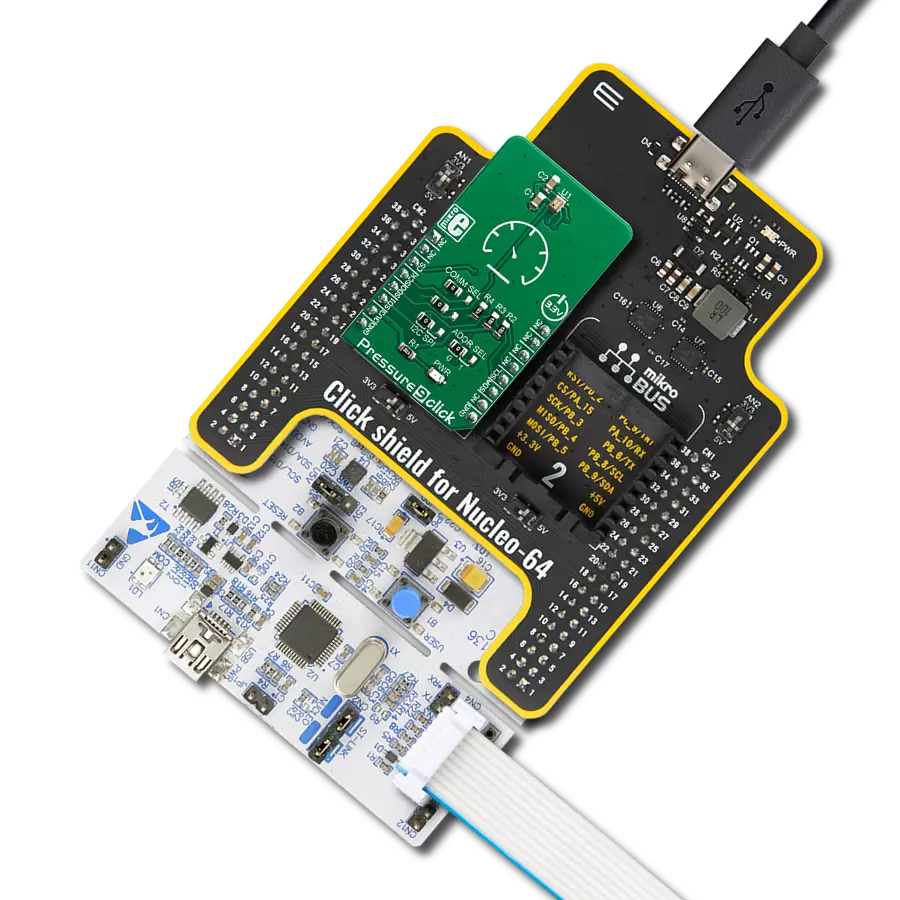
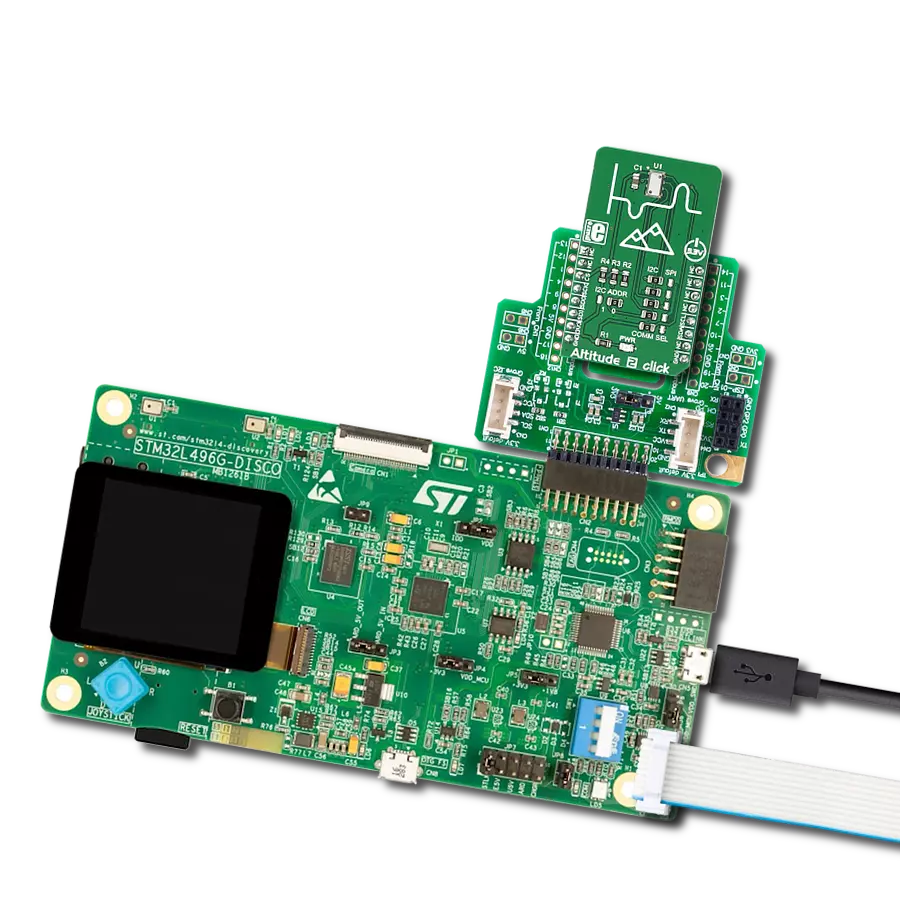
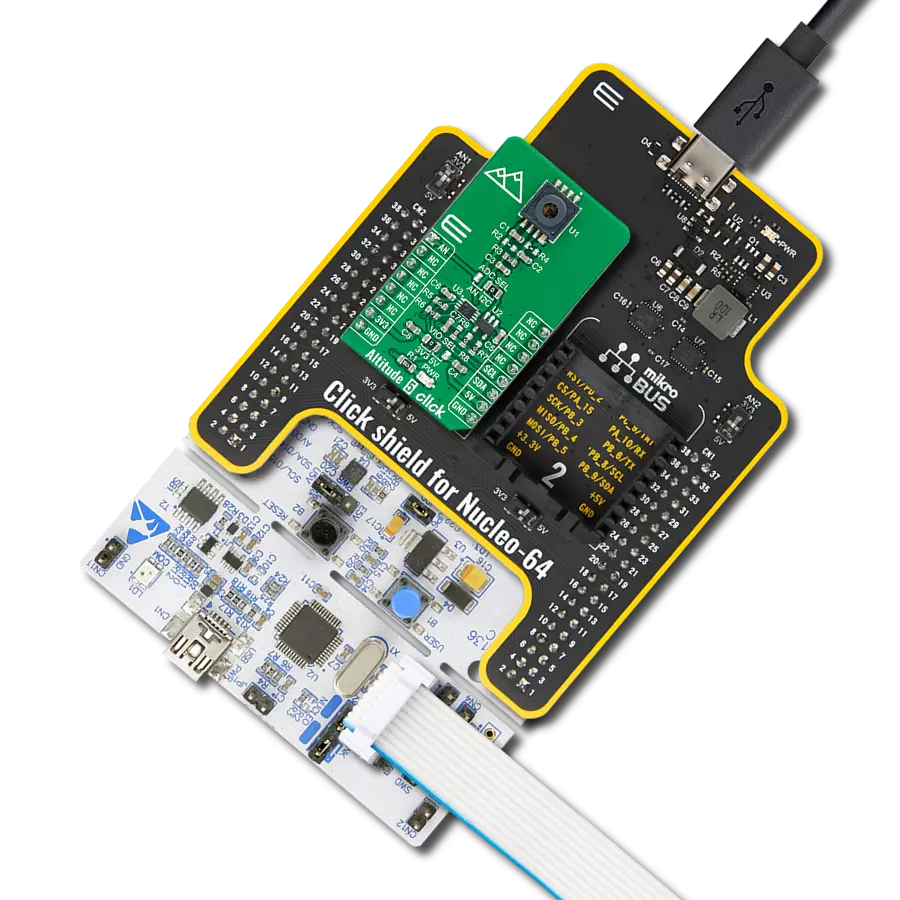
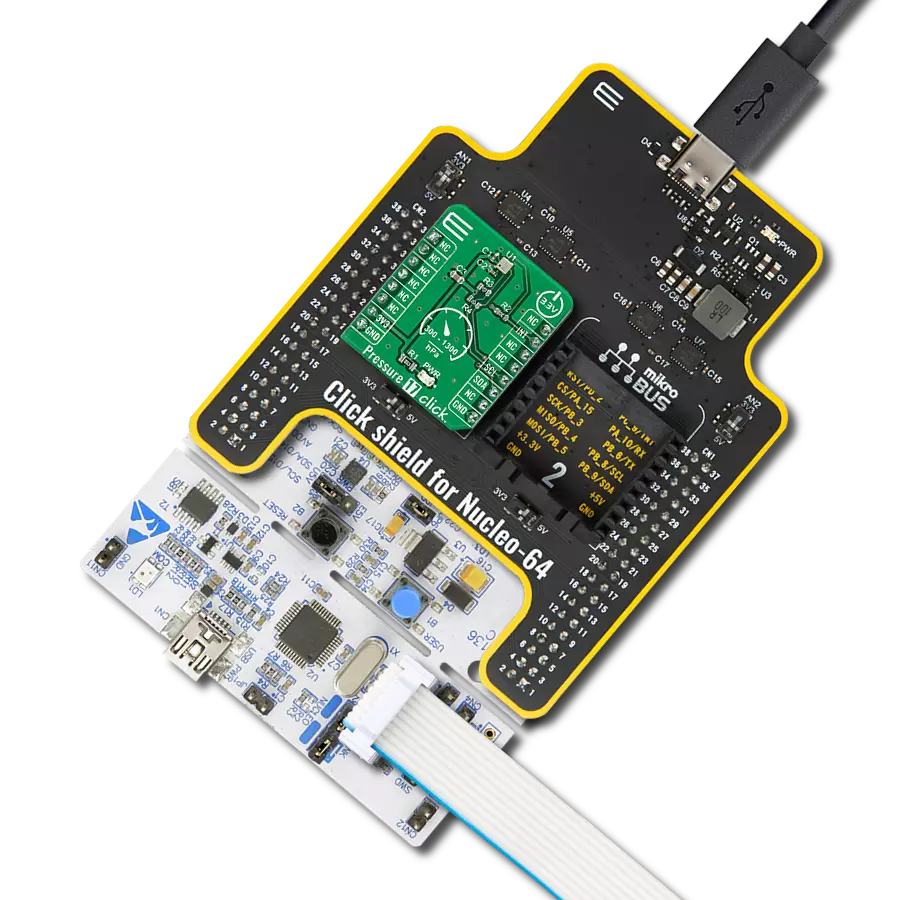
Unleash the full potential of your projects with our digital pressure measurement solution, engineered to set new standards in reliability and performance
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Pressure 7 Click is based on the MS5837, a pressure sensor from TE Connectivity. This is a highly integrated piezo-resistive absolute pressure sensor, based on the MEMS technology by TE Connectivity, which can measure the pressure in the range from 0 to 30 bar, and the temperature in the range from -20° to +85° C. The MEMS (micro electromechanical sensor) is placed in a hermetically sealed, anti-magnetic stainless-steel cap, protected with the special gel. This makes the sensor itself water-resistant. Besides the piezo-resistive sensor, the MS5837 module also contains the highly integrated ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) which contains all the necessary components that are required to convert the uncompensated voltage from the MEMS into 24-bit digital data. The MS5837 sensor offers the standard I2C interface for the communication with the host MCU, using only a few commands. The advanced ASIC which contains the 24bit delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC), provides a very high resolution of 0.2 mbar per step, as well as the fast conversion time, down to 0.5 ms. The already low power consumption can be further regulated by utilizing different output sample rates (OSR), within the
range from 256 to 8192. The OSR setting is contained within a single command, which is sent from the host MCU to initiate the conversion. The OSR directly affects both the current consumption of the MS5837 sensor, as well as the conversion time: the higher the OSR ratio, the more current is required, and less time to complete the conversion cycle. The user application should perform a reset of the MS5837 sensor module before reading the compensation parameters from the PROM. These compensation parameters should be stored by the application for the later use. When the MS5837 module receives the conversion command over the I2C interface, it will start the thermal and pressure conversion process. After the conversion, the data is clocked out when ADC Read command is received. After receiving the raw conversion data from the MS5837, the application should convert this data, applying the previously stored calibration parameters. The output data rate, as well as the specific conversion type (thermal or pressure conversion) depend on the received command. The MS5837 datasheet offers detailed explanation of the command byte. The conversion data is available over the I2C interface, as mentioned before. The I2C bus lines (SDA and SCL)
are routed to the respective I2C mikroBUS™ pins which are pulled up by resistors on the Click board™ itself, allowing the Click board™ to be used right out of the box. The datasheet of the MS5837 sensor module also offers conversion formulas and algorithms which can be used to convert the raw binary values from the respective PROM registers to physical, human-readable format. However, Pressure 7 click comes with the library that contains functions which output converted and properly formatted thermal and pressure readings. In addition to the MS5837 sensor module, Pressure 7 click incorporates an additional IC. It is the PCA9306, a well-known bi-directional I2C level translator from Texas Instruments, used on many different Click board™ designs, due to its simplicity and reliability. Since the MS5837 sensor is limited to 3.3V operation, this IC allows it to be used with the 5V logic level, expanding the connectivity of the Pressure 7 click to MCUs which use 5V levels for the I2C communication. The logic voltage level selection can be made by switching the small onboard SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL, to a proper position (3V3 or 5V).
Features overview
Development board
Clicker 2 for Kinetis is a compact starter development board that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F microcontroller, the MK64FN1M0VDC12 from NXP Semiconductors, two mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a JTAG programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Its compact design with clear and easily recognizable silkscreen markings allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and
features quickly. Each part of the Clicker 2 for Kinetis development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the Clicker 2 for Kinetis programming method, using a USB HID mikroBootloader or an external mikroProg connector for Kinetis programmer, the Clicker 2 board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Micro-B cable, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or
using a Li-Polymer battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, reset button, and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. Clicker 2 for Kinetis is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
ARM Cortex-M4
MCU Memory (KB)
1024
Silicon Vendor
NXP
Pin count
121
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Pressure 7 Click driver.
Key functions:
pressure7_read_PROM- This function reads calibration data from PROMpressure7_start_measurement- This function starts measurement and calculation datapressure7_get_sensor_data- This function reads pressure and temperature data
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Pressure7 Click example
*
* # Description
* This example reads sensor temperature and pressure output on every 3 seconds and
* prints it on UART Terminal.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialize Logger and Click object and call pressure7_read_PROM() function.
*
* ## Application Task
* Get sensor data on every 3 seconds and send measured temperature and pressure to logger.
*
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "pressure7.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static pressure7_t pressure7;
static log_t logger;
static float Temperature = 0;
static float Pressure = 0;
static uint8_t prom_exit_value;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
pressure7_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
pressure7_cfg_setup( &cfg );
PRESSURE7_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
pressure7_init( &pressure7, &cfg );
pressure7_default_cfg ( &pressure7 );
Delay_ms ( 200 );
// Read calibrated data from the PROM
prom_exit_value = pressure7_read_prom( &pressure7 );
if ( prom_exit_value == PRESSURE7_PROM_READ_OK )
{
log_info( &logger, "Read PROM - OK !\r\n" );
}
else
{
log_info( &logger, "Read PROM - ERROR!\r\n" );
}
Delay_ms ( 100 );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
pressure7_start_measurement( &pressure7 );
pressure7_get_sensor_data( &pressure7, &Temperature, &Pressure );
log_printf( &logger, "Temperature: %f C\r\n", Temperature );
log_printf( &logger, "Pressure: %f\r\n", Pressure );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END