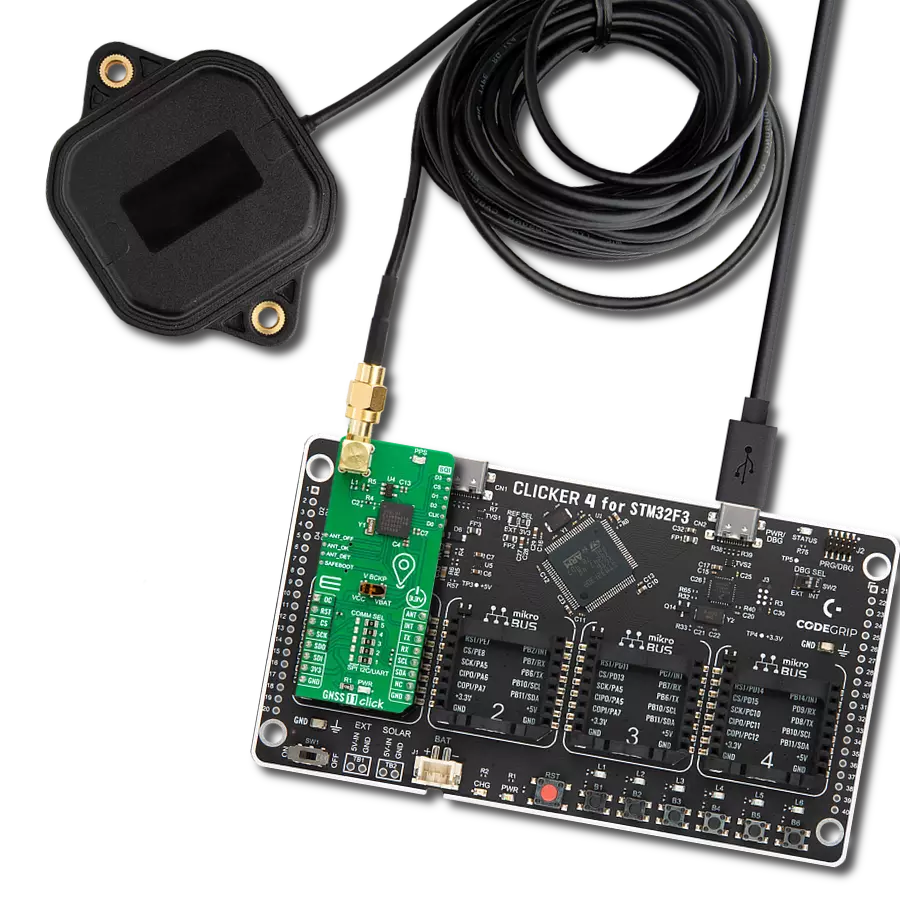
Devoted to heightening the travel experience, this solution functions as a guiding beacon, shedding light on routes and destinations and instilling confidence for exploration
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
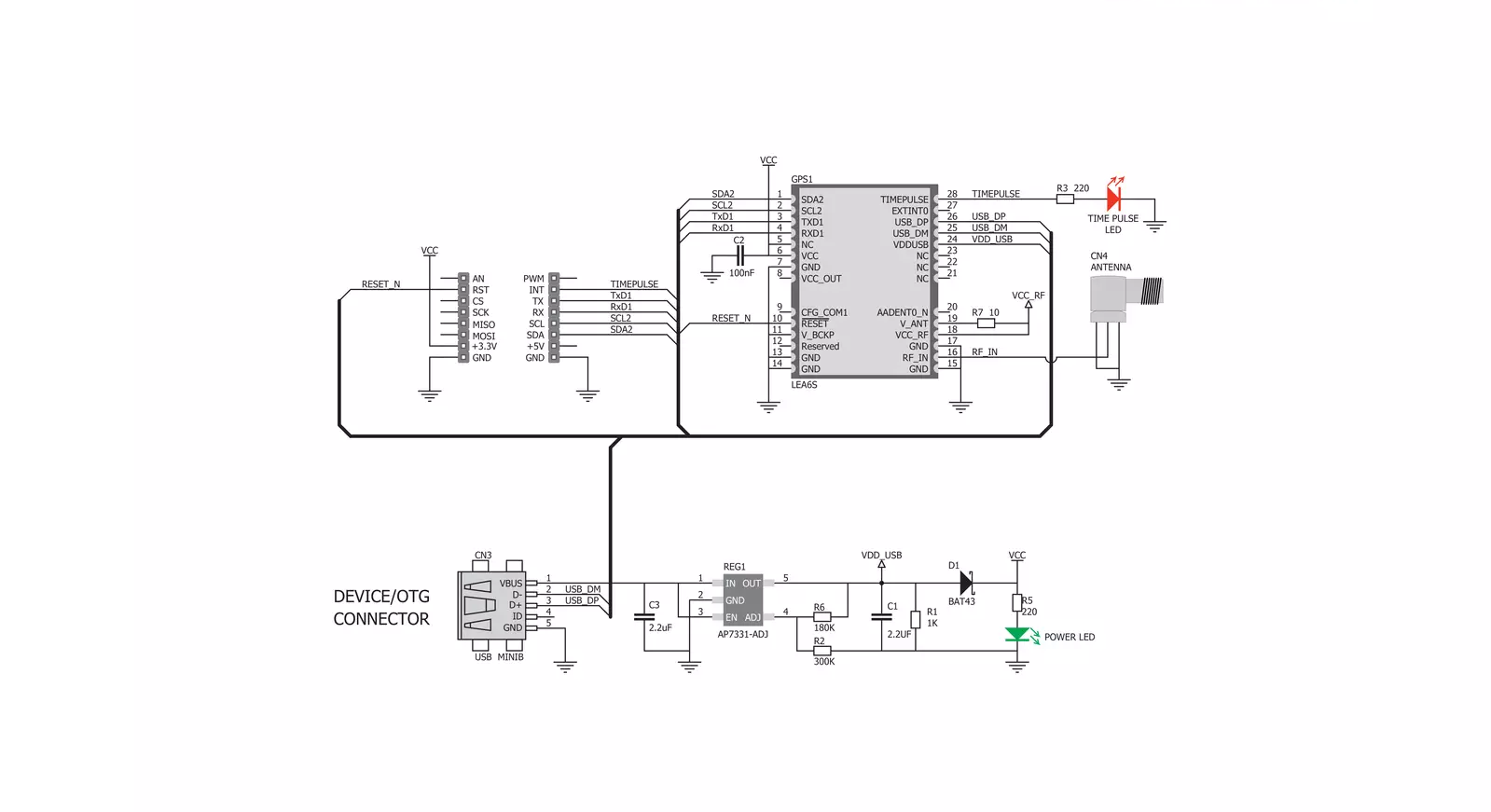
GPS Click is based on the LEA-6S, a high-performance position engine module from u-blox. The versatile, standalone LEA-6S receiver combines extensive features with flexible connectivity options. Its ease of integration results in fast time-to-market for various automotive and industrial applications. The positioning engine consists of cold start navigation, AssitsNow Autonomous for faster acquisition, configurable power management, a hybrid GPS/SBAS engine (WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS), and anti-jamming technology. The GPS module needs an SMA GPS antenna for the GPS applications, which can be bought from Mikroe separately. Different power modes (Maximum performance, Eco, Power Save) allow you to control the acquisition and tracking engines to balance performance and power consumption. During a Cold start, a receiver in Maximum Performance Mode continuously deploys the acquisition engine to search for all satellites. Once the receiver has a position fix (or if pre-positioning information is available), the acquisition
engine continues to search for all visible satellites that are not being tracked. During a Cold start, a receiver in Eco Mode works exactly as in Maximum Performance Mode. Once a position can be calculated and a sufficient number of satellites are tracked, the acquisition engine is powered off, resulting in significant power savings. The tracking engine continuously tracks acquired satellites and acquires other available or emerging satellites. Note that even if the acquisition engine is powered off, satellites continue to be acquired. Power Save Mode reduces system power consumption by selectively switching receiver parts on and off. GPS click can simultaneously track up to 16 satellites while searching for new ones. The LEA-6S module’s TTFF (time to first fix) is less than one second — this is the measure of time necessary for a GPS receiver to get satellite signals and navigation data, and based on this information, calculate a position (a fix). The GPS Click is equipped with a TIME PULSE LED as a 1PPS LED for that purpose. The Time Pulse has a 99%
accuracy, and its frequency range is adjustable from 0.25Hz to 1kHz. The Time Pulse can be tracked over the TP pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, too. GPS Click as default communication with the host MCU uses a standard 2-Wire UART interface with commonly used UART RX and TX and supports 4800 and 9600bps, depending on settings. The I2C-compatible Display Data Channel (DDC) can also be used to interface host MCU. It is a standard mode compliant with a maximum bandwidth of 100kbps. On the other hand, GPS Click supports a full-speed USB 2.0 at 1.2Mbps. If such a case emerges, you can always reset the module over the RST pin. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
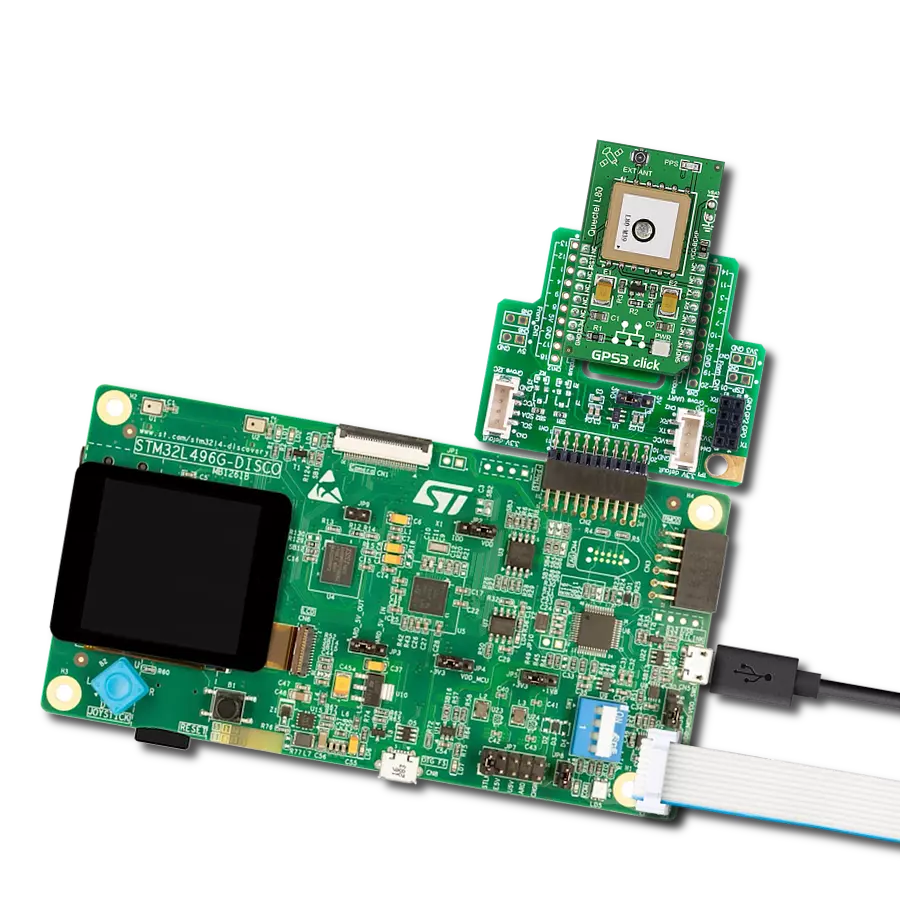
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
You complete me!
Accessories
Active GPS antenna is designed to enhance the performance of your GPS and GNSS Click boards™. This external antenna boasts a robust construction, making it ideal for various weather conditions. With a frequency range of 1575.42MHz and a 50Ohm impedance, it ensures reliable signal reception. The antenna delivers a gain of greater than -4dBic within a wide angular range, securing over 75% coverage. The bandwidth of +/- 5MHz further guarantees precise data acquisition. Featuring a Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP), this antenna offers stable signal reception. Its compact dimensions of 48.53915mm and a 2-meter cable make it easy to install. The magnetic antenna type with an SMA male connector ensures a secure and convenient connection. If you require a dependable external antenna for your locator device, our active GPS antenna is the perfect solution.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for GPS Click driver.
Key functions:
gps_generic_parser- Generic parser functiongps_generic_read- Generic read functiongps_module_wakeup- Wake-up module
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Gps Click example
*
* # Description
* This example reads and processes data from GPS Clicks.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes driver and wake-up module.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the received data and parses it.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - gps_process ( ) - The general process of collecting data the module sends.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "gps.h"
#include "string.h"
#define PROCESS_COUNTER 15
#define PROCESS_RX_BUFFER_SIZE 600
#define PROCESS_PARSER_BUFFER_SIZE 600
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static gps_t gps;
static log_t logger;
static char current_parser_buf[ PROCESS_PARSER_BUFFER_SIZE ];
// ------------------------------------------------------- ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS
static void gps_process ( void )
{
int32_t rsp_size;
uint16_t rsp_cnt = 0;
char uart_rx_buffer[ PROCESS_RX_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
uint16_t check_buf_cnt;
uint8_t process_cnt = PROCESS_COUNTER;
// Clear parser buffer
memset( current_parser_buf, 0 , PROCESS_PARSER_BUFFER_SIZE );
while( process_cnt != 0 )
{
rsp_size = gps_generic_read( &gps, &uart_rx_buffer, PROCESS_RX_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( rsp_size > 0 )
{
// Validation of the received data
for ( check_buf_cnt = 0; check_buf_cnt < rsp_size; check_buf_cnt++ )
{
if ( uart_rx_buffer[ check_buf_cnt ] == 0 )
{
uart_rx_buffer[ check_buf_cnt ] = 13;
}
}
// Storages data in parser buffer
rsp_cnt += rsp_size;
if ( rsp_cnt < PROCESS_PARSER_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
strncat( current_parser_buf, uart_rx_buffer, rsp_size );
}
// Clear RX buffer
memset( uart_rx_buffer, 0, PROCESS_RX_BUFFER_SIZE );
}
else
{
process_cnt--;
// Process delay
Delay_100ms( );
}
}
}
static void parser_application ( char *rsp )
{
char element_buf[ 200 ] = { 0 };
log_printf( &logger, "\r\n-----------------------\r\n" );
gps_generic_parser( rsp, GPS_NEMA_GPGGA, GPS_GPGGA_LATITUDE, element_buf );
if ( strlen( element_buf ) > 0 )
{
log_printf( &logger, "Latitude: %.2s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 2 ] );
gps_generic_parser( rsp, GPS_NEMA_GPGGA, GPS_GPGGA_LONGITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, "Longitude: %.3s degrees, %s minutes \r\n", element_buf, &element_buf[ 3 ] );
memset( element_buf, 0, sizeof( element_buf ) );
gps_generic_parser( rsp, GPS_NEMA_GPGGA, GPS_GPGGA_ALTITUDE, element_buf );
log_printf( &logger, "Altitude: %s m", element_buf );
}
else
{
log_printf( &logger, "Waiting for the position fix..." );
}
}
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
gps_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
gps_cfg_setup( &cfg );
GPS_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
gps_init( &gps, &cfg );
gps_module_wakeup( &gps );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
gps_process( );
parser_application( current_parser_buf );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END