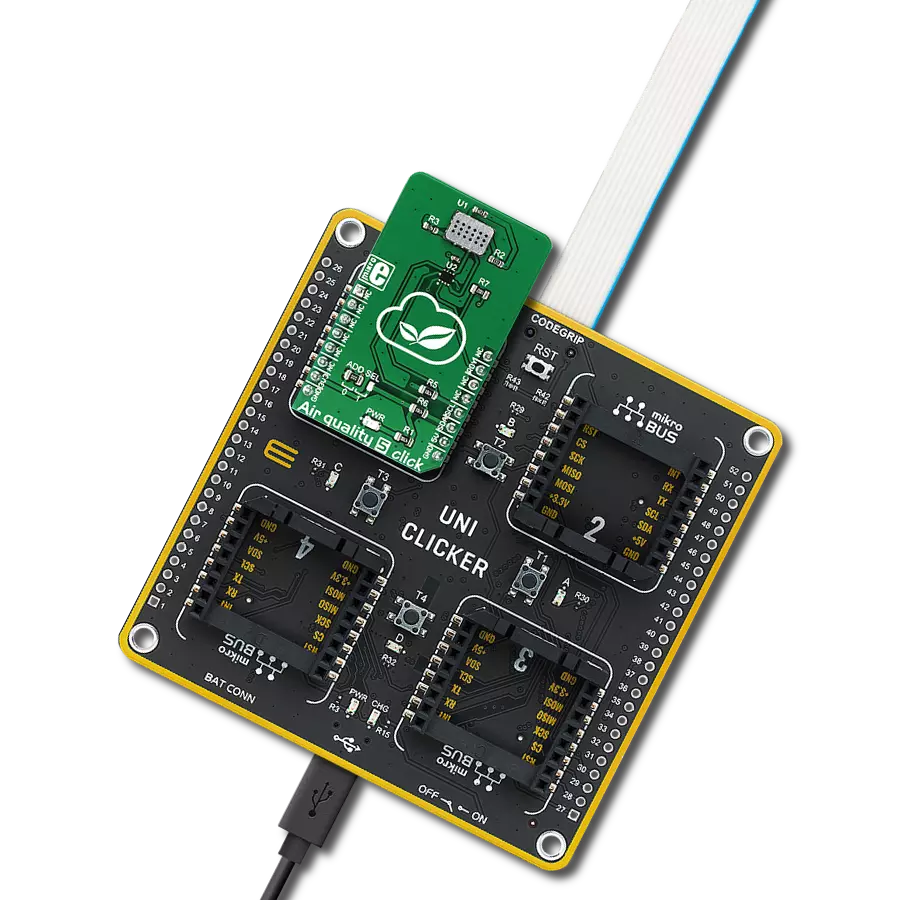
With real-time alerts and actionable insights, our monitor solution transforms air quality management into a dynamic and responsive process for safer living
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
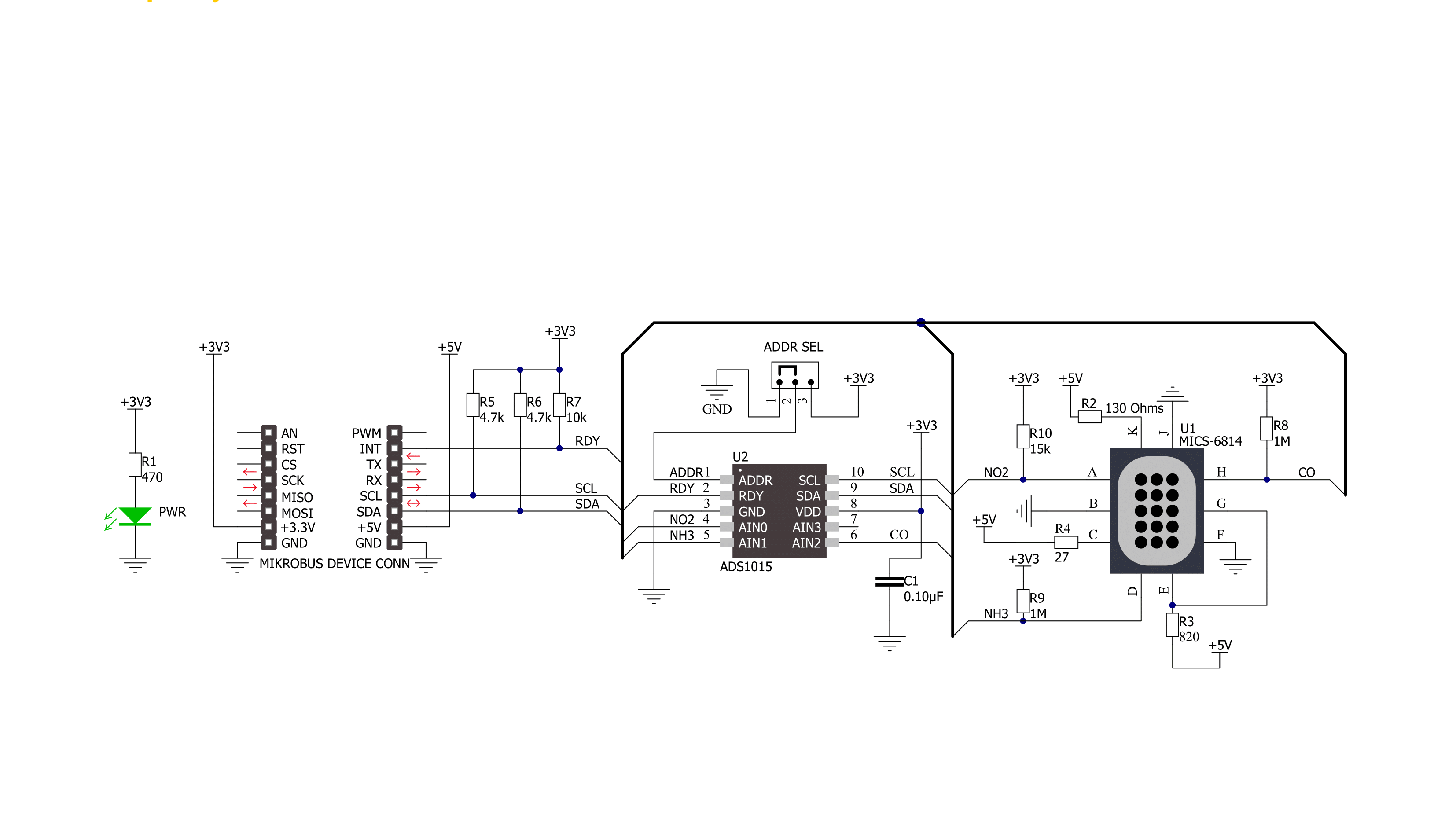
Air Quality 5 Click is based on the MiCS-6814, a compact triple MOS sensor from SGX Sensortech with three fully independent sensors. The Click board™ also contains the ADS1015, a low-power 12-bit ADC with Internal reference and a programmable comparator from Texas Instruments. The MiCS-6814 sensor comprises three independent metal oxide sensors heated by three separate heater structures. Chemicals absorbed by the metal oxide surface change the resistive properties of the sensor. The typical baseline resistance may vary a lot from sensor to sensor, which can be affected by the measurement conditions, sensor aging, and several other factors. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically monitor the relative change of the sensing resistance against the baseline resistance. It allows the development of applications that detect relative gas concentration changes rather than measuring the absolute gas concentration values. As mentioned, there are three sensors on
the same die. Each of them reacts with a different type of gas. There is a RED sensor, which reacts with the reducing gas agents, an OX sensor, which reacts with the oxidizing gas agents, and a sensor that reacts with NH3. These sensors provide readings (in ppm) for eight different gasses, which are interesting to monitor in the automotive, industry, or agriculture-polluted atmosphere. Every heating structure is powered from the mikroBUS™ 5V power rail via the resistor recommended by the manufacturer. This ensures the maximum life cycle of the device is achieved since current ratings above the recommended would damage the sensors and heaters. It is recommended to pre-heat the sensors for at least 30 seconds before valid readings can be made. The longer the pre-heat period is, the more accurate the measurement becomes. The changes in the sensor resistance are measured and sampled by the onboard ADC. The ADS1015 ADC has four multiplexed inputs, of which three are
connected to each sensor. The ADC has an internal reference, is simple to operate, offers inputs that can handle voltages across the sensors, and requires a low number of external components. These attributes make it perfectly suitable for this Click board™. In addition, it is possible to change the I2C address of the device. This is done by using the SMD jumper labeled as ADD SEL. This jumper allows the selection of the I2C LSB bit state (0 or 1), allowing more than one Click board™ on the same I2C bus. The ADS1015 IC also has a READY pin, which signals or alerts the host MCU that the conversion is ready for reading. This pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ INT pin and labeled as RDY. More information on configuring and using this pin can be found in the ADS1015 datasheet. Both 5V and 3.3V rails from the mikroBUS™ are used. The ADC is powered by a 3.3V rail, but the sensor requires a 5V rail. Therefore, the Click board™ requires both 3.3V and 5V pins to be supplied with the power.
Features overview
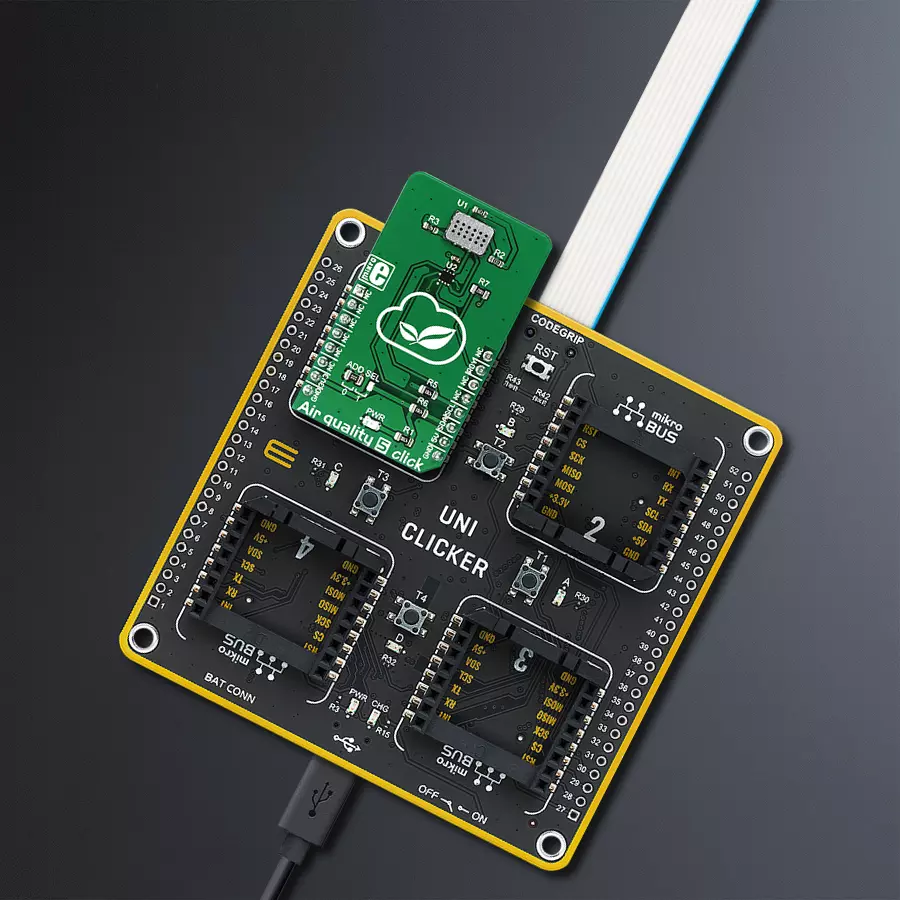
Development board
UNI Clicker is a compact development board designed as a complete solution that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It supports a wide range of microcontrollers, such as different ARM, PIC32, dsPIC, PIC, and AVR from various vendors like Microchip, ST, NXP, and TI (regardless of their number of pins), four mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, a USB connector, LED indicators, buttons, a debugger/programmer connector, and two 26-pin headers for interfacing with external electronics. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology, it allows you to build
gadgets with unique functionalities and features quickly. Each part of the UNI Clicker development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition to the possibility of choosing the UNI Clicker programming method, using a third-party programmer or CODEGRIP/mikroProg connected to onboard JTAG/SWD header, the UNI Clicker board also includes a clean and regulated power supply module for the development kit. It provides two ways of board-powering; through the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector, where onboard voltage regulators provide the appropriate voltage levels to each component on the board, or using a Li-Po/Li
Ion battery via an onboard battery connector. All communication methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board (plus USB HOST/DEVICE), including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, a standardized socket for the MCU card (SiBRAIN standard), and several user-configurable buttons and LED indicators. UNI Clicker is an integral part of the Mikroe ecosystem, allowing you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
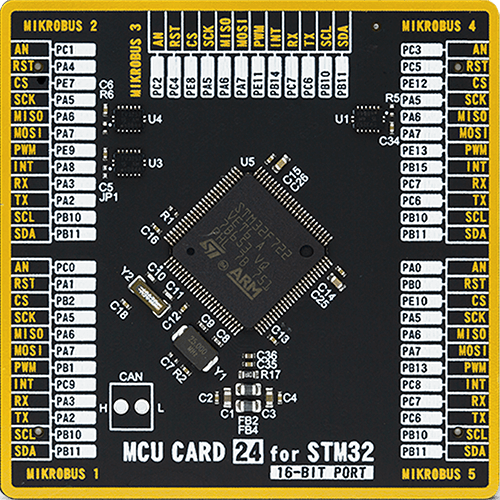
MCU Card / MCU
Type
8th Generation
Architecture
ARM Cortex-M7
MCU Memory (KB)
512
Silicon Vendor
STMicroelectronics
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
262144
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Air Quality 5 Click driver.
Key functions:
airq5_write_data- Functions for write data in registerairq5_read_data- Functions for read data from registerairq5_set_configuration- Functions for configuration
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Airquality5 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application can detect gas pollution for a number of different gases.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes device and configuration chip.
*
* ## Application Task
* Reads the values of CO, NH3 and NO2 sensor and logs data on USBUART every 500ms.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "airquality5.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static airquality5_t airquality5;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
airquality5_cfg_t cfg;
airquality5.data_config = 0x8583;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
airquality5_cfg_setup( &cfg );
AIRQUALITY5_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
airquality5_init( &airquality5, &cfg );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
// Task implementation.
uint16_t NO2_sensor_data;
uint16_t NH3_sensor_data;
uint16_t CO_sensor_data;
CO_sensor_data = airq5_read_sensor_data( &airquality5, AIRQ5_DATA_CHANNEL_CO );
NO2_sensor_data = airq5_read_sensor_data( &airquality5, AIRQ5_DATA_CHANNEL_NO2 );
log_printf( &logger, " NO2 data: %d\r\n", NO2_sensor_data );
NH3_sensor_data = airq5_read_sensor_data( &airquality5, AIRQ5_DATA_CHANNEL_NH3 );
log_printf( &logger, " NH3 data: %d\r\n", NH3_sensor_data );
CO_sensor_data = airq5_read_sensor_data( &airquality5, AIRQ5_DATA_CHANNEL_CO );
log_printf( &logger," CO data: %d\r\n", CO_sensor_data );
log_printf( &logger, " -------- ");
Delay_ms ( 200 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END