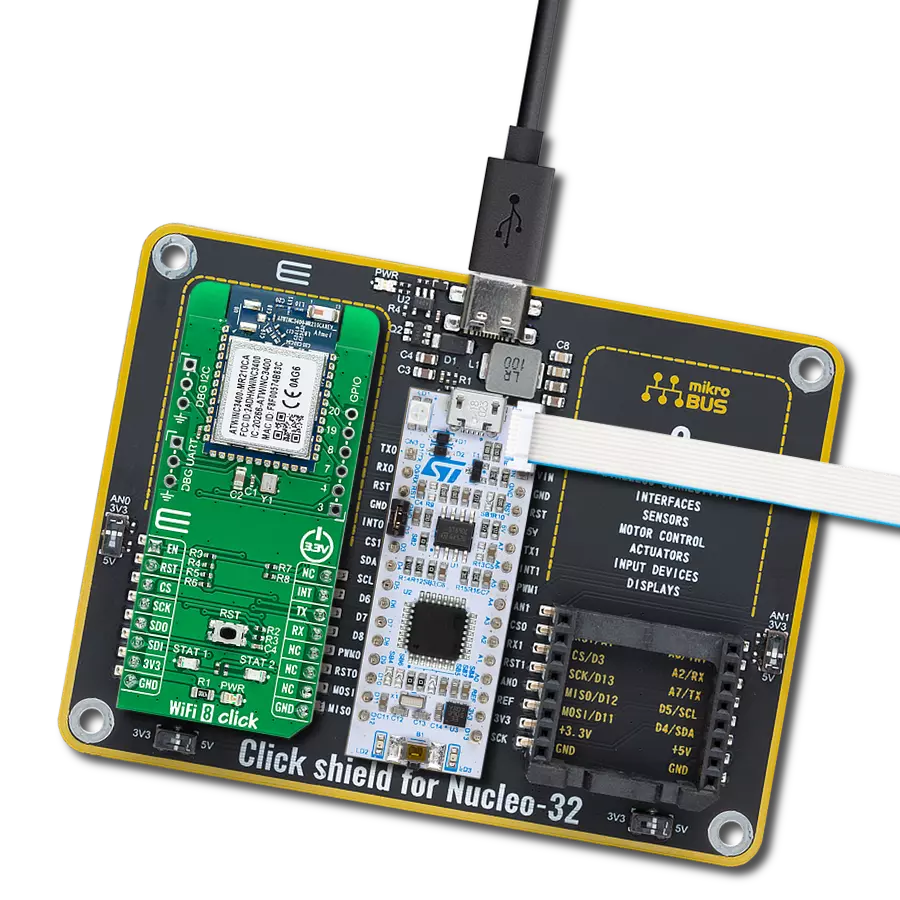
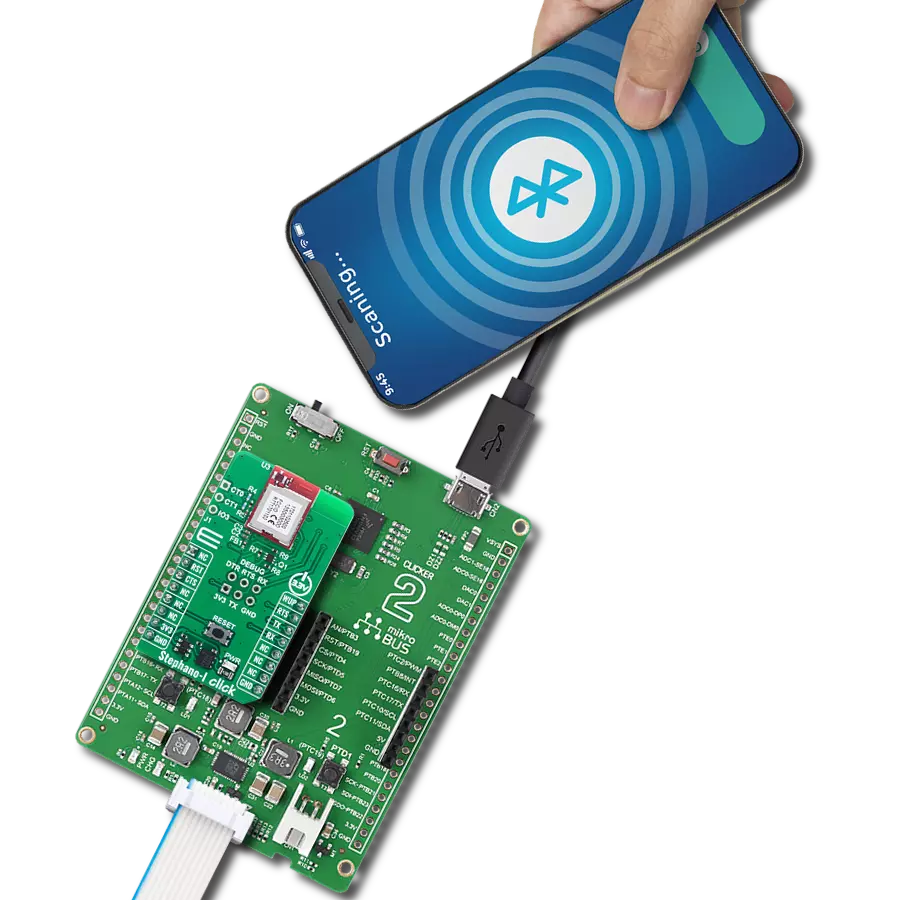
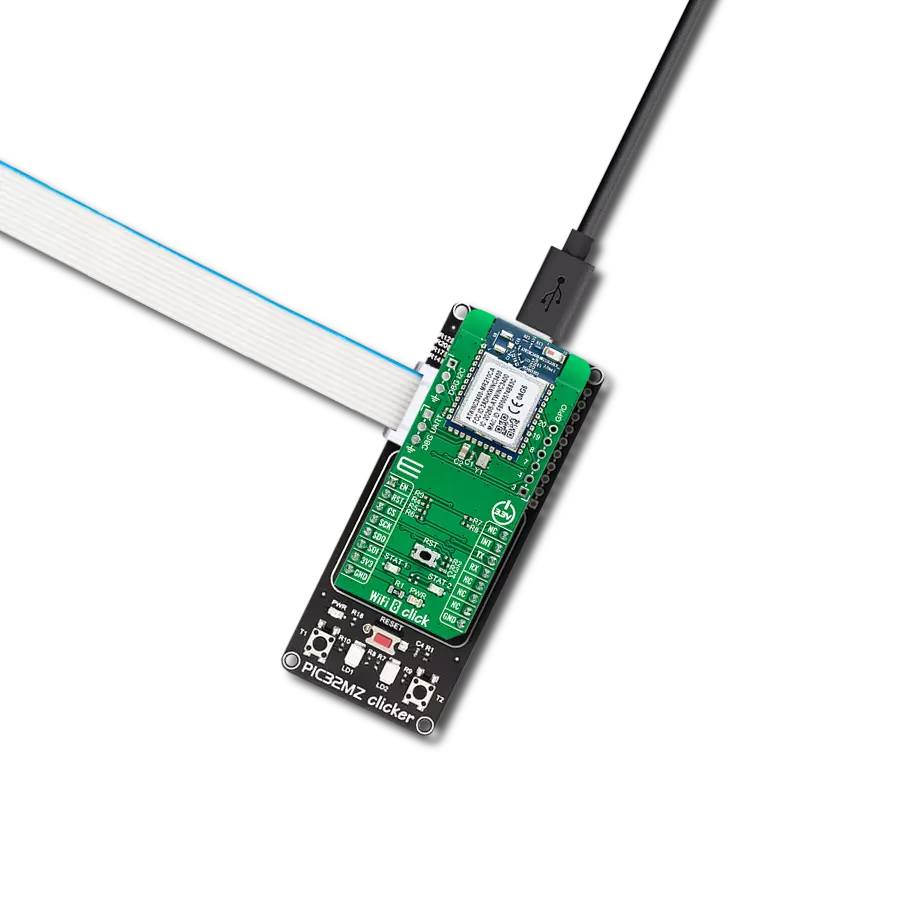
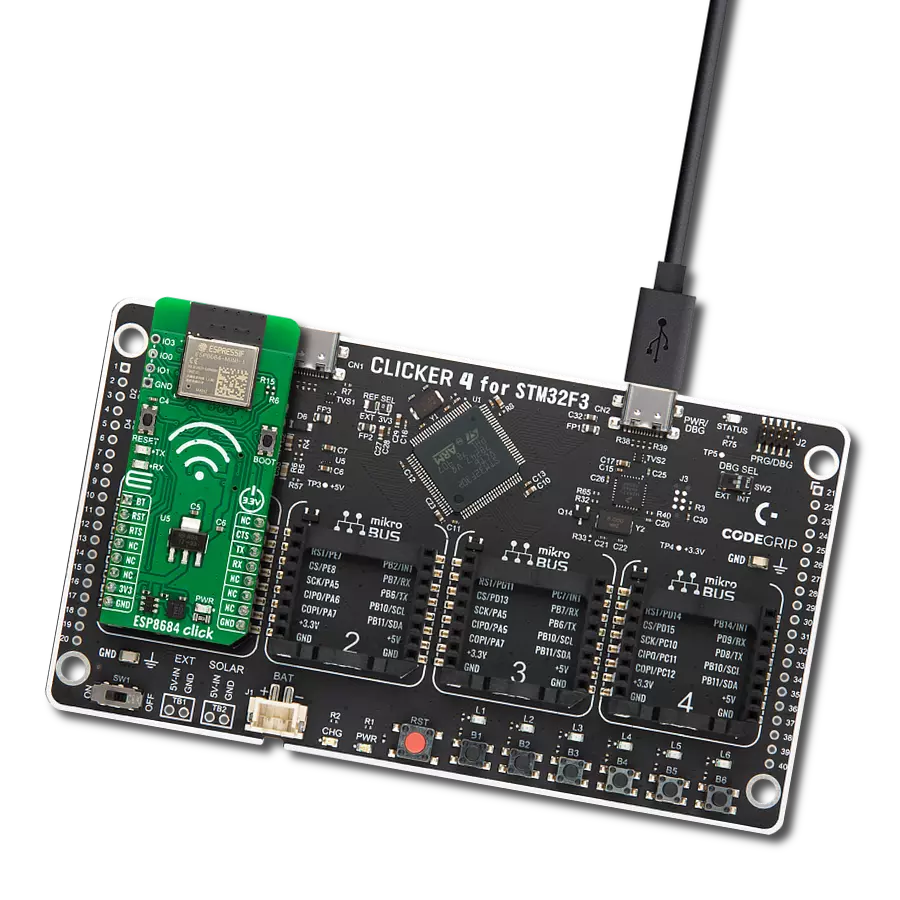
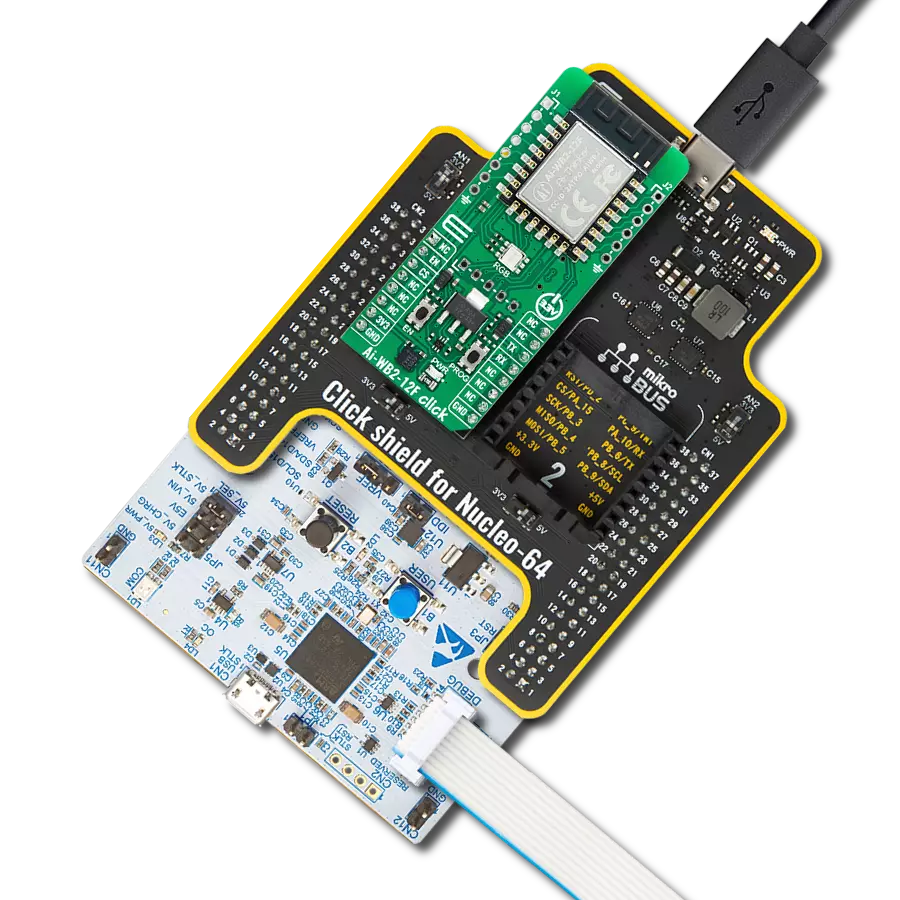
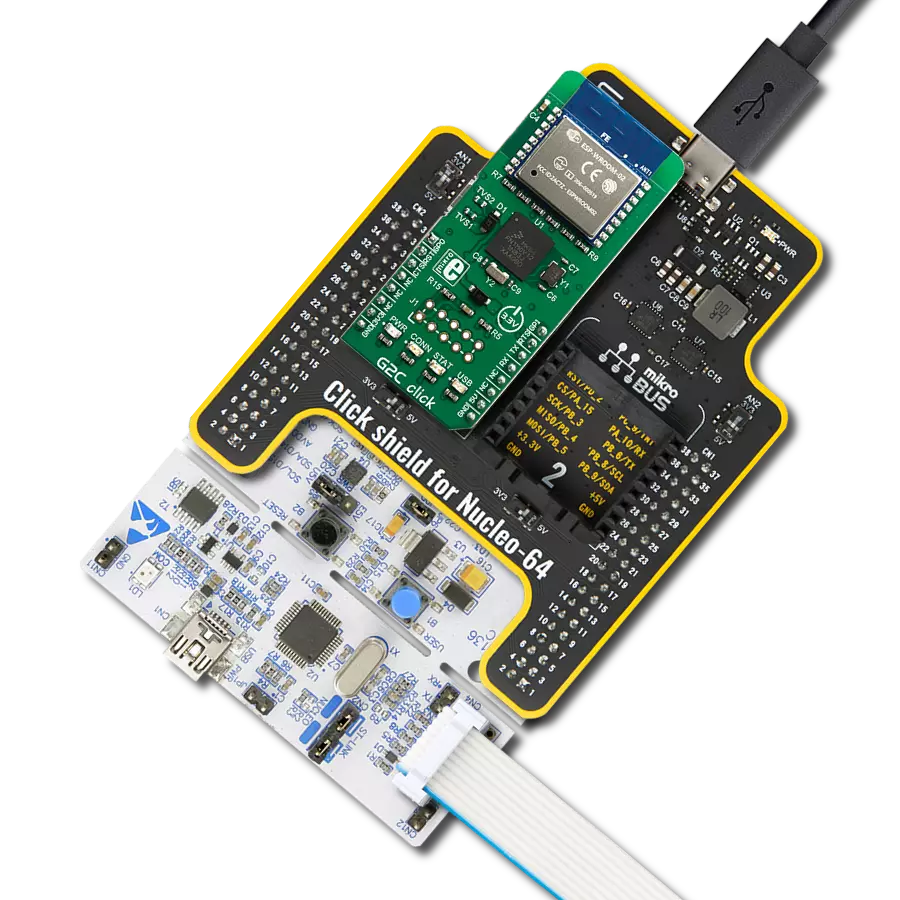
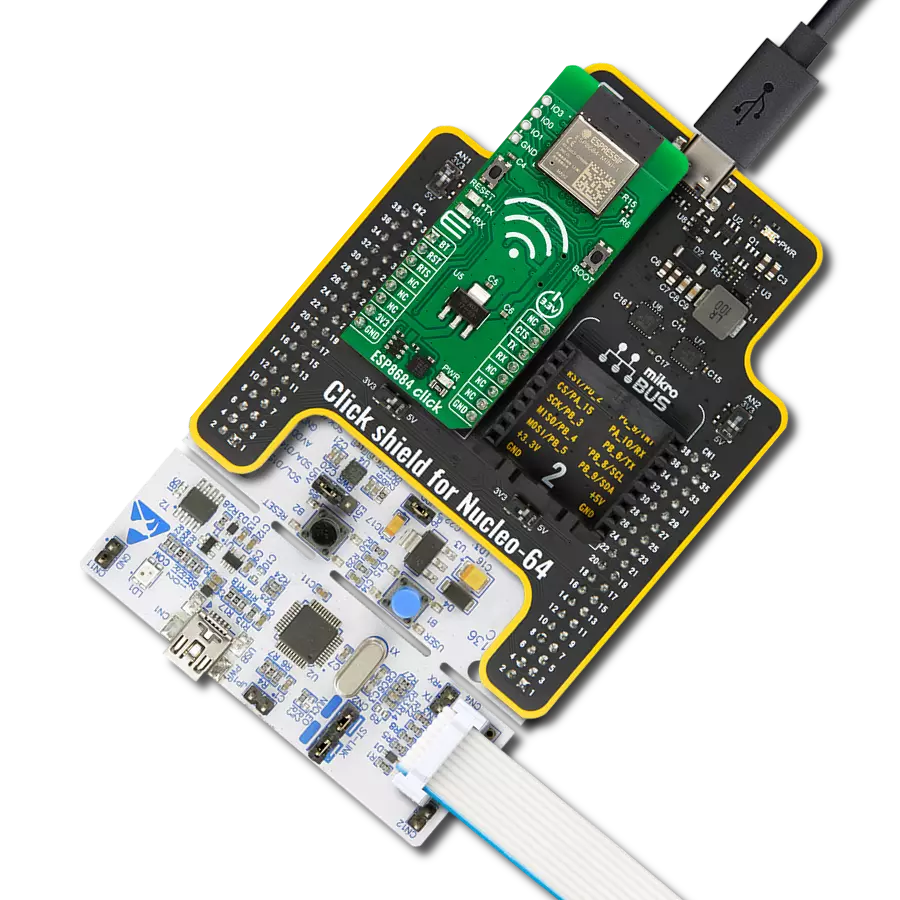
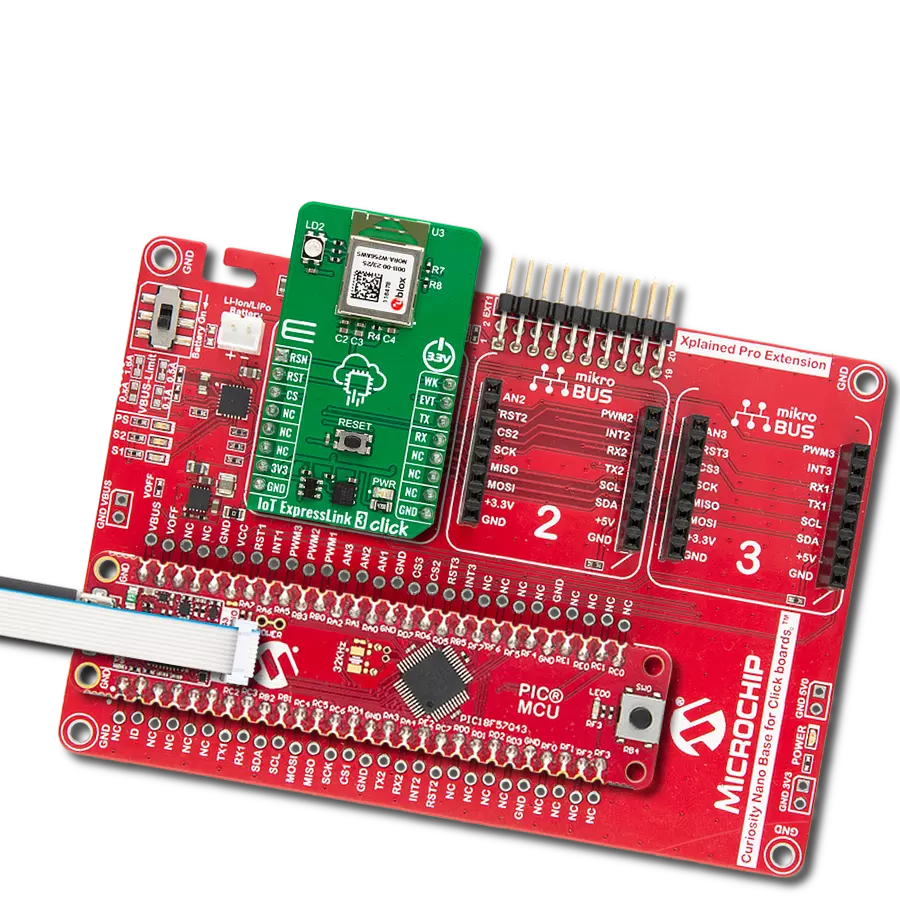
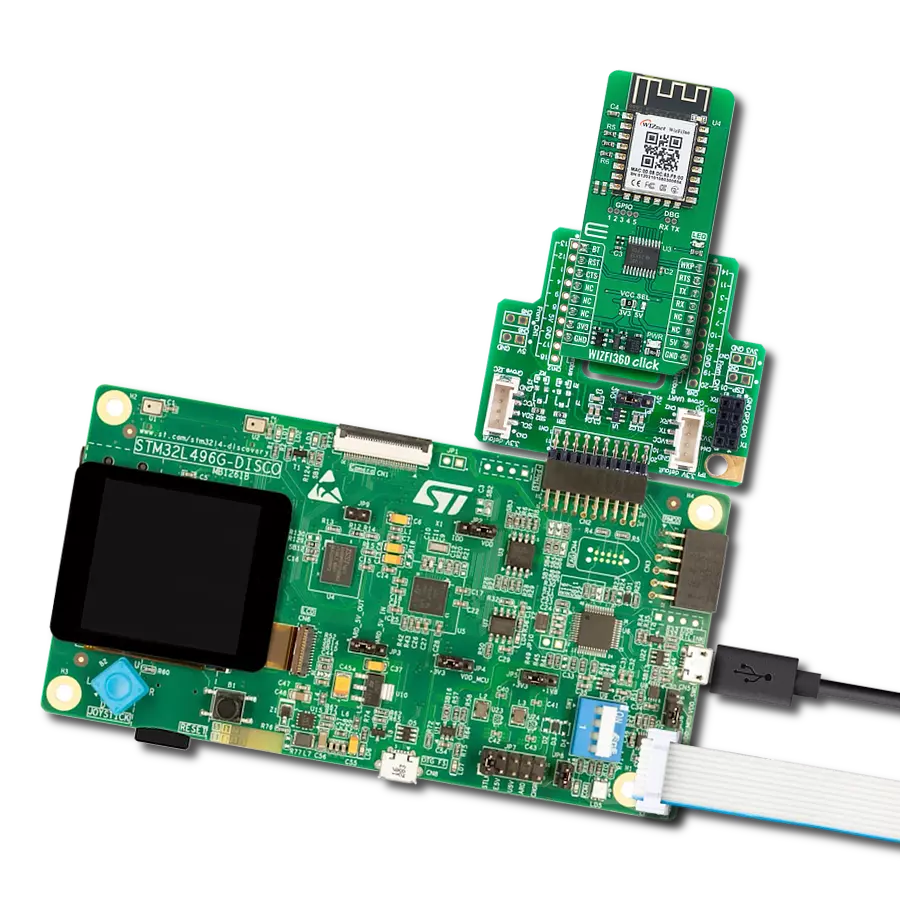
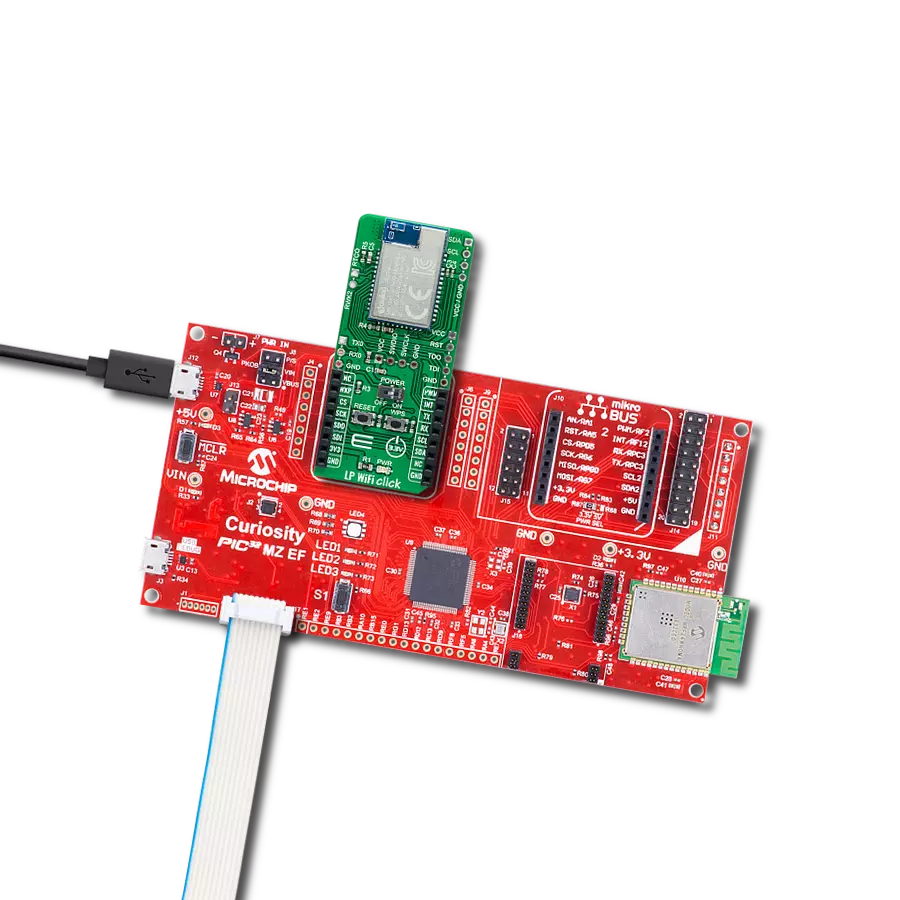
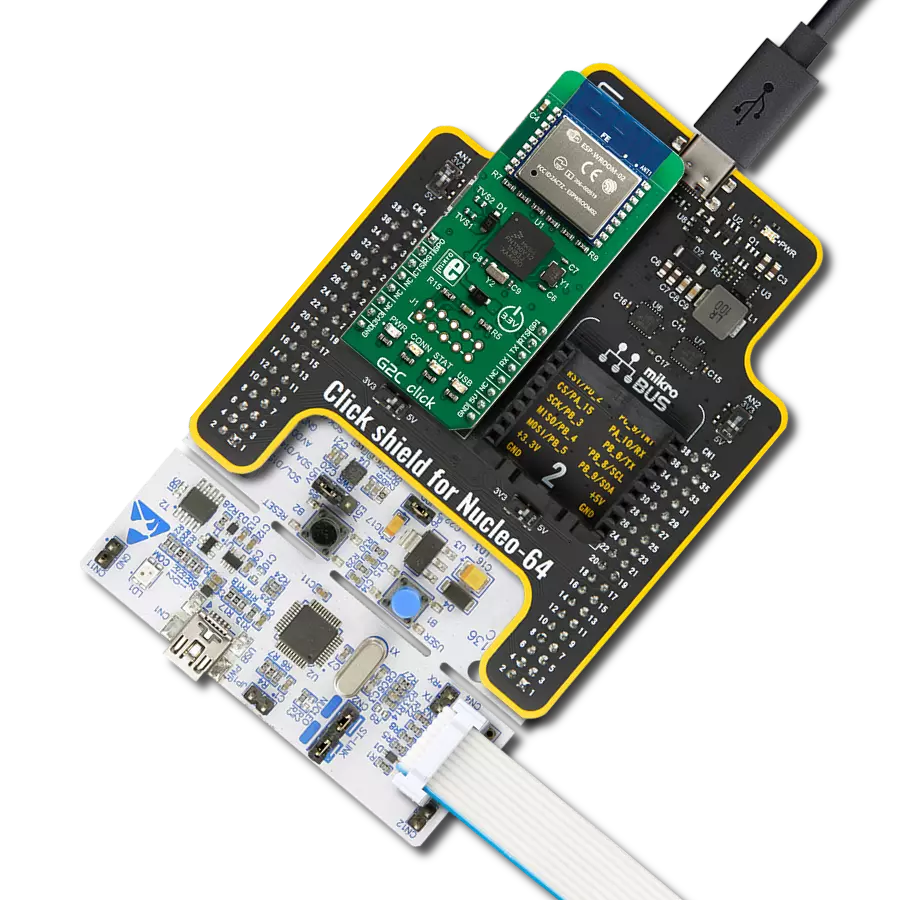
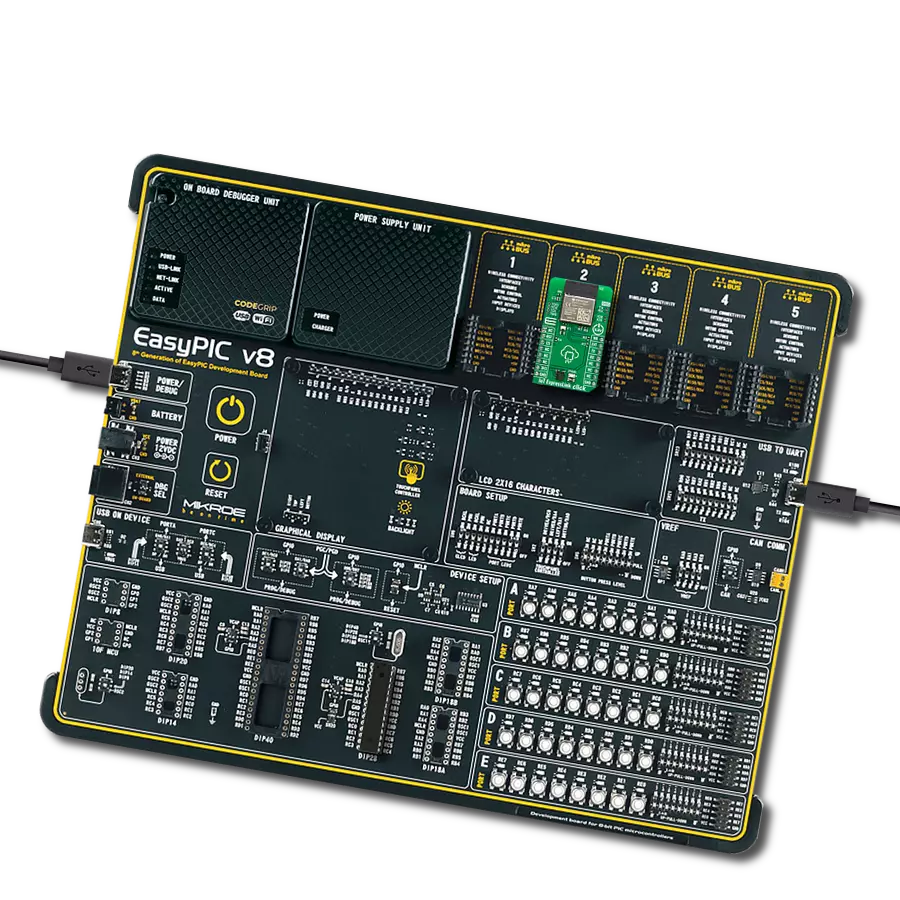
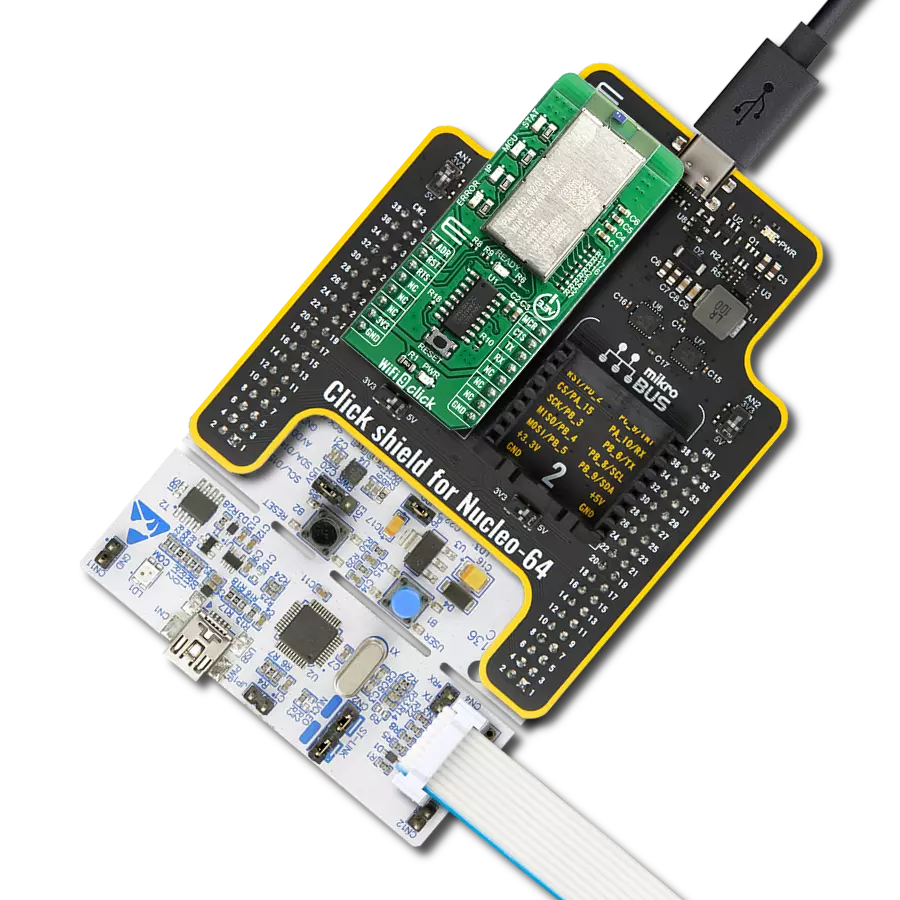
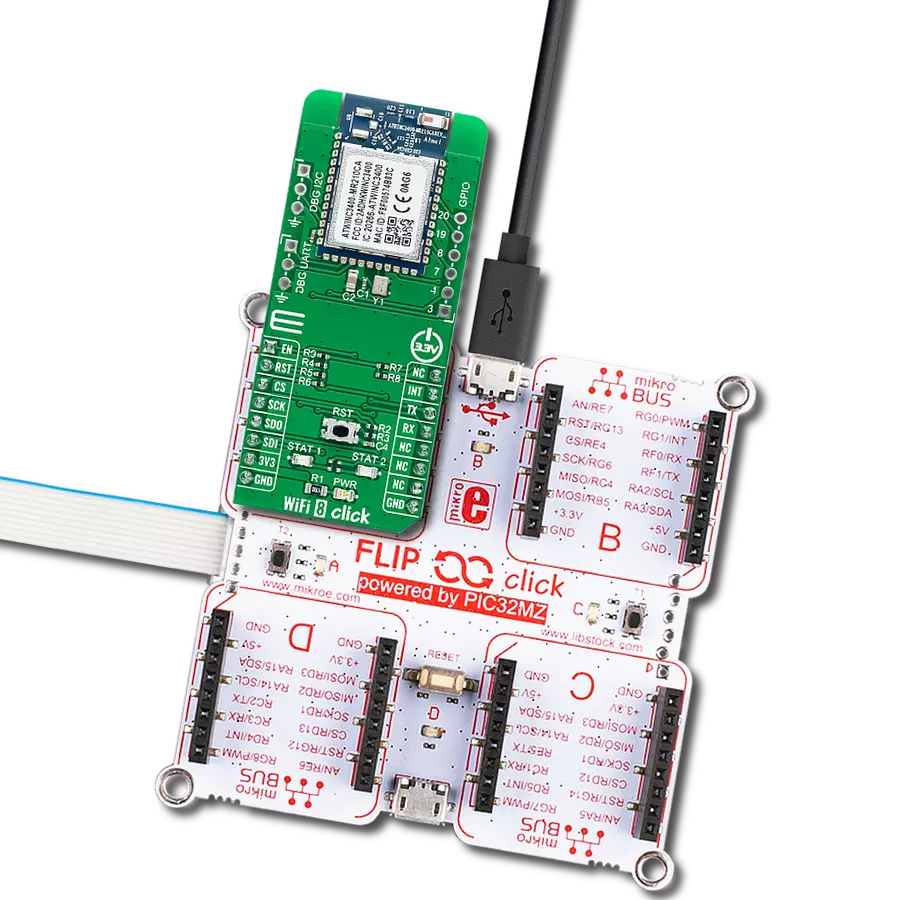
Driven by a commitment to simplicity and security, our purpose is to make it easy for users to securely connect their devices to the cloud and effortlessly integrate with the extensive offerings of AWS services.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
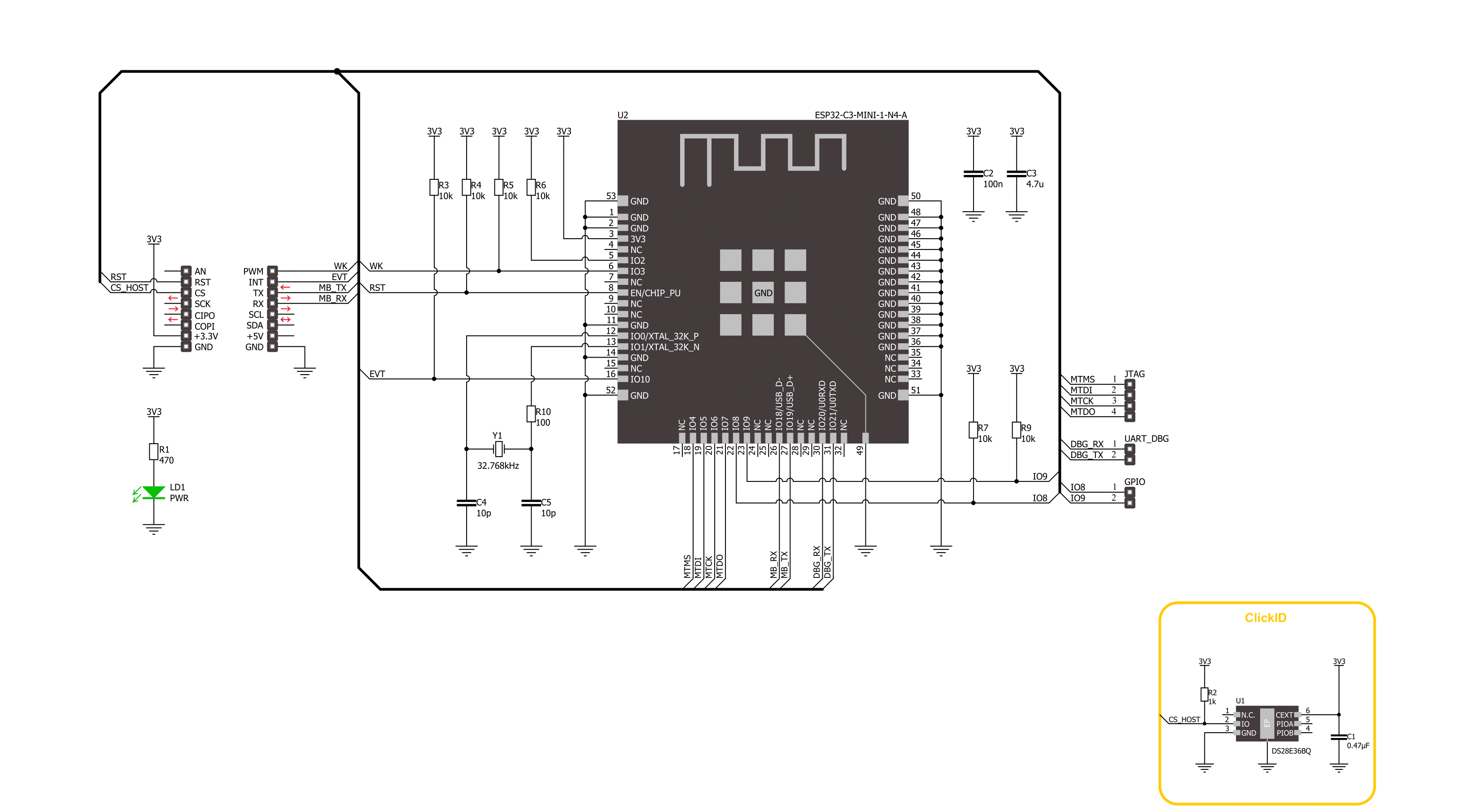
IoT ExpressLink Click is based on the ESP32-C3-MINI-1-N4-A, a 2.4GHz WiFi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth® 5 LE combo module from Espressif Systems that comes with an onboard PCB antenna and AWS IoT ExpressLink firmware (locked to the AWS). This module's core is the ESP32C3 series of SoC RISCV single-core 32-bit microprocessor (ESP32-C3FN4), a chip with an embedded flash of 4MB and a clock speed of up to 160MHz. Since flash is packaged in the ESP32-C3FN4 chip rather than integrated into the module, the ESP32-C3-MINI-1-N4-A has a smaller package size. Thanks to its rich set of features necessary to implement IoT ExpressLink services, this Click board™ is ideal for smart homes, industrial automation, health care,
consumer electronics, and generic IoT sensor hubs and data logger applications. The IoT ExpressLink Click interfaces with a host MCU through UART communication, which involves sending AT commands using RX and TX pins operating at a rate of 115200bps. Besides the UART pins, this Click board™ also employs other pins of the mikroBUS™ socket to enhance its functionality. For example, the WK pin is utilized as a module wake-up pin, the EVT pin detects significant events during operation, and the device enable pin RST offers a switch operation to turn ON/OFF the module. On the left side of the board, it is possible to find an additional unpopulated header that offers full support for debugging capabilities. With this
header, the user can use a JTAG interface for debugging, available through the JTAG interface pins (TDO, TCK, TDI, and TMS). On the right side of the board, there is also a set of unpopulated headers like extra UART pins for debugging and a header with user-configurable general-purpose I/O pins. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino Mega 2560 is a robust microcontroller platform built around the ATmega 2560 chip. It has extensive capabilities and boasts 54 digital input/output pins, including 15 PWM outputs, 16 analog inputs, and 4 UARTs. With a 16MHz crystal
oscillator ensuring precise timing, it offers seamless connectivity via USB, a convenient power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. This all-inclusive board simplifies microcontroller projects; connect it to your computer via USB or power it up
using an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. Notably, the Mega 2560 maintains compatibility with a wide range of shields crafted for the Uno, Duemilanove, or Diecimila boards, ensuring versatility and ease of integration.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
8192
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino Mega comes equipped with four mikroBUS™ sockets, with two in the form of a Shuttle connector, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino Mega board with no effort. Featuring an AVR 8-bit microcontroller with advanced RISC architecture, 54 digital I/O pins, and Arduino™ compatibility, the Arduino Mega board offers limitless possibilities for prototyping and creating diverse applications. This board is controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and debug the Arduino Mega board efficiently out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB B port on the board. Simplify your project development with the integrated ATmega16U2 programmer and unleash creativity using the extensive I/O options and expansion capabilities. There are eight switches, which you can use as inputs, and eight LEDs, which can be used as outputs of the MEGA2560. In addition, the shield features the MCP1501, a high-precision buffered voltage reference from Microchip. This reference is selected by default over the EXT REF jumper at the bottom of the board. You can choose an external one, as you would usually do with an Arduino Mega board. There is also a GND hook for testing purposes. Four additional LEDs are PWR, LED (standard pin D13), RX, and TX LEDs connected to UART1 (mikroBUS™ 1 socket). This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino Mega board with Click Shield for Arduino Mega, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for IoT ExpressLink Click driver.
Key functions:
iotexpresslink_reset_device- This function resets device by toggling the RST pin state.iotexpresslink_send_cmd- This function send command string by using UART serial interface.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief IoT ExpressLink Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of IoT ExpressLink Click board by bridging the USB UART
* to mikroBUS UART which allows the Click board to establish a connection with
* the IoT ExpressLink over the Quick Connect demo application without an AWS account.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver, resets the Click board to factory default settings, reads
* and displays the vendor model and thing name on the USB UART, sets the WiFi credentials,
* and attempts to connect to the AWS Cloud. If the initial attempt fails and the error
* message "Failed to access network" or "Failed to login AWS (MQTT) broker" appears,
* check the WiFi credentials and try running the example again.
*
* ## Application Task
* All data received from the USB UART will be forwarded to mikroBUS UART, and vice versa.
* At this point you should disconnect from the UART terminal and run the Quick Connect
* demo application.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t iotexpresslink_process ( uart_t *uart )
* - static err_t iotexpresslink_read_response ( iotexpresslink_t *ctx )
*
* @note
* To run the demo, follow the below steps:
* 1. If you opened a terminal application in the previous step, be sure to disconnect that
* application from the serial port.
* 2. Download the Quick Connect executable:
* Mac: https://quickconnectexpresslinkutility.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/QuickConnect_v1.9_macos.x64.tar.gz
* Windows: https://quickconnectexpresslinkutility.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/QuickConnect_v1.9_windows.x64.zip
* Linux: https://quickconnectexpresslinkutility.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/QuickConnect_v1.9_linux.x64.tar.gz
* 3. Unzip the package, and follow the steps from the README file.
*
* The demo will connect to IoT ExpressLink and give you an URL that you can use to visualize data
* flowing from the device to the cloud using AT+SEND commands. The demo will run for up
* to two minutes, and afterwards, you will be able to type AT+SEND commands yourself and
* see the data coming in on the visualizer.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "iotexpresslink.h"
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 500
// Enter valid WiFi credentials below
#define WIFI_SSID "MikroE Public" // WiFi SSID
#define WIFI_PASS "mikroe.guest" // WiFi Password
static iotexpresslink_t iotexpresslink;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
/**
* @brief IoT ExpressLink clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length.
* @note None.
*/
static void iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief IoT ExpressLink data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #iotexpresslink_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t iotexpresslink_process ( iotexpresslink_t *ctx ) ;
/**
* @brief IoT ExpressLink read response function.
* @details This function waits for a response message, reads and displays it on the USB UART.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #iotexpresslink_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t iotexpresslink_read_response ( iotexpresslink_t *ctx );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
iotexpresslink_cfg_t iotexpresslink_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
iotexpresslink_cfg_setup( &iotexpresslink_cfg );
IOTEXPRESSLINK_MAP_MIKROBUS( iotexpresslink_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == iotexpresslink_init( &iotexpresslink, &iotexpresslink_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_printf( &logger, "Reset device\r\n\n" );
iotexpresslink_reset_device ( &iotexpresslink );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, "Factory reset\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_FACTORY_RESET );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, "Vendor model\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_CONF_CHECK );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SEPARATOR );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CONF_KEY_ABOUT );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
log_printf( &logger, "Thing name\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_CONF_CHECK );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SEPARATOR );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CONF_KEY_THING_NAME );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
log_printf( &logger, "WiFi SSID\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_CONF );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SEPARATOR );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CONF_KEY_SSID );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SIGN_EQUAL );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_SSID );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
log_printf( &logger, "WiFi Password\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_CONF );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SEPARATOR );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CONF_KEY_PASSPHRASE );
strcat ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_SIGN_EQUAL );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PASS );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
log_printf( &logger, "Try to connect\r\n" );
strcpy ( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_CMD_CONNECT );
iotexpresslink_send_cmd ( &iotexpresslink, app_buf );
iotexpresslink_read_response ( &iotexpresslink );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
log_printf( &logger, "Now close the UART terminal and switch to the QuickConnect app\r\n" );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
uart_set_blocking( &logger.uart, false );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
app_buf_len = uart_read( &logger.uart, app_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( app_buf_len > 0 )
{
uart_write ( &iotexpresslink.uart, app_buf, app_buf_len );
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
}
app_buf_len = uart_read( &iotexpresslink.uart, app_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( app_buf_len > 0 )
{
uart_write ( &logger.uart, app_buf, app_buf_len );
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static err_t iotexpresslink_process ( iotexpresslink_t *ctx )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t rx_size = 0;
rx_size = iotexpresslink_generic_read( ctx, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
if ( ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ) && ( app_buf_len > 0 ) )
{
buf_cnt = PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE - ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE - buf_cnt ], buf_cnt );
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ buf_cnt++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
if ( app_buf_len < PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
app_buf_len++;
}
}
}
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_OK;
}
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_ERROR;
}
static err_t iotexpresslink_read_response ( iotexpresslink_t *ctx )
{
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint32_t timeout = 30000;
memset( app_buf, 0, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
app_buf_len = 0;
iotexpresslink_process( ctx );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_RSP_OK ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_RSP_ERR ) ) )
{
iotexpresslink_process( ctx );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > timeout )
{
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
iotexpresslink_process( ctx );
if ( app_buf_len > 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%s\r\n", app_buf );
}
if ( strstr( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_RSP_OK ) )
{
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, IOTEXPRESSLINK_RSP_ERR ) )
{
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_ERROR_CMD;
}
iotexpresslink_clear_app_buf( );
return IOTEXPRESSLINK_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:WiFi