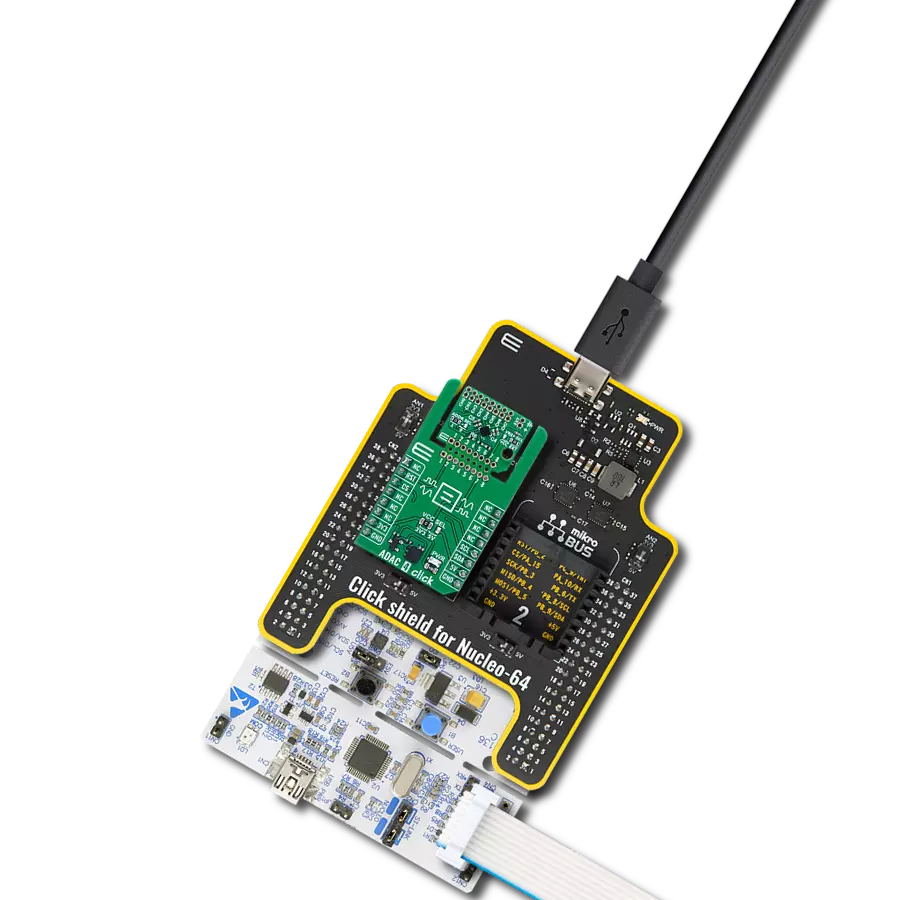
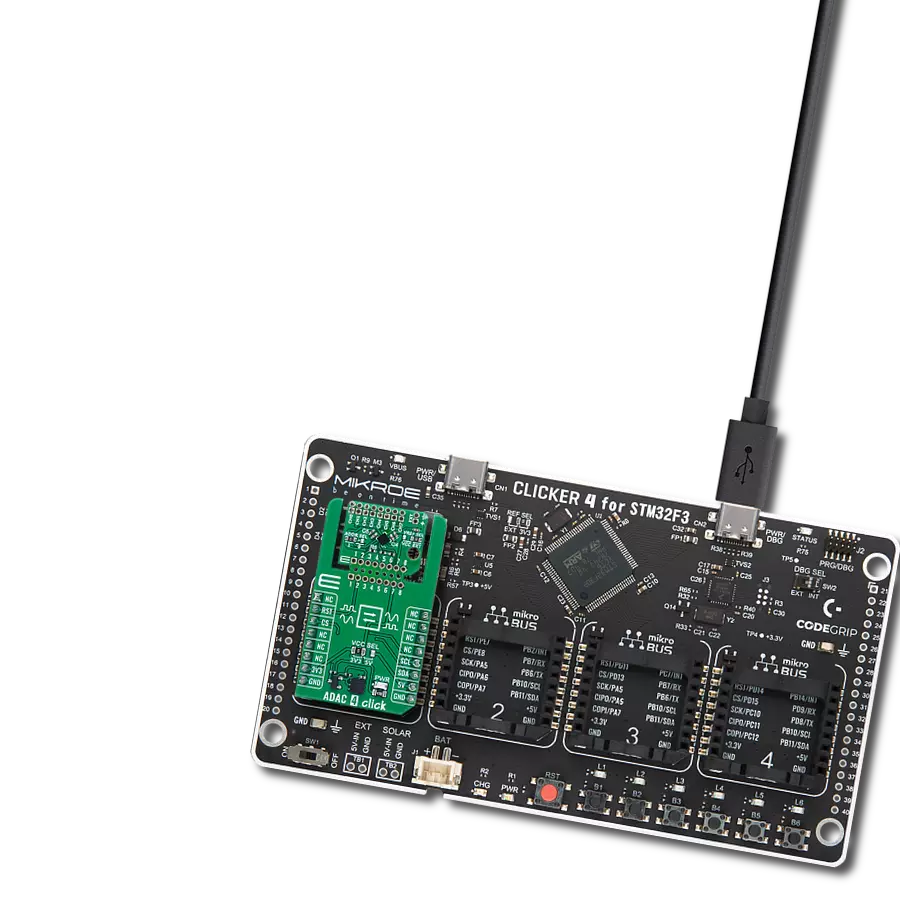
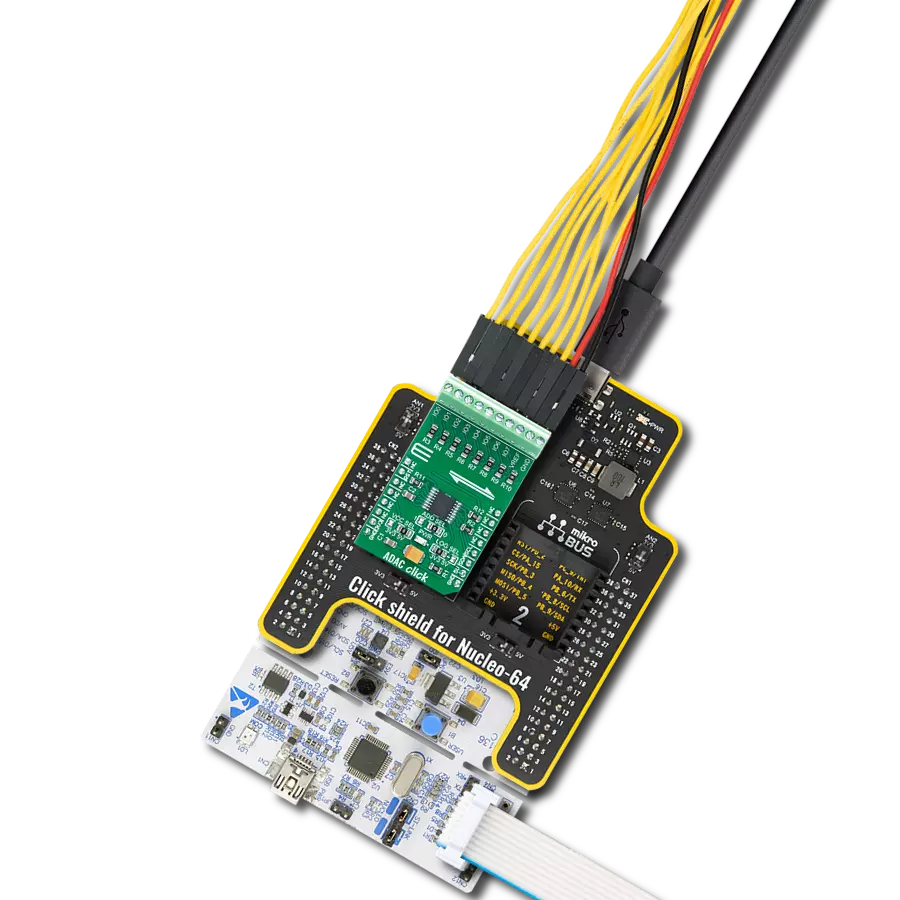
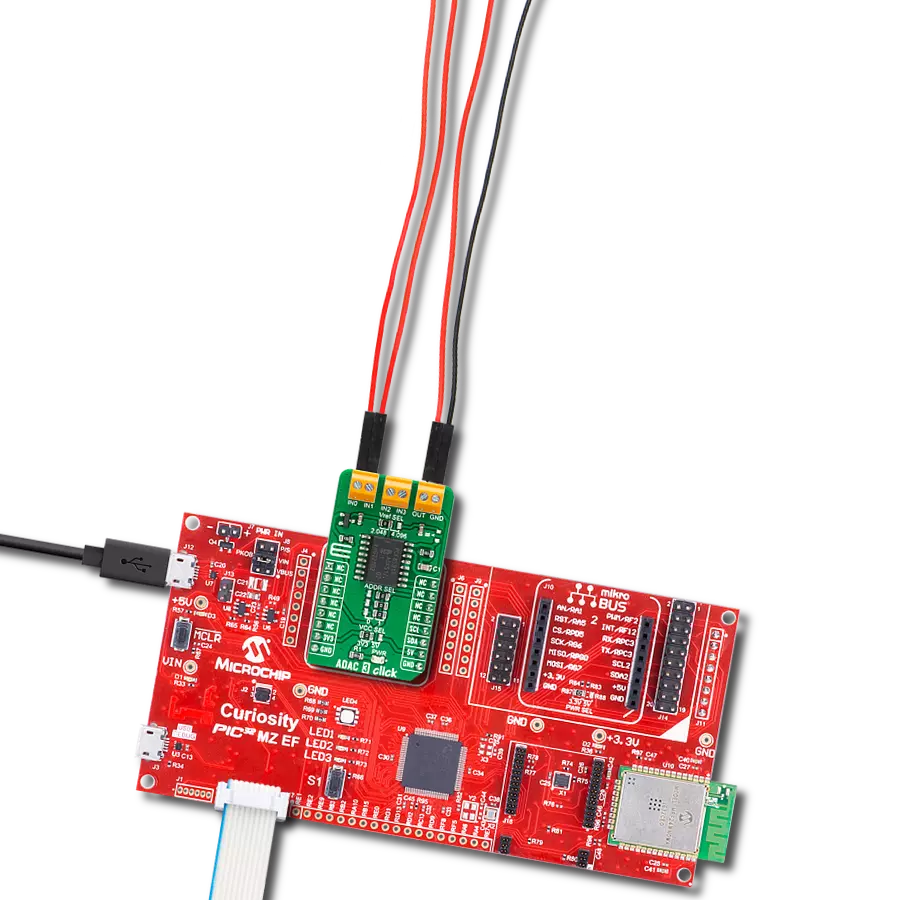
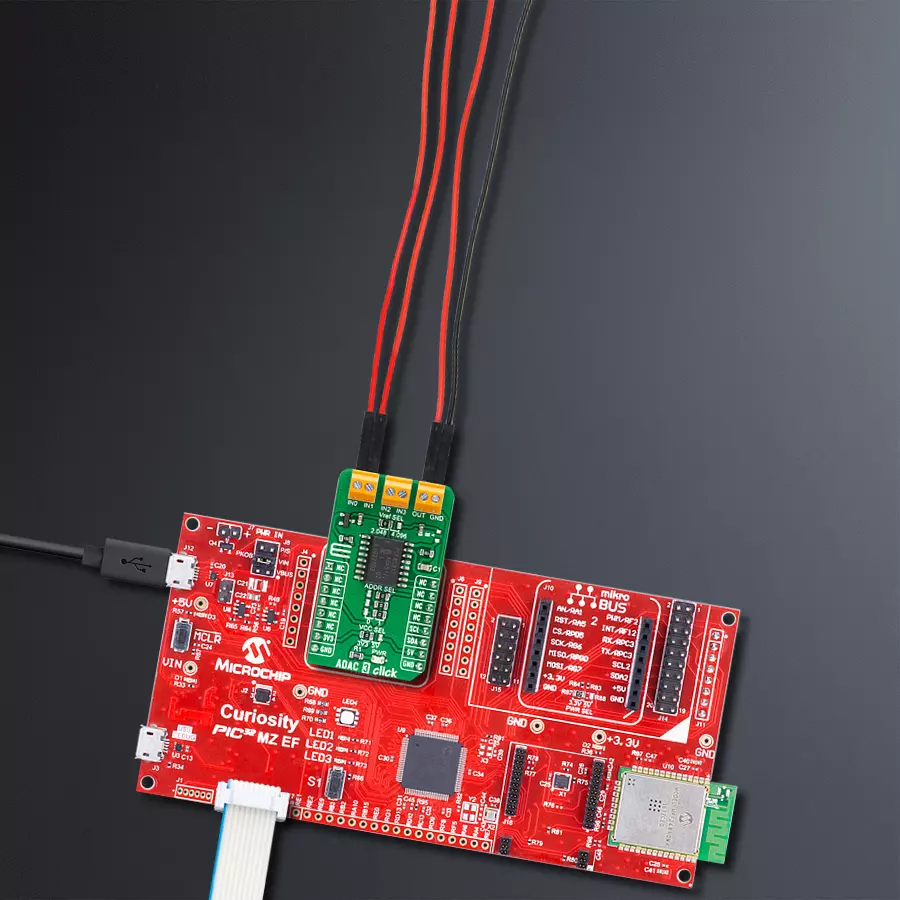
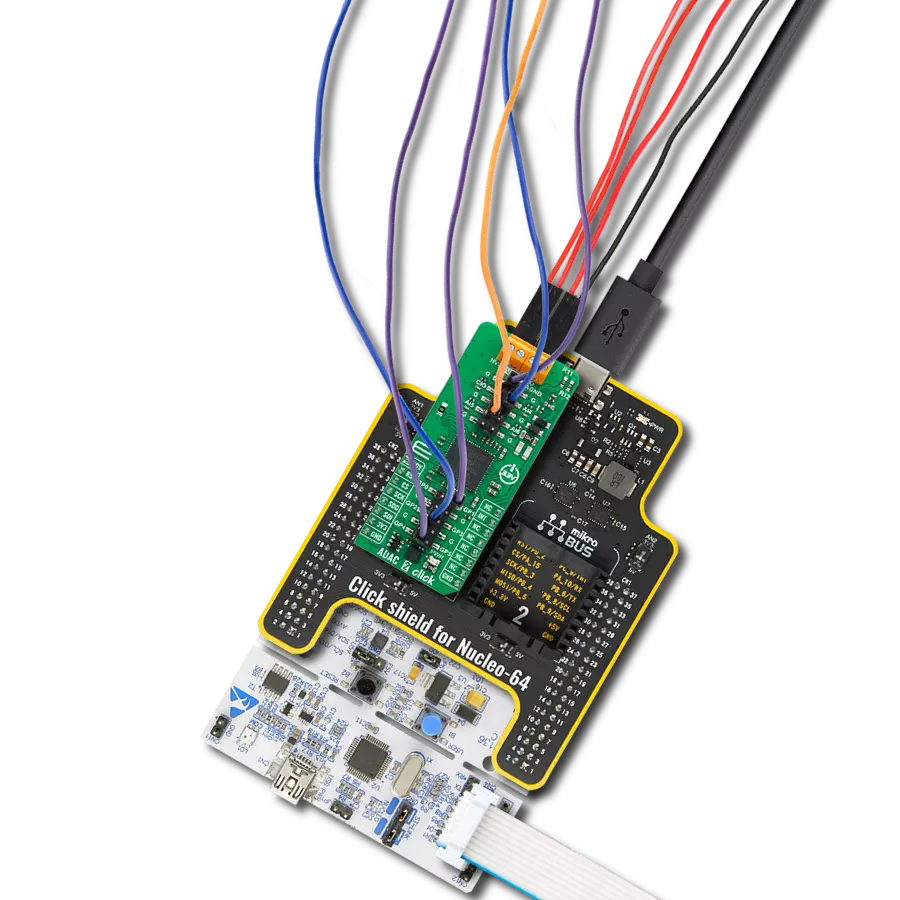
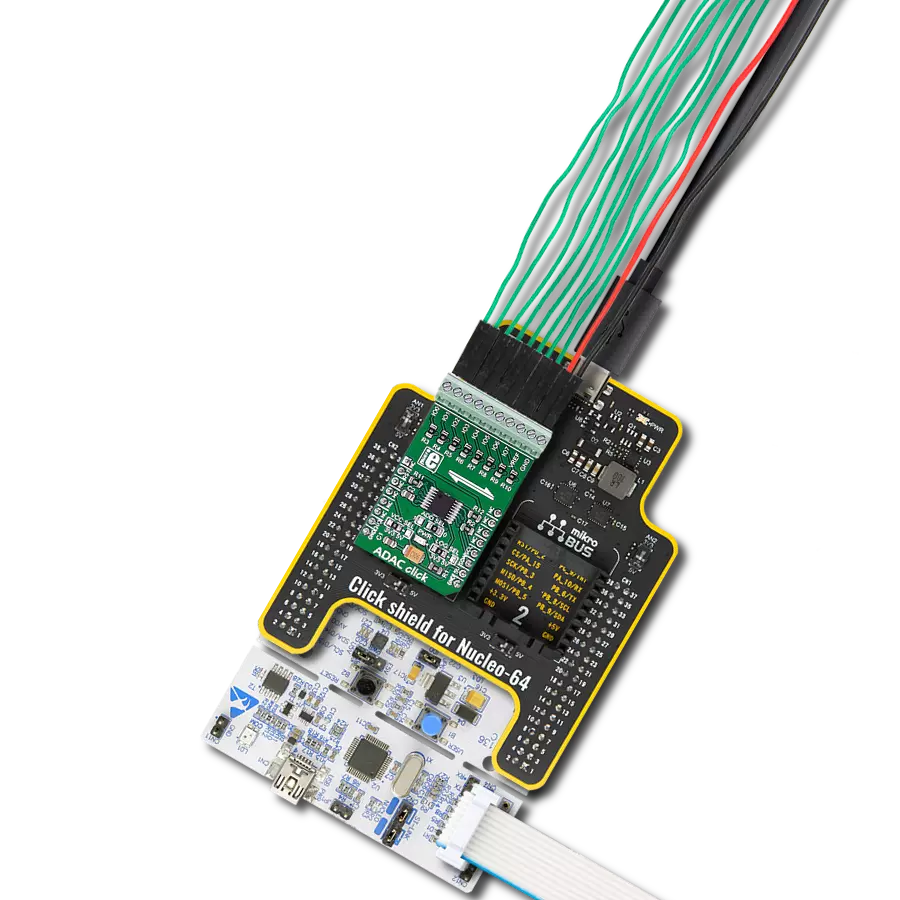
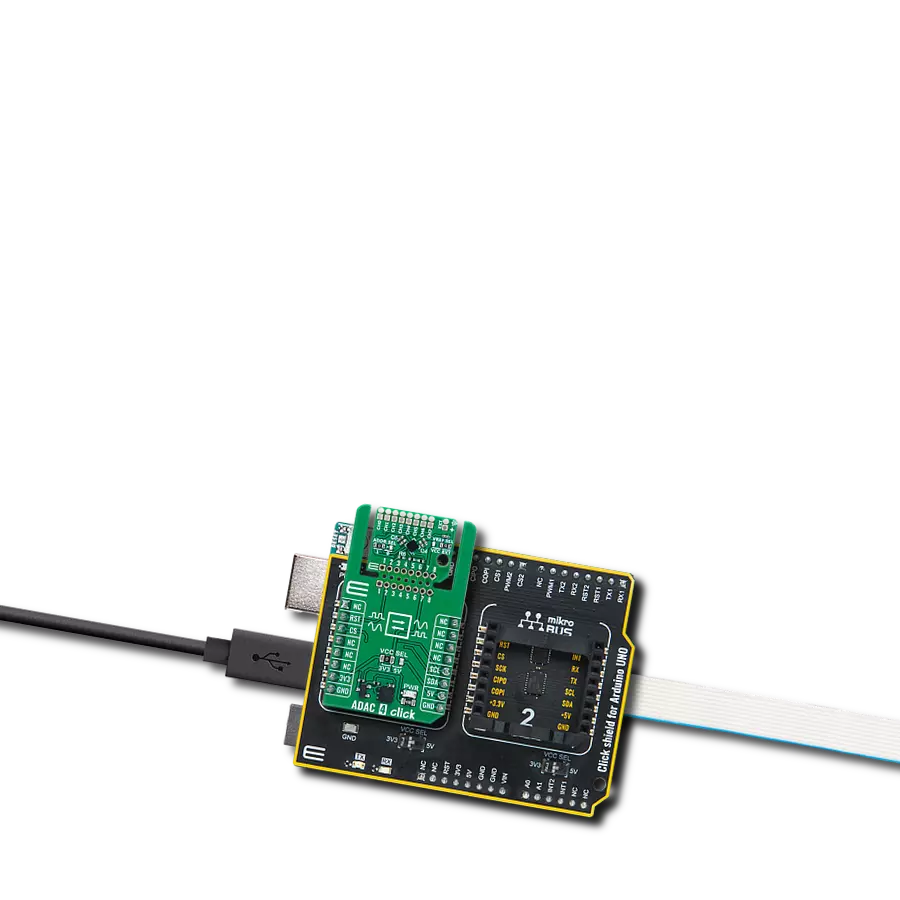
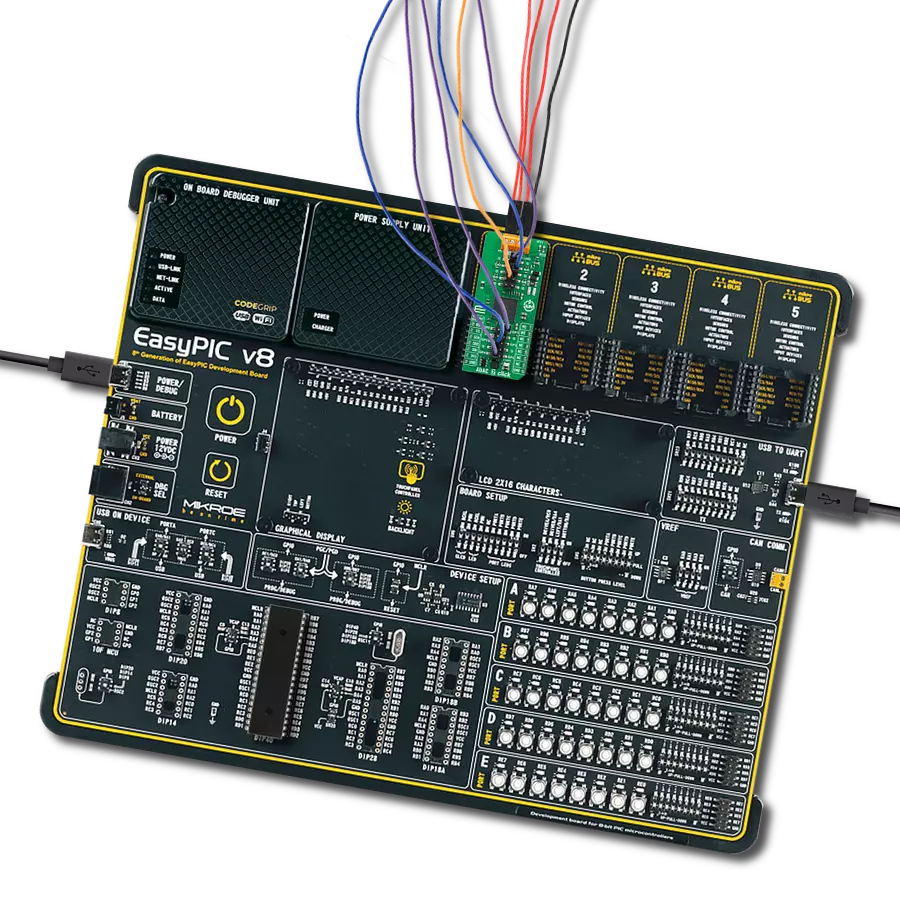
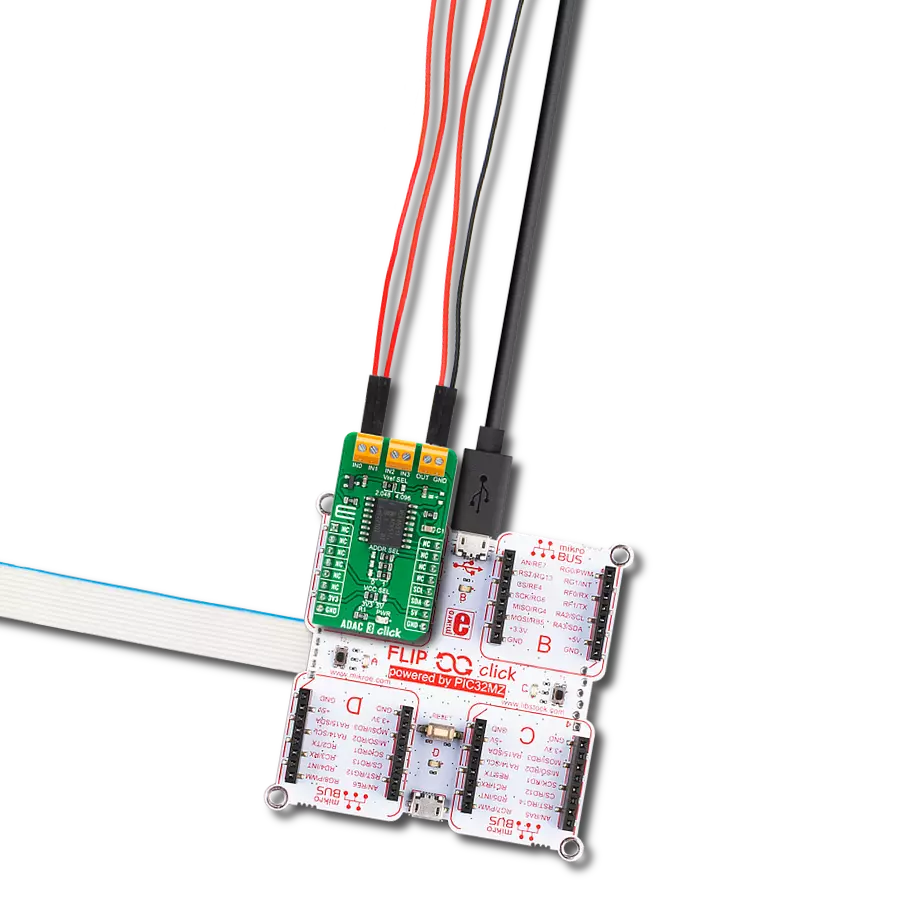
High-performance data acquisition solution
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
ADAC 3 Click is based on the PCF8591, a low-power CMOS data acquisition device from NXP Semiconductors. The PCF8591 comes with four analog inputs configurable as single-ended or differential inputs used to measure voltages, alongside one analog output representing an 8-bit digital-to-analog converter. In addition to measuring voltage, the user can create them as desired and even use DAC and ADC together to generate an input to a circuit and measure the results with the ADC, making it suitable for various control, monitoring, or measurement applications. By its internal structure, the PCF8591 also consists of
an analog input multiplexing circuit and an on-chip track and hold function alongside a serial interface block. This Click board™ communicates with MCU using the standard I2C 2-Wire interface with a maximum clock frequency of 100kHz. The PCF8591 has a 7-bit slave address with the first four MSBs fixed to 1001. The address pins A0, A1, and A2 are programmed by the user and determine the value of the last three LSBs of the slave address, which can be selected by positioning onboard SMD jumpers labeled as ADDR SEL to an appropriate position marked as 0 or 1. Besides, the user can choose the PCF8591
reference voltage value by positioning the SMD jumper labeled VREF SEL, choosing between 2,048 and 4,096V provided by MAX6104 and MAX6106. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.

Features overview
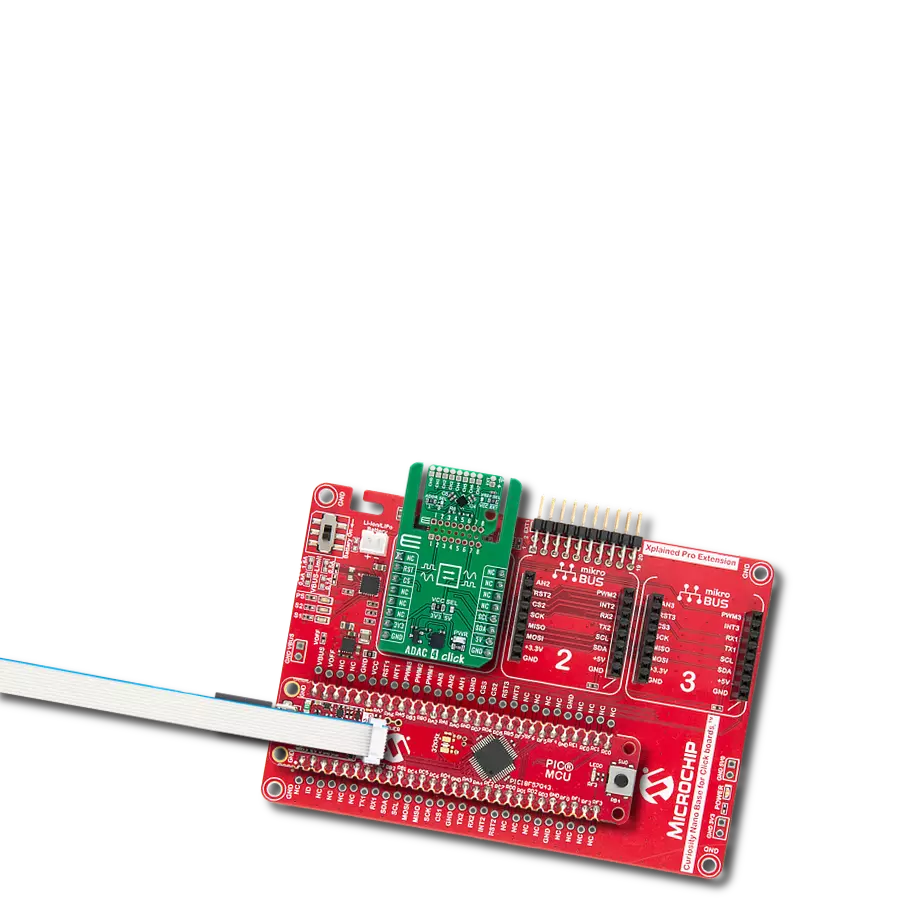
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for ADAC 3 Click driver.
Key functions:
adac3_write_controlThis function writes a control byte by using I2C serial interface.adac3_write_dacThis function writes a DAC byte by using I2C serial interface.adac3_read_adcThis function reads the AD conversion byte by using I2C serial interface.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief ADAC3 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of ADAC 3 Click board by setting the DAC output
* and reading the ADC results from 2 single-ended channels (AIN0, AIN1) and from a
* differential channel (AIN2+, AIN3-).
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and performs the Click default configuration which enables
* DAC output, sets the analog input mode to single-ended (AIN0, AIN1) and
* differential (AIN2+, AIN3-), and enables the auto increment mode.
*
* ## Application Task
* Sets the DAC output increasing the value by 1 after each iteration, and reads the
* ADC results from 2 single-ended and 1 differential channels, and displays the results
* on the USB UART every 100ms approximately.
*
* @note
* Inputs should be connected to GND when not in use.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "adac3.h"
static adac3_t adac3;
static log_t logger;
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
adac3_cfg_t adac3_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
adac3_cfg_setup( &adac3_cfg );
ADAC3_MAP_MIKROBUS( adac3_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == adac3_init( &adac3, &adac3_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
if ( ADAC3_ERROR == adac3_default_cfg ( &adac3 ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Default configuration." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
static uint8_t dac = 0;
uint8_t ain0, ain1, ain2_ain3_diff;
if ( ADAC3_OK == adac3_write_dac ( &adac3, dac ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " DAC : %u mV\r\n",
( uint16_t ) ( ( ADAC3_VREF_2048mV / ADAC3_RESOLUTION ) * dac++ ) );
}
if ( ADAC3_OK == adac3_read_adc ( &adac3, &ain0 ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " AIN0+: %u mV\r\n",
( uint16_t ) ( ( ADAC3_VREF_2048mV / ADAC3_RESOLUTION ) * ain0 ) );
}
if ( ADAC3_OK == adac3_read_adc ( &adac3, &ain1 ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " AIN1+: %u mV\r\n",
( uint16_t ) ( ( ADAC3_VREF_2048mV / ADAC3_RESOLUTION ) * ain1 ) );
}
if ( ADAC3_OK == adac3_read_adc ( &adac3, &ain2_ain3_diff ) )
{
log_printf ( &logger, " AIN2+ - AIN3-: %d mV\r\n\n",
( int16_t ) ( ( ADAC3_VREF_2048mV / ADAC3_RESOLUTION ) * ( int8_t ) ain2_ain3_diff ) );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:ADC-DAC