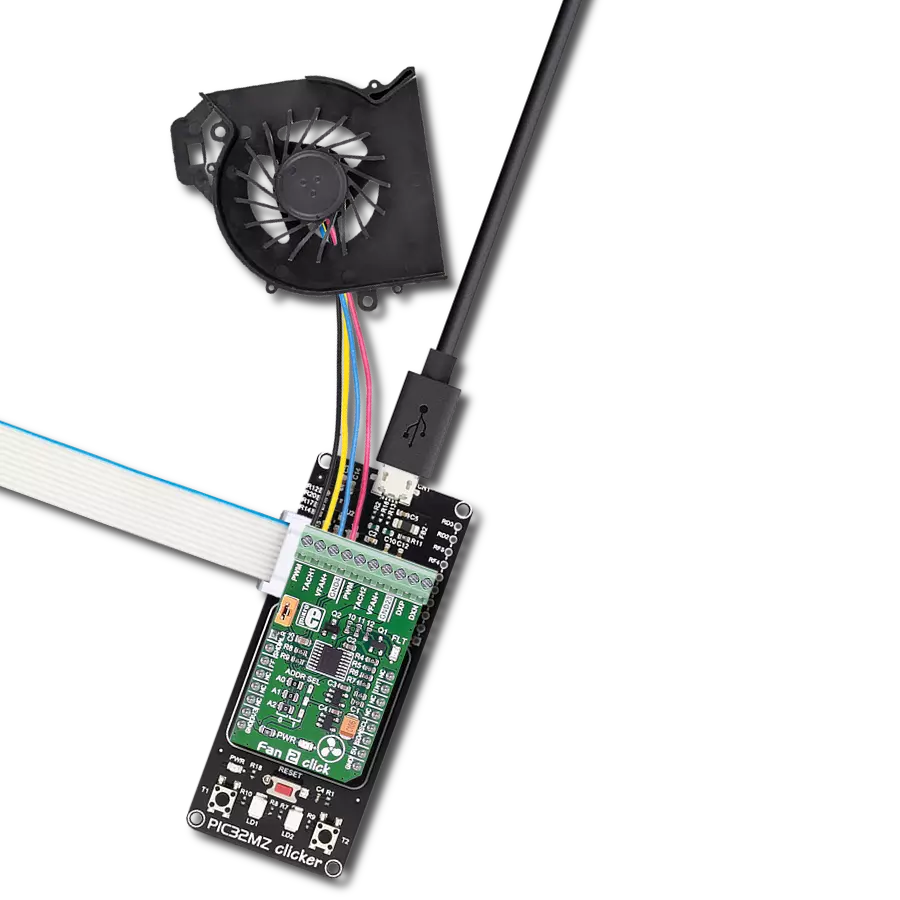
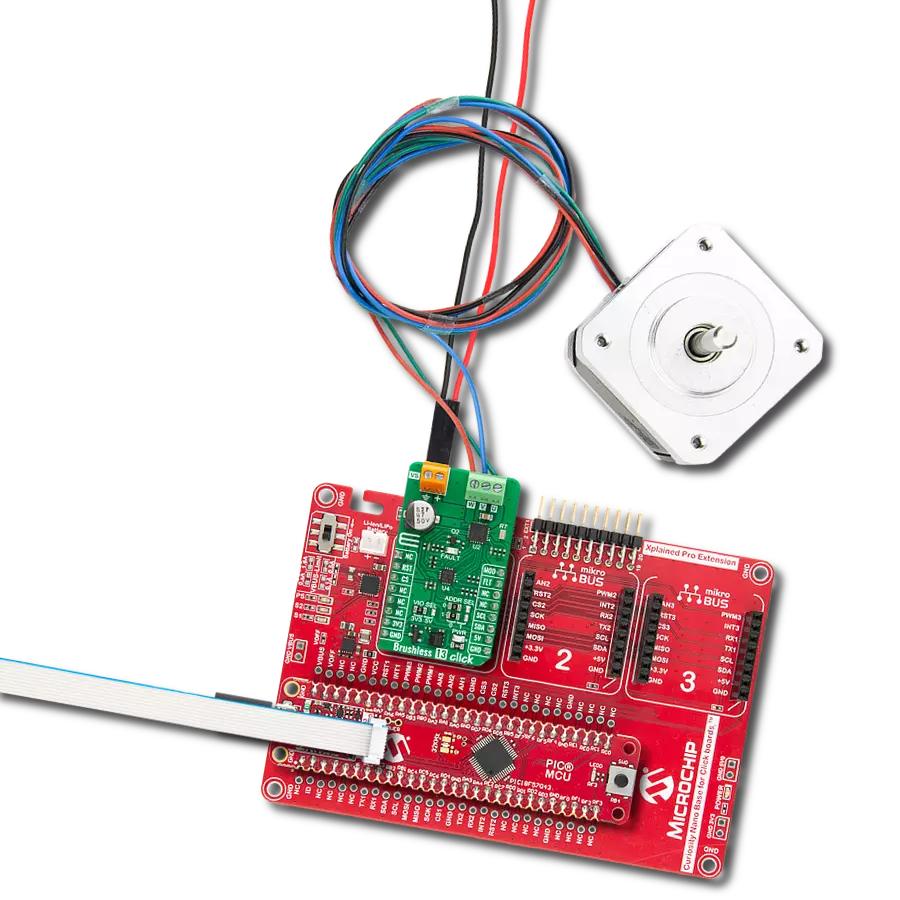
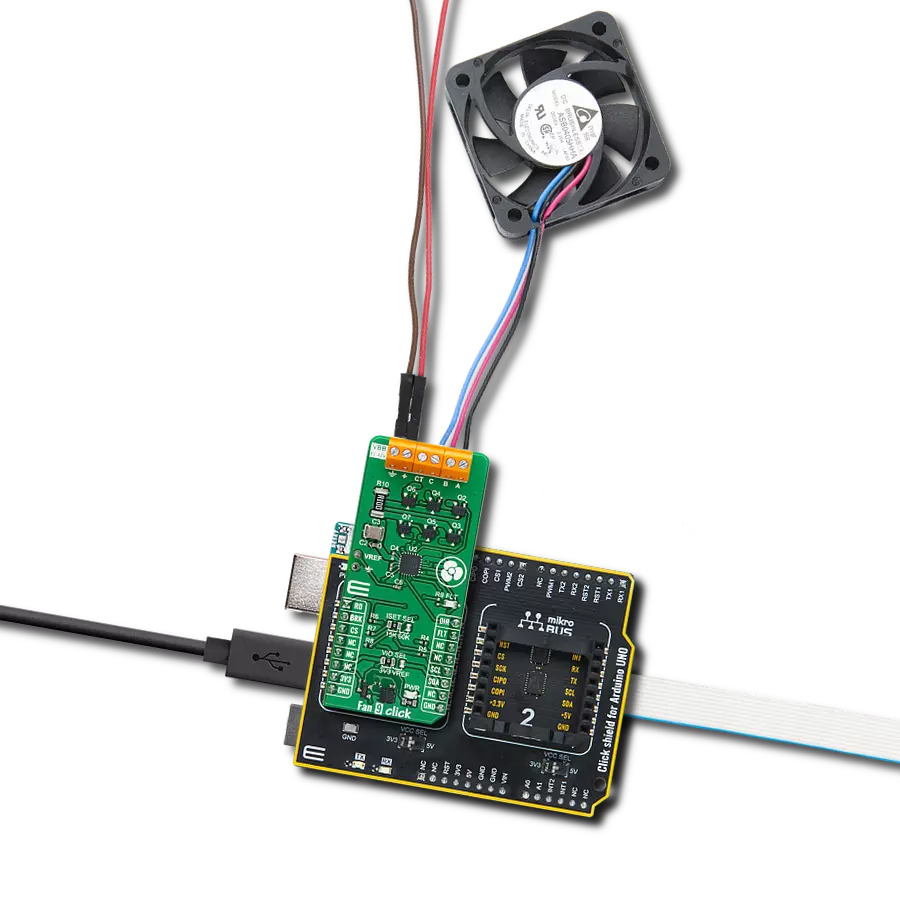
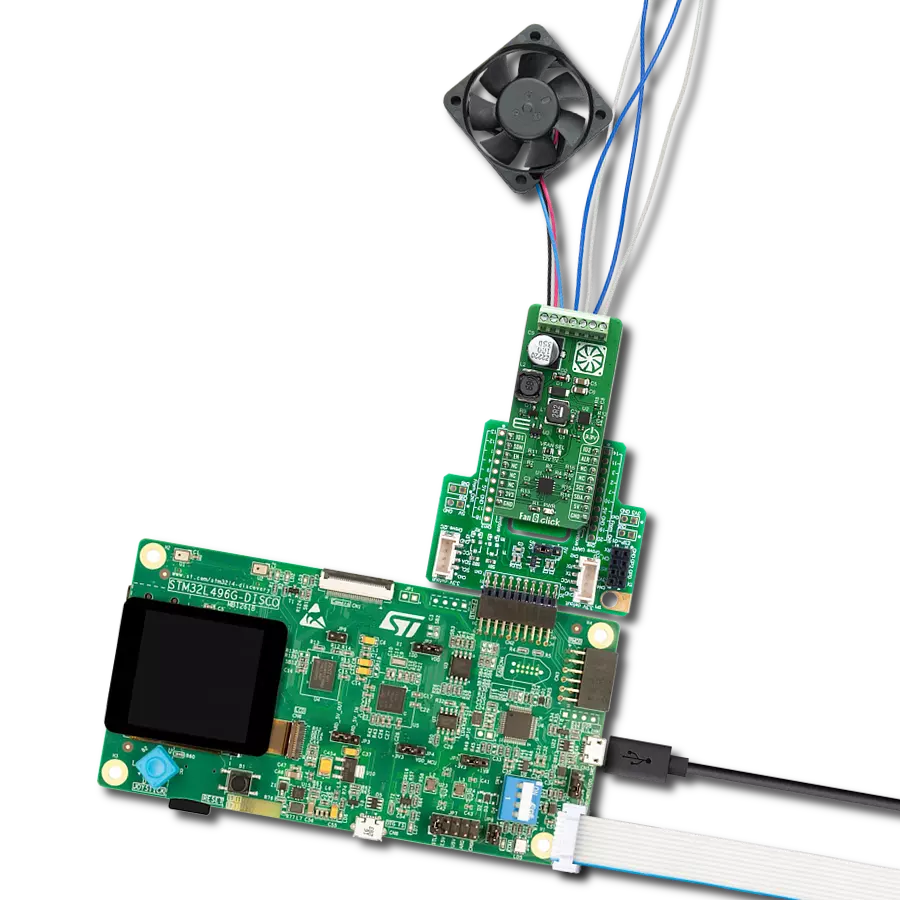
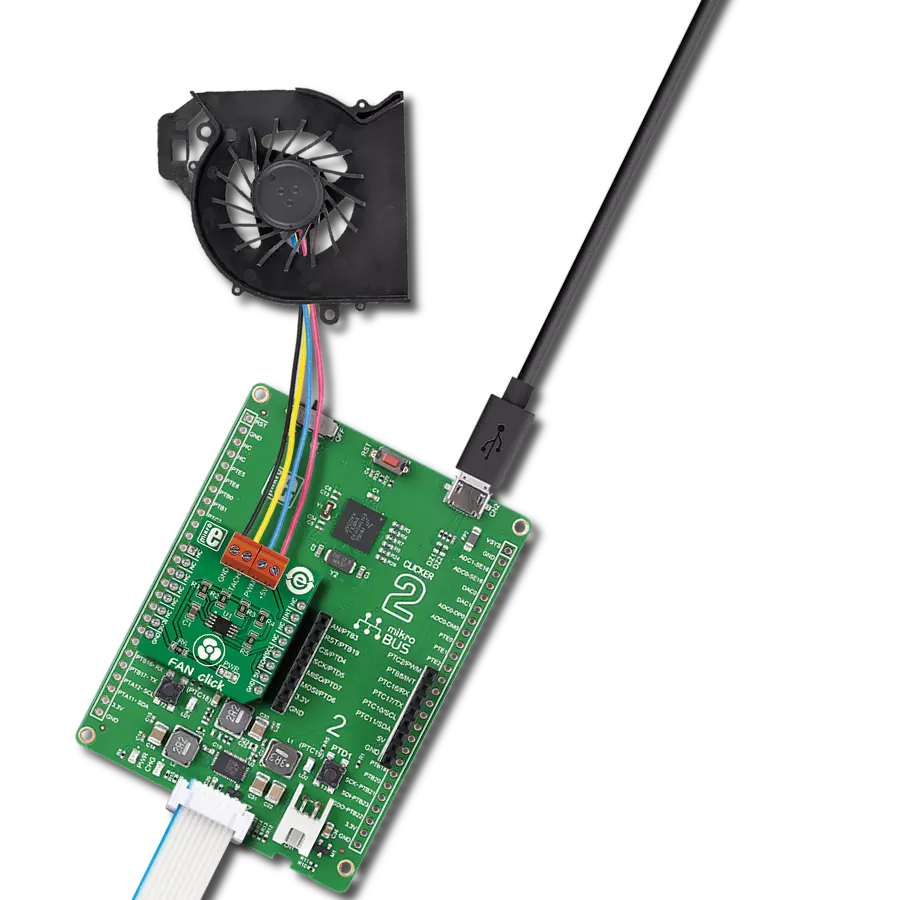
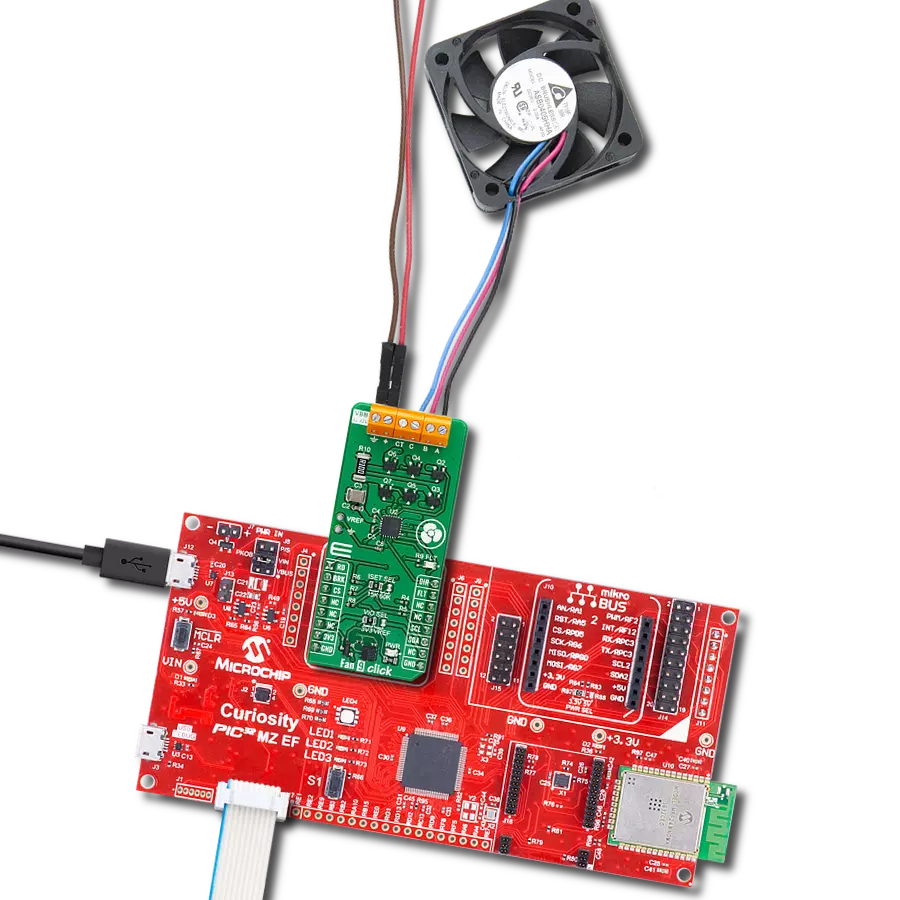
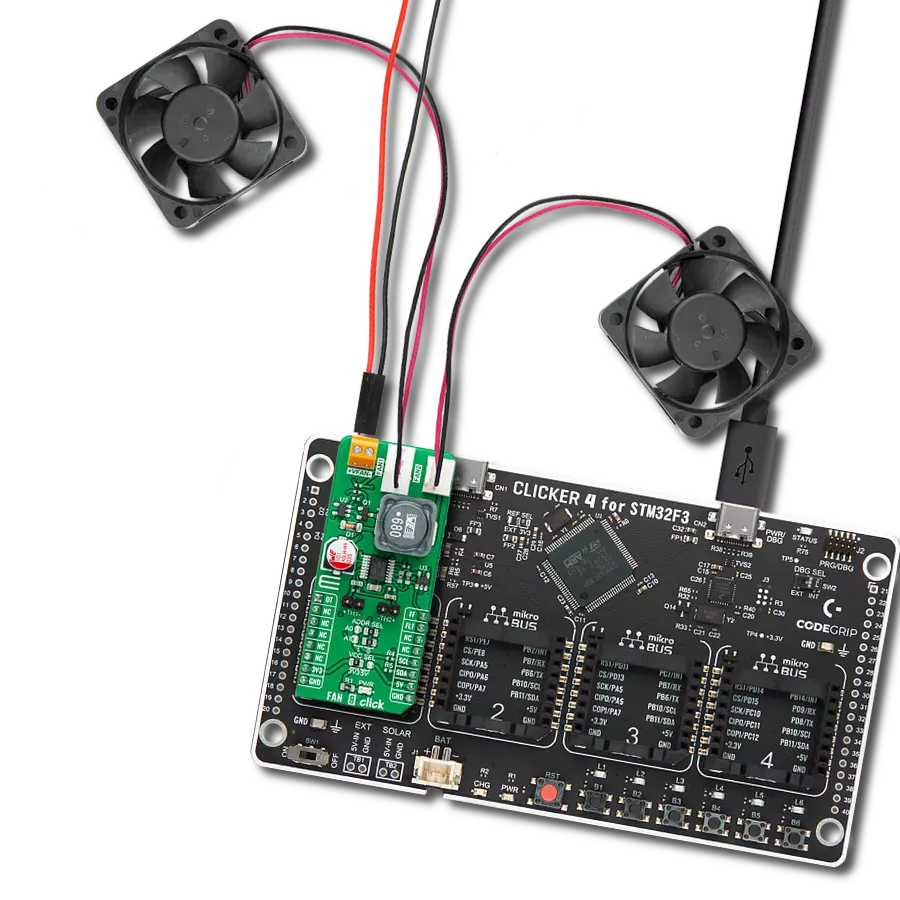
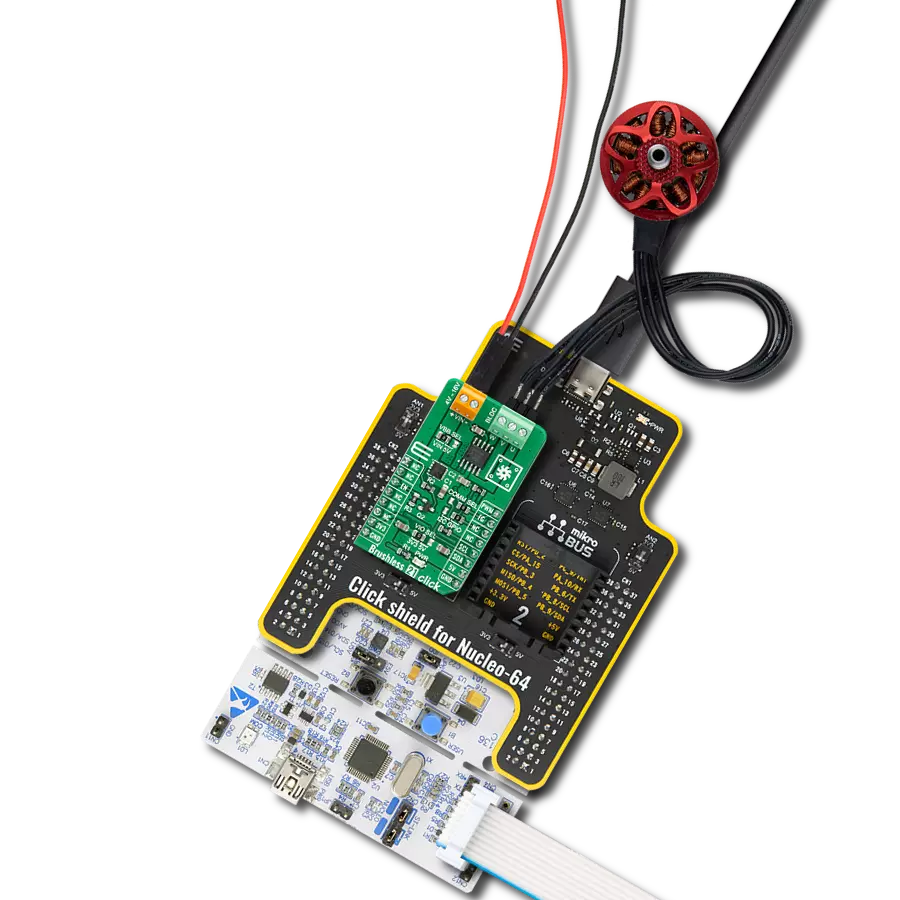
Experience the versatility of our brushless motor drivers, crafted to deliver unmatched efficiency and control across a spectrum of applications.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Brushless 11 Click is based on the A4931, a 3-phase brushless DC motor pre-driver from Allegro Microsystems. It uses six external N-channel MOSFETs to drive a 3-phase BLDC motor. The internal charge pump generates a supply to drive the high-side MOSFETs while the voltage is internally monitored. In case of a fault condition, the device outputs are disabled. The pre-driver features several protection mechanisms, including fault shutdown, overvoltage protection, overtemperature protection, hall state reporting, and mock detect function. The A4931 also features the HBIAS function, which provides a power
supply voltage of 7.5V with a current limited to 30mA. This referent voltage powers the logic sections of the pre-driver and the external Hall elements. These elements can be connected over the 6-pin header, labeled as positive and negative A, B, and C channel inputs. To set the motor direction, this Click board™ uses a DIR switch. Set the position 1 for rotating forward and 0 position for rotating reverse. Brushless 11 Click is controlled by the host MCU through GPIO logic states. The enable input terminal on pin EN is used for external PWM, with typically PWM frequencies in the 20 to 30kHz range. To use brakes and stop the
motor, you should write a logic LOW on the BRK pin, which activates the Brake mode. This input overrides the enable input and also the lock detect function. Both the EN and BRK pins are pulled up. There are FG1 and FG2 pins that let you accurately measure motor rotation. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Nucleo 32 with STM32F031K6 MCU board provides an affordable and flexible platform for experimenting with STM32 microcontrollers in 32-pin packages. Featuring Arduino™ Nano connectivity, it allows easy expansion with specialized shields, while being mbed-enabled for seamless integration with online resources. The
board includes an on-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer, supporting USB reenumeration with three interfaces: Virtual Com port, mass storage, and debug port. It offers a flexible power supply through either USB VBUS or an external source. Additionally, it includes three LEDs (LD1 for USB communication, LD2 for power,
and LD3 as a user LED) and a reset push button. The STM32 Nucleo-32 board is supported by various Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IAR™, Keil®, and GCC-based IDEs like AC6 SW4STM32, making it a versatile tool for developers.
Microcontroller Overview
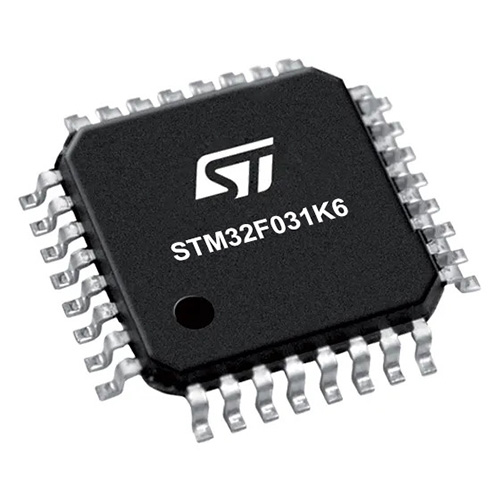
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
Accessories
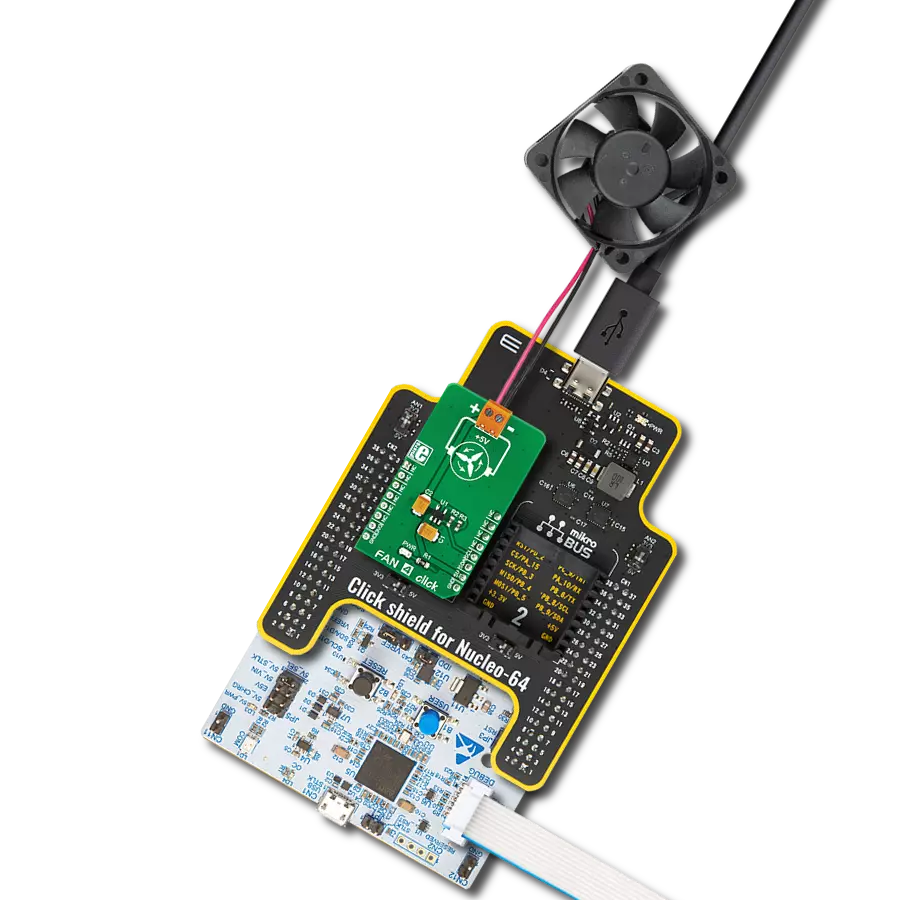
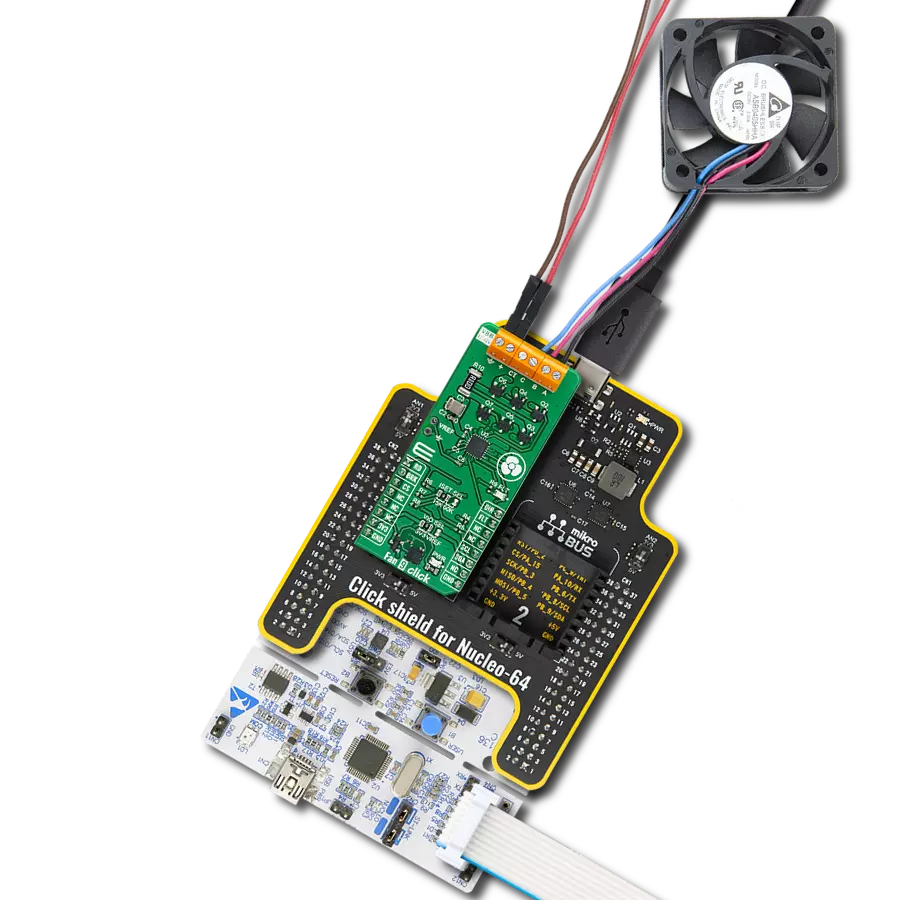
Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is the perfect way to expand your development board's functionalities with STM32 Nucleo-32 pinout. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 provides two mikroBUS™ sockets to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™. We are fully stocked with everything, from sensors and WiFi transceivers to motor control and audio amplifiers. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is compatible with the STM32 Nucleo-32 board, providing an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new ideas and quickly create prototypes with any STM32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The STM32 Nucleo-32 boards do not require any separate probe as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer and come with the STM32 comprehensive software HAL library and various packaged software examples. This development platform provides users with an effortless and common way to combine the STM32 Nucleo-32 footprint compatible board with their favorite Click boards™ in their upcoming projects.
Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor with a Hall sensor represents a high-performance motor from the 42BLF motor series. This motor, wired in a star configuration, boasts a Hall Effect angle of 120°, ensuring precise and reliable performance. With a compact motor length of 47mm and a lightweight design tipping the scales at just 0.29kg, this BLDC motor is engineered to meet your needs. Operating flawlessly at a voltage rating of 24VDC and a speed range of 4000 ± 10% RPM, this motor offers consistent and dependable power. It excels in a normal operational temperature range from -20 to +50°C, maintaining efficiency with a rated current of 1.9A. Also, this product seamlessly integrates with all Brushless Click boards™ and those that require BLDC motors with Hall sensors.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Brushless 11 Click driver.
Key functions:
brushless11_get_fg1_pin- Brushless 11 get FG1 pin state function.brushless11_set_brake- Brushless 11 set motor brake state function.brushless11_set_speed- Brushless 11 set motor speed.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Brushless 11 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of the Brushless 11 Click board by driving the
* motor at different speeds.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration.
*
* ## Application Task
* Controls the motor speed by changing the PWM duty cycle every second.
* The duty cycle ranges from 10% to 100%.
* Each step will be logged on the USB UART where you can track the program flow.
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "brushless11.h"
static brushless11_t brushless11;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
brushless11_cfg_t brushless11_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
brushless11_cfg_setup( &brushless11_cfg );
BRUSHLESS11_MAP_MIKROBUS( brushless11_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( PWM_ERROR == brushless11_init( &brushless11, &brushless11_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( BRUSHLESS11_ERROR == brushless11_default_cfg ( &brushless11 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Motor brake is off \r\n" );
brushless11_set_brake( &brushless11, BRUSHLESS11_BRAKE_OFF );
for ( uint8_t speed_cnt = 10; speed_cnt <= 100; speed_cnt += 10 )
{
brushless11_set_speed( &brushless11, speed_cnt );
log_printf( &logger, " Speed is: %d%% \r\n", ( uint16_t ) speed_cnt );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
log_printf( &logger, " Motor brake is on \r\n" );
brushless11_set_brake( &brushless11, BRUSHLESS11_BRAKE_ON );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Brushless