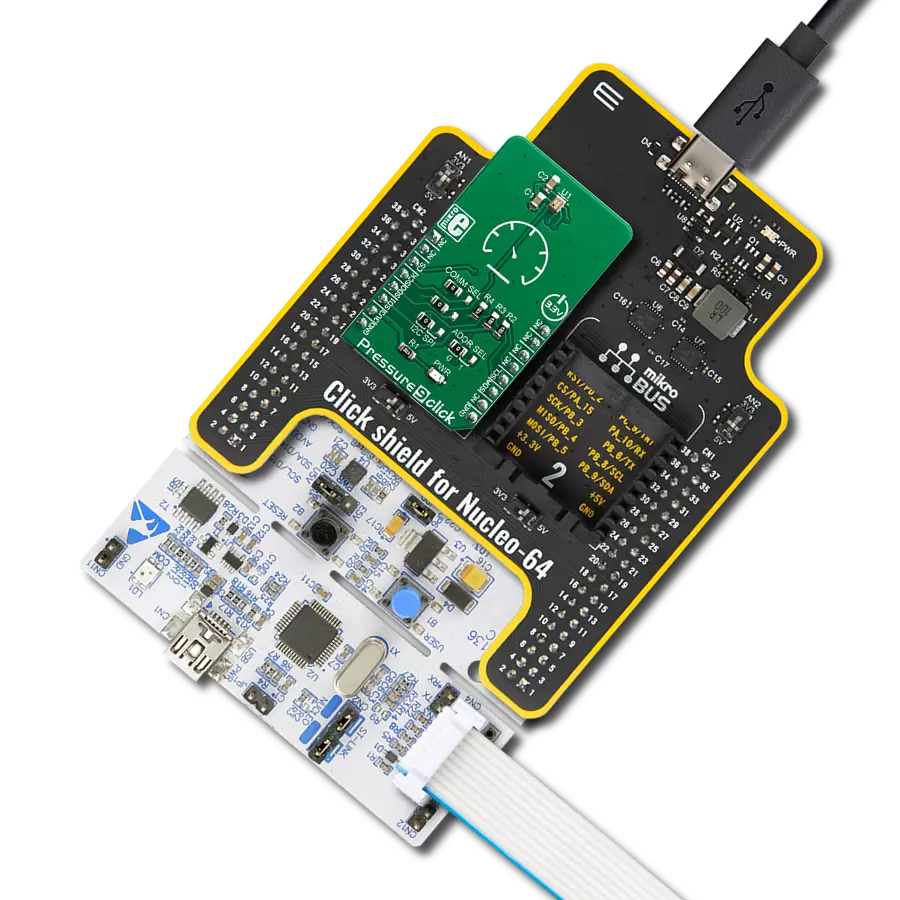
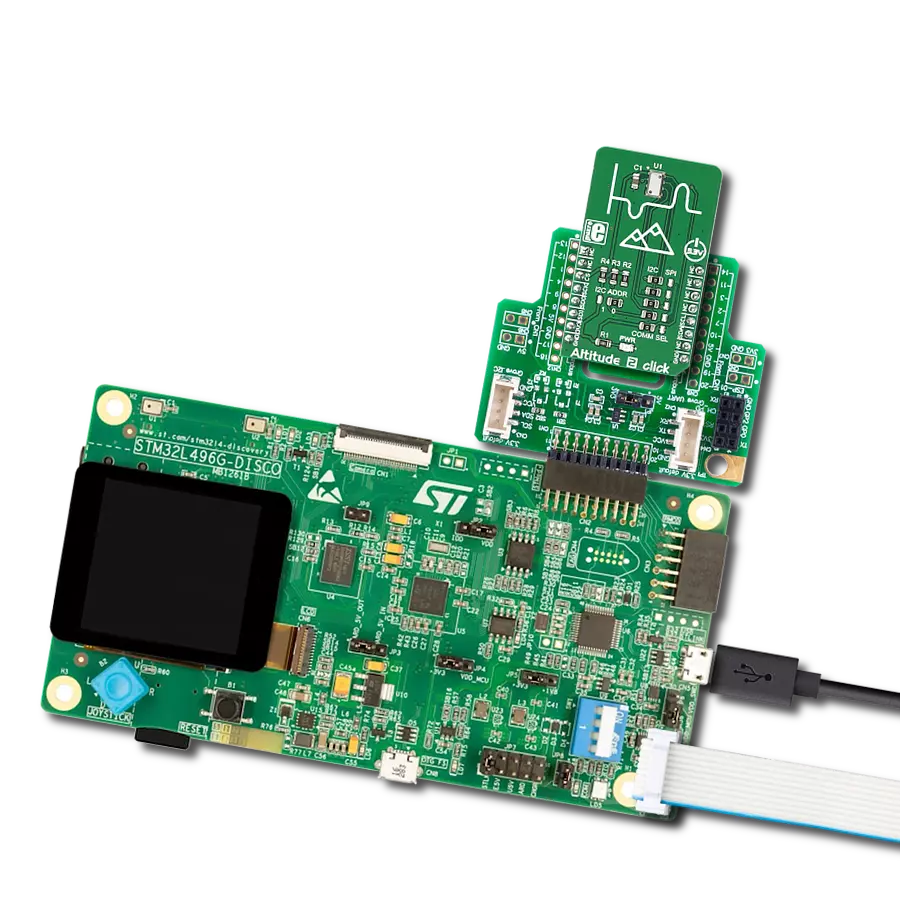
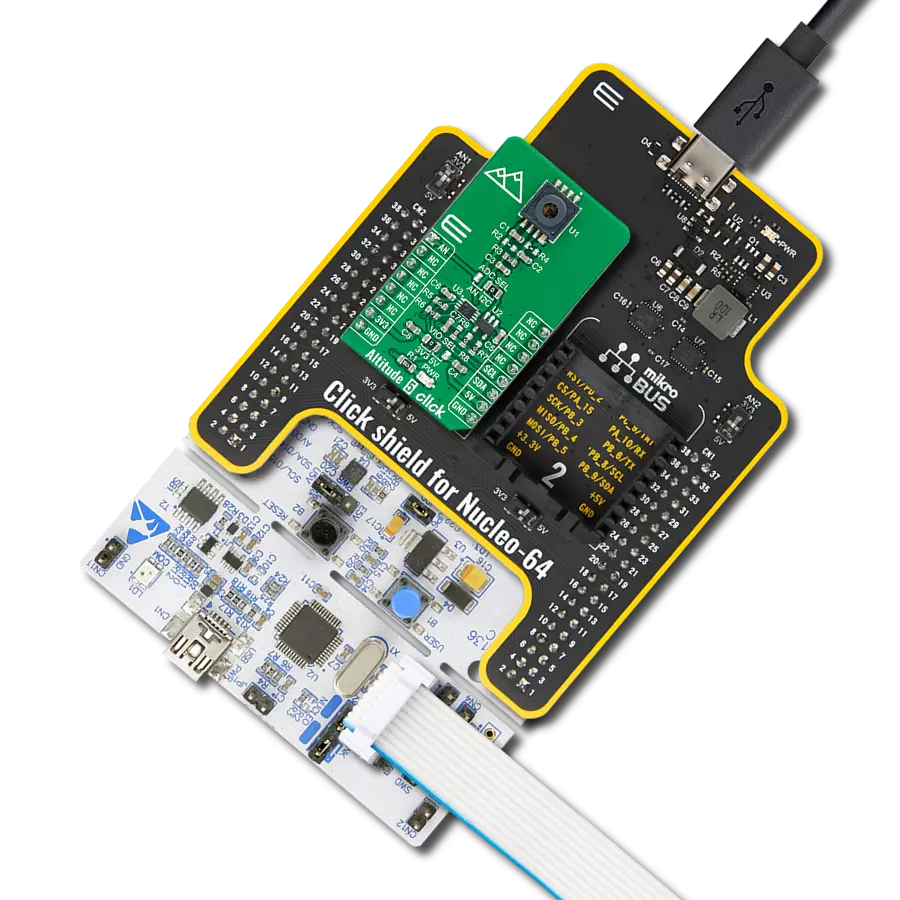
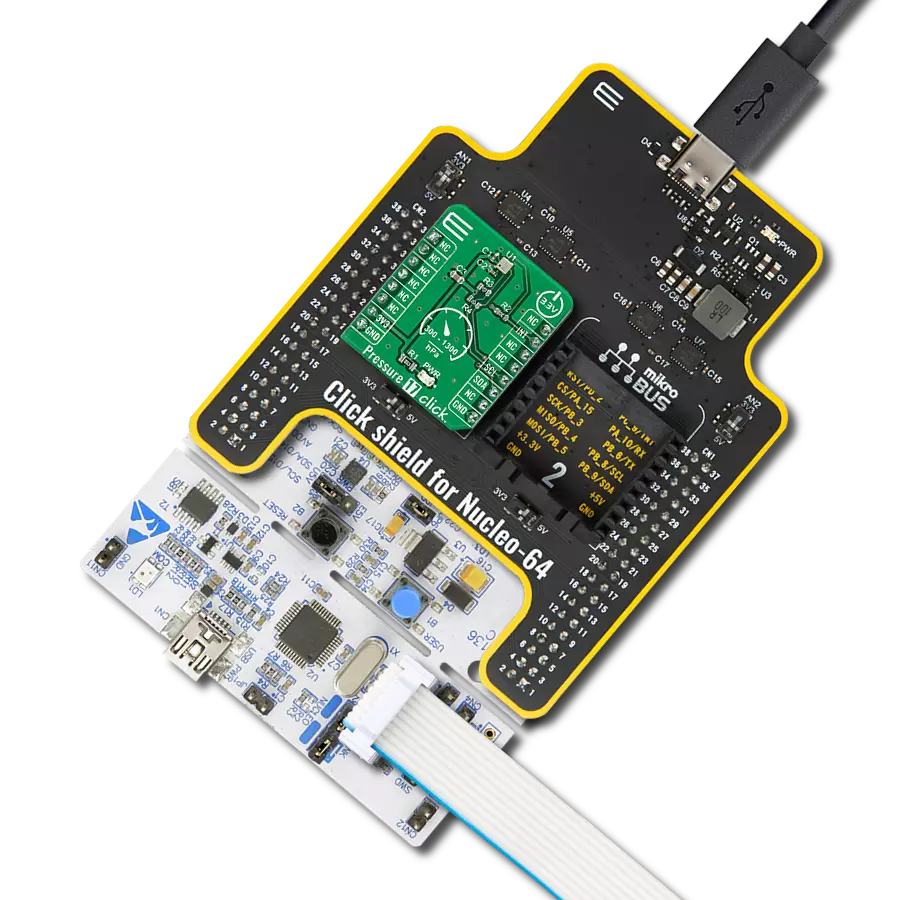
Step into the world of precise pressure measurement with our innovative manometer, engineered to enhance the quality and performance of your systems and processes.
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
Manometer 2 Click is based on the MS5525DSO, a digital pressure sensor based on leading MEMS technology from TE Connectivity. The click is designed to run on a 3.3V power supply. It communicates with the target microcontroller over an I2C or SPI interface. The MS5525DSO is a new Digital Small Outline pressure sensor generation with SPI and I2C bus interface designed for high-volume OEM users. The sensor module includes a pressure sensor and an ultra
low power 24-bit ∆Σ ADC with internal factory-calibrated coefficients. It provides a 24-bit digital pressure and temperature value and different operation modes that allow users to optimize conversion speed and current consumption. The MS5525DSO consists of a piezo-resistive sensor and a sensor interface IC. The main function of the MS5525DSO is to convert the uncompensated analog output voltage from the piezo-resistive pressure sensor to a 24-bit digital value and
provide a 24-bit digital value for the temperature of the sensor. Manometer 2 click measures the absolute pressure of 1PSI max through the barbed port. This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board is a fully integrated 32-bit development platform featuring the high-performance PIC32MZ EF Series (PIC32MZ2048EFM) that has a 2MB Flash, 512KB RAM, integrated FPU, Crypto accelerator, and excellent connectivity options. It includes an integrated programmer and debugger, requiring no additional hardware. Users can expand
functionality through MIKROE mikroBUS™ Click™ adapter boards, add Ethernet connectivity with the Microchip PHY daughter board, add WiFi connectivity capability using the Microchip expansions boards, and add audio input and output capability with Microchip audio daughter boards. These boards are fully integrated into PIC32’s powerful software framework, MPLAB Harmony,
which provides a flexible and modular interface to application development a rich set of inter-operable software stacks (TCP-IP, USB), and easy-to-use features. The Curiosity PIC32 MZ EF development board offers expansion capabilities making it an excellent choice for a rapid prototyping board in Connectivity, IOT, and general-purpose applications.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
PIC32
MCU Memory (KB)
2048
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
524288
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
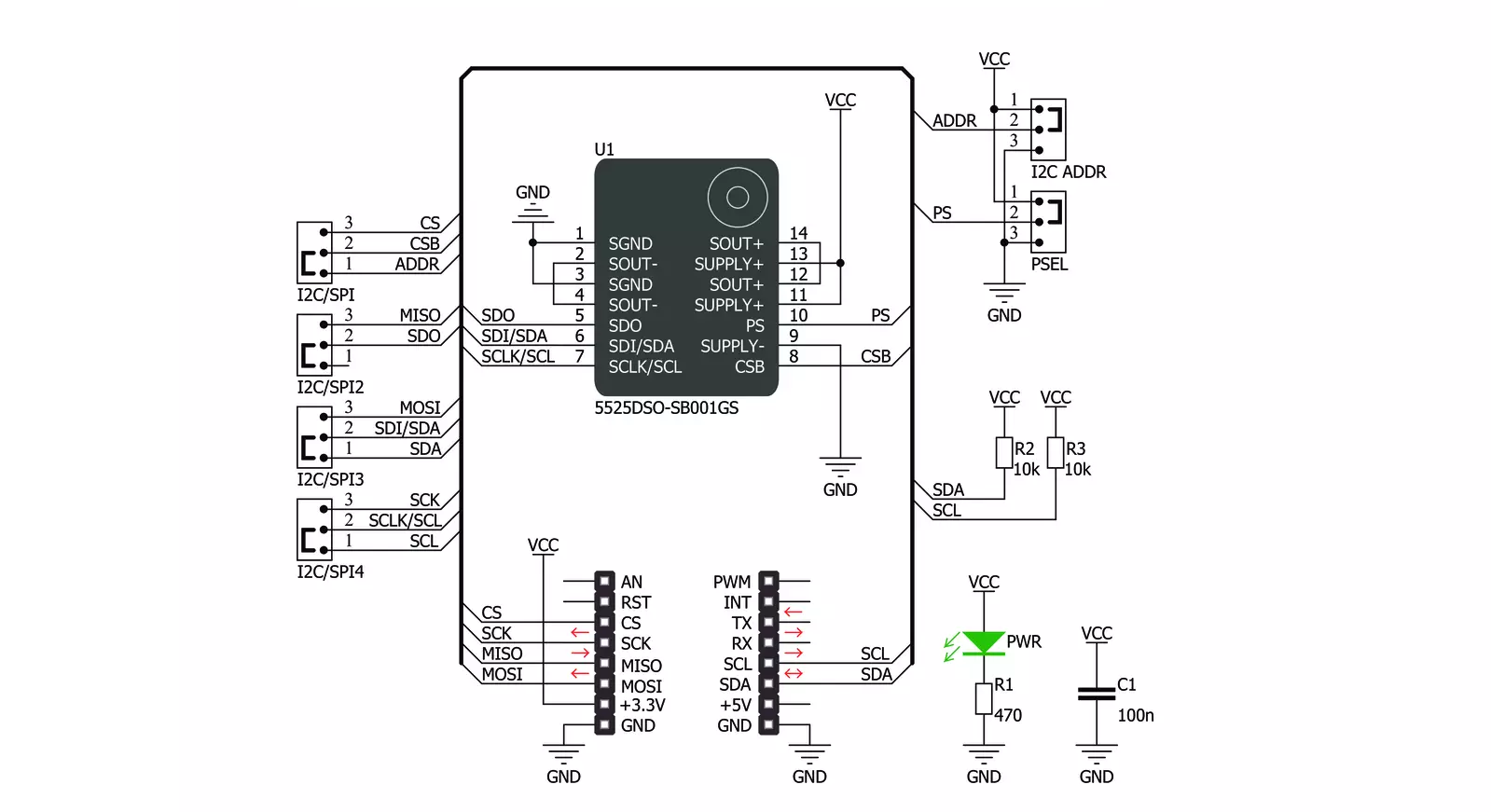
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for Manometer 2 Click driver.
Key functions:
manometer2_read_coef- Generic read data function
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief Manometer2 Click example
*
* # Description
* This application is digital pressure sensor.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* Initialization driver enable's - I2C,
* initialization Manometer 2 sensor MS5525DSO-SB001GS by read coeffitient value
* and start write log.
*
* ## Application Task
* This is a example which demonstrates the use of Manometer 2 Click board.
* Measured pressure and temperature value from sensor, calculate pressure [ PSI ] and temperature [ �C ],
* results are being sent to the Usart Terminal where you can track their changes.
* All data logs on usb uart for aproximetly every 3 sec when the data value changes.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "manometer2.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static manometer2_t manometer2;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( void )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
manometer2_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
manometer2_cfg_setup( &cfg );
MANOMETER2_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
manometer2_init( &manometer2, &cfg );
manometer2_read_coef( &manometer2 );
log_printf( &logger, " Initialization \r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, "----------------------------- \r\n" );
Delay_100ms( );
}
void application_task ( )
{
float temperature;
float pressure;
temperature = manometer2_get_temperature( &manometer2, MANOMETER2_CONVERT_4096 );
Delay_10ms( );
pressure = manometer2_get_pressure( &manometer2, MANOMETER2_CONVERT_4096 );
Delay_10ms( );
log_printf( &logger, " Pressure : %.2f PSI \r\n", pressure );
log_printf( &logger, " Temperature: %.2f C \r\n", temperature );
log_printf( &logger, "----------------------------- \r\n" );
Delay_1sec( );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END