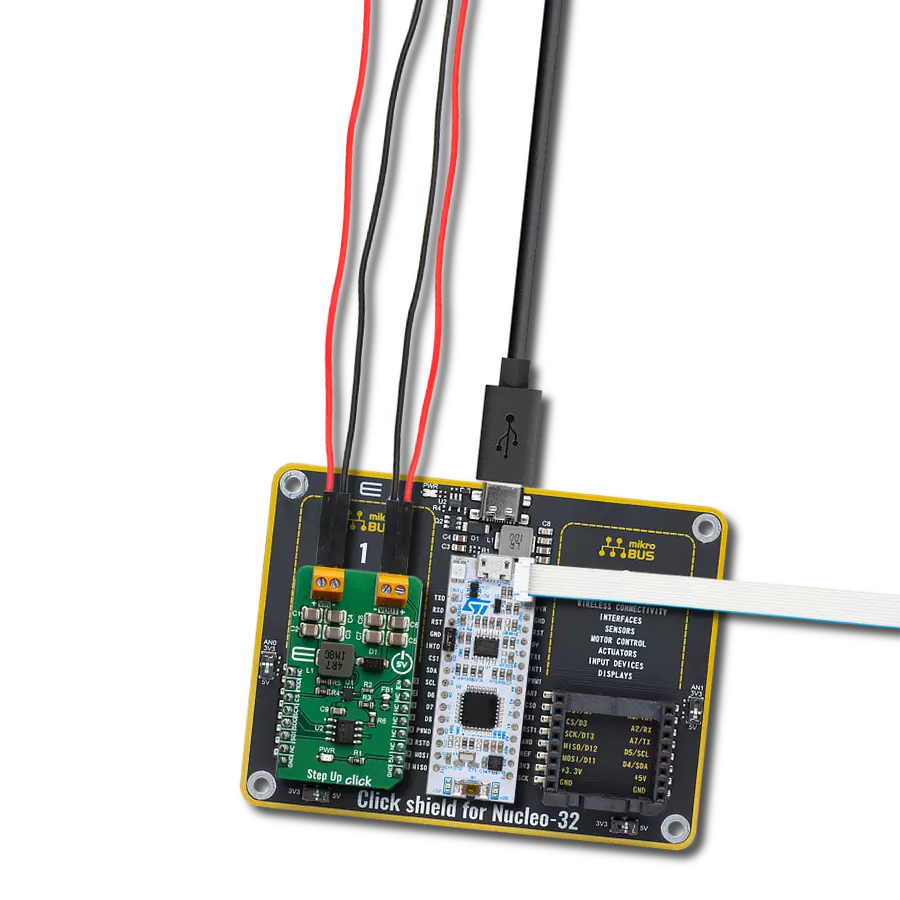
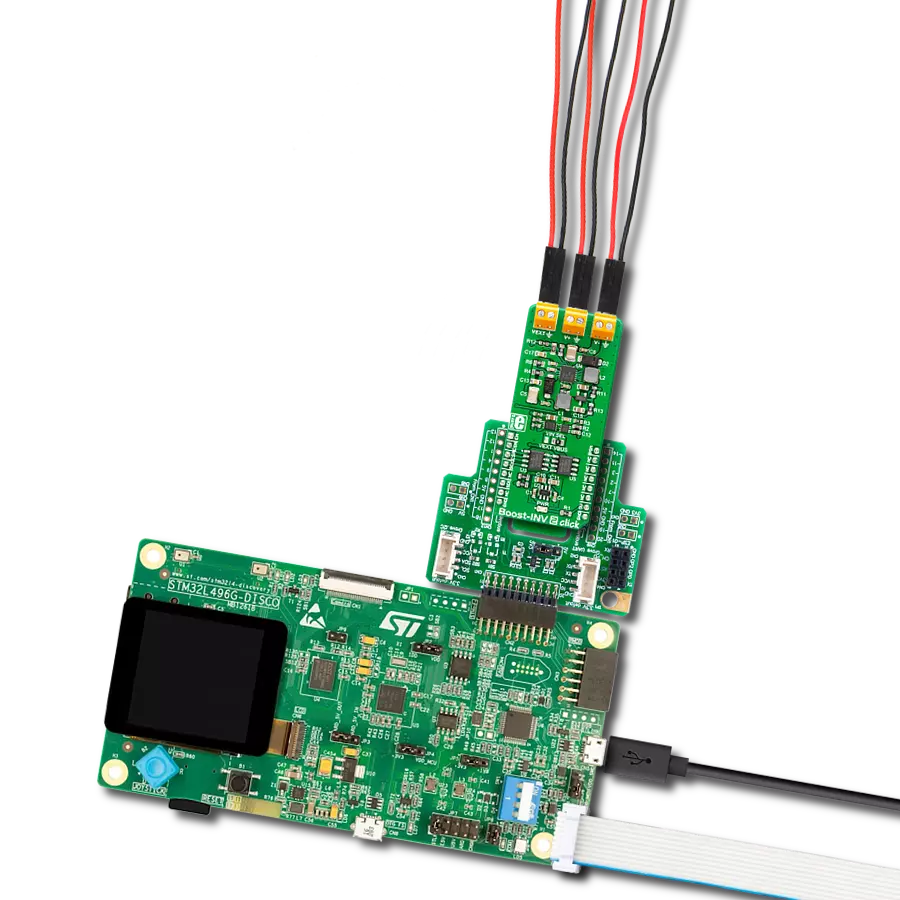
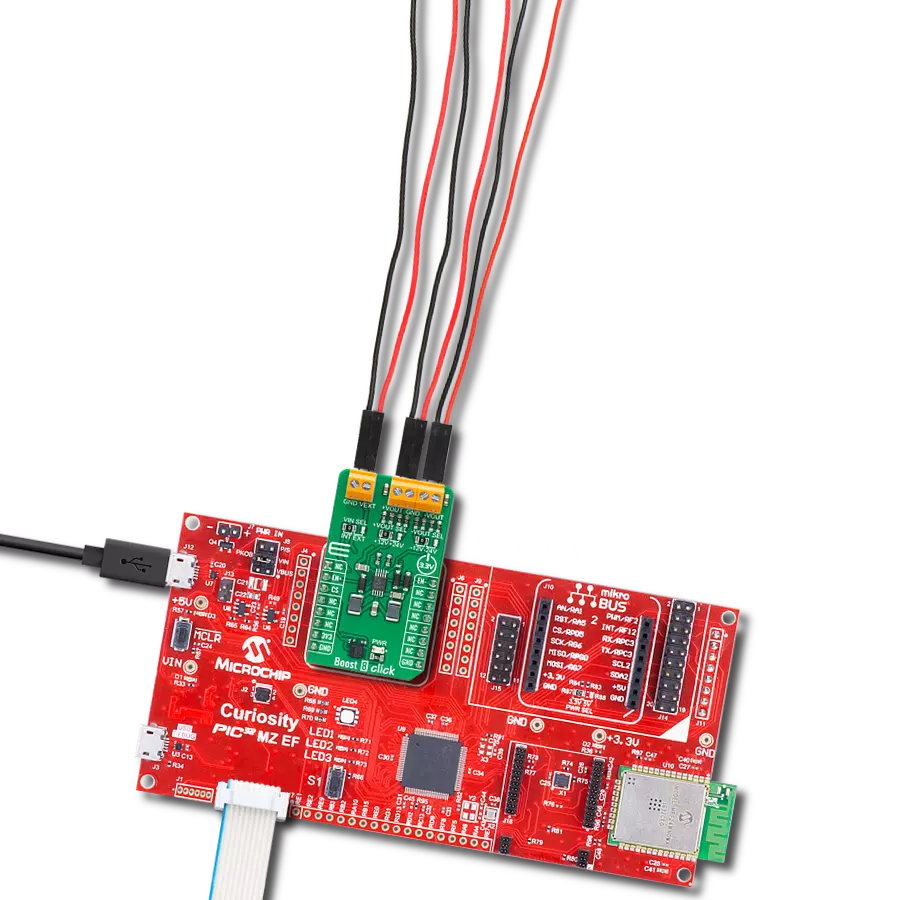
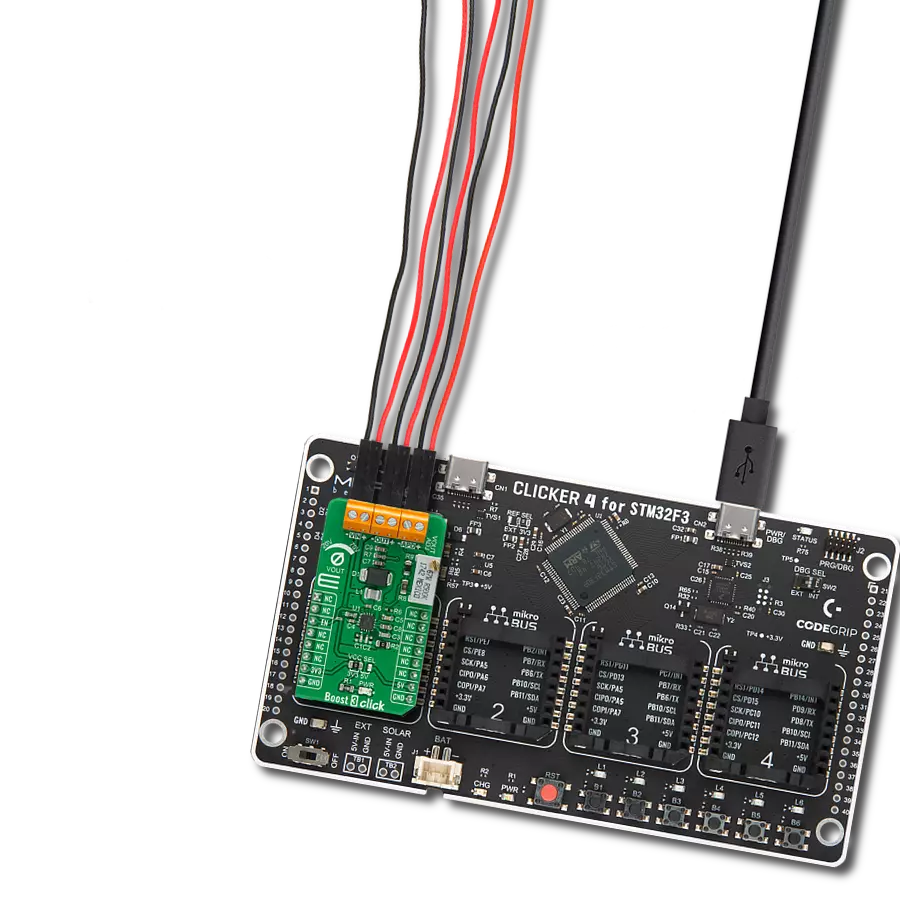
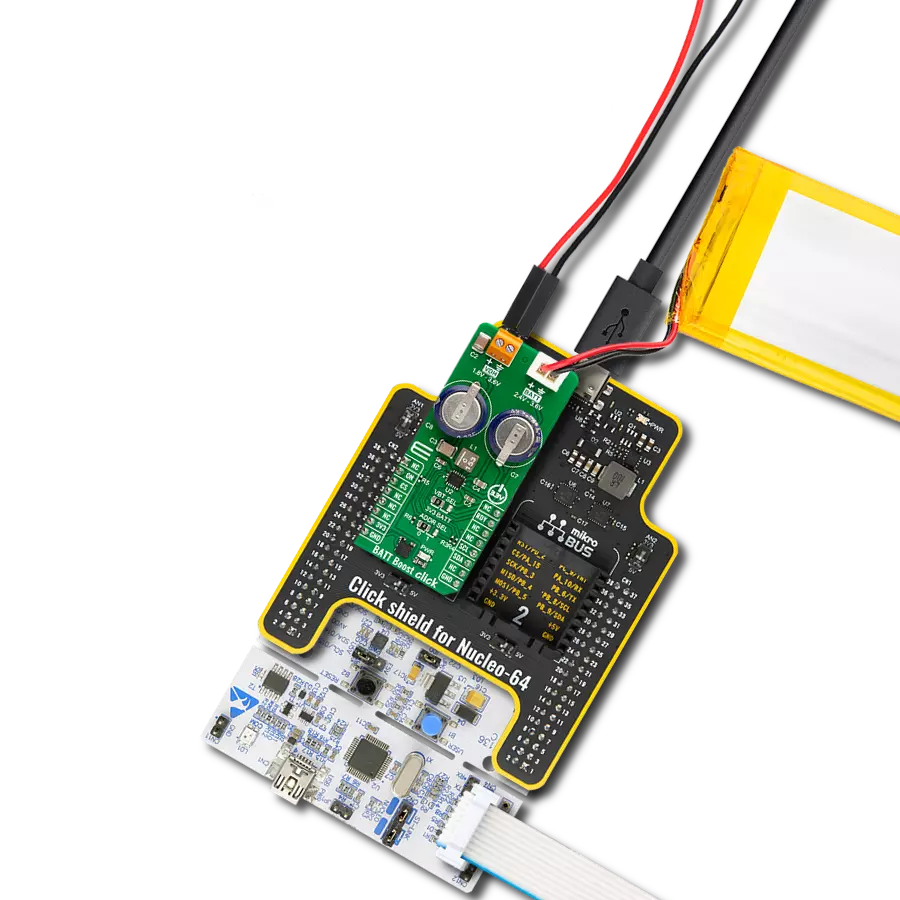
Provide a reliable voltage boost for powering low-power sensors or other industrial electronics from low-voltage sources
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
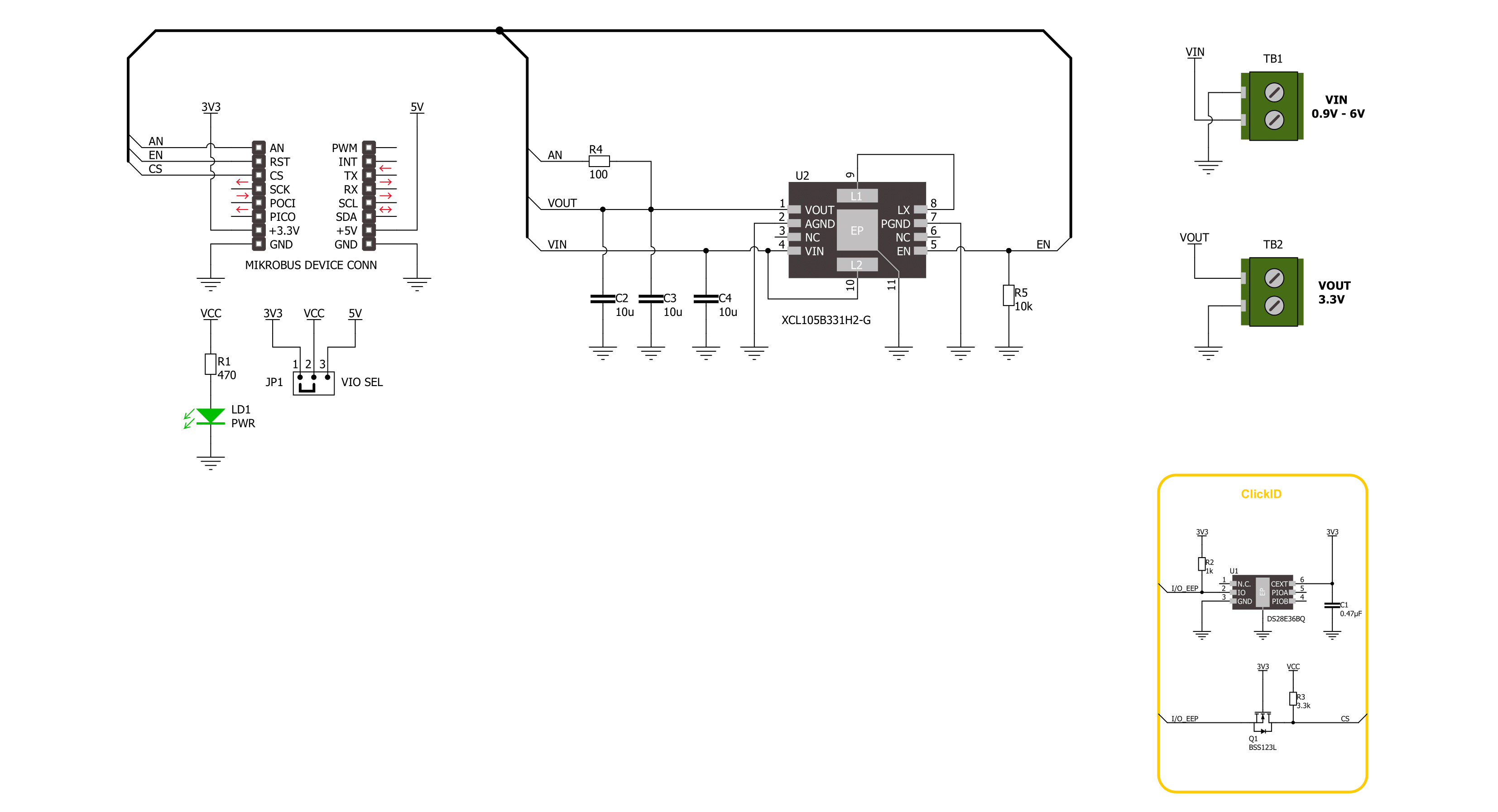
Boost 11 Click is based on the XCL105B331H2-G, a synchronous step-up DC/DC converter from TOREX Semi. This component includes a reference voltage source, ramp wave circuit, error amplifier, PWM comparator, phase compensation circuit, N-channel driver FET, P-channel synchronous switching FET, and current limiter circuit. It can start operating from an input voltage of 0.9V, making it suitable for devices using single Alkaline or Nickel-metal hydride batteries. The operating voltage range spans from 0.9V to 6V, which applies to the VIN terminal. This versatility makes it ideal for industrial equipment, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, wearables, and any applications
prioritizing battery life. The XCL105B331H2-G operates by using the error amplifier to compare the internal reference voltage with the feedback voltage. The resulting output undergoes phase compensation and is fed to the PWM comparator. This comparator matches the signal from the error amplifier with the ramp wave circuit output, sending the resulting signal to the buffer driver circuit to control the PWM duty cycle. This continuous process stabilizes the output voltage, fixed at 3.3V and available at the VOUT terminal. Additionally, an output signal is available on the AN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. The Boost 11 Click uses the EN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket in addition to the
AN pin. When the EN pin is set to a high logic level, the output voltage is raised via the Start-Up mode, initiating normal operation. When set to a low logic level, the IC enters Standby mode, significantly reducing current consumption. This Click board™ can operate with either 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VIO SEL jumper. This way, both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs can use the communication lines properly. Also, this Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
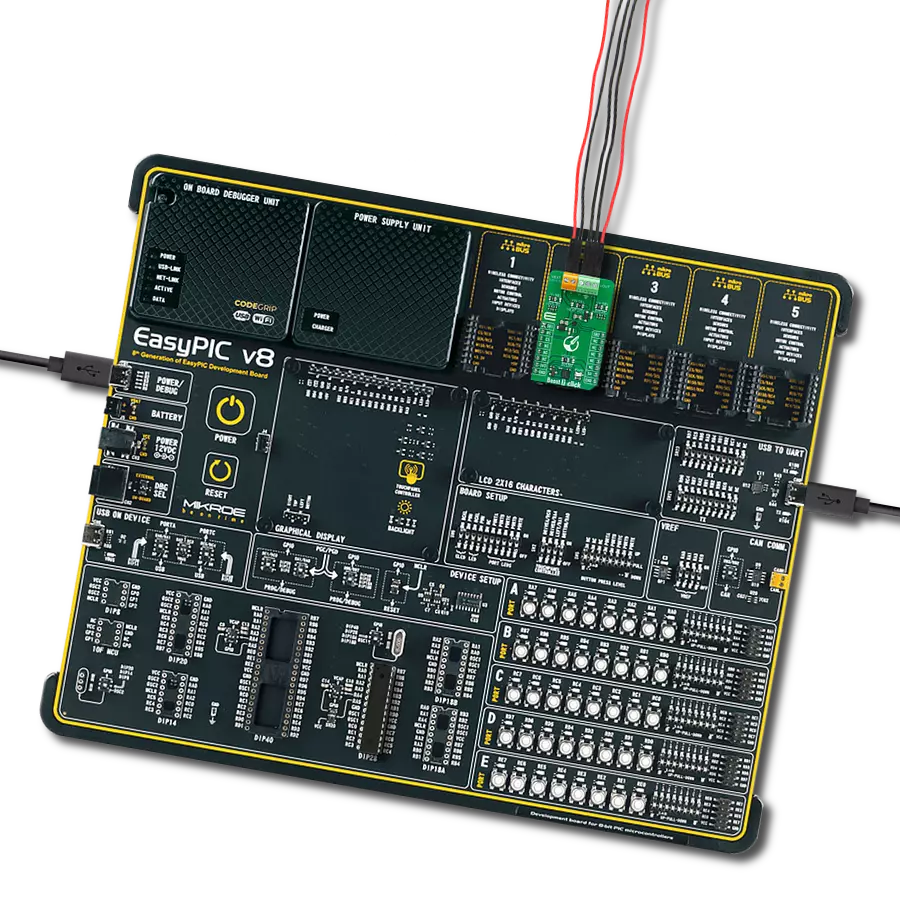
Development board
EasyAVR v7 is the seventh generation of AVR development boards specially designed for the needs of rapid development of embedded applications. It supports a wide range of 16-bit AVR microcontrollers from Microchip and has a broad set of unique functions, such as a powerful onboard mikroProg programmer and In-Circuit debugger over USB. The development board is well organized and designed so that the end-user has all the necessary elements in one place, such as switches, buttons, indicators, connectors, and others. With four different connectors for each port, EasyAVR v7 allows you to connect accessory boards, sensors, and custom electronics more
efficiently than ever. Each part of the EasyAVR v7 development board contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. An integrated mikroProg, a fast USB 2.0 programmer with mikroICD hardware In-Circuit Debugger, offers many valuable programming/debugging options and seamless integration with the Mikroe software environment. Besides it also includes a clean and regulated power supply block for the development board. It can use a wide range of external power sources, including an external 12V power supply, 7-12V AC or 9-15V DC via DC connector/screw terminals, and a power source via the USB Type-B (USB-B)
connector. Communication options such as USB-UART and RS-232 are also included, alongside the well-established mikroBUS™ standard, three display options (7-segment, graphical, and character-based LCD), and several different DIP sockets which cover a wide range of 16-bit AVR MCUs. EasyAVR v7 is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem for rapid development. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping and development thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
32
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
40
RAM (Bytes)
2048
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Boost 11 Click driver.
Key functions:
boost11_active_mode- This function activates the boost operating mode.boost11_read_an_pin_voltage- This function reads results of AD conversion of the AN pin and converts them to proportional voltage level.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief Boost 11 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of Boost 11 Click board
* by controlling the output state.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization of GPIO module, log UART, and activate the boost operating mode.
*
* ## Application Task
* The demo application reads measurements of the output voltage level [V].
* Results are being sent to the UART Terminal, where you can track their changes.
*
* @author Nenad Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "boost11.h"
static boost11_t boost11; /**< Boost 11 Click driver object. */
static log_t logger; /**< Logger object. */
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
boost11_cfg_t boost11_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
boost11_cfg_setup( &boost11_cfg );
BOOST11_MAP_MIKROBUS( boost11_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( ADC_ERROR == boost11_init( &boost11, &boost11_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
boost11_active_mode( &boost11 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
float voltage = 0;
if ( BOOST11_OK == boost11_read_an_pin_voltage ( &boost11, &voltage ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Output Voltage : %.3f[V]\r\n\n", voltage );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END