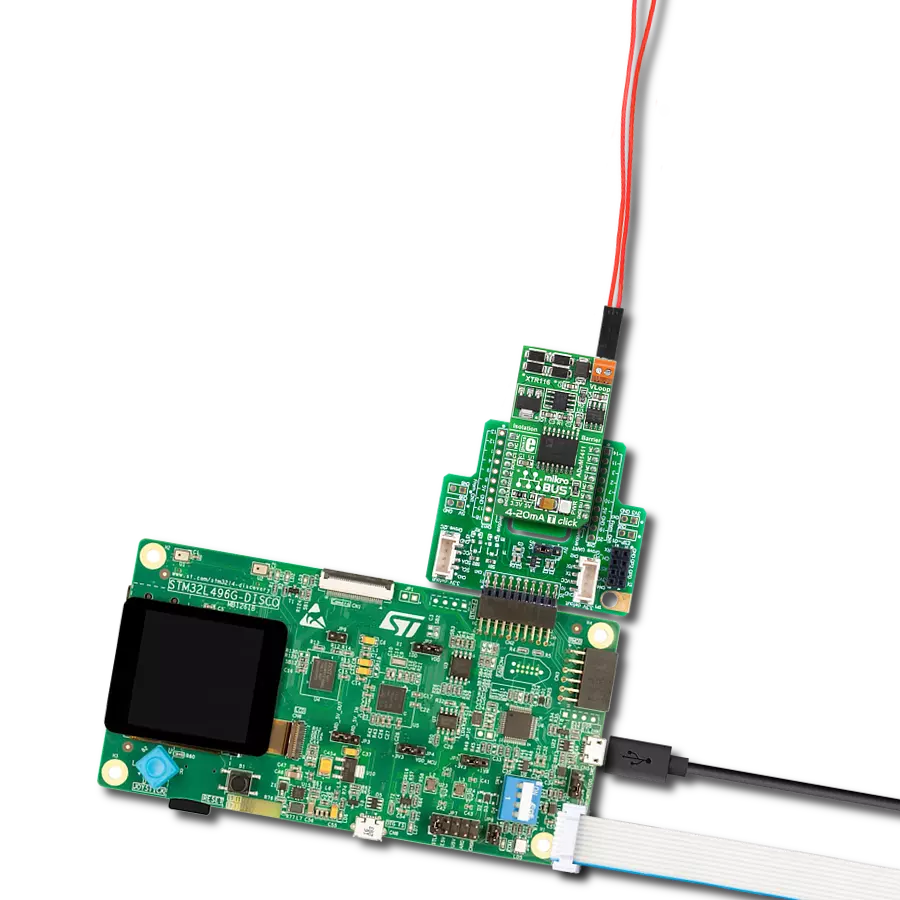
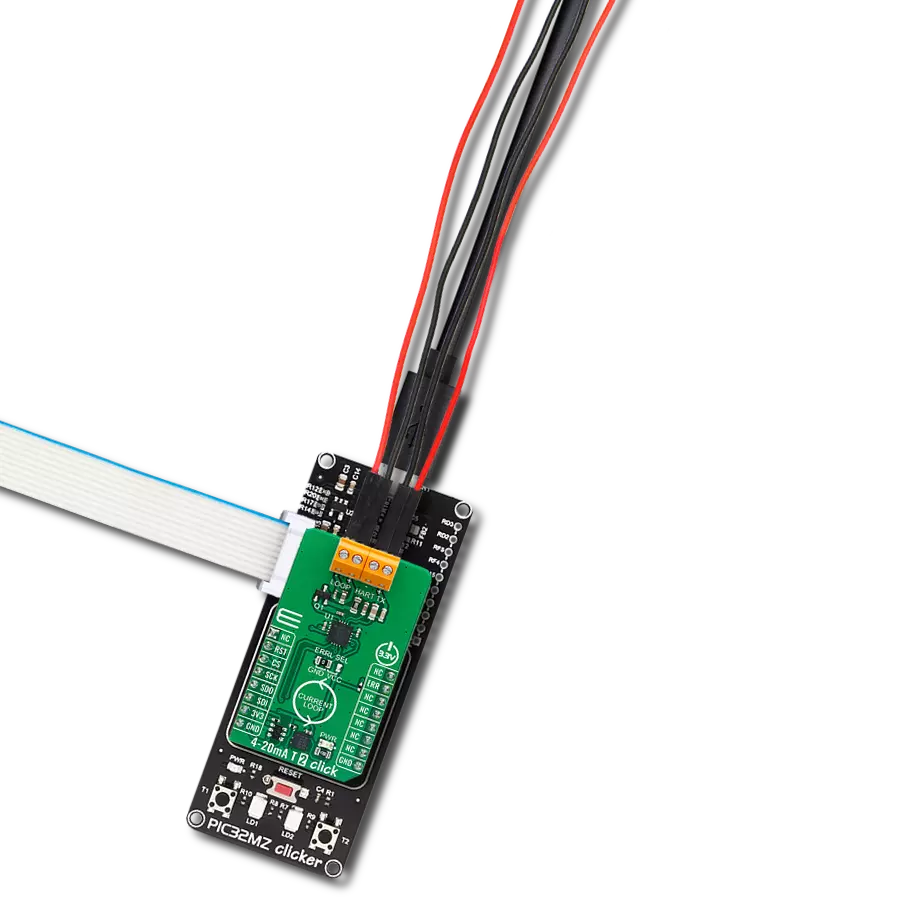
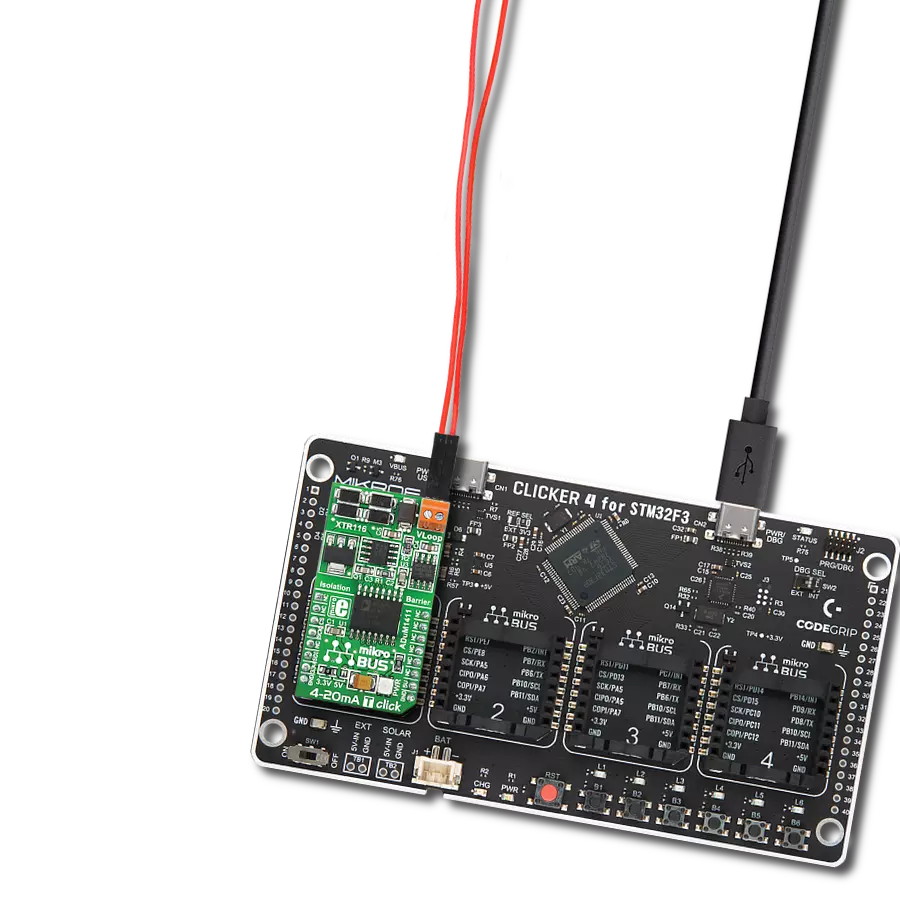
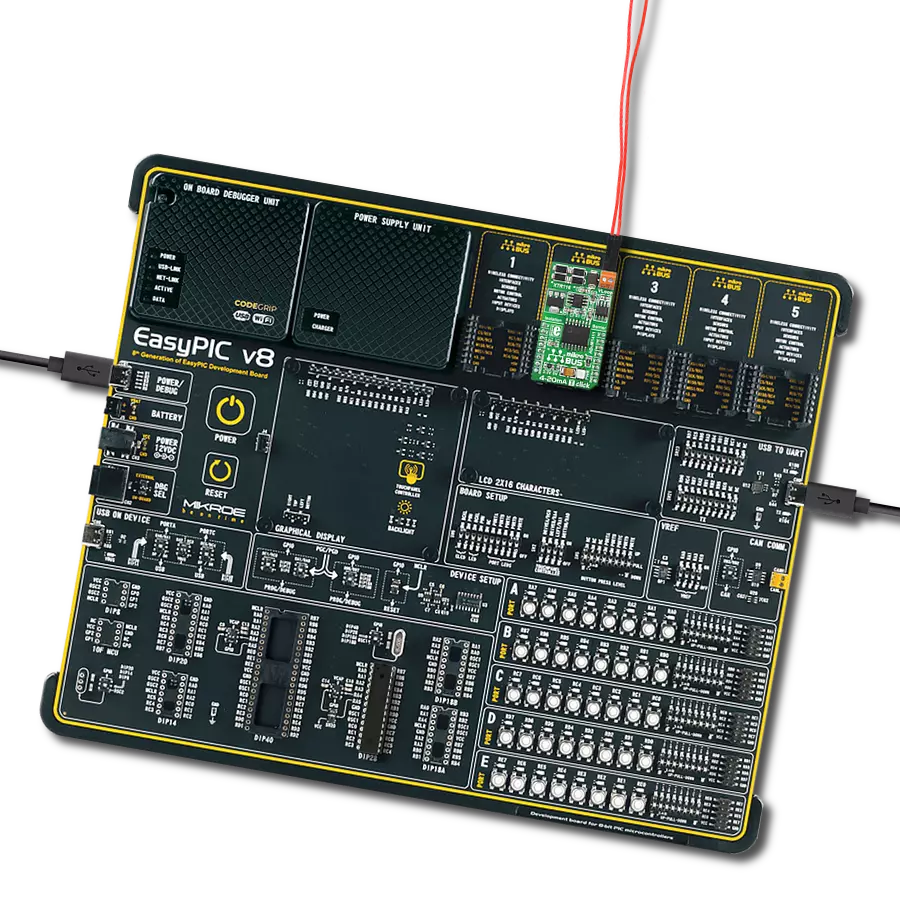
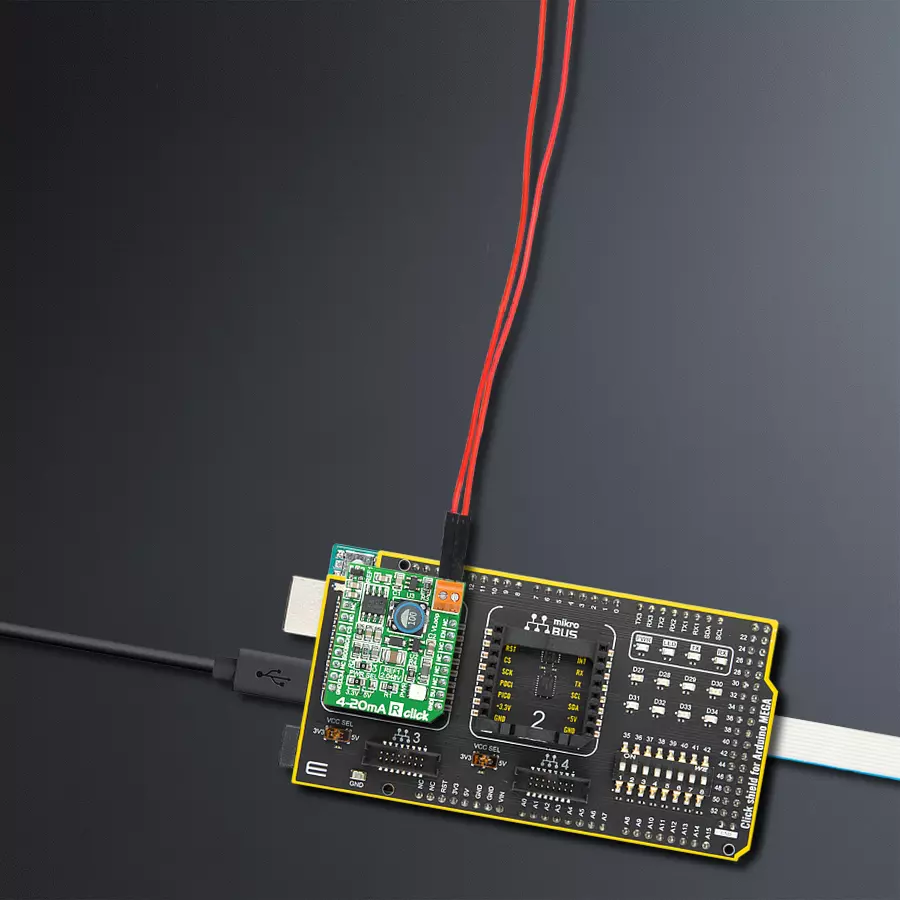
Compact and efficient solution for receiving and monitoring current in industrial systems
A
A
Hardware Overview
How does it work?
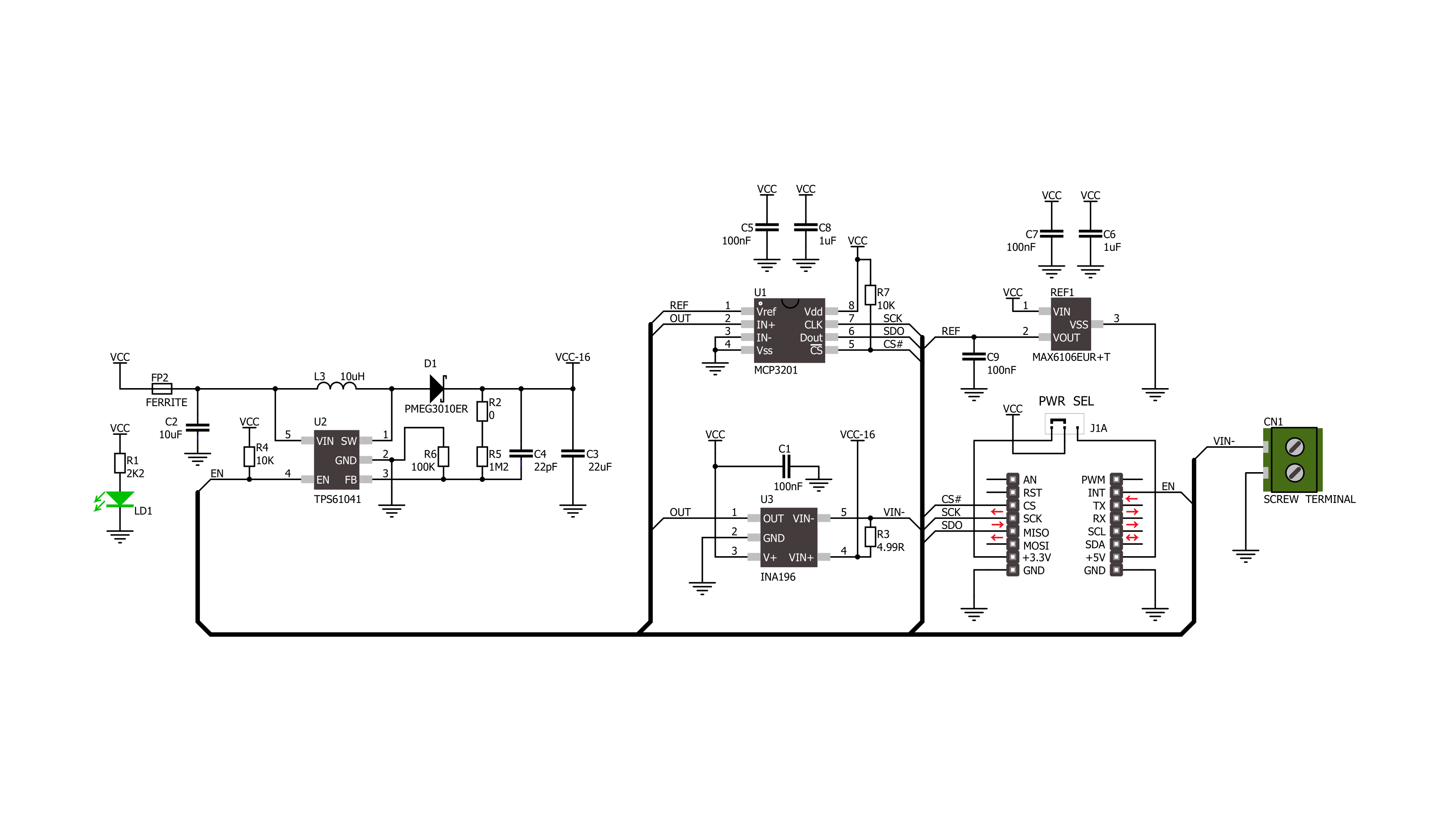
4-20mA R Click is based on the INA196, a current shunt monitor with a voltage output from Texas Instruments. The INA196 can sense drops across a shunt at a range of voltages without interference with its supply voltage and uses 500KHz bandwidth in current control loops. The 4-20mA R Click receives output current from 4 to 20mA from a compatible transmitter and converts it into low voltage. The transmitted loop current on this board comes directly to the load side of the INA196 shunt resistor from a VLOOP screw terminal. The
differential input voltage to the INA196 supply side comes from a TPS61041, a DC/DC boost converter from Texas Instruments. By default configuration, it provides a 16V and can be enabled over the EN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket. In addition, by replacing the R2 0ohm resistor with other values, it can also convert other voltages. The output of the INA196 then comes to the MCP3201, a 12-bit ADC from the Microchip. It communicates with the host microcontroller over an SPI serial interface of the mikroBUS™ socket, with the referent voltage of
2.048V. The ADC receives its reference from the MAX6106, a voltage reference LDO from Analog Devices. This Click board™ can operate either with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels selected via the PWR SEL jumper. This way, it is allowed for both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library containing easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
Features overview
Development board
Arduino Mega 2560 is a robust microcontroller platform built around the ATmega 2560 chip. It has extensive capabilities and boasts 54 digital input/output pins, including 15 PWM outputs, 16 analog inputs, and 4 UARTs. With a 16MHz crystal
oscillator ensuring precise timing, it offers seamless connectivity via USB, a convenient power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. This all-inclusive board simplifies microcontroller projects; connect it to your computer via USB or power it up
using an AC-to-DC adapter or battery. Notably, the Mega 2560 maintains compatibility with a wide range of shields crafted for the Uno, Duemilanove, or Diecimila boards, ensuring versatility and ease of integration.
Microcontroller Overview
MCU Card / MCU

Architecture
AVR
MCU Memory (KB)
256
Silicon Vendor
Microchip
Pin count
100
RAM (Bytes)
8192
You complete me!
Accessories
Click Shield for Arduino Mega comes equipped with four mikroBUS™ sockets, with two in the form of a Shuttle connector, allowing all the Click board™ devices to be interfaced with the Arduino Mega board with no effort. Featuring an AVR 8-bit microcontroller with advanced RISC architecture, 54 digital I/O pins, and Arduino™ compatibility, the Arduino Mega board offers limitless possibilities for prototyping and creating diverse applications. This board is controlled and powered conveniently through a USB connection to program and debug the Arduino Mega board efficiently out of the box, with an additional USB cable connected to the USB B port on the board. Simplify your project development with the integrated ATmega16U2 programmer and unleash creativity using the extensive I/O options and expansion capabilities. There are eight switches, which you can use as inputs, and eight LEDs, which can be used as outputs of the MEGA2560. In addition, the shield features the MCP1501, a high-precision buffered voltage reference from Microchip. This reference is selected by default over the EXT REF jumper at the bottom of the board. You can choose an external one, as you would usually do with an Arduino Mega board. There is also a GND hook for testing purposes. Four additional LEDs are PWR, LED (standard pin D13), RX, and TX LEDs connected to UART1 (mikroBUS™ 1 socket). This Click Shield also has several switches that perform functions such as selecting the logic levels of analog signals on mikroBUS™ sockets and selecting logic voltage levels of the mikroBUS™ sockets themselves. Besides, the user is offered the possibility of using any Click board™ with the help of existing bidirectional level-shifting voltage translators, regardless of whether the Click board™ operates at a 3.3V or 5V logic voltage level. Once you connect the Arduino Mega board with Click Shield for Arduino Mega, you can access hundreds of Click boards™, working with 3.3V or 5V logic voltage levels.
Used MCU Pins
mikroBUS™ mapper
Take a closer look
Click board™ Schematic
Step by step
Project assembly
Track your results in real time
Application Output
1. Application Output - In Debug mode, the 'Application Output' window enables real-time data monitoring, offering direct insight into execution results. Ensure proper data display by configuring the environment correctly using the provided tutorial.

2. UART Terminal - Use the UART Terminal to monitor data transmission via a USB to UART converter, allowing direct communication between the Click board™ and your development system. Configure the baud rate and other serial settings according to your project's requirements to ensure proper functionality. For step-by-step setup instructions, refer to the provided tutorial.

3. Plot Output - The Plot feature offers a powerful way to visualize real-time sensor data, enabling trend analysis, debugging, and comparison of multiple data points. To set it up correctly, follow the provided tutorial, which includes a step-by-step example of using the Plot feature to display Click board™ readings. To use the Plot feature in your code, use the function: plot(*insert_graph_name*, variable_name);. This is a general format, and it is up to the user to replace 'insert_graph_name' with the actual graph name and 'variable_name' with the parameter to be displayed.

Software Support
Library Description
This library contains API for 4-20mA R Click driver.
Key functions:
c420mar_read_data- This function reads the 16-bit current value from the SPI data register, and then normalizes and converts it to float
Open Source
Code example
The complete application code and a ready-to-use project are available through the NECTO Studio Package Manager for direct installation in the NECTO Studio. The application code can also be found on the MIKROE GitHub account.
/*!
* \file
* \brief 420MaR Click example
*
* # Description
* This example showcases how to initialize, configure and use the 4-20 mA R Click. It is a
* simple SPI communication module that acts as a receiver in a 4-20 current loop. The Click
* reads current data and converts the analog signal to a digital 12-bit format.
*
* The demo application is composed of two sections :
*
* ## Application Init
* This function initializes and configures the logger and Click modules.
*
* ## Application Task
* This function reads and displays current data every half a second.
*
* \author MikroE Team
*
*/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------- INCLUDES
#include "board.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "c420mar.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------------ VARIABLES
static c420mar_t c420mar;
static log_t logger;
// ------------------------------------------------------ APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
void application_init ( )
{
log_cfg_t log_cfg;
c420mar_cfg_t cfg;
/**
* Logger initialization.
* Default baud rate: 115200
* Default log level: LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG
* @note If USB_UART_RX and USB_UART_TX
* are defined as HAL_PIN_NC, you will
* need to define them manually for log to work.
* See @b LOG_MAP_USB_UART macro definition for detailed explanation.
*/
LOG_MAP_USB_UART( log_cfg );
log_init( &logger, &log_cfg );
log_info( &logger, "---- Application Init ----" );
// Click initialization.
c420mar_cfg_setup( &cfg );
c420MAR_MAP_MIKROBUS( cfg, MIKROBUS_1 );
c420mar_init( &c420mar, &cfg );
}
void application_task ( )
{
float current;
current = c420mar_read_data( &c420mar );
log_printf( &logger, "-----------------------------\r\n" );
log_printf( &logger, " * Current: %.3f mA * \r\n", current );
Delay_ms ( 500 );
}
int main ( void )
{
/* Do not remove this line or clock might not be set correctly. */
#ifdef PREINIT_SUPPORTED
preinit();
#endif
application_init( );
for ( ; ; )
{
application_task( );
}
return 0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
Additional Support
Resources
Category:Current