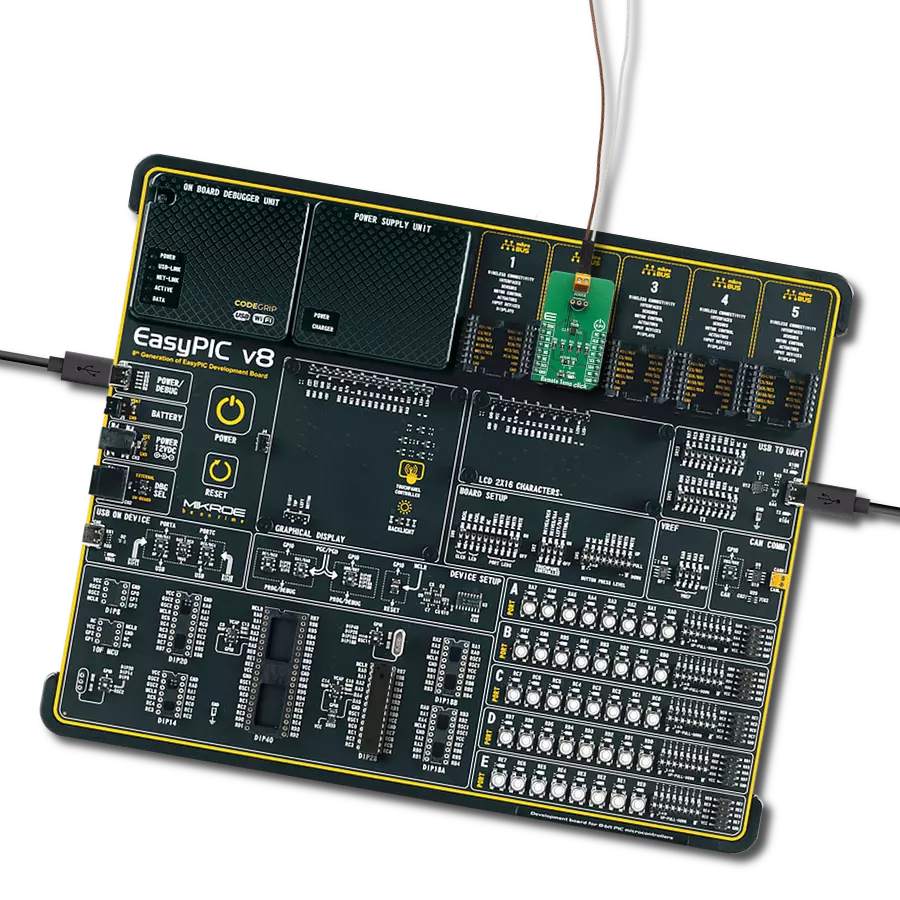
放松,让我们的远程温度感测技术消除温度管理的猜测,确保您的资产始终受到保护。
A
A
硬件概览
它是如何工作的?
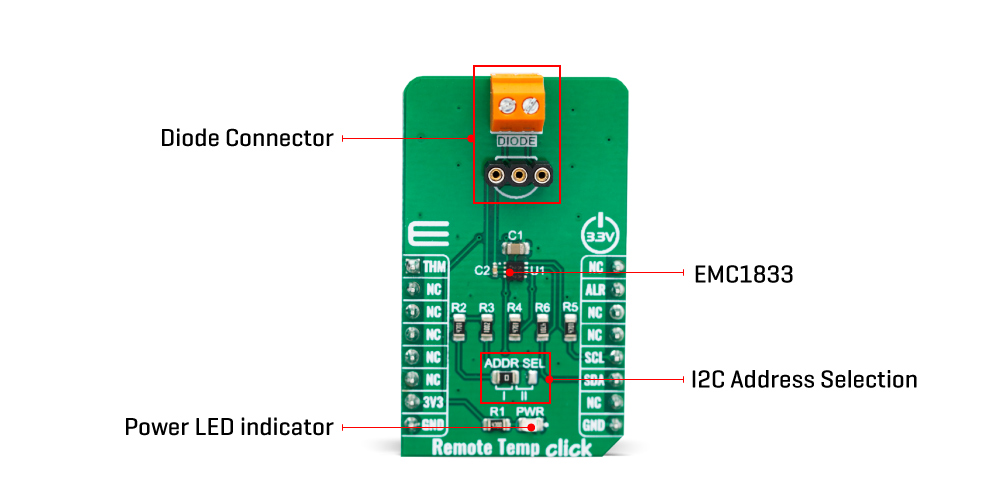
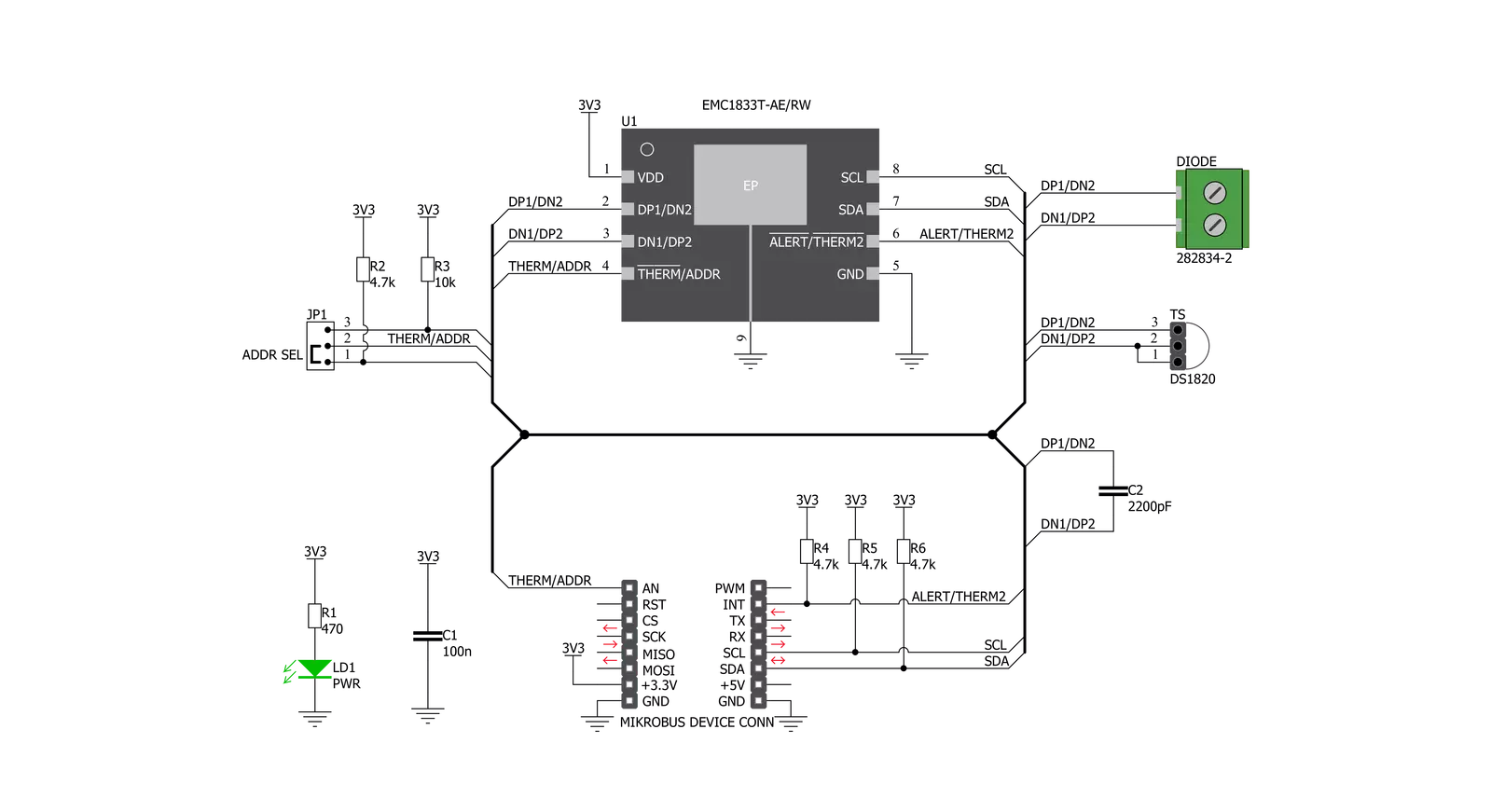
Remote Temp Click基于Microchip生产的EMC1833,这是一个±1°C的SMBus/I2C兼容的本地/远程温度传感器,具有超温警报功能。该传感器能够测量自身温度,以及远程BJT结的温度,后者可以是离散的PNP或NPN晶体管,也可以是某些集成组件的基片(通常是CPU、FPGA、ASIC或GPU)。离散PNP晶体管的集电极连接到DP引脚,基极连接到EMC1833的DN引脚,发射极接地。离散NPN晶体管(2N3904)的集电极和基极连接到DP引脚,而发射极连接到EMC1833的DN引脚。反并联连接的离散NPN晶体管,第一个晶体管的集电极和基极连接到第二个晶体管的发射极和EMC1833的DN2引脚,第一个晶体管的发射极连接到第二个晶体管的集电极和基极以及EMC1833的DP2引脚。当将其用作远程温度传感器时,离散元件有一些特定的要求:例如,它必须是小信号BJT。有关更多信息,请参考EMC1833的数据表,其中还说明了用于最高和最低预期温度的前向电压范围和其他在选择晶
体管时应考虑的参数。离散元件可以连接到Click board™边缘的螺钉端子上。EMC1833具有11位ADC,从而获得0.125°C的分辨率。温度测量结果存储在内部和外部温度寄存器中。外部和内部温度测量结果都以11位格式存储,其中8位最高有效位(MSB)存储在高字节寄存器中,而3位最低有效位(LSB)存储在低字节寄存器的三个MSB位置中。低字节寄存器的所有其他位都设置为零。EMC1833 IC在对BJT结自动发送偏置电流的同时,对给定电流的BJT结进行前向电压采样并计算温度。ADC在21毫秒的时间内积分结果,以降低噪声。因此,温度采集并不特别快。作为回报,温度测量结果更加准确可靠。远程测量的准确性取决于远程BJT结的理想因子。并非所有外部二极管,无论是处理器还是离散的,都具有相同的值。理想因子的这种变化会引入温度测量中的误差,必须加以修正。因此,EMC1833具有可编程的外部二极管理想因子,可以通过更改适当寄存器中的值轻松设置。EMC1833 IC还
具有ALERT报告功能。如果超出了编程的阈值,ALERT引脚将断言为低逻辑电平。当ALERT引脚被断言时,它将保持锁存状态,直到其STATUS寄存器在超温条件不再存在后被读取。清除ALERT中断的另一种方法是响应警报响应地址。这是一种全局I2C/SMBus协议,其中主MCU在接收到中断后广播一个接收字节传输。生成此中断的一个(或多个)从设备将会响应,发送它们的I2C从设备地址,遵循总线仲裁规则。该协议在EMC1833数据表中有更详细的解释。ALERT引脚路由到mikroBUS™的INT引脚,并通过电阻上拉。通过从VDD引脚通过外部电阻拉出已知电流来执行从设备地址解码,从而使引脚电压根据相应的电流/电阻关系降低。该Click Board™设计仅使用3.3V逻辑电平运行。在将Click board™与逻辑电平为5V的MCU一起使用之前,应执行适当的逻辑电压级转换。一旦插入开发系统的mikroBUS™插座中,它就可以立即使用。
功能概述
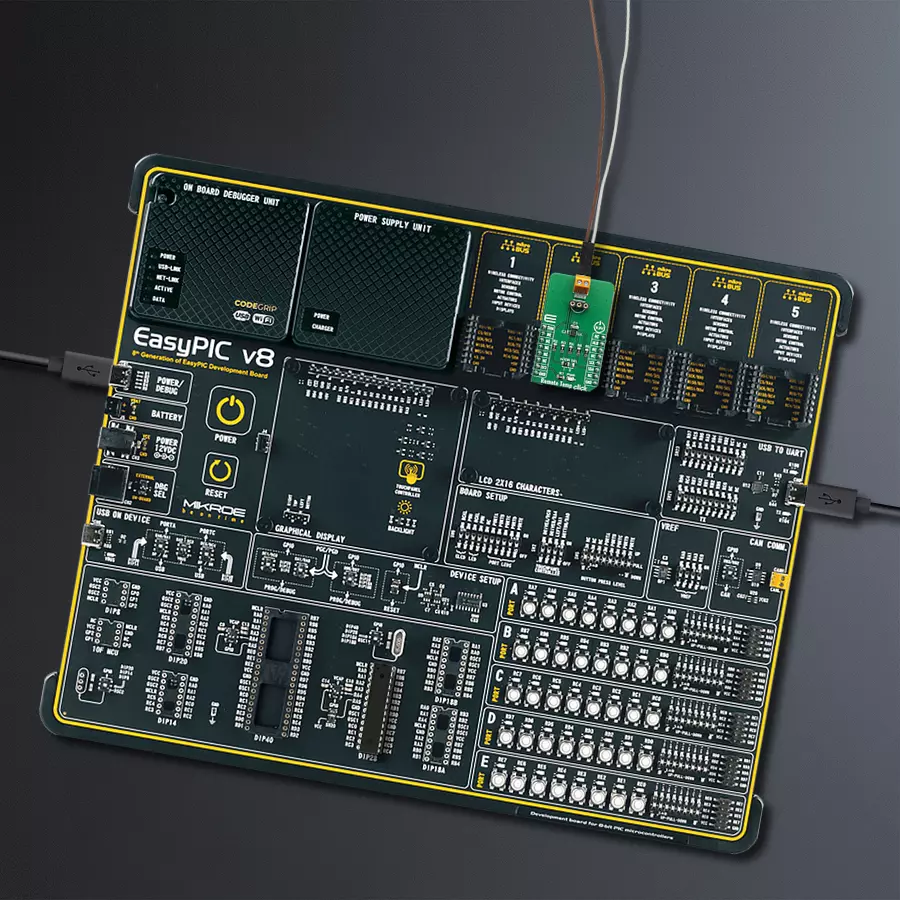
开发板
EasyPIC v8 是一款专为快速开发嵌入式应用的需求而特别设计的开发板。它支持许多高引脚计数的8位PIC微控制器,来自Microchip,无论它们的引脚数量如何,并且具有一系列独特功能,例如首次集成的调试器/程序员。开发板布局合理,设计周到,使得最终用户可以在一个地方找到所有必要的元素,如开关、按钮、指示灯、连接器等。得益于创新的制造技术,EasyPIC v8 提供了流畅而沉浸式的工作体验,允许在任何情况下、任何地方、任何时候都能访问。
EasyPIC v8 开发板的每个部分都包含了使同一板块运行最高效的必要组件。除了先进的集成CODEGRIP程 序/调试模块,该模块提供许多有价值的编程/调试选项和与Mikroe软件环境的无缝集成外,该板还包括一个干净且调节过的开发板电源供应模块。它可以使用广泛的外部电源,包括电池、外部12V电源供应和通过USB Type-C(USB-C)连接器的电源。通信选项如USB-UART、USB DEVICE和CAN也包括在内,包括 广受好评的mikroBUS™标准、两种显示选项(图形和
基于字符的LCD)和几种不同的DIP插座。这些插座覆盖了从最小的只有八个至四十个引脚的8位PIC MCU的广泛范围。EasyPIC v8 是Mikroe快速开发生态系统的一个组成部分。它由Mikroe软件工具原生支持,得益于大量不同的Click板™(超过一千块板),其数量每天都在增长,它涵盖了原型制作和开发的许多方面。
微控制器概述
MCU卡片 / MCU

建筑
PIC
MCU 内存 (KB)
24
硅供应商
Microchip
引脚数
28
RAM (字节)
2048
使用的MCU引脚
mikroBUS™映射器
“仔细看看!”
Click board™ 原理图
一步一步来
项目组装
软件支持
库描述
该库包含 这个库包含了Remote Temp Click 驱动程序的 API。
关键函数:
remotetemp_int_get- 获取INT引脚的状态。remotetemp_an_get- 获取AN引脚的状态。remotetemp_set_range- 设置温度范围。
开源
代码示例
完整的应用程序代码和一个现成的项目可以通过NECTO Studio包管理器直接安装到NECTO Studio。 应用程序代码也可以在MIKROE的GitHub账户中找到。
/*!
* \file
* \brief RemoteTemp Click example
*
* # Description
* This application reads remote temperature data.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes I2C driver, sets range, configures device and sets threshold values.
*
* ## Application Task
* Executes all 'remotetemp_aux_getXxx()' functions.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "remotetemp.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static remotetemp_t remotetemp;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void remotetemp_aux_get_fault ( remotetemp_t *ctx )
{
uint8_t aux_byte[ 1 ];
remotetemp_read( ctx, REMOTETEMP_EXTERNAL_DIODE_FAULT_STATUS, &aux_byte[ 0 ], 1 );
if ( aux_byte[ 0 ] != 0 )
{
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x02 ) == 0x02 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 1 \r\n" );
}
}
}
void remotetemp_aux_get_high_limit_status ( remotetemp_t *ctx )
{
float internal_temp;
float external_1_temp;
float external_2_temp;
uint8_t aux_byte[ 1 ];
remotetemp_read( ctx, REMOTETEMP_HIGH_LIMIT_STATUS, &aux_byte[ 0 ], 1 );
if ( aux_byte[ 0 ] != 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "> high threshold limit exceeded by : \r\n" );
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x01 ) == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - internal diode \r\n" );
internal_temp = remotetemp_get_internal_diode( ctx );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", internal_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x02 ) == 0x02 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 1 \r\n" );
external_1_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_1_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x04 ) == 0x04 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 2 \r\n" );
external_2_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 2 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_2_temp );
}
}
}
void remotetemp_aux_get_low_limit_status ( remotetemp_t *ctx )
{
float internal_temp;
float external_1_temp;
float external_2_temp;
uint8_t aux_byte[ 1 ];
remotetemp_read( ctx, REMOTETEMP_LOW_LIMIT_STATUS, &aux_byte[ 0 ], 1 );
if ( aux_byte[ 0 ] != 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "> > low threshold limit exceeded by : \r\n" );
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x01 ) == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - internal diode \r\n" );
internal_temp = remotetemp_get_internal_diode( ctx );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", internal_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x02 ) == 0x02 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 1 \r\n" );
external_1_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_1_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x04 ) == 0x04 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 2 \r\n" );
external_2_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 2 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_2_temp );
}
}
}
void remotetemp_aux_get_therm_limit_status ( remotetemp_t *ctx )
{
float internal_temp;
float external_1_temp;
float external_2_temp;
uint8_t aux_byte[ 1 ];
remotetemp_read( ctx, REMOTETEMP_THERM_LIMIT_STATUS, &aux_byte[ 0 ], 1 );
if ( aux_byte[ 0 ] != 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "> therm threshold limit exceeded by : \r\n" );
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x01 ) == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - internal diode \r\n" );
internal_temp = remotetemp_get_internal_diode( ctx );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", internal_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x02 ) == 0x02 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 1 \r\n" );
external_1_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 1 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_1_temp );
}
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x04 ) == 0x04 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 2 \r\n" );
external_2_temp = remotetemp_get_external_diode( ctx, 2 );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %f degC \r\n", external_2_temp );
}
}
}
void remotetemp_aux_get_hottest_status ( remotetemp_t *ctx )
{
float hottest_temp;
uint8_t aux_byte[ 1 ];
remotetemp_read( ctx, REMOTETEMP_HOTTEST_STATUS, &aux_byte[ 0 ], 1 );
if ( aux_byte[ 0 ] != 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "> hottest diode : \r\n" );
if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x01 ) == 0x01 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - internal diode \r\n" );
}
else if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x02 ) == 0x02 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 1 \r\n" );
}
else if ( ( aux_byte[ 0 ] & 0x04 ) == 0x04 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " - external diode 2 \r\n" );
}
hottest_temp = remotetemp_get_hottest_diode( ctx );
log_printf( &logger, " - temperature : %.2f degC \r\n", hottest_temp );
}
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n" );
}
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
remotetemp_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
remotetemp_cfg_setup( &cfg );
REMOTETEMP_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
remotetemp_init( &remotetemp, &cfg );
Delay_ms ( 300 );
remotetemp_default_cfg( &remotetemp );
log_printf( &logger, "> app init done \r\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
remotetemp_aux_get_fault( &remotetemp );
remotetemp_aux_get_high_limit_status( &remotetemp );
remotetemp_aux_get_low_limit_status( &remotetemp );
remotetemp_aux_get_therm_limit_status( &remotetemp );
remotetemp_aux_get_hottest_status( &remotetemp );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END