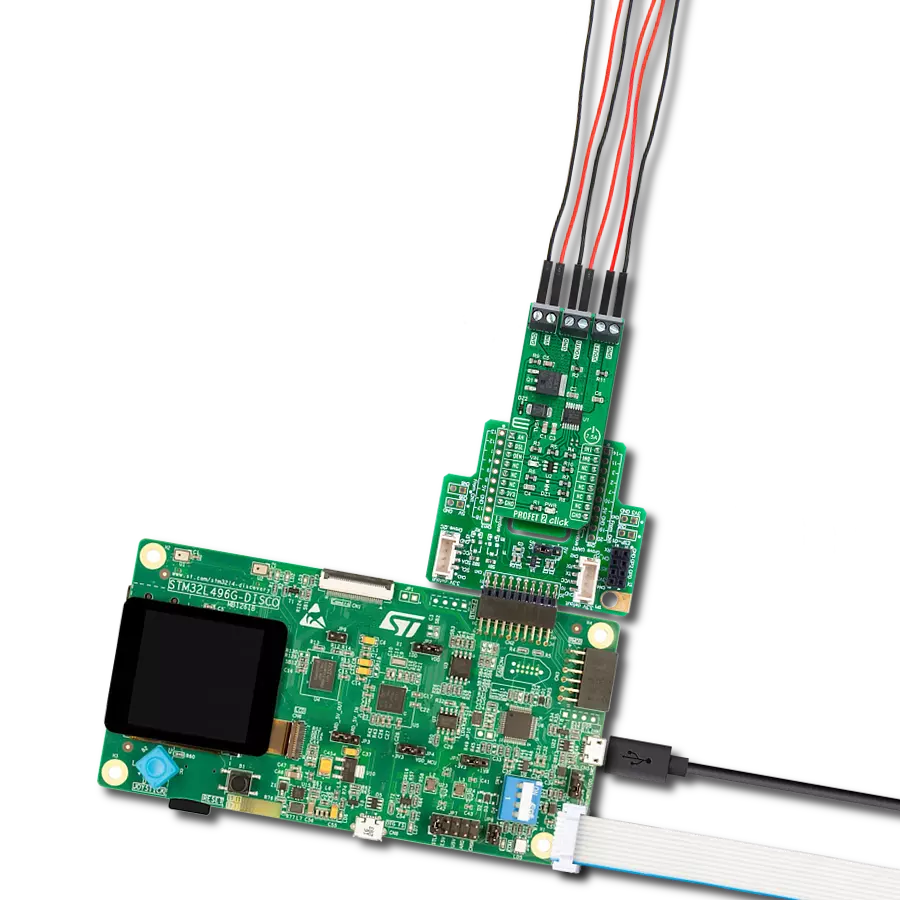
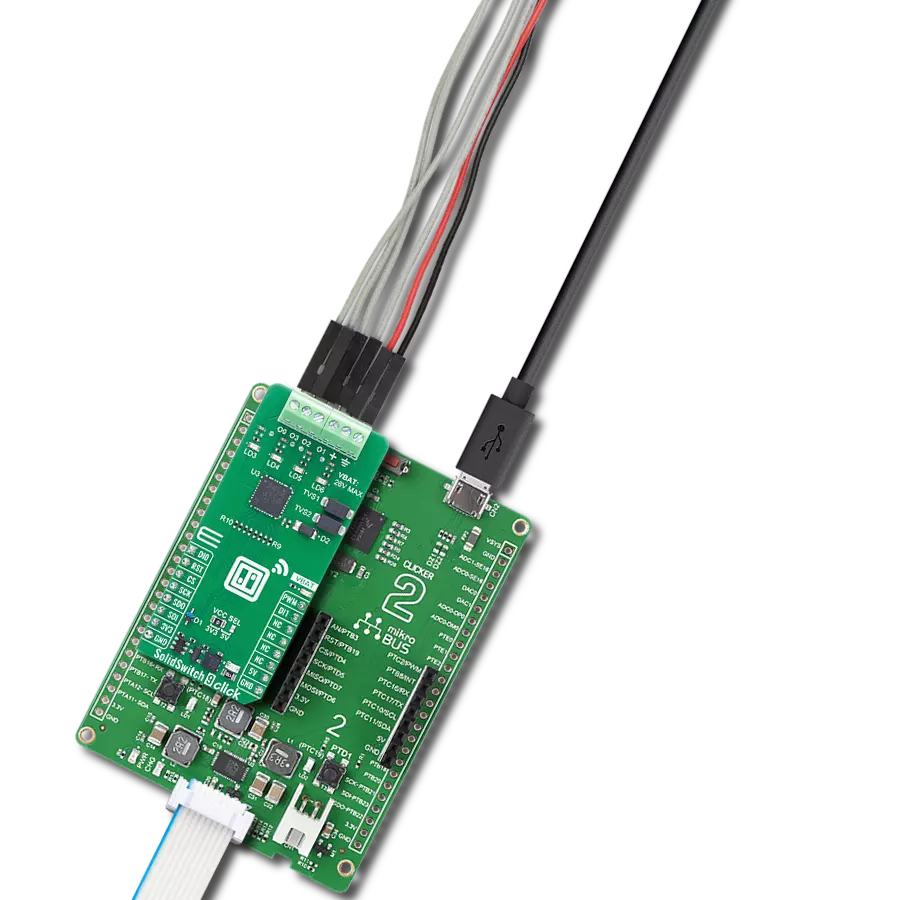
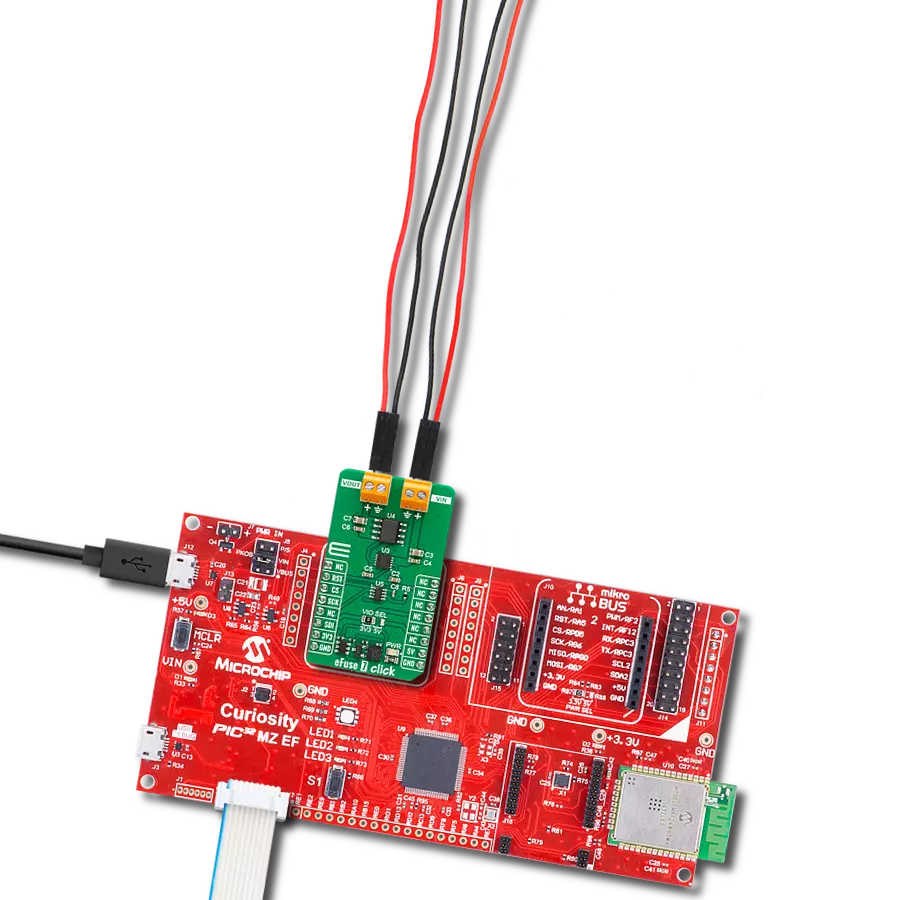
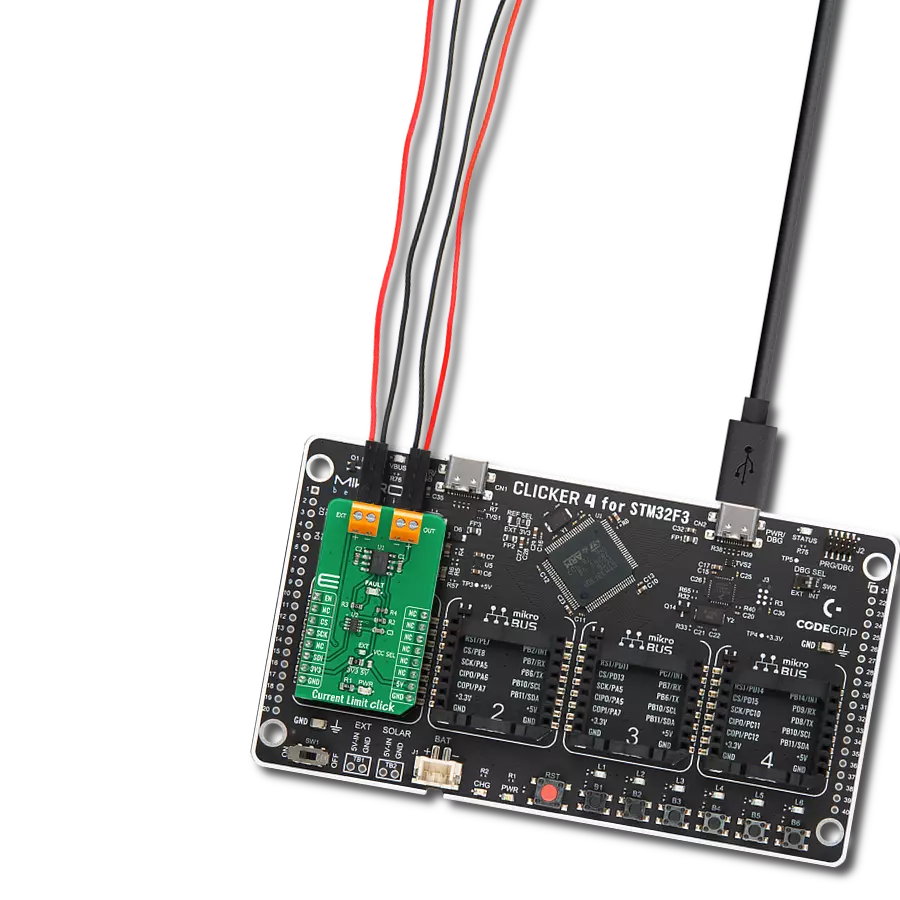
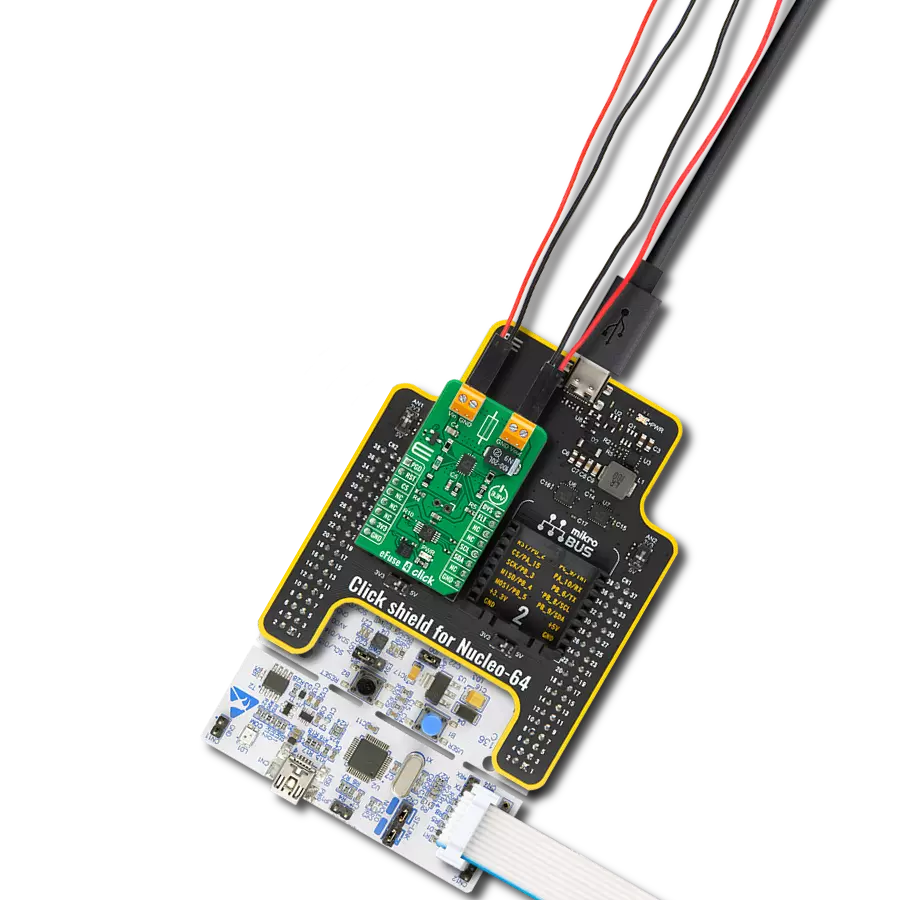
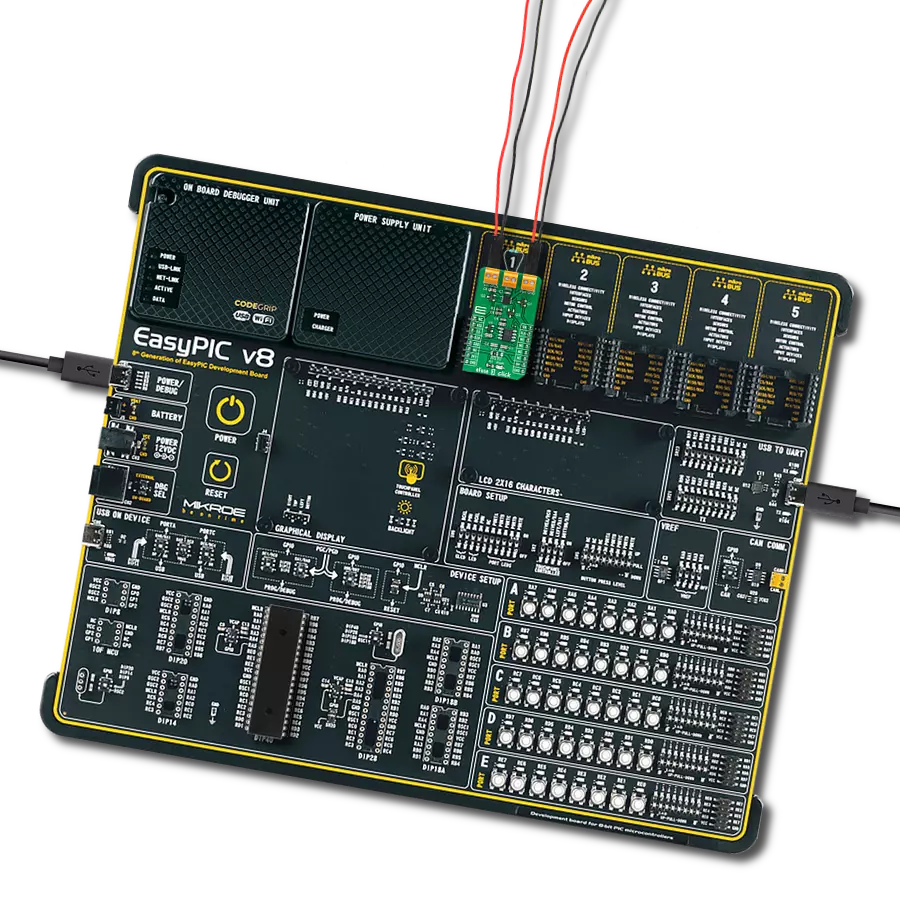
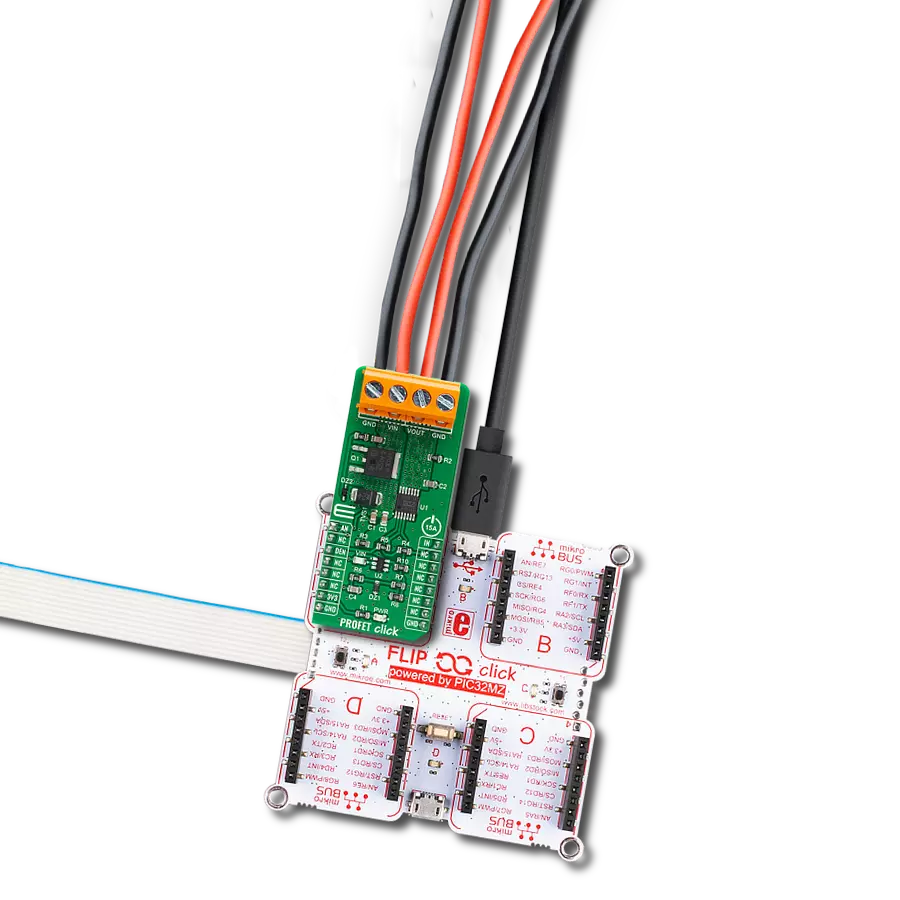
High-side switching with advanced protection and diagnostics perfect for automotive lighting, motor control, and solenoid applications
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
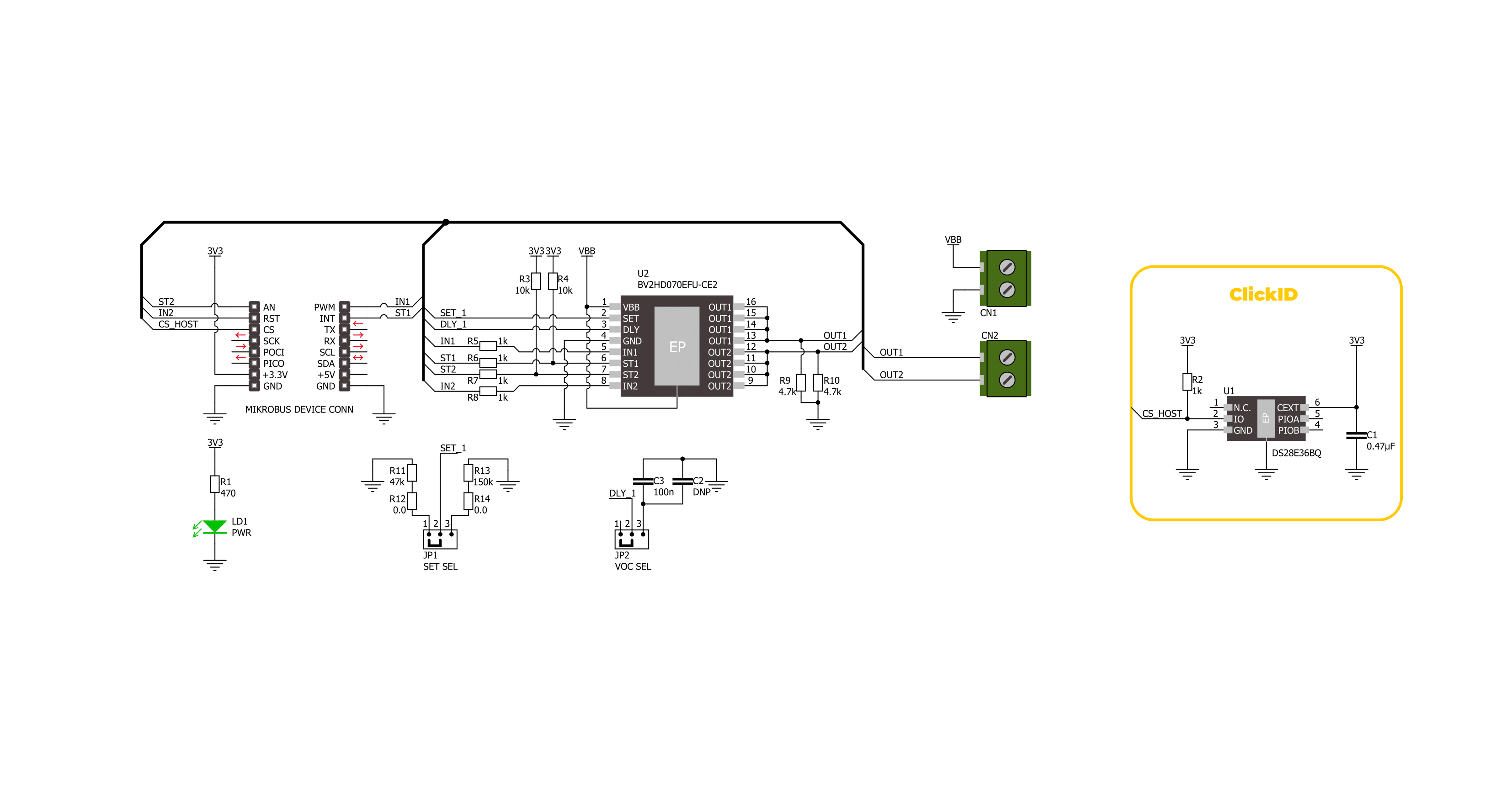
IPD 2 Click is based on the BV2HD070EFU-C, an automotive-grade two-channel high-side switch from ROHM Semiconductor, designed to handle resistive, inductive, and capacitive loads in automotive applications. The BV2HD070EFU-C features a 70mΩ on-resistance high-side switch and incorporates advanced protection and diagnostic functionalities to ensure reliable operation in demanding environments. This Click board™ is particularly suitable for automotive applications, supporting various types of loads such as lights, solenoids, and motors. It provides an efficient, reliable, and compact solution for high-side switching requirements, ensuring stable performance and enhanced safety in automotive systems. The BV2HD070EFU-C is AEC-Q100 qualified (Grade 1) and operates across a wide input voltage range of 6V to 28V, supplied via the VDD terminal. Its comprehensive protection suite includes overcurrent detection (OCD) with a
configurable mask function, ensuring precise fault management and preventing unintended load disconnection. Additional safety features include thermal shutdown protection, which halts operation under excessive temperature conditions, and undervoltage lockout (UVLO) to safeguard against unstable power supply conditions. Moreover, the switch includes an open load detection function, providing feedback when the load is disconnected or the circuit is incomplete. This Click board™ uses several pins of the mikroBUS™ socket for control and diagnostics. The IN1 and IN2 pins serve as control signals, enabling activation of the respective outputs marked as 1 and 2 on the output OUT terminal. For monitoring and fault detection, the board includes a diagnostic output function accessible via the ST1 and ST2 pins of the mikroBUS™ socket, providing real-time feedback on abnormalities. In addition to these control and diagnostic pins, the board features two
configuration jumpers. The first, SET SEL, allows users to configure the overcurrent limit between 1A and the default value of 2.3A. While the BV2HD070EFU-C supports overcurrent limits of up to approximately 10A, users can achieve this by replacing the selected resistance as specified in the datasheet recommendations. The second jumper, VOC SEL, activates a functionality that optimizes the time required to achieve precise overcurrent protection for the connected load. This feature is enabled by default, ensuring enhanced load safety and performance without additional configuration. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. It also comes equipped with a library containing functions and example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for IPD 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
ipd2_enable_out1- This function enables OUT1 by setting the IN1 pin to high logic state.ipd2_disable_out1- This function disables OUT1 by setting the IN1 pin to low logic state.ipd2_get_st1_pin- This function returns the ST1 pin logic state.
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* @file main.c
* @brief IPD 2 Click Example.
*
* # Description
* This example demonstrates the use of IPD 2 Click by toggling the output state.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initializes the driver and logger.
*
* ## Application Task
* Toggles OUT1 and OUT2 state every 3 seconds and displays both outputs state and
* status diagnostics pin state. If the status pin is HIGH it indicates that the fault
* condition on this output has occurred and the output is disabled.
*
* @author Stefan Filipovic
*
*/
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "ipd2.h"
static ipd2_t ipd2; /**< IPD 2 Click driver object. */
static log_t logger; /**< Logger object. */
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg; /**< Logger config object. */
ipd2_cfg_t ipd2_cfg; /**< Click config object. */
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, " Application Init " );
// Click initialization.
ipd2_cfg_setup( &ipd2_cfg );
IPD2_MAP_MIKROBUS( ipd2_cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
if ( DIGITAL_OUT_UNSUPPORTED_PIN == ipd2_init( &ipd2, &ipd2_cfg ) )
{
log_error( &logger, " Communication init." );
for ( ; ; );
}
log_info( &logger, " Application Task " );
}
void application_task ( void )
{
ipd2_enable_out1 ( &ipd2 );
ipd2_disable_out2 ( &ipd2 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " OUT1: enabled\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " OUT2: disabled\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " ST1: %s\r\n", ( char * ) ( ipd2_get_st1_pin ( &ipd2 ) ? "high" : "low" ) );
log_printf( &logger, " ST2: %s\r\n\n", ( char * ) ( ipd2_get_st2_pin ( &ipd2 ) ? "high" : "low" ) );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
ipd2_disable_out1 ( &ipd2 );
ipd2_enable_out2 ( &ipd2 );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " OUT1: disabled\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " OUT2: enabled\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " ST1: %s\r\n", ( char * ) ( ipd2_get_st1_pin ( &ipd2 ) ? "high" : "low" ) );
log_printf( &logger, " ST2: %s\r\n\n", ( char * ) ( ipd2_get_st2_pin ( &ipd2 ) ? "high" : "low" ) );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Power Switch