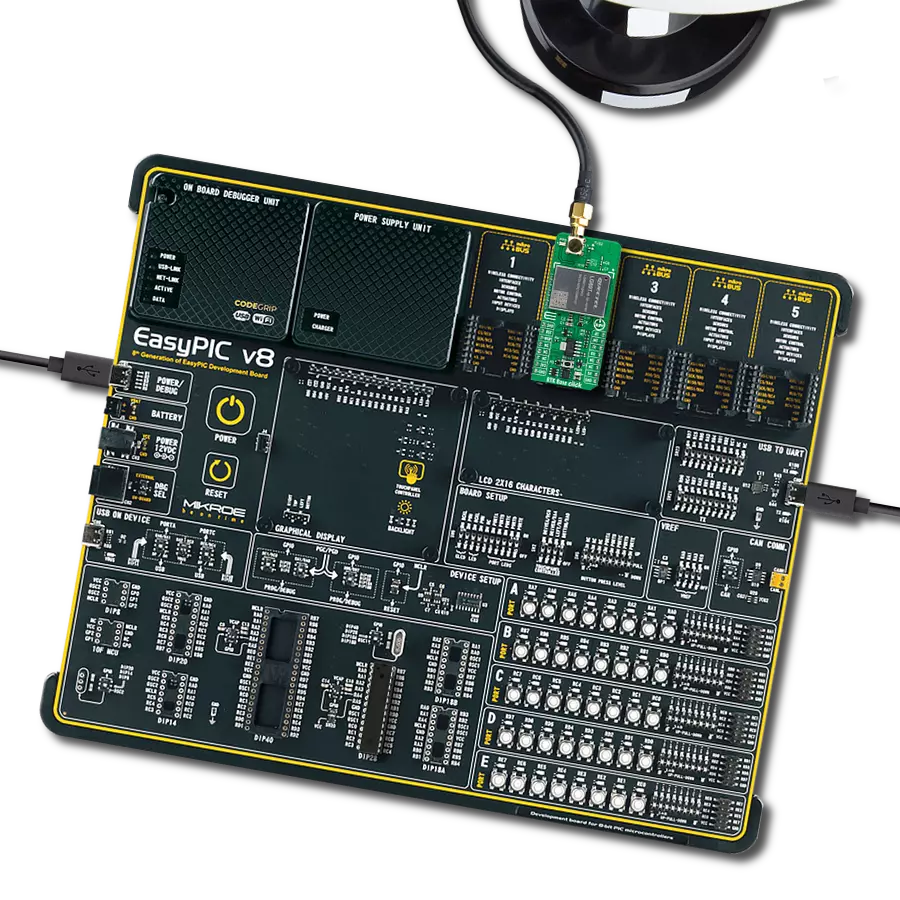
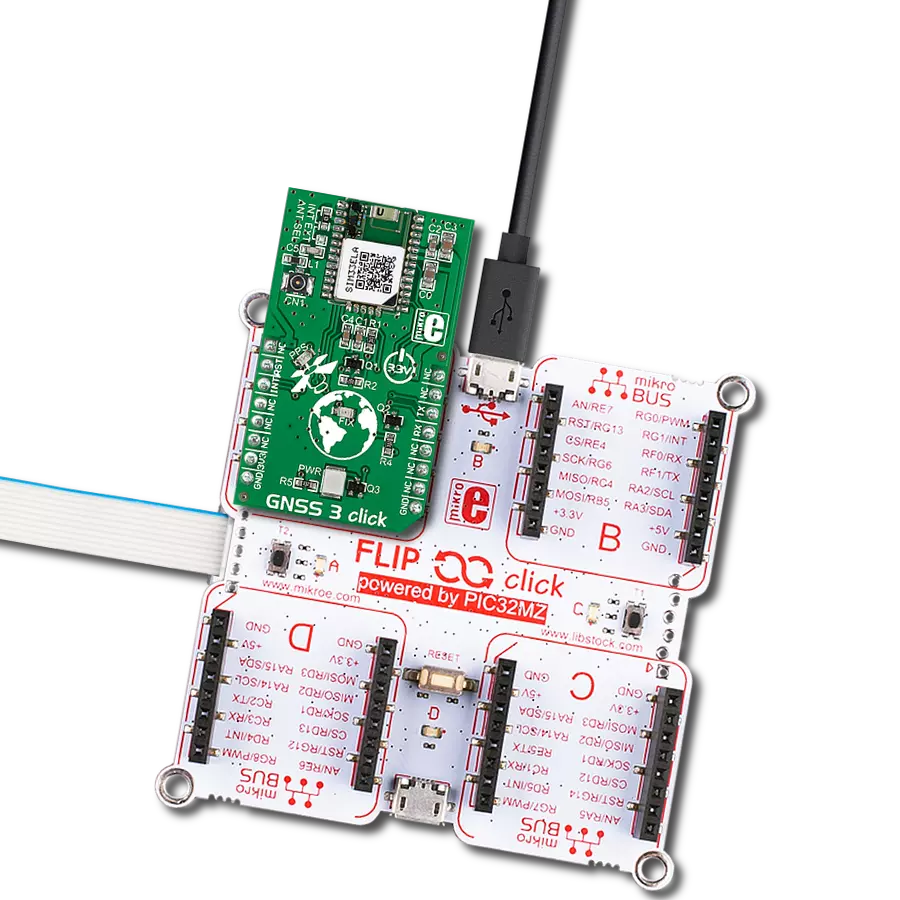
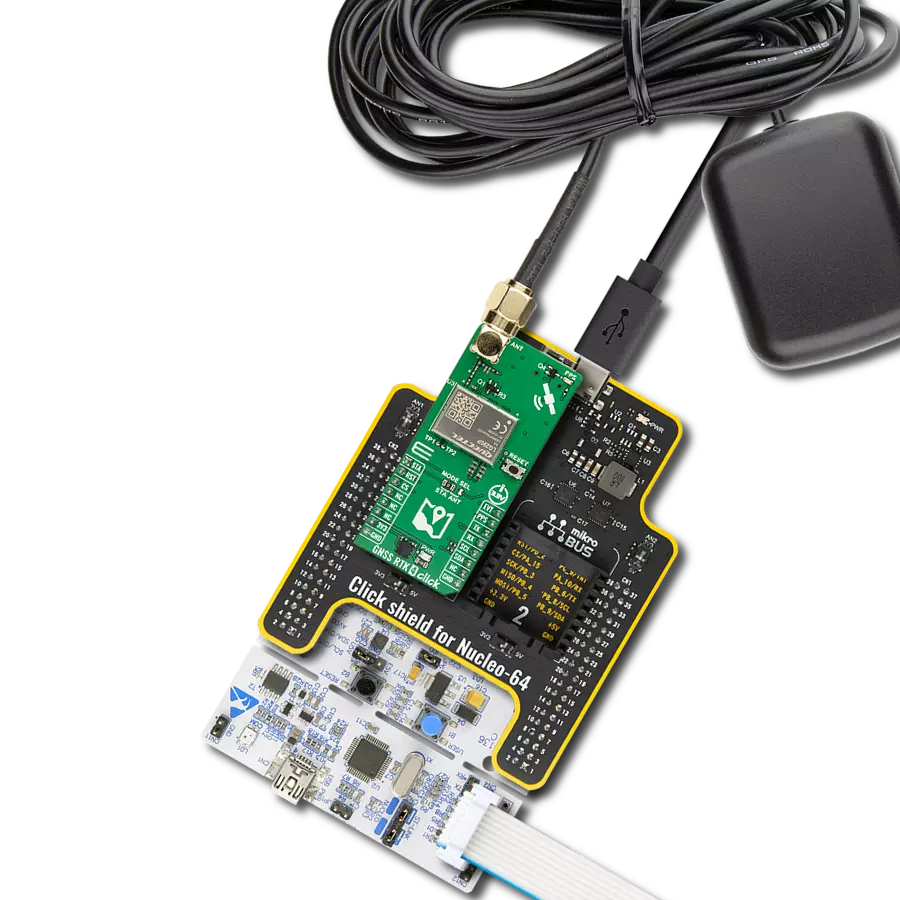
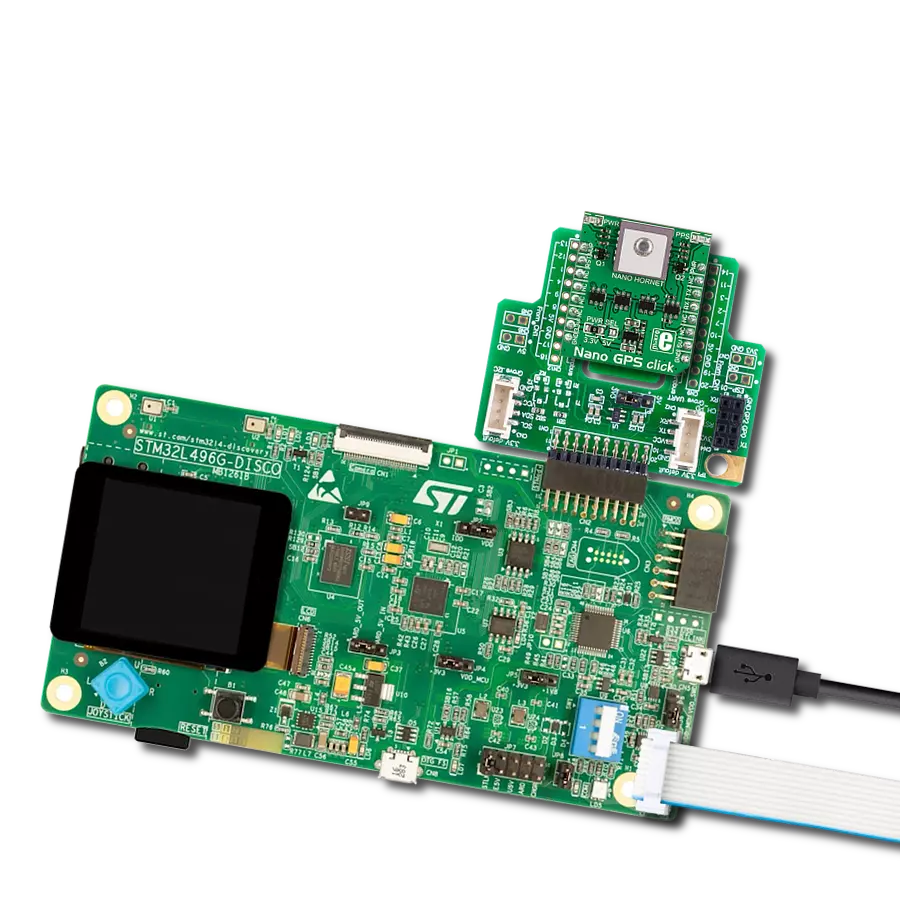
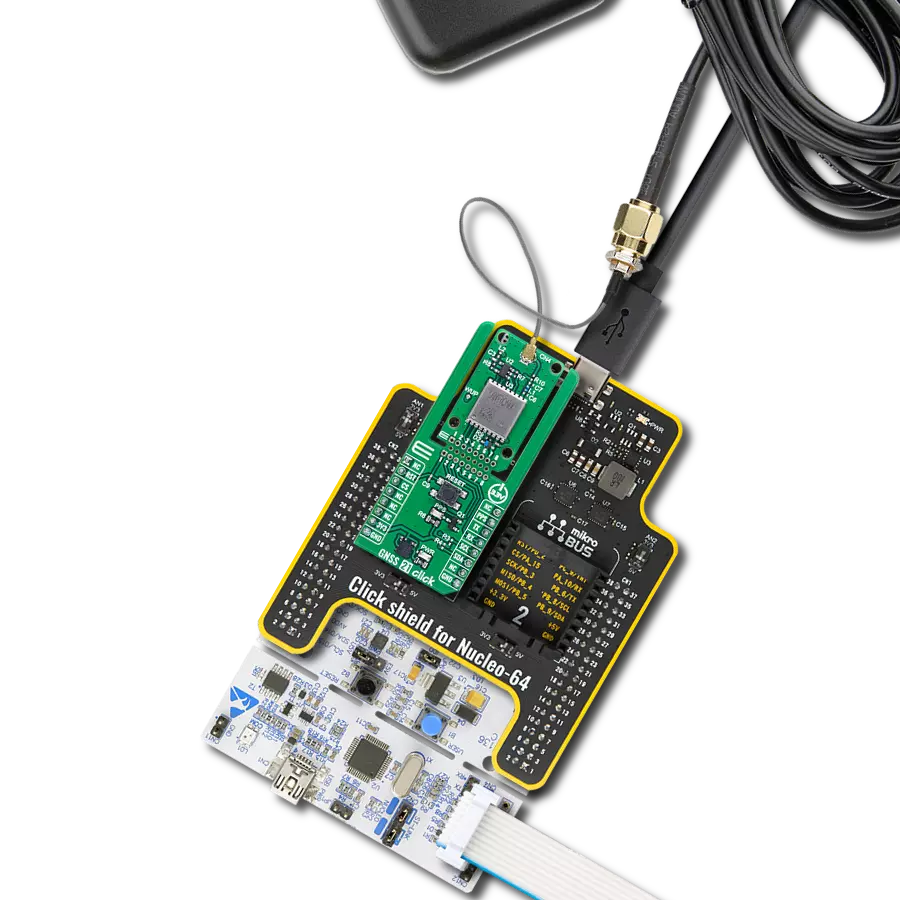
Our GNSS breakthrough not only helps you find your way but also ensures that every experience along the journey is extraordinary
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
GNSS 12 Click is based on the CAM-M8C, a concurrent GNSS chip antenna module from u-blox. The CAM-M8C is built on the high-performing M8 GNSS engine and utilizes simultaneous reception of up to three GNSS systems (GPS/Galileo together with BeiDou or GLONASS). It offers high sensitivity and minimal acquisition times while maintaining low power consumption and provides outstanding positioning accuracy even in GNSS-hostile environments. It also supports message integrity protection, geofencing, and spoofing detection with configurable interface settings to easily fit applications, such as industrial and automotive. The CAM-M8C communicates with the host MCU using the UART interface at 115200bps as its default communication protocol but also has other interfaces, such as SPI and I2C. The interface is selected by positioning SMD jumpers labeled COMM SEL in an appropriate position. Note that all
the jumpers' positions must be on the same side, or the Click board™ may become unresponsive. In addition, this board also uses several mikroBUS™ pins. The reset pin routed on the RST pin of the mikroBUS™ socket provides the general reset ability, while the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket represents an external interrupt. An interrupt feature can be used for wake-up functions in the power save mode and aiding. In the case of the primary supply failure, this Click board™ can use a backup supply voltage from a connected battery to help the internal RTC to run still, providing a timing reference for the receiver. Backup voltage also supplies battery-backed RAM, saving all relevant data in the backup RAM to allow a hot or warm start later. If the backup battery is disconnected, the module performs a cold start during a Power-Up sequence. In addition to precise positioning, the GNSS 12 Click also has an accurate timing signal indicated through an
orange LED indicator marked as PPS. Besides an integrated omnidirectional GNSS chip antenna, the GNSS 12 Click possesses the N.FL antenna connector for connecting the appropriate active antenna offered by Mikroe for improved range and received signal strength. Thanks to the LNA pin, routed to the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, it is possible to control the use of the external antenna through the MAX40200, and thus the power consumption in the power save mode. Also, for the simplest possible implementation of SMA antennas on these types of connectors, the MMCX-SMA Cable from our offer is recommended. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
UNI-DS v8 is a development board specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of microcontrollers, such as different STM32, Kinetis, TIVA, CEC, MSP, PIC, dsPIC, PIC32, and AVR MCUs regardless of their number of pins, and a broad set of unique functions, such as the first-ever embedded debugger/programmer over WiFi. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others, in one place. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, UNI-DS v8 provides a fluid and immersive working experience, allowing access anywhere and under any
circumstances at any time. Each part of the UNI-DS v8 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An advanced integrated CODEGRIP programmer/debugger module offers many valuable programming/debugging options, including support for JTAG, SWD, and SWO Trace (Single Wire Output)), and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides, it also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including a battery, an external 12V power supply, and a power source via the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. Communication options such as USB-UART, USB
HOST/DEVICE, CAN (on the MCU card, if supported), and Ethernet is also included. In addition, it also has the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and two display options for the TFT board line of products and character-based LCD. UNI-DS v8 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU
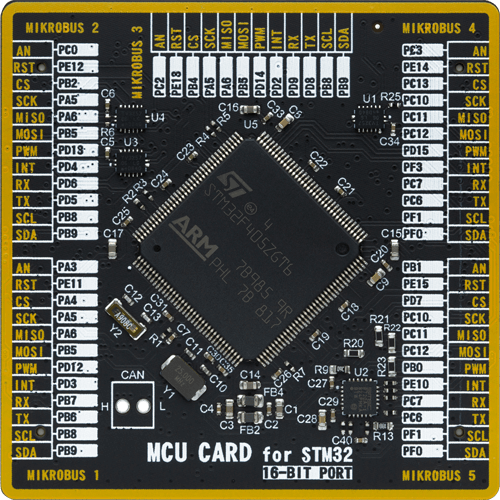
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
144
RAM (Bytes)
196608
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for GNSS 12 Click driver.
Key functions:
gnss12_reset_device- This function resets the device by toggling the RST pingnss12_generic_read- This function reads a desired number of data bytes from the modulegnss12_parse_gngga- This function parses the GNGGA data from the read response buffer
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief GNSS12 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of GNSS 12 Click by reading and displaying
* the GNSS coordinates.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and resets the Click board.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the received data, parses the GNGGA info from it, and once it receives
* the position fix it will start displaying the coordinates on the USB UART.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void gnss12_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t gnss12_process ( gnss12_t *ctx )
* - static void gnss12_parser_application ( char *rsp )
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gnss12.h"
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 200
static gnss12_t gnss12;
static log_t logger;
static char app_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static int32_t app_buf_cnt = 0;
/**
* @brief GNSS 12 clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length and counter.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void gnss12_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief GNSS 12 data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #gnss12_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read or Application buffer overflow.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t gnss12_process ( gnss12_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief GNSS 12 parser application.
* @param[in] rsp Response buffer.
* @details This function logs GNSS data on the USB UART.
* @return None.
* @note None.
*/
static void gnss12_parser_application ( char *rsp );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
gnss12_cfg_t gnss12_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
gnss12_cfg_setup( &gnss12_cfg );
GNSS12_MAP_MIKROBUS( gnss12_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
err_t init_flag = gnss12_init( &gnss12, &gnss12_cfg );
if ( ( UART_ERROR == init_flag ) || ( I2C_MASTER_ERROR == init_flag ) || ( SPI_MASTER_ERROR == init_flag ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
gnss12_reset_device ( &gnss12 );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
gnss12_process( &gnss12 );
if ( app_buf_len > ( sizeof ( GNSS12_RSP_GNGGA ) + GNSS12_GNGGA_ELEMENT_SIZE ) )
{
gnss12_parser_application( app_buf );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void gnss12_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
app_buf_cnt = 0;
}
static err_t gnss12_process ( gnss12_t *ctx )
{
int32_t rx_size = 0;
char rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
if ( GNSS12_DRV_SEL_UART == ctx->drv_sel )
{
rx_size = gnss12_generic_read( ctx, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
else if ( ( GNSS12_DRV_SEL_I2C == ctx->drv_sel ) || ( GNSS12_DRV_SEL_SPI == ctx->drv_sel ) )
{
if ( GNSS12_OK == gnss12_generic_read( ctx, rx_buf, 1 ) )
{
if ( GNSS12_DUMMY != rx_buf[ 0 ] )
{
rx_size = 1;
}
}
}
if ( rx_size > 0 )
{
int32_t buf_cnt = 0;
if ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
gnss12_clear_app_buf( );
return GNSS12_ERROR;
}
else
{
buf_cnt = app_buf_len;
app_buf_len += rx_size;
}
for ( int32_t rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ ( buf_cnt + rx_cnt ) ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
}
else
{
app_buf_len--;
buf_cnt--;
}
}
return GNSS12_OK;
}
return GNSS12_ERROR;
}
static void gnss12_parser_application ( char *rsp )
{
char element_buf[ 100 ] = { 0 };
if ( GNSS12_OK == gnss12_parse_gngga( rsp, GNSS12_GNGGA_LATITUDE, element_buf ) )
{
static uint8_t wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
if ( strlen( element_buf ) > 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n Latitude: %.2s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 2 ] );
gnss12_parse_gngga( rsp, GNSS12_GNGGA_LONGITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Longitude: %.3s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 3 ] );
memset( element_buf, 0, sizeof( element_buf ) );
gnss12_parse_gngga( rsp, GNSS12_GNGGA_ALTITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, " Altitude: %s m \r\n", element_buf );
wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
}
else
{
if ( wait_for_fix_cnt % 5 == 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Waiting for the position fix...\r\n\n" );
wait_for_fix_cnt = 0;
}
wait_for_fix_cnt++;
}
gnss12_clear_app_buf( );
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END