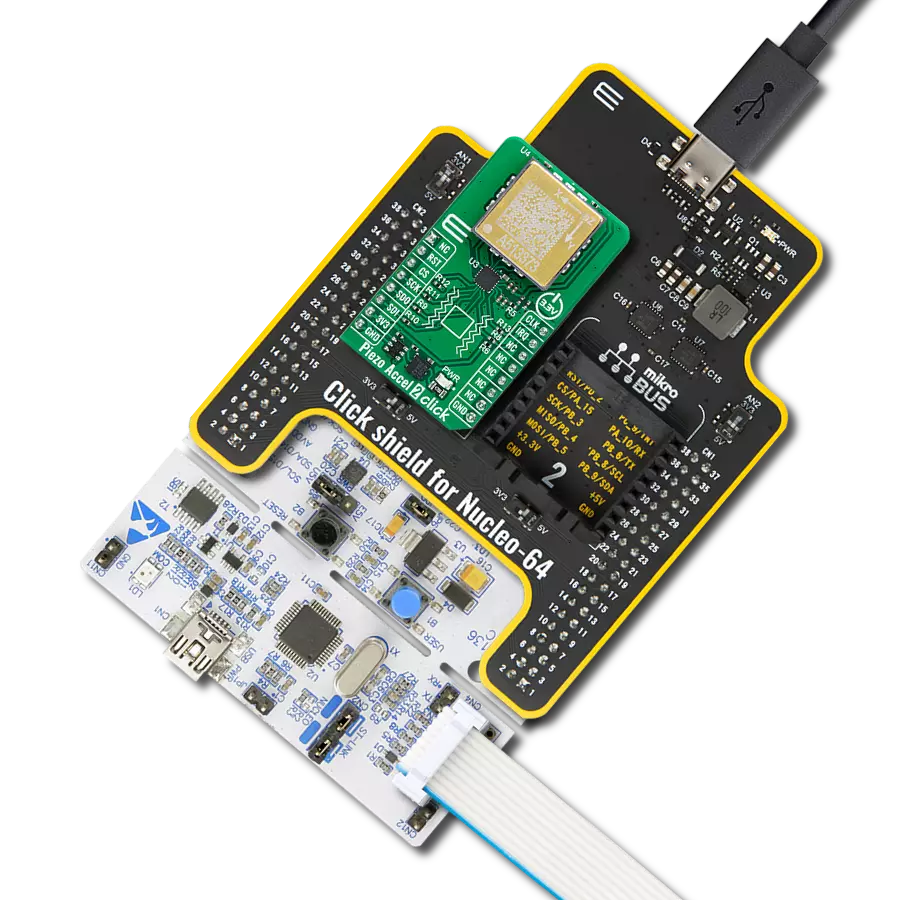
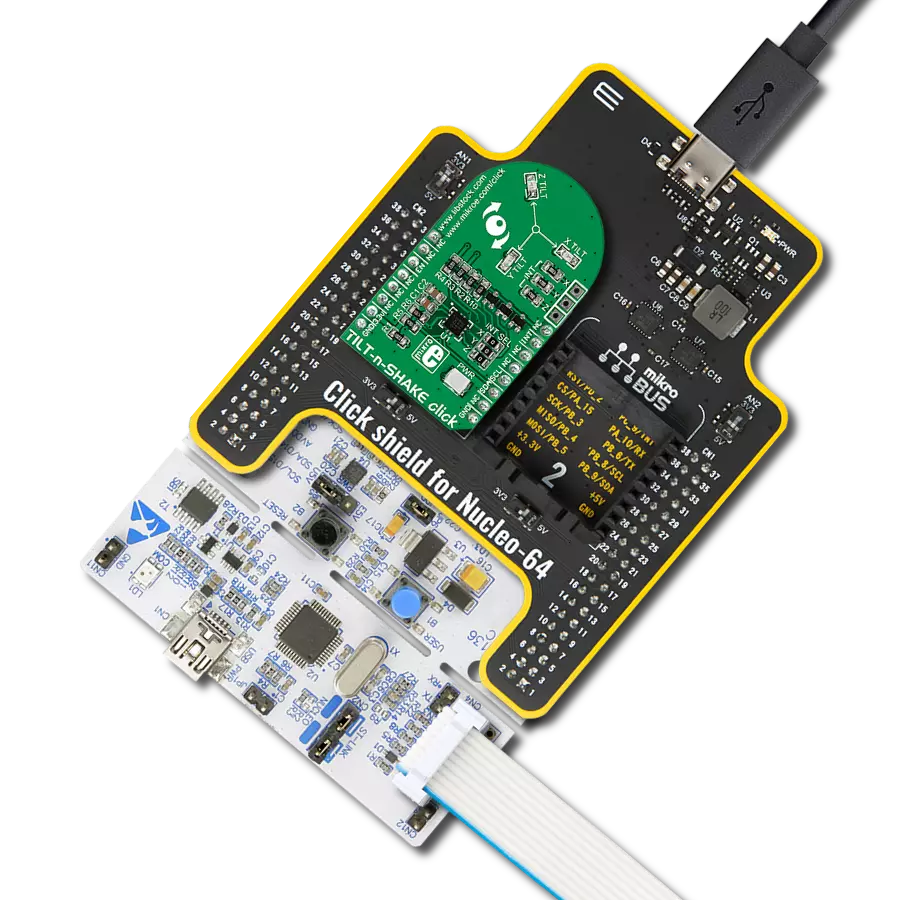
Achieve detection and measurement of both rotational movements and linear acceleration in three dimensions
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
MPU IMU Click is based on the MPU-6000, an integrated 6-axis motion device that combines a 3-axis gyroscope and accelerometer and a DMP (digital motion processor) from TDK InvenSense. The onboard gyroscope has a high sensitivity with a user-programmable full-scale range of ±250, ±500, ±1000, and ±2000dps, while the accelerometer has a full-scale programmable range of ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, and ±16g. This integrated circuit has high vibration tolerance, where its digital output of 6 or 9-axis MotionFusion data consists of a rotation matrix, quaternion, Euler angle, or row data format. The DMP engine offloads complex MotionFusion, sensor timing synchronization, and gesture detection. The MPU-6000 has an integrated digital output temperature sensor and
embedded algorithms for run-time bias and compass calibration, with no user intervention required. An on-chip 1024 Byte FIFO buffer allows the system to read data in burst and enter a low-power mode, lowering system power consumption. MPU IMU Click allows using both I2C and SPI interfaces with a maximum frequency of 400kHz for I2C and 1MHz for SPI communication (20MHz for reading sensor and interrupt registers). The selection can be made by positioning SMD jumpers marked as SPI/I2C to an appropriate position. Note that all the jumpers' positions must be on the same side, or the Click board™ may become unresponsive. While the I2C interface is selected, the MPU-6000 allows choosing its I2C slave address using the I2C ADD SMD jumper to an
appropriate position marked as 0 and 1. This Click board™ also supports electronic video stabilization and GPS synchronization over a digital FSY pin. Programmable interrupt over an INT pin supports gesture recognition, panning, zooming, scrolling, free fall interrupt, high-G interrupt, zero-motion detection, and more. A pedometer functionality is also implemented, allowing the target board's MCU to sleep while DMP maintains the step count. This Click board™ can only be operated with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino UNO is a versatile microcontroller board built around the ATmega328P chip. It offers extensive connectivity options for various projects, featuring 14 digital input/output pins, six of which are PWM-capable, along with six analog inputs. Its core components include a 16MHz ceramic resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an
ICSP header, and a reset button, providing everything necessary to power and program the board. The Uno is ready to go, whether connected to a computer via USB or powered by an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. As the first USB Arduino board, it serves as the benchmark for the Arduino platform, with "Uno" symbolizing its status as the
first in a series. This name choice, meaning "one" in Italian, commemorates the launch of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. Initially introduced alongside version 1.0 of the Arduino Software (IDE), the Uno has since become the foundational model for subsequent Arduino releases, embodying the platform's evolution.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
28
RAM (Bytes)
2048
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino UNO has two proprietary mikroBUS™ sockets, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino UNO board without effort. The Arduino Uno, a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P, provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with the ATmega328P microcontroller from various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which six can be used as PWM outputs), six analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and reset button. Most of the ATmega328P microcontroller pins are brought to the IO pins on the left and right edge of the board, which are then connected to two existing mikroBUS™ sockets. This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino UNO board with our Click Shield for Arduino UNO, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for MPU IMU Click driver.
Key functions:
mpuimu_read_accel- This function read Accel X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axismpuimu_read_gyro- This function read Gyro X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axismpuimu_read_temperature- This function reads temperature data
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief MpuImu Click example
*
* # Description
* MPU IMU Click carries the integrated 6-axis motion tracking device
* that combines 3-axis gyroscope and accelerometer.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Application Init performs Logger and Click initialization.
*
* ## Application Task
* Measured Accel and Gyro coordinates (X,Y,Z) and Temperature in degrees C
* are being sent to the UART where you can track their changes.
* All data logs on USB UART for every 1 sec.
*
* \author Mihajlo Djordjevic
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "mpuimu.h"
float temperature;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static mpuimu_t mpuimu;
static log_t logger;
mpuimu_accel_data_t accel_data;
mpuimu_gyro_data_t gyro_data;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
mpuimu_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
// Click initialization.
mpuimu_cfg_setup( &cfg );
MPUIMU_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
mpuimu_init( &mpuimu, &cfg );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " ---- MPU IMU Click ----\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
mpuimu_default_cfg ( &mpuimu );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " ---- Initialization ---\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
mpuimu_read_accel( &mpuimu, &accel_data );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
mpuimu_read_gyro( &mpuimu, &gyro_data );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
temperature = mpuimu_read_temperature( &mpuimu );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " Accel | Gyro \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " X = %d | X = %d \r\n", accel_data.accel_x, gyro_data.gyro_x );
log_printf( &logger, " Y = %d | Y = %d \r\n", accel_data.accel_y, gyro_data.gyro_y );
log_printf( &logger, " Z = %d | Z = %d \r\n", accel_data.accel_z, gyro_data.gyro_z );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " TEMP = %0.2f C\r\n", temperature );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------\r\n" );
software_reset ( &mpuimu );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Motion