Our wireless combo solution harmonizes the strengths of WiFi and BLE, creating a symphony of connectivity for a smarter, more efficient world.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
ESP8684 Click is based on the ESP8684-MINI-1, a highly integrated WiFi, and a Bluetooth 5 module from Espressif Systems. It is based on the ESP8684H2 embedded 32-bit RISC-V single-core processor operating at up to 120MHz frequency. The processor also has an on-chip 576KB of ROM and 272KB of SRAM memory, supporting flash in-circuit programming (ICP). It also features an internal co-existence mechanism between WiFi and Bluetooth to share the same printed PCB antenna. The downside is that you can’t use both WiFi and Bluetooth at the same time. ESP8684 Click is an IEEE802.11b/g/n-compliant and supports 20MHz bandwidth in the 2.4GHz band. In 1T1R mode, it can achieve data rates of up to 72.2Mbps. In addition, the module supports WiFi Multimedia (WMM), fragmentation and defragmentation, transmit opportunity (TXOP), automatic beacon monitoring hardware (hardware TSF), and more. As for Bluetooth, the module can achieve
speeds of 125kbps, 500kbps, 1Mbps, and 2Mbps. The security features secure boot, flash encryption, 1024-bit OTP up to 256 bits for use, cryptographic hardware acceleration, and more. This Click board™ is equipped with a USB type C connector and circuits that allow you to establish direct communication between the ESP8684 module and a PC. This communication can be used for testing purposes or for upgrading the software. For uploading software to the ESP8684 module, there is an auto-reset circuit and the CP2102N, a USB-to-UART bridge from Silicon Labs. Two LEDs, RX and TX, are there to visually confirm the data exchange over this bridge. In addition, two buttons, RESET and BOOT, allow you to enter the ESP8684’s boot mode. Finally, a header contains 3 GPIOs and a GND for user configuration and can be used for an analog interface. ESP8684 Click uses a standard 2-Wire UART interface to communicate with the host MCU with commonly
used UART RTS and CTS control flow pins. Besides the available software and libraries we provide, you can use a set of AT commands to program the ESP8684 module. In addition to the UART bridge and two onboard buttons, you can enter the ESP8684’s boot mode via RST and BT pins of the mikroBUS™ socket. Thanks to the onboard NCP1117 LDO, which converts USB voltage into the 3.3V necessary for operation, this board can be standalone independent of the mikroBUS™ socket. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
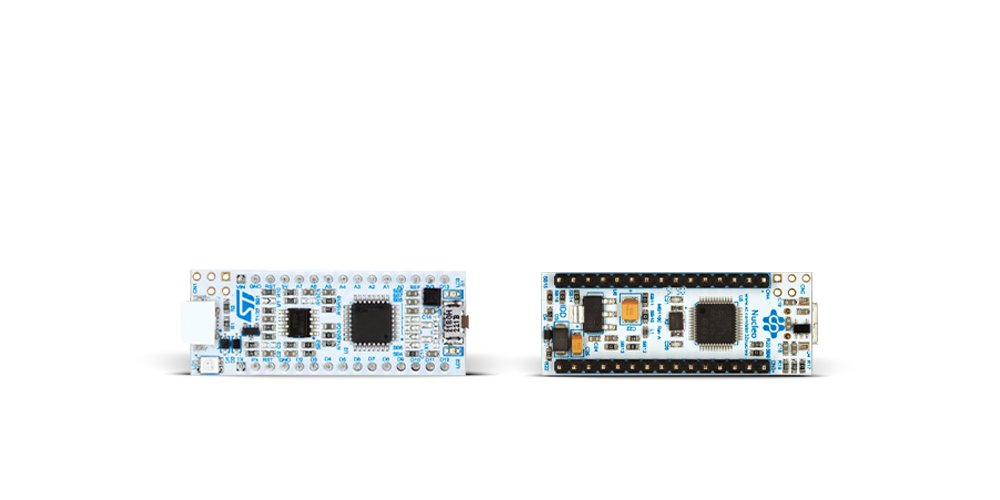
Nucleo 32 with STM32F031K6 MCU board provides an affordable and flexible platform for experimenting with STM32 microcontrollers in 32-pin packages. Featuring Arduino™ Nano connectivity, it allows easy expansion with specialized shields, while being mbed-enabled for seamless integration with online resources. The
board includes an on-board ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer, supporting USB reenumeration with three interfaces: Virtual Com port, mass storage, and debug port. It offers a flexible power supply through either USB VBUS or an external source. Additionally, it includes three LEDs (LD1 for USB communication, LD2 for power,
and LD3 as a user LED) and a reset push button. The STM32 Nucleo-32 board is supported by various Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) such as IAR™, Keil®, and GCC-based IDEs like AC6 SW4STM32, making it a versatile tool for developers.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M0
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
32
RAM (Bytes)
4096
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is the perfect way to expand your development board's functionalities with STM32 Nucleo-32 pinout. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 provides two mikroBUS™ sockets to add any functionality from our ever-growing range of Click boards™. We are fully stocked with everything, from sensors and WiFi transceivers to motor control and audio amplifiers. The Click Shield for Nucleo-32 is compatible with the STM32 Nucleo-32 board, providing an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new ideas and quickly create prototypes with any STM32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption, and features. The STM32 Nucleo-32 boards do not require any separate probe as they integrate the ST-LINK/V2-1 debugger/programmer and come with the STM32 comprehensive software HAL library and various packaged software examples. This development platform provides users with an effortless and common way to combine the STM32 Nucleo-32 footprint compatible board with their favorite Click boards™ in their upcoming projects.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
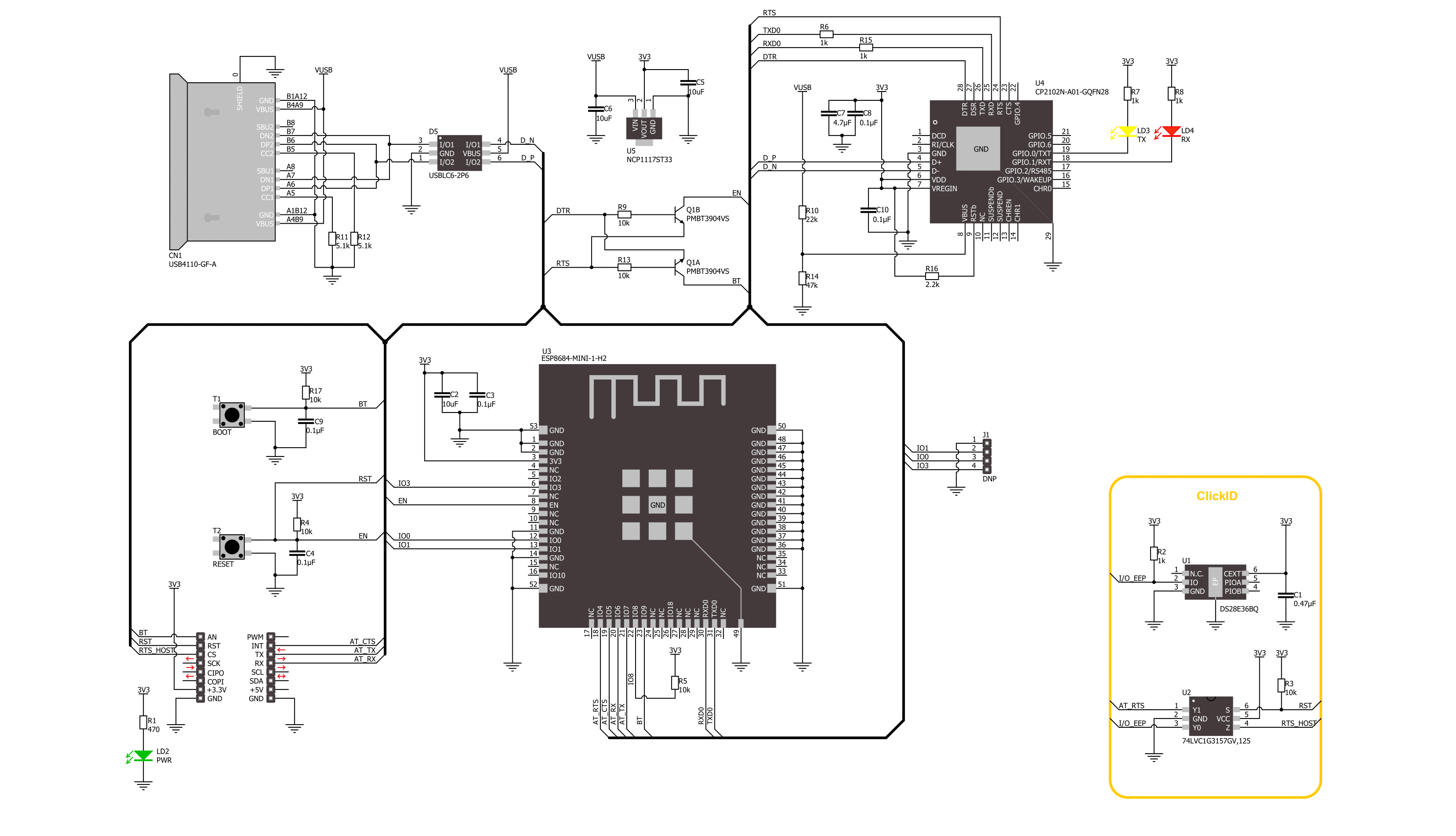
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ESP8684 Click driver.
Key functions:
esp8684_send_cmd- ESP8684 send command with arguments function.esp8684_send_query_cmd- ESP8684 send query command function.esp8684_connect_to_network- ESP8684 connect to network function.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief ESP8684 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example connects to the desired WiFi network and then
* connects to the TCP/UDP server, writes then reads data to and from it.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes driver and wifi communication, then connects to the desired WiFi network
* and sends data to the TCP/UDP server.
*
* ## Application Task
* Writes and reads data from TCP/UDP server, processes all incoming data
* and displays them on the USB UART.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - void esp8684_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - void esp8684_log_app_buf ( void )
* - err_t esp8684_process ( void )
* - err_t esp8684_rsp_check ( uint8_t *response )
* - void esp8684_error_check( err_t error_flag )
* - void esp8684_send_message ( uint8_t *link_id, uint8_t *message )
* - void esp8684_con_device_to_network ( void )
* - void esp8684_send_data ( void )
*
* @author Stefan Ilic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "esp8684.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "conversions.h"
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 200
#define ESP8684_SSID "MikroE Public"
#define ESP8684_PASSWORD "mikroe.guest"
#define ESP8684_DATA "MikroE ESP8684 Click"
// TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
#define TCP_LINK_ID "0" // TCP link ID
#define UDP_LINK_ID "1" // UDP link ID
esp8684_t esp8684;
log_t logger;
uint8_t app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
err_t app_error_flag;
/**
* @brief ESP8684 clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 log application buffer.
* @details This function logs application buffer and reset its length.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
err_t esp8684_process ( void );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 response check function.
* @details This function checks the response of the sent command.
* @param[in] response : Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - Responded as expected.
* @li @c -1 - The response isn't the same..
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
err_t esp8684_rsp_check ( uint8_t *response );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 error check function.
* @details This function checks if error has occurred.
* @param[in] error_flag : Data to be checked.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_error_check( err_t error_flag );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 send message function.
* @details This function is used to send messages to the host.
* @param[in] link_id : Host link id.
* @param[in] message : Message to be sent.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_send_message ( uint8_t *link_id, uint8_t *message );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 connect device to the network.
* @details This function is used to connect device to network.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_con_device_to_network ( void );
/**
* @brief ESP8684 send message to the host.
* @details This function is used to send messages to the host.
* @return Nothing.
* @note None.
*/
void esp8684_send_data ( void );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
esp8684_cfg_t esp8684_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
esp8684_cfg_setup( &esp8684_cfg );
ESP8684_MAP_MIKROBUS( esp8684_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( UART_ERROR == esp8684_init( &esp8684, &esp8684_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
esp8684_default_cfg( &esp8684 );
Delay_ms( 3000 );
esp8684_process( );
esp8684_clear_app_buf( );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_AT, NULL );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_RST, NULL );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_READY );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_process( );
esp8684_clear_app_buf();
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_GMR, NULL );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
// Communication initialization
esp8684_con_device_to_network ( );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
log_printf( &logger, "Sending and reading data from the TCP/UDP server \r\n" );
esp8684_send_data( );
Delay_ms( 5000 );
}
void main ( void )
{
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
}
void esp8684_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
void esp8684_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
esp8684_clear_app_buf( );
}
err_t esp8684_process ( void )
{
err_t return_flag = ESP8684_ERROR;
int32_t rx_size;
uint8_t rx_buff[ ESP8684_RX_DRV_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
rx_size = esp8684_generic_read( &esp8684, rx_buff, ESP8684_RX_DRV_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = 0;
return_flag = ESP8684_OK;
if ( app_buf_len + rx_size >= ESP8684_RX_DRV_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
esp8684_clear_app_buf( );
return_flag = ESP8684_OVERFLOW;
}
else
{
buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
app_buf_len += rx_size;
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buff[ rx_cnt ] != 0 )
{
app_buf[ ( buf_cnt + rx_cnt ) ] = rx_buff[ rx_cnt ];
}
else
{
buf_cnt--;
app_buf_len--;
}
}
}
return return_flag;
}
err_t esp8684_rsp_check ( uint8_t *response )
{
uint16_t timeout_cnt = 0;
uint16_t timeout = 50000;
err_t error_flag = esp8684_process( );
if ( ( error_flag != ESP8684_OK ) && ( error_flag != ESP8684_ERROR ) )
{
return error_flag;
}
while ( ( strstr( app_buf, response ) == 0 ) && ( strstr( app_buf, ESP8684_RSP_ERROR ) == 0 ) )
{
error_flag = esp8684_process( );
if ( ( error_flag != ESP8684_OK ) && ( error_flag != ESP8684_ERROR ) )
{
return error_flag;
}
timeout_cnt++;
if ( timeout_cnt > timeout )
{
esp8684_clear_app_buf( );
return ESP8684_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
esp8684_log_app_buf();
return ESP8684_OK;
}
void esp8684_error_check( err_t error_flag )
{
if ( ( ESP8684_OK != error_flag ) && ( error_flag != ESP8684_ERROR ) )
{
switch ( error_flag )
{
case ( ESP8684_OVERFLOW ):
log_error( &logger, " Overflow!" );
break;
case ( ESP8684_TIMEOUT ):
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
break;
default:
break;
}
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n-----------------------------------\r\n" );
}
void esp8684_send_message ( uint8_t *link_id, uint8_t *message )
{
uint8_t cmd_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
uint8_t message_len_buf[ 5 ] = { 0 };
uint16_t message_len = strlen( message );
uint16_to_str( message_len, message_len_buf );
l_trim( message_len_buf );
r_trim( message_len_buf );
strcpy( cmd_buf, link_id );
strcat( cmd_buf, "," );
strcat( cmd_buf, message_len_buf );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPSEND, cmd_buf );
if ( ESP8684_OK == esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_READY_FOR_SEND ) )
{
esp8684_generic_write( &esp8684, message, strlen(message) );
esp8684_generic_write( &esp8684, "\032", 1 );
}
}
void esp8684_con_device_to_network ( void )
{
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CWMODE, "1" );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_connect_to_network( &esp8684, ESP8684_SSID, ESP8684_PASSWORD );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPMUX, "1" );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPRECVMODE, "0" );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_query_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPSTATE );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
}
void esp8684_send_data ( void )
{
esp8684_connect_for_trans( &esp8684, "TCP", TCP_LINK_ID, REMOTE_IP, REMOTE_PORT );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_connect_for_trans( &esp8684, "UDP", UDP_LINK_ID, REMOTE_IP, REMOTE_PORT );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_message( TCP_LINK_ID, ESP8684_DATA );
Delay_ms( 500 );
log_printf( &logger, "Read data TCP: \r\n" );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_RECEIVE );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 1000 );
esp8684_send_message( UDP_LINK_ID, ESP8684_DATA );
Delay_ms( 500 );
log_printf( &logger, "Read data UDP: \r\n" );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_RECEIVE );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPCLOSE, TCP_LINK_ID );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
esp8684_send_cmd( &esp8684, ESP8684_CMD_CIPCLOSE, UDP_LINK_ID );
app_error_flag = esp8684_rsp_check( ESP8684_RSP_OK );
esp8684_error_check( app_error_flag );
Delay_ms( 500 );
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:WiFi