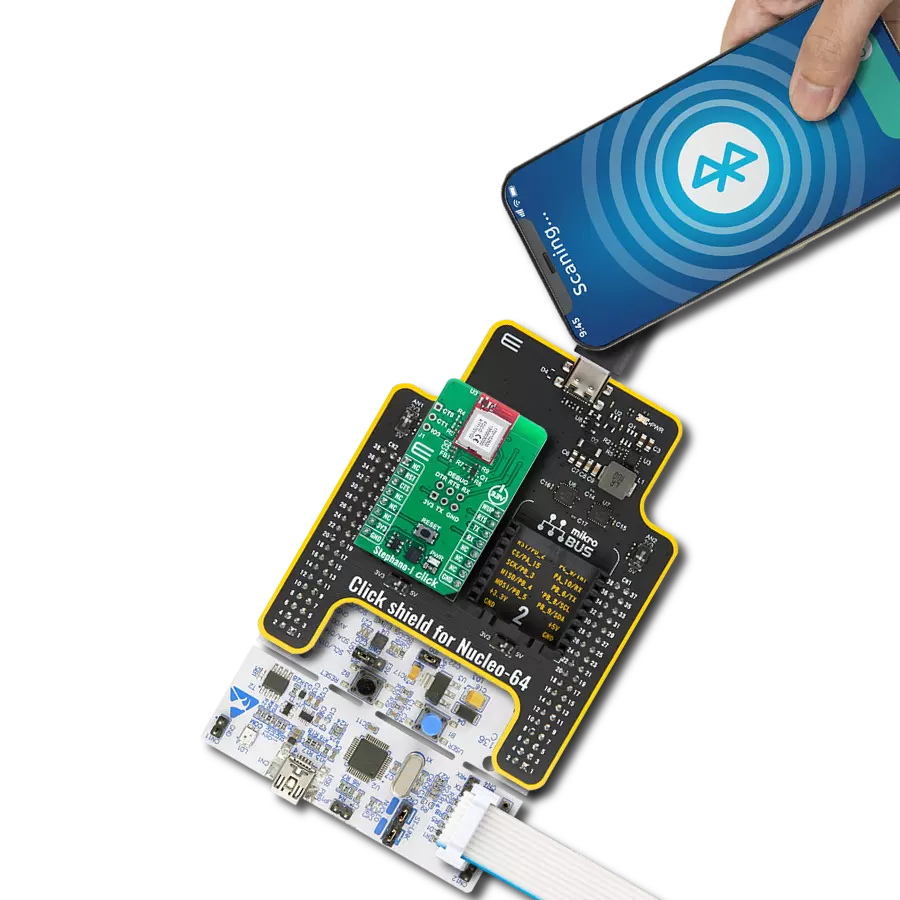
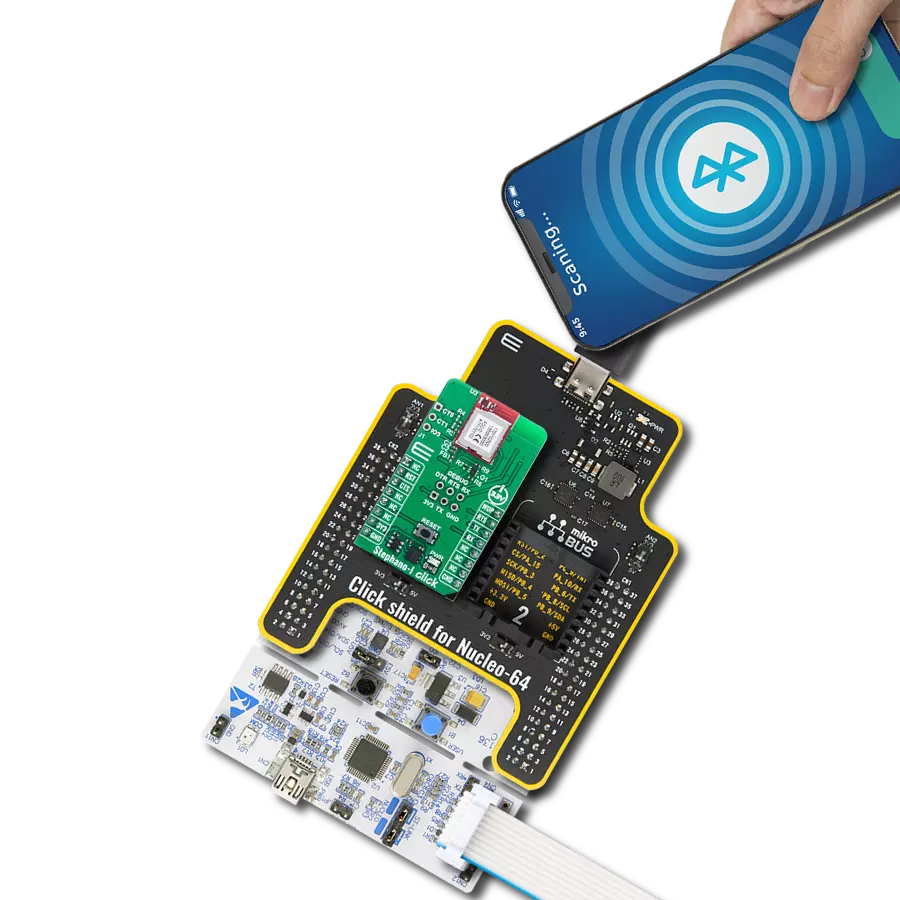
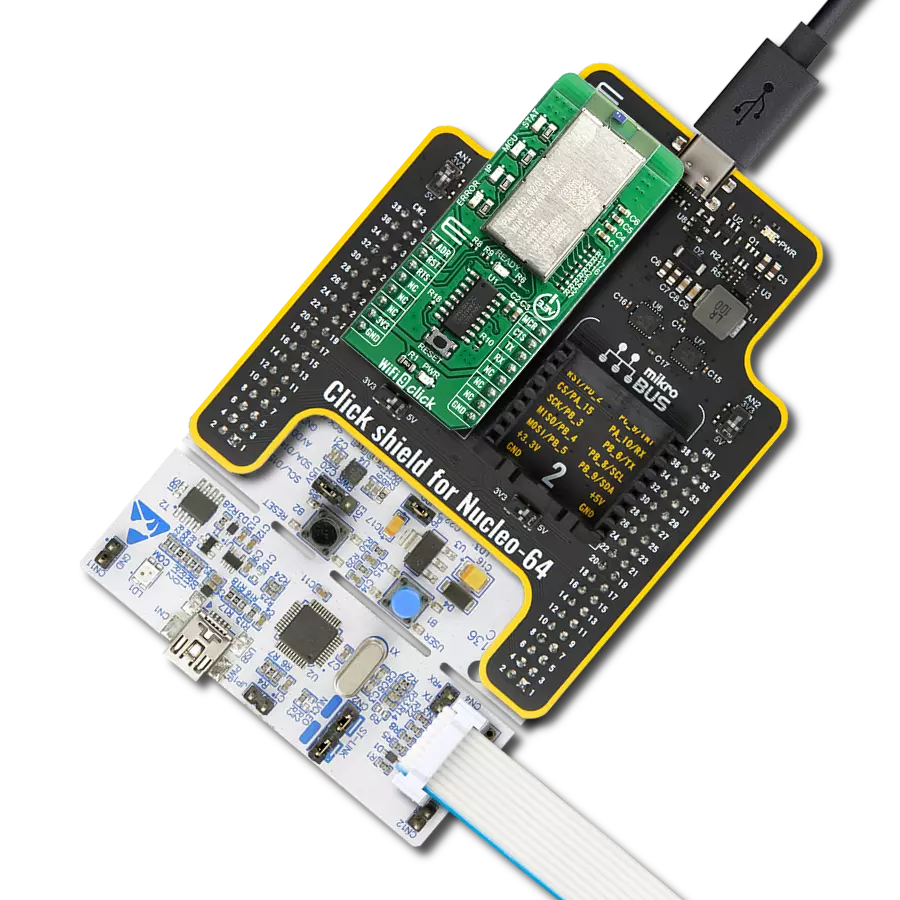
Reliable Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity with secure, dual-mode wireless communication perfect for industrial automation, connected buildings, and IoT devices
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
NINA-W152 Click is based on the NINA-W152, a professional-grade multi-radio module from u-blox. This module has Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, integrating Wi-Fi 802.11b/g/n and dual-mode Bluetooth (Bluetooth BR/EDR v4.2+EDR and Bluetooth Low Energy v4.2) within a compact form factor. The internal PIFA antenna ensures optimal performance, allowing the module to operate simultaneously on both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. This dual-mode operation makes it an excellent choice for acting as a gateway between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi or Ethernet networks. Certified across multiple regions, including the UK, US, Canada, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, and South Africa, the NINA-W152 complies with RED standards, making it suitable for global deployment. Security is a key feature of the NINA-W152. It supports secure boot, ensuring the module only operates with authentic u-blox software. Additionally, it provides robust end-to-end security on the wireless link, utilizing the latest 802.11i standards (WPA2/WPA3) and enterprise security protocols, making it ideal for secure IoT applications in telematics, industrial automation, connected buildings, wireless sensors, point-of-sale systems, and medical devices. This Click board™ establishes communication between the NINA-W152 and the host MCU through a UART interface, using standard UART RX and TX pins and hardware flow control via CTS and RTS pins. The
default communication speed is set at 115200bps, ensuring efficient data exchange. The host MCU configures wireless communication and other features using high-level AT commands, making it easy to manage without requiring in-depth knowledge of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth protocols. Additionally, the board includes an SPI interface with a maximum clock speed of 10MHz, allowing the NINA-W152 to operate exclusively in "SPI peripheral mode," where the host MCU, running in "SPI host mode," sends commands to the NINA module. To properly use the CS pin, users must select the appropriate interface (UART or SPI) and determine whether the CS pin will function as the UART CTS or SPI Chip Select pin. This is achieved by setting the CS SEL jumper to the correct position. In addition to the standard interface pins, the module uses other mikroBUS™ pins, such as the SRY pin, which acts as an SPI data-ready output, and the reset pin (RST) for module resetting. The NINA-W152 software extends the UART interface beyond the usual RX, TX, CTS, and RTS signals by including the DSR (Data Set Ready) and DTR (Data Terminal Ready) pins, available on the unpopulated J1 header. These pins manage the state of the NINA-W152-04B. Depending on the configuration, the DSR pin can enter command mode, disconnect or toggle the connectable status, enable or disable the rest of the UART interface, or enter/leave Sleep/Stop
operation modes. This functionality is also accessible via the ESC pin on the mikroBUS™ socket. Additional features on this board include the SYS BOOT jumper, which selects the system boot mode based on its position. Position 1 is for normal boot from internal flash, while position 0 is for ESP boot mode (factory boot). The board also features SW1 and SW2 buttons for system control. When both buttons are pressed simultaneously, the module enters bootloader mode. If this state is maintained for over 10 seconds without sending commands to the bootloader via UART, the u-connectXpress application will automatically boot, restoring the module settings to their factory defaults. Pressing only the SW1 button will restore the UART serial settings to their default values. This board also features an unpopulated J2 header with four general-purpose input pins and one general-purpose I/O pin. Additionally, the Click board™ includes a user-configurable RGB LED indicator labeled LD2, which indicates various module statuses. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Flip&Click PIC32MZ is a compact development board designed as a complete solution that brings the flexibility of add-on Click boards™ to your favorite microcontroller, making it a perfect starter kit for implementing your ideas. It comes with an onboard 32-bit PIC32MZ microcontroller, the PIC32MZ2048EFH100 from Microchip, four mikroBUS™ sockets for Click board™ connectivity, two USB connectors, LED indicators, buttons, debugger/programmer connectors, and two headers compatible with Arduino-UNO pinout. Thanks to innovative manufacturing technology,
it allows you to build gadgets with unique functionalities and features quickly. Each part of the Flip&Click PIC32MZ development kit contains the components necessary for the most efficient operation of the same board. In addition, there is the possibility of choosing the Flip&Click PIC32MZ programming method, using the chipKIT bootloader (Arduino-style development environment) or our USB HID bootloader using mikroC, mikroBasic, and mikroPascal for PIC32. This kit includes a clean and regulated power supply block through the USB Type-C (USB-C) connector. All communication
methods that mikroBUS™ itself supports are on this board, including the well-established mikroBUS™ socket, user-configurable buttons, and LED indicators. Flip&Click PIC32MZ development kit allows you to create a new application in minutes. Natively supported by Mikroe software tools, it covers many aspects of prototyping thanks to a considerable number of different Click boards™ (over a thousand boards), the number of which is growing every day.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic

Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for NINA-W152 Click driver.
Key functions:
ninaw152_reset_device- This function resets the device by toggling the RST pin state.ninaw152_send_cmd- This function sends a specified command to the click module.ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par- This function sends a command with specified parameter to the click module.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief NINA-W152 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* Application example shows device capability of connecting to a WiFi network and
* sending TCP/UDP messages to an echo server, or processing data from a connected BT device.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger.
*
* ## Application Task
* Application task is split in few stages:
* - NINAW152_POWER_UP:
* Powers up the device, performs a factory reset and reads system information.
*
* - NINAW152_CONFIGURE_CONNECTION:
* Configures connection to WiFi or BT depending on the selected example.
*
* - NINAW152_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
* Checks the connection to WiFi access point.
*
* - NINAW152_EXAMPLE:
* Depending on the selected demo example, it sends a TCP/UDP message to an echo server over a WiFi network or
* processes all data from a connected BT device and sends back an adequate response message.
*
* By default, the WiFi TCP/UDP example is selected.
*
* ## Additional Function
* - static void ninaw152_clear_app_buf ( void )
* - static void ninaw152_log_app_buf ( void )
* - static err_t ninaw152_process ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
* - static err_t ninaw152_read_response ( ninaw152_t *ctx, uint8_t *rsp )
* - static err_t ninaw152_power_up ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
* - static err_t ninaw152_config_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
* - static err_t ninaw152_check_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
* - static err_t ninaw152_example ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
*
* @note
* For the BT example, we have used the Serial Bluetooth Terminal smartphone application for the test.
* A smartphone and the Click board must be paired to exchange messages.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "ninaw152.h"
// Example selection macros
#define EXAMPLE_WIFI 0 // Example of sending messages to a TCP/UDP echo server over WiFi
#define EXAMPLE_BT 1 // Example of processing data from BT connected device
#define DEMO_EXAMPLE EXAMPLE_WIFI // Example selection macro
// WiFi credentials
#define WIFI_SSID "MikroE Public"
#define WIFI_PASSWORD "mikroe.guest"
// WiFi TCP/UDP example parameters
#define REMOTE_IP "77.46.162.162" // TCP/UDP echo server IP address
#define REMOTE_PORT "51111" // TCP/UDP echo server port
// Message content
#define MESSAGE_CONTENT "NINA-W152 Click board - demo example."
// Application buffer size
#define APP_BUFFER_SIZE 600
#define PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE 200
/**
* @brief Example states.
* @details Predefined enum values for application example state.
*/
typedef enum
{
NINAW152_POWER_UP = 1,
NINAW152_CONFIGURE_CONNECTION,
NINAW152_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION,
NINAW152_EXAMPLE
} ninaw152_app_state_t;
static ninaw152_t ninaw152;
static log_t logger;
static uint8_t app_buf[ APP_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
static int32_t app_buf_len = 0;
static ninaw152_app_state_t app_state = NINAW152_POWER_UP;
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 clearing application buffer.
* @details This function clears memory of application buffer and reset its length.
* @note None.
*/
static void ninaw152_clear_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 log application buffer.
* @details This function logs data from application buffer to USB UART.
* @note None.
*/
static void ninaw152_log_app_buf ( void );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 data reading function.
* @details This function reads data from device and concatenates data to application buffer.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - Read some data.
* @li @c -1 - Nothing is read.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_process ( ninaw152_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 read response function.
* @details This function waits for a response message, reads and displays it on the USB UART.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @param[in] rsp Expected response.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK response.
* @li @c -2 - Timeout error.
* @li @c -3 - Command error.
* @li @c -4 - Unknown error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_read_response ( ninaw152_t *ctx, uint8_t *rsp );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 power up function.
* @details This function powers up the device, performs a factory reset and reads system information.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK.
* @li @c != 0 - Read response error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_power_up ( ninaw152_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 config connection function.
* @details This function configures connection to WiFi or BT depending on the selected example.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK.
* @li @c != 0 - Read response error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_config_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 check connection function.
* @details This function checks the connection to WiFi access point.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK.
* @li @c != 0 - Read response error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_check_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx );
/**
* @brief NINA-W152 example function.
* @details This function performs a WiFi TCP/UDP or a BT device terminal example.
* @param[in] ctx : Click context object.
* See #ninaw152_t object definition for detailed explanation.
* @return @li @c 0 - OK.
* @li @c != 0 - Read response error.
* See #err_t definition for detailed explanation.
* @note None.
*/
static err_t ninaw152_example ( ninaw152_t *ctx );
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
ninaw152_cfg_t ninaw152_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
ninaw152_cfg_setup( &ninaw152_cfg );
NINAW152_MAP_MIKROBUS( ninaw152_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( NINAW152_OK != ninaw152_init( &ninaw152, &ninaw152_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
app_state = NINAW152_POWER_UP;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> APP STATE - POWER UP <<<\r\n\n" );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
switch ( app_state )
{
case NINAW152_POWER_UP:
{
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_power_up( &ninaw152 ) )
{
app_state = NINAW152_CONFIGURE_CONNECTION;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> APP STATE - CONFIGURE CONNECTION <<<\r\n\n" );
}
break;
}
case NINAW152_CONFIGURE_CONNECTION:
{
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_config_connection( &ninaw152 ) )
{
app_state = NINAW152_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> APP STATE - CHECK CONNECTION <<<\r\n\n" );
}
break;
}
case NINAW152_WAIT_FOR_CONNECTION:
{
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_check_connection( &ninaw152 ) )
{
app_state = NINAW152_EXAMPLE;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> APP STATE - EXAMPLE <<<\r\n\n" );
}
break;
}
case NINAW152_EXAMPLE:
{
ninaw152_example( &ninaw152 );
break;
}
default:
{
log_error( &logger, " APP STATE." );
break;
}
}
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
static void ninaw152_clear_app_buf ( void )
{
memset( app_buf, 0, app_buf_len );
app_buf_len = 0;
}
static void ninaw152_log_app_buf ( void )
{
for ( int32_t buf_cnt = 0; buf_cnt < app_buf_len; buf_cnt++ )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", app_buf[ buf_cnt ] );
}
}
static err_t ninaw152_process ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
{
uint8_t rx_buf[ PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE ] = { 0 };
int32_t overflow_bytes = 0;
int32_t rx_cnt = 0;
int32_t rx_size = ninaw152_generic_read( ctx, rx_buf, PROCESS_BUFFER_SIZE );
if ( ( rx_size > 0 ) && ( rx_size <= APP_BUFFER_SIZE ) )
{
if ( ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) > APP_BUFFER_SIZE )
{
overflow_bytes = ( app_buf_len + rx_size ) - APP_BUFFER_SIZE;
app_buf_len = APP_BUFFER_SIZE - rx_size;
memmove ( app_buf, &app_buf[ overflow_bytes ], app_buf_len );
memset ( &app_buf[ app_buf_len ], 0, overflow_bytes );
}
for ( rx_cnt = 0; rx_cnt < rx_size; rx_cnt++ )
{
if ( rx_buf[ rx_cnt ] )
{
app_buf[ app_buf_len++ ] = rx_buf[ rx_cnt ];
}
}
return NINAW152_OK;
}
return NINAW152_ERROR;
}
static err_t ninaw152_read_response ( ninaw152_t *ctx, uint8_t *rsp )
{
#define READ_RESPONSE_TIMEOUT_MS 60000
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
ninaw152_clear_app_buf ( );
ninaw152_process( ctx );
while ( ( 0 == strstr( app_buf, rsp ) ) &&
( 0 == strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_RSP_ERROR ) ) )
{
ninaw152_process( ctx );
if ( timeout_cnt++ > READ_RESPONSE_TIMEOUT_MS )
{
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
log_error( &logger, " Timeout!" );
return NINAW152_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 200 );
ninaw152_process( ctx );
if ( strstr( app_buf, rsp ) )
{
ninaw152_log_app_buf( );
log_printf( &logger, "--------------------------------\r\n" );
return NINAW152_OK;
}
else if ( strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_RSP_ERROR ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " CMD!" );
return NINAW152_ERROR_CMD;
}
log_error( &logger, " Unknown!" );
return NINAW152_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
static err_t ninaw152_power_up ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
{
err_t error_flag = NINAW152_OK;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Perform device hardware reset.\r\n" );
ninaw152_reset_device ( ctx );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_GREETING );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Check communication.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_AT );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Reset to factory settings.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_FACTORY_RESET );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Reboot device.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_REBOOT_DEVICE );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_GREETING );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Get device model ID.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_GET_MODEL_ID );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Get device software version ID.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_GET_SW_VERSION );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Get device serial number.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_GET_SERIAL_NUM );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
return error_flag;
}
static err_t ninaw152_config_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
{
err_t error_flag = NINAW152_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_WIFI )
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Get network host name.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_check( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_NETWORK_HOST_NAME );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Set WiFi SSID.\r\n" );
#define WIFI_CONFIG_ID "0"
#define WIFI_PARAM_TAG_SSID "2"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, WIFI_CONFIG_ID );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PARAM_TAG_SSID );
strcat ( app_buf, ",\"" );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_SSID );
strcat ( app_buf, "\"" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WIFI_STATION_CONFIG, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Set WiFi authentication type to WPA/WPA2/WPA3.\r\n" );
#define WIFI_PARAM_TAG_AUTH "5"
#define WIFI_PARAM_VAL1_WPA_WPA2_WPA3 "2"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, WIFI_CONFIG_ID );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PARAM_TAG_AUTH );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PARAM_VAL1_WPA_WPA2_WPA3 );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WIFI_STATION_CONFIG, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Set WiFi Password.\r\n" );
#define WIFI_PARAM_TAG_PASSWORD "8"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, WIFI_CONFIG_ID );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PARAM_TAG_PASSWORD );
strcat ( app_buf, ",\"" );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_PASSWORD );
strcat ( app_buf, "\"" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WIFI_STATION_CONFIG, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Activate WiFi config and try to connect.\r\n" );
#define WIFI_ACTION_ACTIVATE "3"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, WIFI_CONFIG_ID );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, WIFI_ACTION_ACTIVATE );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WIFI_STATION_CONFIG_ACTION, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_BT )
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Get BT local name.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_check( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_BT_LOCAL_NAME );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return error_flag;
}
static err_t ninaw152_check_connection ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
{
err_t error_flag = NINAW152_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_WIFI )
uint8_t * __generic_ptr urc_buf_ptr = 0;
ninaw152_process( ctx );
// Wait for WiFi link connected and two network-up URC events
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_WIFI_LINK_CONNECTED );
if ( urc_buf_ptr )
{
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( urc_buf_ptr + 1, NINAW152_URC_NETWORK_UP );
}
if ( urc_buf_ptr )
{
if ( strstr( urc_buf_ptr + 1, NINAW152_URC_NETWORK_UP ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
ninaw152_process( ctx );
ninaw152_log_app_buf( );
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
// Check WiFi status
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WIFI_STATION_STATUS );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
else
{
error_flag |= NINAW152_ERROR;
}
}
else
{
error_flag |= NINAW152_ERROR;
}
#endif
return error_flag;
}
static err_t ninaw152_example ( ninaw152_t *ctx )
{
err_t error_flag = NINAW152_OK;
#if ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_WIFI )
uint8_t * __generic_ptr urc_buf_ptr = 0;
uint8_t urc_buf[ 30 ] = { 0 };
uint8_t tcp_peer_handle[ 2 ] = { 0 };
uint8_t udp_peer_handle[ 2 ] = { 0 };
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Create and connect TCP socket to remote IP and port.\r\n" );
#define SCHEME_AT_TCP "at-tcp"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, SCHEME_AT_TCP );
strcat ( app_buf, "://" );
strcat ( app_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat ( app_buf, ":" );
strcat ( app_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_CONNECT_PEER, app_buf );
error_flag = ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED );
if ( ( NINAW152_OK == error_flag ) && ( strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) ) )
{
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) + strlen ( NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED );
tcp_peer_handle[ 0 ] = *urc_buf_ptr;
}
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Create and connect UDP socket to remote IP and port.\r\n" );
#define SCHEME_AT_UDP "at-udp"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, SCHEME_AT_UDP );
strcat ( app_buf, "://" );
strcat ( app_buf, REMOTE_IP );
strcat ( app_buf, ":" );
strcat ( app_buf, REMOTE_PORT );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_CONNECT_PEER, app_buf );
error_flag = ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED );
if ( ( NINAW152_OK == error_flag ) && ( strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) ) )
{
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) + strlen ( NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED );
udp_peer_handle[ 0 ] = *urc_buf_ptr;
}
if ( tcp_peer_handle[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Write message to TCP socket and read response.\r\n" );
#define DATA_FORMAT_STRING "0"
#define DATA_FORMAT_BINARY "2"
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, tcp_peer_handle );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, DATA_FORMAT_STRING );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WRITE_DATA, app_buf );
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) )
{
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) + strlen ( NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) + 2;
memcpy ( urc_buf, urc_buf_ptr, app_buf_len - ( urc_buf_ptr - app_buf ) - 2 );
strcpy ( app_buf, tcp_peer_handle );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, DATA_FORMAT_BINARY );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, urc_buf );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par ( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_READ_DATA, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA );
}
}
if ( udp_peer_handle[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Write message to UDP socket and read response.\r\n" );
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
strcpy ( app_buf, udp_peer_handle );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, DATA_FORMAT_STRING );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, MESSAGE_CONTENT );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_WRITE_DATA, app_buf );
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) )
{
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) + strlen ( NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA ) + 2;
memcpy ( urc_buf, urc_buf_ptr, app_buf_len - ( urc_buf_ptr - app_buf ) - 2 );
strcpy ( app_buf, udp_peer_handle );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, DATA_FORMAT_BINARY );
strcat ( app_buf, "," );
strcat ( app_buf, urc_buf );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par ( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_READ_DATA, app_buf );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_READ_SOCKET_DATA );
}
}
if ( tcp_peer_handle[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Close TCP socket.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_CLOSE_PEER, tcp_peer_handle );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_PEER_DISCONNECTED );
}
if ( udp_peer_handle[ 0 ] )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Close UDP socket.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_CLOSE_PEER, udp_peer_handle );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_PEER_DISCONNECTED );
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
#elif ( DEMO_EXAMPLE == EXAMPLE_BT )
uint8_t * __generic_ptr urc_buf_ptr = 0;
uint8_t bt_peer_handle[ 2 ] = { 0 };
uint32_t timeout_cnt = 0;
#define BT_TERMINAL_TIMEOUT_MS 60000
#define BT_TERMINAL_MESSAGE_FREQ_MS 5000
#define TERMINATION_CMD "END"
#define TERMINATION_RESPONSE "Acknowledged, the connection will be terminated in a few seconds."
#define TERMINATION_TIMEOUT "Timeout, closing the connection in a few seconds."
#define NEW_LINE_STRING "\r\n"
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Waiting for a BT peer to establish connection with the Click board...\r\n" );
while ( NINAW152_OK != ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) );
urc_buf_ptr = strstr( app_buf, NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED ) + strlen ( NINAW152_URC_PEER_CONNECTED );
bt_peer_handle[ 0 ] = *urc_buf_ptr;
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Entering data mode. URC and AT commands are not accepted in this mode.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_ENTER_DATA_MODE );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Waiting for data (up to 60 seconds)...\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Connection will be terminated if the Click receives an \"END\" string.\r\n" );
for ( ; ; )
{
ninaw152_clear_app_buf( );
if ( NINAW152_OK == ninaw152_process( ctx ) )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
timeout_cnt = 0;
ninaw152_process( ctx );
ninaw152_log_app_buf( );
if ( strstr( app_buf, TERMINATION_CMD ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Terminate connection on demand.\r\n" );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, TERMINATION_RESPONSE, strlen ( TERMINATION_RESPONSE ) );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, NEW_LINE_STRING, strlen ( NEW_LINE_STRING ) );
break;
}
}
timeout_cnt++;
if ( 0 == ( timeout_cnt % BT_TERMINAL_MESSAGE_FREQ_MS ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Sending \"%s\" message to connected device.\r\n", ( char * ) MESSAGE_CONTENT );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, MESSAGE_CONTENT, strlen ( MESSAGE_CONTENT ) );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, NEW_LINE_STRING, strlen ( NEW_LINE_STRING ) );
}
if ( BT_TERMINAL_TIMEOUT_MS < timeout_cnt )
{
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Terminate connection due to 60s timeout expiration.\r\n" );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, TERMINATION_TIMEOUT, strlen ( TERMINATION_TIMEOUT ) );
ninaw152_generic_write ( ctx, NEW_LINE_STRING, strlen ( NEW_LINE_STRING ) );
break;
}
Delay_ms ( 1 );
}
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Switching back to command mode.\r\n" );
ninaw152_set_esc_pin ( ctx, 1 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
ninaw152_set_esc_pin ( ctx, 0 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
log_printf( &logger, ">>> Closing BT peer connection.\r\n" );
ninaw152_send_cmd_with_par( ctx, NINAW152_CMD_CLOSE_PEER, bt_peer_handle );
error_flag |= ninaw152_read_response( ctx, NINAW152_RSP_OK );
#else
#error "No demo example selected"
#endif
return error_flag;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END